chapt31 - Strive Studios
advertisement

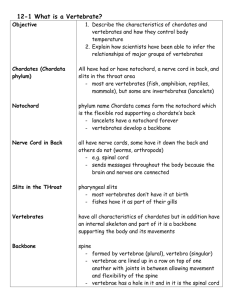
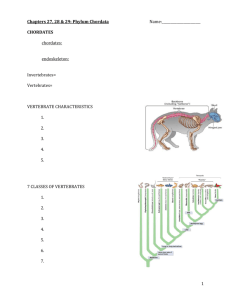
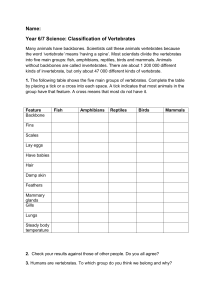
Chapter 31 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. All of the following are characteristics of vertebrates except: A. kidneys for excretory organs B. jaws C. internal skeleton D. open circulatory system 2. Vertebrates without jaws would be the: A. rays B. turtles C. lampreys D. eels 3. The following are differences between amphibians and reptiles except: A. Amphibians have smooth non-scaly skin, whereas reptiles are covered with scales and their skin is dry. B. All reptiles respire by the use of lungs, while some amphibians use gills or skin. C. Amphibian eggs are laid in water; reptilians eggs do not need to be near water. D. Reptiles are ectothermic while amphibians are endothermic. 4. Which phylum contains the vertebrates? A. Arthropoda B. Chordata C. Annelida D. Mollusca E. Porifera 5. A notochord is A. a strip of cartilage that forms a back and tail in all vertebrates. B. a stiff dorsal supporting rod. C. a primitive form of bone vertebra that develops into the backbone. D. the early nerve structure that becomes the spinal cord. E. All of the choices are correct. 6. The term based on the Greek word for "back" and "string" is A. echinoderm. B. protostome. C. cephalochordata. D. deuterostome. E. notochord. 7. The most likely ancestors of the chordates are considered to be echinoderms because A. tunicates are echinoderms. B. there is a direct lineage from sea stars to tunicates. C. embryonic development of echinoderms are similar to primitive chordate embryos. D. All of choices are correct. 8. Which statement about the chordates is NOT correct? A. Chordates have segmentation. B. Chordates have bilateral symmetry. C. Invertebrate chordates are marine and filter feeding. D. Adult lancelets have all the characteristics that distinguish chordates from members of other phyla. E. Adult tunicates lack all the characteristics that distinguish chordates from members of other phyla. 9. The three defining characteristics of chordates are A. segmentation/dorsal hollow nerve cord/gill arches or pharyngeal pouches B. dorsal hollow nerve cord/notochord/bilateral symmetry C. bilateral symmetry/segmentation/well-developed coelom D. well-developed coelom/gill arches or pharyngeal pouches/notochord E. gill arches or pharyngeal pouches/dorsal hollow nerve cord/notochord 10. In vertebrates, the _______ is/are usually replaced by ________. A. pharyngeal pouches; gill arches B. dorsal hollow nerve cord; a ventral solid nerve cord C. gill arches; pharyngeal pouches D. notochord; a dorsal hollow nerve cord E. notochord; a vertebral column 11. Which of these is NOT one of the characteristics of a vertebrate? A. radial symmetry B. segmentation C. extreme cephalization D. closed circulation E. coelom 12. The cartilaginous fishes include all EXCEPT A. goldfish. B. sharks. C. skates. D. rays. 13. Although adult tunicates are stuck to the ocean bottom, they are considered early relatives of vertebrates because A. tunicate gill slits are like ribs. B. tunicate adults have a notochord. C. tunicate larvae have a notochord. D. all vertebrate embryos go through a stage that resembles adult tunicates. 14. The lancelets or Branchiostoma are found A. in tropical Amazon streams. B. as parasites inside the tracts of fish. C. very rarely in mountain streams, where they are almost extinct. D. commonly in the sandy bottoms of coastal waters around the world. 15. Sharks A. lack bone skeletons. B. have placoid scales. C. have a keen sense of smell. D. have teeth derived from epidermal scales. E. All of the choices are correct. 16. Which of these is NOT a characteristic of a shark? A. separate gill slits B. skeleton of cartilage C. a sucker used to attach to prey D. small toothlike scales over skin surface 17. In schooling, fish rely on sensitivity to vibration and water currents. This is provided by cells located inside A. the caudal fin. B. the gills. C. the swim bladder. D. the lateral line. E. all of the scales. 18. The fish group that is closest to the ancestral amphibians, according to mitochondrial DNA analysis, is the A. darters. B. lungfishes. C. bass and bluegill. D. sturgeon and catfish. E. lobe-finned relatives of the coelacanth. 19. The discovery of a living coelacanth off the coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean in 1938 proved that it A. was a modern fish unrelated to fossil coelacanths. B. was the "missing link'' between fish and amphibians. C. can now climb onto land and travel some distances. D. had changed very little and had not gone extinct. E. was both the "missing link" and it could climb onto land and travel. 20. Which of these characteristics is NOT found in the amphibians? A. thin moist skin B. 2-chambered heart C. small inefficient lungs D. aquatic larvae E. eggs with gelatinous covering 21. The amphibians' unique contribution to the evolution of land vertebrates was A. respiration by gills. B. respiration through the skin. C. the leathery waterproof egg shell. D. development of the tail for propulsion. E. separation of lung-gill and systemic (body) circulation. 22. The term "amphibian" is based on the Greek words referring to A. wet and slimy. B. living in two environments, land and water. C. soft skin. D. four footed. E. breathing by lungs or gills. 23. Amphibians were the dominant animal life during the ________ period. A. Jurassic B. Carboniferous C. Devonian D. Silurian E. Cambrian 24. The amphibians' common receptacle for the urinary, genital, and digestive canals is the A. vulva. B. glottis. C. cloaca. D. tympanum. E. operculum. 25. Lungless salamanders lack lungs and breathe through their skins after they lose their gills. You would expect lungless salamanders to A. prefer drier habitats. B. prefer stagnant water. C. be larger than most salamanders. D. be restricted to smaller and/or thinner body plans. 26. Most salamanders fertilize A. using spermatophores. B. externally in water. C. internally by copulation. D. just like frogs. 27. The term based on the Greek word for "outer" and "heat" is A. ectotherm. B. endotherm. C. heterotherm. D. homeotherm. E. ectoderm. 28. Which of these characteristics first developed in reptiles? A. amniotic egg B. scales on skin C. four-legged body D. skull and vertebral column E. animals living completely on land 29. The end of the Cretaceous period is known as the A. age of amphibians. B. age of dinosaurs. C. time when reptiles first arose. D. time when the dinosaurs died out. 30. When a snake flicks its tongue out, it must return the tip of its tongue to the ______ in the roof of its mouth to detect the "taste." A. ectothermic regulator B. keratin C. amnion D. facial pits E. Jacobson's organ 31. Characteristics of birds include all of the following EXCEPT A. reptile-like scales and claws. B. constant warm body temperature. C. modified reptilian scales as feathers. D. hard-shelled egg. E. 3-chambered heart. 32. Because most birds hurtle through the air at high speeds, they must have A. a crop and a gizzard. B. highly sensitive sensory systems. C. complex songs. D. eggs and no placenta. 33. Generally the breathing system in birds A. is identical to the human breathing system. B. is merely accelerated by the flight muscles. C. resembles the positive pressure system of a frog. D. is a one-way circulation of air so constant oxygen absorption can meet the high oxygen demand. 34. Which of these characteristics is NOT associated with flight requirements in birds? A. feet with claws B. light hollow bones C. a light horny beak with no teeth D. respiratory air spaces within tissues, including bones E. an enlarged breastbone with strong muscles attached 35. Mammals are different from birds in all these characteristics EXCEPT A. hair. B. mammary glands. C. constant body temperature. D. young born alive. 36. The Greek term for the "pouch" in Australian animals is A. monotreme. B. marsupium. C. mamma. D. placenta. E. carnivora. 37. The organ of nutrition used in fetal development in the most successful mammals is the A. mammary gland. B. egg. C. pouch. D. placenta. E. marsupium. 38. The duckbill platypus is an exception to many mammals because it A. lacks hair. B. is ‘‘cold-blooded.'' C. doesn't secrete milk. D. doesn't give birth but lays eggs. E. All of the choices are correct. 39. Although the first mammals separated from reptiles by the mid-dinosaur era, the great radiation of mammals occurred in the A. Jurassic. B. Cretaceous. C. Cenozoic. D. Paleozoic. E. Precambrian. 40. Based on the figure shown above A. both taxa are responding to the same environmental conditions in the same way. B. the insects are obviously more successful. C. mammals are obviously more successful. D. All of the choices are correct. E. Both groups may be responding to environmental changes but with different success. 41. The most likely factor causing the major pattern seen in the figure shown above is A. size of organisms. B. food supply and food requirements. C. nervous system development and intelligence. D. ectothermy and homeothermy. 42. Which of the following is NOT one of the basic characteristics of Chordates? A. a dorsal supporting rod called a notochord B. a tail C. a dorsal tubular nerve cord D. pharyngeal pouches that develop into gills and lungs in humans 43. Of the following, which category is miss-matched with its partner? A. Agnathans–jawless fish B. Placoderms–jawed fish C. Chondricthyes–bony fishes D. Osteichthyes–bony fishes 44. The evolution of amphibians has been proposed to occur due to some/or all of the following EXCEPT A. loss of aquatic habitats in the environment. B. lobed finned fish used their limbs to move from pond to pond and natural selection prevailed. C. the supply of food on land and the lack of predators promoted more adaptations to the land environment. D. All of the choices are possible reasons. 45. Which of the following is NOT an Amphibian? A. frogs and toads B. salamanders and newts C. caecilians D. therapsids 46. All of the following characterize amphibians EXCEPT they A. are usually tetrapods. B. undergo metamorphosis. C. have a 3-chambered heart. D. have gills as an adult. 47. In the kingdom Animalia, which of the following is NOT an invertebrate? A. Platyhelminthes B. Rotifera C. Chordata D. Amphibia 48. The position of mammals in evolution is best described as A. they dominate life in the sea. B. they were among the first animals to live on land and their variety outstrips all living things known. C. they arose from mammal-like reptiles in the Triassic but remained small and insignificant while dinosaurs dominated the land. D. mammals gave rise to birds. E. All of the choices are correct. 49. All chordates are also vertebrates. True False 50. Vertebrates are segmented. True False 51. All invertebrate chordates are sessile marine forms as adults, obtaining nutrients by filter feeding. True False 52. Cambrian fossils show numerous vertebrates as well as all the modern invertebrate phyla. True False 53. Reptiles are thought to be the ancestral group from which both birds and mammals arose. True False 54. The most successful mammals belong to the group of marsupials. True False 55. The most common of the fishes are the ray-finned fishes. True False 56. Milk is produced by modified sweat glands in the duckbill platypus. True False 57. In humans the pharyngeal pouches of the embryo develop into auditory tubes, tonsils, thymus glands, and the parathyroid glands. True False 58. That pharyngeal pouches are seen only during embryonic development in most vertebrates is supporting information for the idea that ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny. True False 59. Give the characteristics that define the chordates. 60. Discuss the characteristics that distinguish the vertebrates from sponges, from annelids, and from invertebrate chordates. 61. Compare the characteristics of reptiles and amphibians, noting the similarities and differences between the groups. Since both contain both land and aquatic species, why is the reproductive cycle so distinct? 62. Compare the characteristics of birds and reptiles, noting the similarities and differences between the groups. 63. Compare the characteristics of mammals and birds, noting the similarities and differences between the groups. Why don't we consider mammals and birds are closely related with a common ancestor, since they are both "warm-blooded?" 64. Why do only mammals have lips? 65. Why are there so many species of insects and so relatively few species of mammals? Chapter 31 KEY 1. D 2. C 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. E 7. C 8. E 9. E 10. E 11. A 12. A 13. C 14. D 15. E 16. C 17. D 18. B 19. D 20. B 21. E 22. B 23. B 24. C 25. D 26. A 27. A 28. A 29. D 30. E 31. E 32. B 33. D 34. A 35. C 36. B 37. D 38. D 39. C 40. E 41. D 42. D 43. C 44. A 45. D 46. D 47. D 48. C 49. FALSE 50. TRUE 51. FALSE 52. FALSE 53. TRUE 54. FALSE 55. TRUE 56. TRUE 57. TRUE 58. TRUE 59. Answers will vary. 60. Answers will vary. 61. Answers will vary. 62. Answers will vary. 63. Answers will vary. 64. Answers will vary. 65. Answers will vary.