Hypothyroidism
advertisement

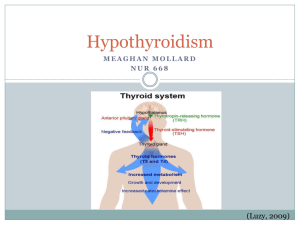
Hypothyroidism Submitted by Frances Barker-Walsh, CHUC of Rockledge, Florida Learning Objectives: 1. Describe what causes hypothyroidism. 2. List at least two symptoms and risk factors of hypothyroidism. 3. Name two tests that are used to diagnose the symptoms. 4. Describe treatment for hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland can no longer produce enough thyroid hormone. The thyroid gland is located in front of your neck and similar in shape to a butterfly. It controls how you are able to use energy. A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid and seen as a swelling on the front of the neck. It can occur because of either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. A goiter can also be caused by tumors or nodules. If the thyroid is not producing enough hormone, it will affect the whole body. If it goes untreated, it can cause the following symptoms: elevated cholesterol, feeling tired/weak weight gain depression dry skin/brittle nails sensitivity to cold chronic constipation memory problems trouble thinking clearly heavy or irregular menstrual periods Hypothyroidism causes the metabolism to slow down and symptoms will get worse if left untreated. It can cause puffiness, slow heart rate and swelling in legs, and can lead to a rare life-threatening coma. Women are most likely to get hypothyroidism and symptoms can be mistaken for menopause. Other risk factors include: being over the age of 60. having rheumatoid arthritis having diabetes pregnancy, Anyone of any age, can have hypothyroidism especially, if there is a family history. The most common type found in the U.S. is Hashimoto's thyroiditis. That means the body's immune system is attacking thyroid tissue. Therefore, the thyroid gland is unable to make enough hormone. Pituitary gland disease, thyroid surgery and radiation therapy for thyroid cancer will also cause low levels of thyroid hormones. Other less common causes include effects from some drugs such as lithium and viral infections. Tests that are used to diagnose hypothyroidism are as simple as having a blood sample taken. TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) is a test which will measure the amount of TSH in the blood. If that test is considered abnormal, then other tests may be done Such as total thyroxine (T4), free thyroxine (FT4), and triiodothyronine (T3). These will be compared to your TSH levels. Things that may affect the tests are medications such as corticosteroids, estrogen, progesterone, or birth control pills; blood thinners like aspirin, heparin, or warfarin; anti seizure medications such as Dilantin or Tegretol; heart medications such as amiodarone or propranolol; lithium, and x-ray contrast medium. Being pregnant can also affect blood test results. The normal range for TSH was 0.4-6 and is now 0.3-3 according to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists revised guidelines. Normal ranges for T4 is 4.5-12.5, for FT4 is 0.7-2, and for T3 is 80220. Other diagnostic tests used to identify thyroid problems are thyroid scan, ultrasound, and biopsy. The recommended treatment for hypothyroidism is to take thyroid replacement medication for the rest of one’s life. The medication most often prescribed is a synthetic thyroid hormone called levothyroxine with the brand names of Levothroid or Synthroid. After starting the medication feelings of fatigue should lessen after one to two weeks.. The medication also gradually lowers cholesterol levels elevated by the disease and may reverse weight gain. The physician generally checks the TSH level two-three months after treatment has started to see if the dosage needs to be adjusted. Excessive amounts of hormone can cause side effects such as increased appetite, insomnia, heart palpations and shakiness. If one has cardiac artery disease or severe hypothyroidism, the physician may start with small dose and gradually increase the dosage. Progressive replacement allows the heart to adjust to increase in metabolism. Certain medications, supplements or food may affect absorption of levothyroxine. This includes a high fiber diet, large amount of soy, iron supplements, cholestyramine, aluminum hydroxide (found in some antacids) and calcium. Once thyroid hormone levels are adjusted with medication, one will need to have a TSH blood test annually to continue to monitor hormone levels. The American Thyroid Association recommends that everyone be screened yearly starting at age 35. Resources: www.mayoclinic.com/.../hypothyroidism/ www.m.webmd.com/.../hypothyroidism-t www.endocrine.niddk.nih.gov/.../hypoth e-Learning QUIZ ID # Web-12-01-13 VALUE: 2 NAHUC CONTACT HOURS Fee: $5 (U.S. Dollars) for NAHUC members, $10 (U.S. Dollars) for non-members Do not send cash. Make check payable to: NAHUC. If overpayment is made, refunds will be issued in the form of NAHUC Buck certificates. Directions: Print, choose the most correct answer based on the article and mail the completed quiz, self-addressed self-stamped return envelope along with appropriate fee to: Linda Winslow 2502 Norwood St Marquette, MI 49855-1240 Only quizzes with at least 70% answered correctly will be awarded contact hours. Please allow up to 6-8 weeks for quizzes to be returned. DEADLINE FOR SUBMISSION OF THIS QUESTIONNAIRE IS November 30, 2014. Member #:________Name:_______________________________________________ Phone number: ___________ Email address: ________________________________ Subject: Hypothyroidism Submitted by: Frances Barker-Walsh, CHUC of Rockledge, Florida Objective: To identify facts about Hypothyroidism Resources: Accompanying article submitted by Frances Barker-Walsh, CHUC Instructions: After reading the article, please circle the best answer. 1. Hypothyroidism occurs when: a. there is an overproduction of thyroid hormone. b. one takes too many vitamins. c. the thyroid does not produce enough hormone. d. an allergy to nuts aggravates the thyroid. 2. Who is most likely to get hypothyroidism? a. A female over the age of 50. b. Someone who is underweight c. Someone who liberally uses ionized salt d. A young male 3. What are some symptoms of hypothyroidism? a. Feeling energetic b. Weight gain, weakness c. Low cholesterol d. Always feeling hot 4. Where is the thyroid gland located? a. Most often at C-3 b. In lower mandible c. In front of neck d. In brain 5. What is a goiter? a. Flattened smooth muscle b. Overdeveloped sinuses c. Visible enlargement of thyroid d. Swelling of face 6. What test is commonly used to diagnose hypothyroidism? a. TSH b. Total protein c. CBC d. Luteinizing hormone 7. What are The American Association of Endocrinologists guidelines for normal range for TSH? a. 0.6-6 b. 0.3- 1.5 c. 0.3-3.5 d. 0.3-3 8. What other tests besides lab tests may be used to identify thyroid problems? a. MRI of Carotids b. X-ray of C-7 c. Thyroid Scan d. Lumbar Puncture 9. When should you be tested for hypothyroidism according to The American Thyroid Association? a. Annually after age 60 b. Only when symptoms are present c. Annually starting at age 35 d. Every five years after menopause 10. Once diagnosed with hypothyroidism: a. one will eventually have to have a thyroidectomy. b. one will eventually develop a goiter. c. one will most likely have to follow a strict diet and exercise program. d. one will most likely have to take a hormone replacement the rest of their life.