CLINICAL PRIORITY ACCESS CRITERIA
advertisement

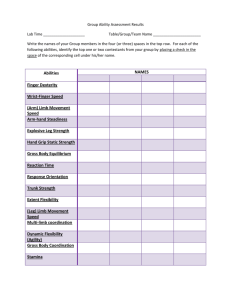
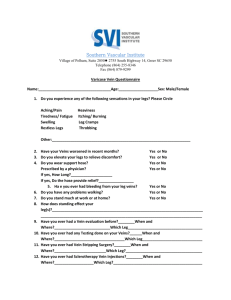
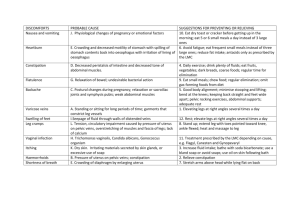
CPAC026 CLINICAL PRIORITY ACCESS CRITERIA Service Category: VASCULAR SURGERY Category Definitions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Category 1. Immediate Seen within 24 hours 2. Urgent Seen within 1 week Patient Type: Outpatient (Assessment) Immediate Urgent Semi-Urgent Routine – – – – Treatment within 24 hours Seen within 1 week Seen within 1 month Seen within 2 months Criteria Haemorrhage. Embolism/Thrombosis. Complete heart block. Critical ischaemic limb (ischaemic ? in evolution). ? Infection. Conditions where there is a: Examples (not an exhaustive list) Ruptured abdominal aneurysm trauma. Critical limb ischaemia. Stroke in evolution. Mesenteric ischaemia. Arterial occlusion (Thrombotic or embolic). Diabetes induced ischaemia. Cellulitis in an ischaemic leg. Osteomyelitis in a diabetic foot. Changing aneurysm (increasing size, tenderness). Deteriorating claudicant. Ischaemic and threatened limb Crescendo TIAs. >90% stenosis of internal carotid (duplex scan positive). Axilliary vein thrombosis. Deep venous thrombosis. Progressive long saphenous vein thrombosis. Painful leg with ulceration or ischaemic necrosis. Cellulitis in diabetic or ischaemic leg Osteomyelitis in diabetic or – Threat to life; or – Limb; or – Stroke threatening. Last updated February 2006 Conditions where there is a threat of pulmonary embolus. Ischaemic rest pain (thrombosis or embolus). Haemorrhage from varicose veins. Active infection in leg with peripheral vascular disease. ischaemic leg. Page 1 of 2 CPAC026 3. Semi-Urgent Seen within 1 month Aortic aneurysm. Not tender, >5 cm. Significant functional impairment threatening quality of life. Severe claudication (< 50m). TIAs. Stenosis of internal carotid >70% Arterio venous access surgery. False aneurysm. Traumatic arteriovenous fistula Pre-ulcerative venous disease. Claudication (> 50m). Post thrombotic limb. Arteriovenous malformations. Sympathetic dystrophy Asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Vasospastic disorders. Small vessel diseases associated with systemic illnesses. Chronic swelling of limb. Varicose veins causing discomfort Varicose veins causing thrombophlebitis except for when porto-systemic shunting is being considered. Excessive sweating of hands or feet Leg ulcer due to venous disease or other cause. Diabetic foot ulcer Not tender. >3.5 and <5 males ?2.5 and <5 cm in females 4. Routine Seen within 2 months Need for renal dialysis within 6 months. Sequelae of trauma. Moderate functional impairment. Carotid bruit. Arteritides. Lymphatic disease. Varicose veins. Hyperhidrosis Leg ulcer Aortic aneurysm NOTE: Oesophageal varices are normally managed within General Surgery. The following conditions will not be seen: Telangiectasia or reticular veins, asymptomatic/cosmetic varicose veins. Refer to Vascular Surgery Vol 30 (1). Last updated February 2006 Page 2 of 2