Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
advertisement

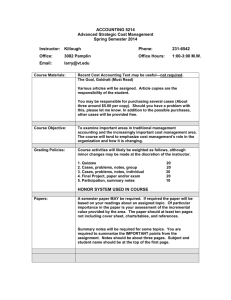
Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems - Learning Targets + Instruments Learning Targets 1 Use appropriate vocabulary related to their investigations of cells and systems. Mr. Birt Learning Instruments Vocabulary covered throughout unit Include: cell theory, osmosis, diffusion, selective permeability, unicellular, multicellular, specialized cells and tissues, organs, systems, arteries, veins, capillaries, terms related to cell structure, heart structure, components of blood, and primary and secondary defense systems 2 Identify characteristics of living things, and describe how different living things exhibit these characteristics. Include: composed of cells; reproduce; grow; repair themselves; require energy; respond to the environment; have a lifespan; produce wastes 3 Describe cell theory. Include: all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic unit of structure and function of any organism; all cells come from pre-existing cells; the activity of an organism as a whole depends on the total activity of all its cells 4 Identify major events and technological innovations that have enabled scientists to increase our understanding of cell biology. 1) INTRO: Bill Nye video – Life Cycles 2) Notes (table) - Characteristics of Living Things 3) Quiz – Characteristics of Living Things 11) Assignment - Cell Theory (text p. 20) 12) Quiz – Cell Theory 11) Assignment - Cell Theory (text p. 20) 12) Quiz – Cell Theory Examples: invention of the light and electron microscope, works of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann 5 Identify and compare major structures in plants and animal cells, and explain their function. Include: cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, vacuoles, cell wall, chloroplasts 6 4) Bill Nye video handout – Cells 5) Assignment – Cell Structures + Functions (text p. 28+29) 6) Handout – Cell Diagram 7) Assignment – 3 Point Approach 8) Project – Incredible Edible Cell 9) Quiz – Cell Diagram 10) Quiz – Cell structures and Functions Demonstrate proper use and care of the Course Intro microscope to observe the general structure of plant and animal cells. Include: preparing wet mounts beginning with the least powerful lens; focussing; drawing specimens; indicating magnification 7 Describe the movement of nutrients and wastes across cell membranes and explain its importance. 13) Notes – Cell Processes 14) Handout – Osmosis and Diffusion 15) Quiz – Cell Processes Include: osmosis, diffusion, selective permeability 8 Differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms. 16) Assignment Handout – Unicellular vs Multicellular 18) Quiz – Cell Specialization 9 Describe why cells and tissues are specialized in multicellular organisms, and observe examples. Include: specialization is needed 17) Assignment Handout – Cell Specialization 18) Quiz – Cell Specialization because all cells in a complex organism do not have access to the external environment 10 Describe structural and functional relationship among cells, tissues, organs, and systems. 19) Assignment Handout – Levels of Organization 20) Quiz – Levels of Organization 11 Describe the structure and function of the heart and the path of blood to and from the heart through its four chambers. 24) Notes – The Heart 25) Handout - Heart Diagram 26) Bill Nye video Handout – The Heart 27) Handout – Circulation Concept Diagram 28) Assignment - Path of Blood 29) Bill Nye Video - Circulation 30) Quiz – Heart Diagram 31) Quiz - Circulation Concept Diagram Include: atria, ventricles, septum, valves, aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava 12 Compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. 21) Assignment – Circulatory System 22) Quiz – Blood Vessels 13 Identify components of blood and describe the function of each. 21) Assignment – Circulatory System (see above) 23) Quiz – Parts of Blood Include: red blood cells carry oxygen; white blood cells fight infection; platelets clot blood; plasma is the liquid part of blood that transports blood cells, dissolved material, nutrients, and waste products 14 Describe, using examples, how individual systems in the human body function interdependently. 32) Assignment – Interaction of Body Systems + Cell Respiration 33) Bill Nye video - Respiration 15 Compare heart rate and respiratory rate before, during, and after various physical activities; explain the observed variations; and discuss implications for overall health. 34) LAB: Heart and Respiratory Rates 16 Identify components of the primary and secondary defense systems of the body and describe their roles. 35) Handout – Immune System 36) Quiz – Immune System Include: primary defense system - skin, tears, ear wax, saliva, gastric juices, cilia hairs; secondary defense system - white blood cells, antibodies 17 Identify medical advances that enhance the human body's defence mechanisms and describe their effects on society. 37) Handout – Medical Advances + Human Body Defences Examples: vaccines, antibiotics 18 Research and describe disorders/diseases 38) Powerpoint Project after unit test that affect body systems, and identify possible preventative measures. Examples: liver disease, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, heart attack, stroke, high/low blood pressure, leukemia, anemia, high cholesterol 19 Describe functional similarities and differences of comparable structures and systems in different groups of living things. Examples: movement, food intake, and digestion of a unicellular organism, an invertebrate, and a vertebrate; gas exchange in plants versus animals 2) Notes (table) - Characteristics of Living Things (see 2 above)