7th Grade Physics Review Sheet
advertisement

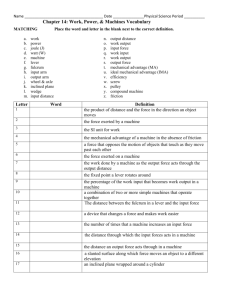
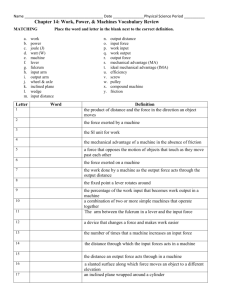
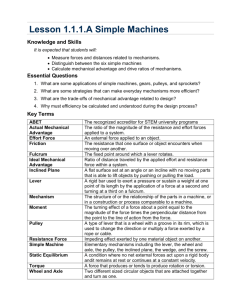
7th Grade Physics Review Sheet 1. Example Problem using the Law of the Lever (the exam will have a similar problem with different numbers): If a lever has a 36 pound weight 6 ft away from the fulcrum, give (a) which direction (up or down) you would have to pull (b) What the effort required is to balance the weight, and (c) What class of lever this is, for each situation below. i. 6 ft from the fulcrum on opposite side of fulcrum from the weight. ii. 3 ft from the fulcrum on opposite side of fulcrum from the weight. iii. 3 ft from the fulcrum on same side of fulcrum as the weight. iv. 9 ft from the fulcrum on opposite side of fulcrum from the weight. v. 8 ft from the fulcrum on same side of fulcrum as the weight 2. A light student wants to balance a heavy student on a see-saw. Give two different actions that would allow them to balance. 3. In the Law of the Lever, what is lever arm times weight called? What is it measured in (English units)? 4. What is the trade off if you have mechanical advantage? For example, to lift a heavy rock, what do you need to do more of in order to lift it with less effort? 5. What position should your bicycle chain be in (front crank and back cassette) to get the most power? To get the most speed? 6. Give examples of common tools and implements that are 1st, 2nd and 3rd class levers. In particular, what class lever is: i. A hammer (give the class for each use [hammering and prying] of the hammer and identify where the effort, load and fulcrum are for each. ii. A wheelbarrow. Identify where effort, load and fulcrum are. iii. Scissors. Identify where effort, load and fulcrum are. iv. Fingernail clippers. Identify where effort, load and fulcrum are. v. Your arm at the elbow joint (give the class for both the tricep and the bicep). Identify where the effort, load and fulcrum are for each. 7. What do you call a material that is very “thermally transparent” (allows warming and cooling effects to pass through easily and quickly)? Give examples of such materials. What do you call a material that is not very “thermally transparent”? Give examples of such materials 8. What is a common trait that many thermal insulators have? (hint: it has to do with where they come from) 9. What happens to almost all materials when they are warming? When they are cooling? What is the difference in the response of solids, liquids and gasses to warming and cooling? 10. What qualities should a surface have to produce reflective images that are clear, have correct color, and are not distorted? 11. If you can see someone else in a mirror, what do you know for sure about them? What is true about each of your lines-of-sight to the spot on the mirror where you can see each other? 12. You see yourself in a mirror. How far is the “mirror-you” from the mirror surface, compared to your distance from the mirror? 13. Explain why the image is upside down on the screen in a camera obscura. 14. If you make the opening larger on a camera obscura, what two changes happen to the image? 15. Draw the correct way to connect copper and zinc strips to form a battery with your tongue. Draw the correct way to do this with three people. 16. What happens when a battery “dies”? 17. Draw a correct diagram of a Voltaic pile and how to hook it up to power a light bulb.