ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - St.Joseph's College
advertisement

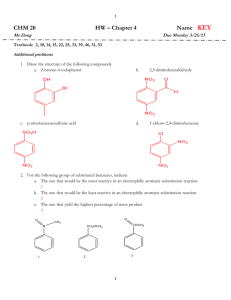
CLASS: M.Sc. CHEMISTRY 13N / 346 St. JOSEPH’S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) TIRUCHIRAPPALLI – 620 002 SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS – NOVEMBER 2013 TIME: 3 Hrs. MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 SEM SET PAPER CODE TITLE OF THE PAPER I 2013 12PCH1101 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – I SECTION – A Answer all the questions: 20 x 1 = 20 Choose the correct answer: 1. Identify the hybridization and the geometry in ethene molecule. 2. 3. 4. 5. a) sp2, pyramidal b) sp2 trigonal planar c) sp2 angular d) none Pick out the aromatic compound in the given list. a) azulene b) pentalene dianion c) cyclobutadiene d) both a & b Identify the intermediate that exists in triplet and in singlet states a) CH3 b) :CH2 c) .. R N: d) both b & c What is the kinetic requirement for a reaction to take place? a) G < 0 b) G f G r c) G > 0 d) all the three a, b & c Which one is the activating substituent in the SNAr mechanism? a) NO2 b) CN c) CHO d) all the three a, b & c Fill in the blanks: 6. The dipole moment is the cross – product of ______ and ______. 7. 8. The magnetic characteristic of an aromatic compound is ______. Predict the product(s) of the given reaction: CCl3.COO ? 9. The rate constant for the second – order reaction has the unit ______. 10. The substituents that increase the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution are termed ______. Answer in one or two sentences: 11. What is the absolute configuration of D(+) glyceraldehydes? 12. What kind of tautomerism is shown by phenol? 13. How is the aromatic character in azulene, regarded? 14. Briefly explain the homoaromaticity? 15. What is the shape of the trimethyl aryl cation? 16. How does the bond cleavage, give rise to different intermediates by the molecule R-X? 17. What is the significance of Hammett equation? 18. What do you mean by ‘isotope effect’? 19. Suppose, the aromatic nucleophilic substitution does go via SN1 mechanism, then, what kind of intermediate is formed? What is the significant chemical change of Gatterman – Koch reaction? SECTION – B Answer all the questions: 5 x 6 = 30 21. a. Draw the structure of threo – chloromalic acid as per fisher projection formula. Arrive at the configuration of each of the chiral centres. 20. OR 22. b. Account for the following: (i) nitrobenzene is more polar than phenol. (ii) trichloro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. (iii)Aniline is less basic than methylamine. a. What are the experimental evidences for the aromaticity? OR 23. b. Discuss in short the Hickel’s Rule of aromaticity with respect to naphthalene. a. Give the two principle ways of generating carbanions. Show how do the carbanions react with other reagents. OR 24. b. Write the Meerwein’s arylation reaction. Propose the mechanism of this reaction. a. Explain the following method of determining the mechanism. i) stereochemical study. OR 25. b. The pKa of p-chlorobenzoic acid is 3.98 and that of benzoic acid in 4.19. Calculate the value for the pCl substituent. What is the significance of the -value? a. Write the mechanism of Reimer – Tiemann reaction. OR b. Write the Sommelet – Hauser Reaction. Propose the mechanism. SECTION – C Answer any FIVE questions: 5 x 10 = 50 26. a. What is Keto – Enol tautomerism? Explain this tautomerism in the given molecules: CH3COCH2 COOH, Ar2CH.CHO. 27. 28. 29. 30. b. Write a short note on hydrogen bonding. a. Explain the alternant and non alternant hydrocarbon, that are aromatic. b. Applying the Craig’s rule, prove the aromatic nature of naphthalene. a. Identify the given reaction. Propose the mechanism. R.CooAg +Br2 RBr + CO2 +AgBr b. Give the two principal mean of generating nitrenes. How does the nitrene react with a) alkene b) alkane a. Explain the isotopic effect with respect to the aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction. b. Prove that Hammett Equation is a linear free energy relationship. a. Cl * NaNH 2 ? Propose the mechanism of the given reaction and predict the product(s). List the evidences of the mechanism. (7) 31. b. Write the mechanism of suffocation of benzene. a. Explain the mechanism of the reaction, by isotopic labeling study. (4) R - COO + BrCN RCN + CO2 +Br b. Why is phenanthrene more aromatic than anthracene? c. Write the mechanism of nitration of benzene. ************** (3) (2) (3)