Medical Terminology
advertisement

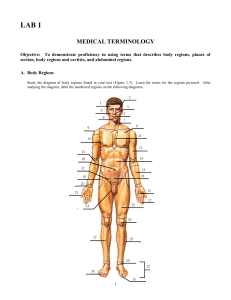
LAB 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Objective: To demonstrate proficiency in using terms that describes body regions, planes of section, body regions and cavities, and abdominal regions. A. Body Regions Study the diagram of body regions found in your text (Figure 1.7). Learn the terms for the regions pictured. After studying the diagram, label the numbered regions on the following diagrams. 2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 10 12 13 14 16 17 15 18 19 20 21 23 22 z 25 24 26 27 28 29 32 30 31 1 34 33 35 36 37 38 40 39 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 2 B. Body Cavities Using models and diagrams locate the cavities listed below and list major organs found in each cavity. Cavity 1. Major Organs Thoracic a. Pleural cavities b. Mediastinum c. Pericardial cavity 2. Abdominal cavity 3. Pelvic cavity 4. Cranial cavity 5. Vertebral (spinal) cavity In addition, locate each of the following cavities: 6. Nasal cavity 7. Oral (buccal) cavity 8. Orbital QUESTIONS 1. What larger cavity do cavities #1, #2 and #3 in the table above belong to? 2. What larger cavity do cavities #2 and #3 belong to? 3. What larger cavity do cavities #4 and #5 belong to? 4. Name the cavity that each of the following would be found in a. Spinal cord e. Spleen b. Esophogus, trachea f. Brain c. Heart g. Eye d. Liver h. Lung 3 C. Label the cavities numbered on the diagrams below 1 3 2 4 6 5 7 8 (entire mid-region) 9 10 11 4 D. Abdominopelvic Regions Locate the following regions on models. List the major organs found in each region using the table given and label the regions on the diagram below. Regions 1. Epigastric 2. Umbilical 3. Hypogastric 4. Right hypochondriac 5. Left hypochondriac 6. Right lumbar 7. Left lumbar 8. Right inguinal (iliac) 9. Left inguinal (iliac) Major Organs 4 1 5 9 6 2 3 7 8 5 E. Body Planes Label the body planes of each diagram 1. 2. 3. QUESTIONS 1. What organ would most likely be affected if injury to the right hypochondriac region occurs? 2. Severe indigestion often presents as pain the ____________________________ region. 3. The urinary bladder is found in the ____________________________ region. 4. The right kidney is in the ______________________________ region. 5. A deep stab wound in the umbilical region would involve injury to what organs? 6. Through what plane would one make a cut to view the lateral aspect of the heart? 7. What would you call the above section if it were through the midline? If it were lateral to the midline? 8. Through what plane would one make a cut to visualize the inferior aspect of the liver? 9. To view the anterior surface of the lung one would make a cut through what plane? 6 F. Terminology Study the directional terms in Table 1.1 of your text and answer the questions below (Questions 7-8 pertain to serous membranes). 1. The head is __________________________ to the neck. 2. The hand is _________________________ to the elbow. 3. The ear is ______________________ to the nose. 4. Skin is ____________________________ to muscle. 5. The heart is _____________________________ to the lungs. 6. The viscera are ___________________________ to the epidermis. 7. The membrane covering the surface of the lungs is the __________________________ pleura. 8. The membrane lining the abdominal cavity is the __________________________ peritoneum. G. Prefixes and Suffixes A large part of anatomy and physiology is vocabulary, therefore it is helpful to learn the meaning of as many prefixes and suffixes as possible. Most of these can be found in your text. Look up the meaning of each prefix or suffix below and use it properly in a sentence. Prefix/Suffix 1. brachi 2. epi 3. endo 4. peri 5. hypo 6. hyper 7. chondr 8. cephal 9. cardio Sentence 10. neuro 11. pleur 12. para 13. a 14. hemi 15. ectomy 7 E. Organ Systems Using the Human Torso models, identify all the organs of each organ system (Text pp. ). Then, using the directional terms from ……….on page ?? of the text, give the locations of the organs in a system relative to the indicated organs and fill in the Table below. 1 ORGAN SYSTEM ORGAN RELATIVE POSITION—use the following terms when applicable: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, superficial, deep, medial, lateral Digestive Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Liver Pancreas Large Intestine Larynx Trachea Lungs Heart Thyroid Pancreas Adrenal Gland Ovaries/Testes Kidneys Ureter Bladder Urethra Liver Thyroid Gland Adrenal Gland Relative to mouth & esophagus: Inferior and superior, respectively Relative to pharynx & stomach: R to esophagus & liver: R to stomach & large intestine: R to small intestines & large intestines: Relative to stomach & small intestines: R to stomach & liver R to pharynx & trachea: R to lungs R to esophagus Relative to lungs & trachea: Relative to trachea & heart: R to stomach Relative to Pancreas & Kidney Relative to the external genitalia Relative to Ureter R to Bladder R to Urethra R to Heart R to diaphragm R to trachea R to kidney Respiratory Circulatory Endocrine Excretory/Urinary Other 8