Experimental Designs Summary
advertisement
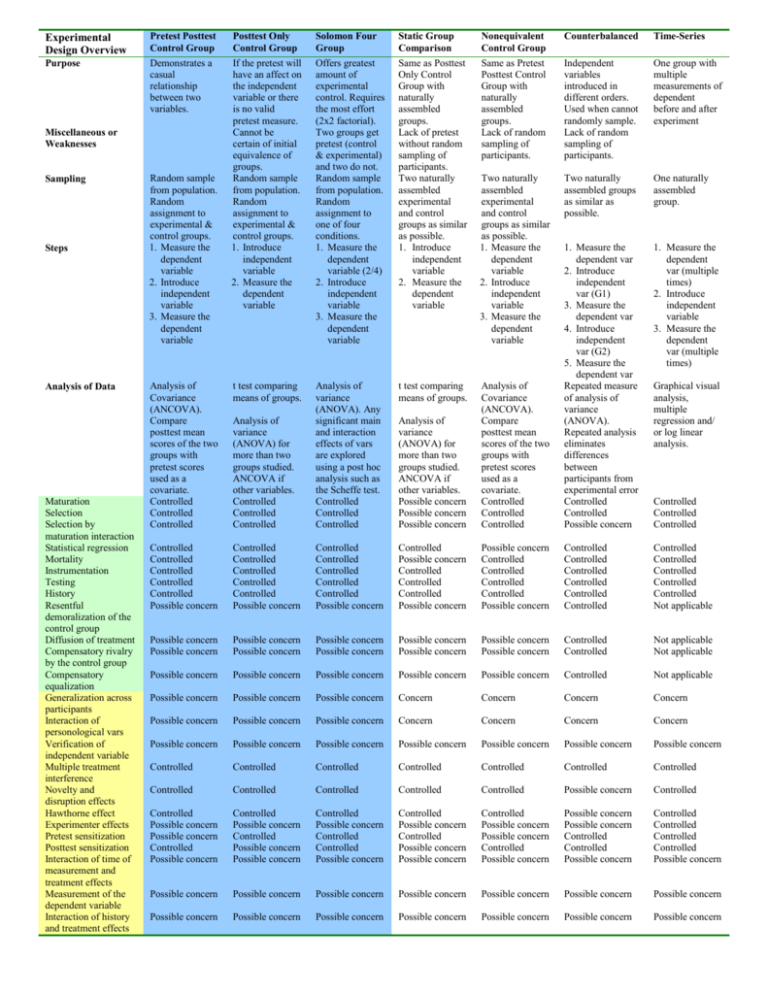
Experimental Design Overview Pretest Posttest Control Group Posttest Only Control Group Solomon Four Group Static Group Comparison Nonequivalent Control Group Counterbalanced Time-Series Purpose Demonstrates a casual relationship between two variables. If the pretest will have an affect on the independent variable or there is no valid pretest measure. Cannot be certain of initial equivalence of groups. Random sample from population. Random assignment to experimental & control groups. 1. Introduce independent variable 2. Measure the dependent variable Offers greatest amount of experimental control. Requires the most effort (2x2 factorial). Two groups get pretest (control & experimental) and two do not. Random sample from population. Random assignment to one of four conditions. 1. Measure the dependent variable (2/4) 2. Introduce independent variable 3. Measure the dependent variable Same as Posttest Only Control Group with naturally assembled groups. Lack of pretest without random sampling of participants. Two naturally assembled experimental and control groups as similar as possible. 1. Introduce independent variable 2. Measure the dependent variable Same as Pretest Posttest Control Group with naturally assembled groups. Lack of random sampling of participants. Independent variables introduced in different orders. Used when cannot randomly sample. Lack of random sampling of participants. One group with multiple measurements of dependent before and after experiment Two naturally assembled experimental and control groups as similar as possible. 1. Measure the dependent variable 2. Introduce independent variable 3. Measure the dependent variable Two naturally assembled groups as similar as possible. One naturally assembled group. 1. Measure the dependent var (multiple times) 2. Introduce independent variable 3. Measure the dependent var (multiple times) Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA). Compare posttest mean scores of the two groups with pretest scores used as a covariate. Controlled Controlled Controlled t test comparing means of groups. t test comparing means of groups. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for more than two groups studied. ANCOVA if other variables. Controlled Controlled Controlled Analysis of variance (ANOVA). Any significant main and interaction effects of vars are explored using a post hoc analysis such as the Scheffe test. Controlled Controlled Controlled Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for more than two groups studied. ANCOVA if other variables. Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA). Compare posttest mean scores of the two groups with pretest scores used as a covariate. Controlled Controlled Controlled 1. Measure the dependent var 2. Introduce independent var (G1) 3. Measure the dependent var 4. Introduce independent var (G2) 5. Measure the dependent var Repeated measure of analysis of variance (ANOVA). Repeated analysis eliminates differences between participants from experimental error Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Not applicable Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Controlled Not applicable Not applicable Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Not applicable Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Concern Concern Concern Concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Concern Concern Concern Concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Controlled Controlled Possible concern Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Possible concern Miscellaneous or Weaknesses Sampling Steps Analysis of Data Maturation Selection Selection by maturation interaction Statistical regression Mortality Instrumentation Testing History Resentful demoralization of the control group Diffusion of treatment Compensatory rivalry by the control group Compensatory equalization Generalization across participants Interaction of personological vars Verification of independent variable Multiple treatment interference Novelty and disruption effects Hawthorne effect Experimenter effects Pretest sensitization Posttest sensitization Interaction of time of measurement and treatment effects Measurement of the dependent variable Interaction of history and treatment effects Random sample from population. Random assignment to experimental & control groups. 1. Measure the dependent variable 2. Introduce independent variable 3. Measure the dependent variable Graphical visual analysis, multiple regression and/ or log linear analysis. Controlled Controlled Controlled