TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT
Training & Development
• Training & development
– Represents ongoing investment in employees & realizes
employees are assets
• Importance of training & development
– Rapid technological changes cause skill obsolescence
– Redesign of work brings need for new skills
– Mergers & acquisitions have increased need for integrating
employees into different cultures
– Employees are moving between employers more often,
necessitating training
– Globalization of business requires new knowledge & skills
Benefits of Training & Development
• Individual employee
– Increased employee marketability
– Increased employee employability security
• Organization
– Improved bottom line, efficiency & profitability
– Increased flexibility in employees who can assume different
& varied responsibilities
– Reduced layers of management
– Makes employees more accountable for results
Setting Training Objectives
• Align/match identified training needs with
training objectives
• Define objectives in specific, measurable terms
– Desired employee behaviors
– Results expected to follow from such behaviors
• One source of information for setting objectives
– Performance deficiency data contained in performance
management system
Organizational Development
• Training programs focus on individual skill
acquisition and development to improve
productivity as well as assist in obtaining strategic
objectives
• In a rapidly changing global environment,
organizations much be able to change in response
by undertaking larger-scale changes
• Such activities constitute organizational
development which focuses on the entire
organization rather than individual employees
Exhibit 9.5
Link Between Training & Performance
Management & Compensation
Training can...
• Increase employees’ knowledge of foreign
competitors and cultures.
• Help ensure that employees have the basic
skills to work with new technology,
• Help employees understand how to work
effectively in teams to contribute to product
and service quality.
Training can...
• Ensure that the company’s culture emphasizes
innovation, creativity, and learning.
• Ensure employment security by providing new ways
for employees to contribute to the company when:
– their jobs change
– their interests change
– their skills become obsolete
• Prepare employees to accept and work more
effectively with each other, particularly with
minorities and women.
Training
• Training is a planned effort by a company to
facilitate the learning of employees.
• High-leverage training:
–
–
–
–
is linked to strategic business goals and objectives,
has top management support,
relies on an instructional design model, and
is benchmarked to programs in other organizations.
• Continuous learning is a learning system that
requires employees to understand the entire work
process and expects them to acquire new skills,
apply them on the job, and share what they have
learned with other employees.
Training Methods
• On-the-Job Training
• Apprenticeship Training
• Informal Learning
• Job Instruction Training
• Lectures
•
•
•
•
Programmed Learning
Audiovisual Training
Simulated Training (also Vestibule Training)
Computer-Based Training (CBT)
• Electronic Performance Support Systems (EPSS)
• Distance and Internet-Based Training
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
8–10
Designing Effective Training Activities
The Training Process
1. Needs Assessment
• Organizational Analysis
• Person Analysis
• Task Analysis
2. Ensuring Employees’ readiness for Training
• Attitudes and Motivation
• Basic Skills
3. Creating a Learning Environment
• Identification of learning objectives and training outcomes
• Meaningful material
• Practice
• Feedback
• Observation of others
• Administering and coordinating program
Designing Effective Training Activities
(cont.)
The Training Process
4. Ensuring Transfer of Training
• Self-management strategies
• Peer and manager support
5. Selecting Training Methods
• Presentational Methods
• Hands-on Methods
•Group Methods
6. Evaluating Training Programs
• Identification of training outcomes and evaluation design.
•Cost-benefit analysis
Needs Assessment
Organizational Analysis
Person Analysis
Task Analysis
Ensuring Employee Readiness for
Training
• Motivation to learn is the desire of the
trainee to learn the content of the training
program.
• Self-efficacy is the employees' belief that
they can successfully learn the content of the
training program.
Ensuring Employee Readiness for
Training
• Managers can increase employees' self-efficacy level by:
– Letting employees know that the purpose of training is to try to
improve performance rather than to identify areas in which
employees are incompetent.
– Providing as much information as possible about the training
program and purpose of training prior to the actual training.
– Showing employees the training success of their peers who are
now in similar jobs.
– Providing employees with feedback that learning is under their
control and they have the ability and the responsibility to
overcome any learning difficulties they experience in the
program.
Basic Skills
CognitiveSAbility verbal
K
comprehension,
I
quantitative
L
ability, and
L
reasoning ability
S
Reading Ability the difficulty
level of
written
materials
Creating a Learning Environment
• Employees need to know why they should
learn.
• Employees need meaningful training content.
• Employees need to have opportunities to
practice.
• Employees need feedback.
Creating a Learning Environment
• Employees learn by observing, experiencing,
and interacting with others.
• Employees need the training program to be
properly coordinated and aadministered.
• Employees need to commit training content
to memory.
Transfer of Training
Climate for
transfer
Opportunity to use
learned capability
Technological
Support
Transfer
of
Training
Self-management
skills
Manager support
Peer Support
Selecting Training Methods
• Presentation Methods
–
–
–
–
Instructor-led classroom instruction
Distance learning
Audiovisual techniques
Mobile technologies
• Hands-on Methods
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
On-the-job training
Self-directed learning
Simulations
Business games and case studies
Behavior modeling
Interactive video
E-learning
Outcomes Used in Evaluating
Training Programs
OUTCOME
WHAT IS MEASURED
•Acquisition of
Knowledge
HOW MEASURED
•Pencil and paper tests
•Work sample
Skill-based Outcomes
•Behavior
•Skills
•Observation
•Work sample
•Ratings
Affective Outcomes
•Motivation
•Reaction to Program
•Attitudes
•Interviews
•Focus groups
•Attitude surveys
Results
•Company Payoff
Return on Investment
•Economic value of
Training
Cognitive Outcomes
•Observation
•Data from information system
or performance records
•Identification and comparison
of costs and benefits of the
program
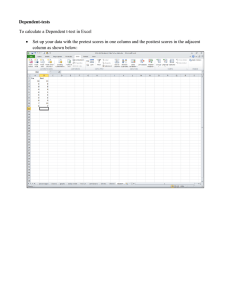
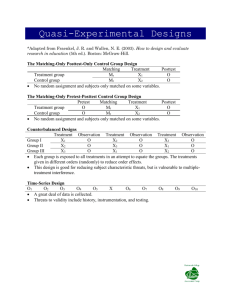
Evaluation Designs
• Pretest/Posttest
with Comparison
Group
• Posttest Only
• Posttest only with
comparison
Group
• Pretest/Posttest
• Time Series
Determining Return on Investment
• Cost-benefit analysis is the process of
determining the economic benefits of a training
program using accounting methods.
• Determining costs
• Determining benefits
• Making the analysis