PERSIAN Chart - classicalempires
advertisement
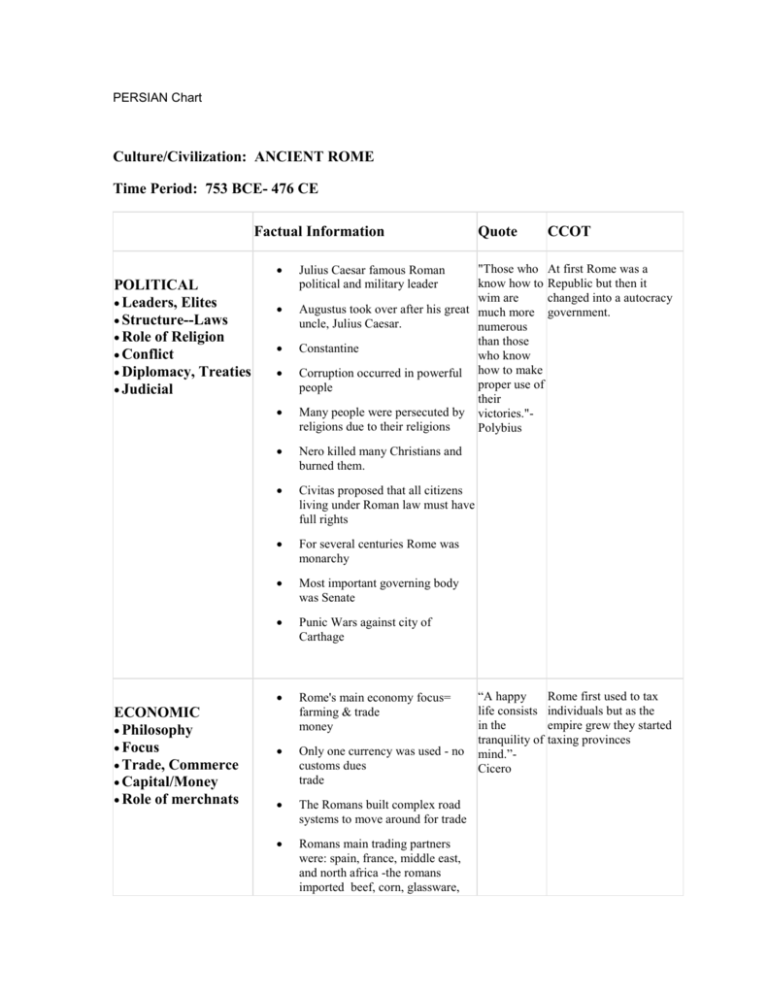
PERSIAN Chart Culture/Civilization: ANCIENT ROME Time Period: 753 BCE- 476 CE Factual Information POLITICAL Leaders, Elites Structure--Laws Role of Religion Conflict Diplomacy, Treaties Judicial ECONOMIC Philosophy Focus Trade, Commerce Capital/Money Role of merchnats Quote CCOT "Those who At first Rome was a know how to Republic but then it wim are changed into a autocracy Augustus took over after his great much more government. uncle, Julius Caesar. numerous than those Constantine who know Corruption occurred in powerful how to make proper use of people their Many people were persecuted by victories."religions due to their religions Polybius Julius Caesar famous Roman political and military leader Nero killed many Christians and burned them. Civitas proposed that all citizens living under Roman law must have full rights For several centuries Rome was monarchy Most important governing body was Senate Punic Wars against city of Carthage Rome's main economy focus= farming & trade money Only one currency was used - no customs dues trade The Romans built complex road systems to move around for trade Romans main trading partners were: spain, france, middle east, and north africa -the romans imported beef, corn, glassware, “A happy life consists in the tranquility of mind.”Cicero Rome first used to tax individuals but as the empire grew they started taxing provinces iron, lead,leather, olive oil, silk, silver, spices, timber , tin, and wine ( etc.) RELIGIOUS Origins Beliefs, Teaching Conversion Holy Books Influence on Society* Rome depended on merchants to trade efficiently so that their economy would prosper Belief in Gods and Goddesses Beliefs of those who were conquered slowly intergrated into Roman culture and Religion and started the Roman belief in Gods Through the study of Greek art, literature, and mythology Greek gods came to be identified with Roman gods Most forms of religious activity required some type of sacrifice to the gods Prayer was also a part of worship but it was difficult to because many gods had more than one name or their sex was unknown As Christian became popular the Bible was read SOCIAL Family Gender Relations Social Classes Inequalities— coercive labor Life Styles Romans first believed in gods and goddesses but other religions were soon brought to Rome such as Christianity and Judaism. “An As the empire was slowly Lower class: slaves, serfs, and imbalance declining, the break slavesAbout 40% of population between the between the low and high Economy depended on slaves They were considered property but rich and poor classes greatly increased is the oldest could buy themselves freedom Throughout the history of Slavery did not suddenly end, but and most fatal ailment Rome, the males always was slowly replaced by paying of all dominated the way the peasants (serfs) to do labor Patricians lived in ravish houses Republics.” - society was run and Plutarch women were given a and often owned a villa in the much lesser role, and it country became her duty to follow Plebians lived in crowded her husband. The contrast apartments called insulae between the lifestyles of The rich lived extravagantly, with the wealthy and the poor many servants, while the peasants is also a constant because suffered with poor conditions, as the rich continue to live such as unsanitary living spaces their ravish lifestyles, the When a Roman woman got poor work in the fields, married, she was under the control and continue to stay at the of her husband bottom of the social class THe husband owned and ruled system. Towards the fall everything and everyone in his of the Roman Empire, the house amount of contrast Men dominated the religious world between the wealthy (patriarchal) Patricians and peasantry Woman's religious roles were mainly associated with fertility and chastity Upper class: senatorial class, equestrial class Middle class: commons (plebs), Latins (freeborn people of Italy), Foreigners (freeborn people who lived in Roman territories), Freedpeople (former slaves) Lower class: slaves Plebians increased, as soon Plebians slowly began to replace slaves. INTELLECTUAL, ARTS Art, Music Writing, Literature Philosophy Math & Science Education Technology “Medicine Some Roman art had greek influence, and some were done on sometimes snatches wood and ivory. away health, There were four styles of roman sometimes art. gives it.”Proportional structures and Ovid through them it could be seen that it reflected the idealism philosophy “Habent sua fata libelli: and realism art. Relief sculptures usually showed “Books have their own heroes or battle victories destinies”their music had Greek influence Ovid discovered new ways to mind for “Either do silver, gold and lead. not attempt Water mills were invented for at all, or go grinding grain through with Concrete was used for building it.”-Ovid and domes and barrel vaults “The spirited Sewage systems Roman number system consisted horse, which of what we know today as roman will try to win the race numerals. of its own Ovid – influential roman poet , accord, will wrote a lot about love run even faster if encouraged”Ovid 2nd century BC illustrated imitations of marble and masonry. Mythical creatures were sometimes shown. 1st century BC – Realism, 3D features of architecture and landscapes . (27 BC – 14 AD) had a scenic design or abstract on a background of a solid color. 1st century ADmythology, abstract patterns and detailed architecture. Using barrel vaults they created aqueducts (well known for it) Roman doctorGalen (100 AD) important because he was the first to write a book and find various symptoms and treatments Studied body by NEAR: GEOGRAPHY Location Physical Movement Human/Environment Region “All roads Founded on the Italian lead to Peninsula Rome.” Located along the Mediterranean Sea Near Tiber River Different types of geography(mountains, forest, deserts) Many hilly land providing protection Temperature doesn’t fluctuate and allows for fertile land and farming Traded and Conquered many areas along Mediterranean Many roads connecting the empire hence the saying “All Roads lead to Rome” “dissecting” animals and wounded gladiators Scholars treasure a book of Ovid’s called Metamorphoses (epic poem of stories) because of its literal structure A city of Rome founded in 753 B.C.E on the Italian peninsula gradually spread to dominate the Mediterranean








