schizophrenia
advertisement

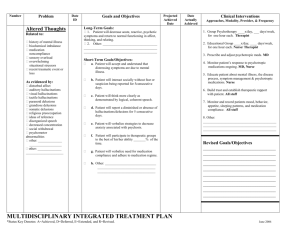
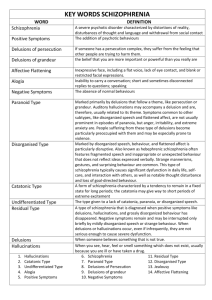
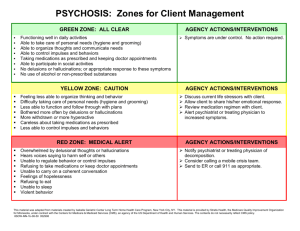
PMHS AP PSYCH Name______________________________ AIM: To describe schizophrenia through film. Take notes as you view the various episodes. PART I: The first clip is a simulation of schizophrenia. It will begin with a normal day in a household and then slowly degenerate into hallucinations and delusions. Write down as many hallucinations and delusions as you can. Hallucinations (things that are seen, heard, tasted, etc.) but are not real Delusions – false beliefs PART II: Zimbardo meets with a schizophrenic patient. He is very intelligent; however, his delusions force him to live on the street. a. In order to get housing, David must take antipsychotic medication from the outreach program. What does David think of this requirement? “There is no real j______________________!” b. When David is asked if it is possible that he has an illness, he denies this possibility. He says there are too many instances of people tracking him. He says he has lost many “books” where his money and ID are contained. He says this has happened THIRTY OR FORTY TIMES!!! He was just innocently making a phone call and “poof!” the books disappear. How does this story fit into David’s DELUSIONS? c. What happens to David several weeks after taping this segment? *Schizophrenics are most likely to HURT themselves, not others (as the last clip just showed). This next clip shows someone who may get violent because of their delusions. PART III: A recent episode of Criminal Minds 1. Ted is the character who has schizophrenia. He hears voices in the form of another male actor. Which is hearing voices? (circle) a. Hallucinations b. Delusions 2. When Ted hears whispering on the train, he thinks everyone is talking about him. False thoughts are also known as: (circle) a. Hallucinations b. Delusions 3. Ted is on the train because his psychiatrist was travelling with him to speak at a conference. There is also an FBI agent on the train and it was her “FBI” book that triggered hallucinations for Ted. Which of these delusions or hallucinations fit Ted’s profile? Explain those that you choose by using an example from film Delusions of persecution (think people are coming after them) Delusions of reference (random events are personal and always about them) Delusions that they are on a special mission (from God or aliens) Delusion that there was a bodily change (an implant or modification of some kind) Auditory Hallucinations Visual Hallucinations PART IV: The real John Nash – an economist suffering from Schizophrenia (the film A Beautiful Mind) is based on his life. This is an excerpt based on the real-life man – A Brilliant Madness. After this clip, you will see portions of the Hollywood film. 1. John Nash was a brilliant mathematician and economist. What triggers Nash’s psychotic break of paranoid schizophrenia? How did the clinician explain this? 2. How did the hospital explain John Nash’s schizophrenia using PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY (popular at the time) 3. How did being in the hospital make John think his delusions were true? 4. In what way did John have delusions that he was on a special mission? 5. If he actually heard voices, what would that be considered? a. Auditory Delusions b. Auditory Hallucinations PART V A Beautiful Mind. John Nash is played by Russell Crowe. 1. In this first scene, John is placed in the hospital. Alicia (John’s wife) learns that he has been talking with imaginary people – like his college roommate. Is seeing a person who is not there aa. Delusion b. Hallucination 2. The hospital gives John Nash ECT – electroconvulsive shock therapy. Describe what this is like. 3. Even though his real-life schizophrenia involved more delusions. The film makes him out to have hallucinations. Why do you think the Hollywood film does this? What ways does the film portray these aspects of paranoid schizophrenia? Delusions of persecution (think people are coming after them) Delusions of reference (random events are personal and always about them) Delusions that they are on a special mission (from God or aliens) Delusion that there was a bodily change (an implant or modification of some kind) Auditory Hallucinations Visual Hallucinations