Chapter 4 objectives Cell Unit Be able to identify the following parts
advertisement

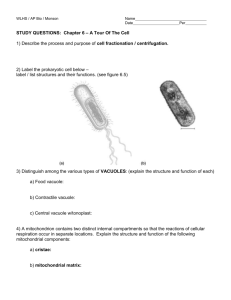
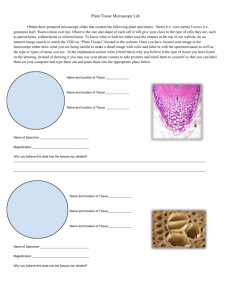
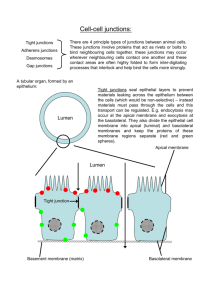
Chapter 4 objectives Cell Unit 1. Be able to identify the following parts of a microscope: ocular, low, medium, and high power objectives, stage, diaphragm. 2. Distinguish between the detail seen and the size of the field of view when viewing a specimen under low verses high power. 3. What limits how big a cell can be and how small? 4. What are the differences between a light microscope, a TEM, and an SEM? What are each used for? Be able to tell from a micrograph which type of microscope was the image taken from. 5. Given the diameter of the field of view and a specimen in this field, determine the approximate size of the specimen 6. Be able to identify on a diagram the following: nucleus, nuclear envelope (membrane), nuclear pore, chromatin, nucleolus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, rough er, smooth er, golgi, transport vesicles, central vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondrion, lysosome, perioxisome, cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, cell wall, plasma membrane, centrioles 7. Describe (match) the functions of the structures listed in #6 8. Identify which structures in #6 are found in prokaryotic cells. Identify which are found in eukaryotic cells. Identify those found in plants and those found in animal cells 9. Describe the different types of cell/cell junctions and give examples of where they are found (tight junctions, gap junctions, anchoring junctions, plasmodesmata 10. List organelles that are “membrane bound” 11. Describe the components of the endomembrane system that would be involved in secreting a protein hormone into the blood. (what are they and how do they play a role in this process) Chapter 4 objectives Cell Unit 1. Be able to identify the following parts of a microscope: ocular, low, medium, and high power objectives, stage, diaphragm. 2. Distinguish between the detail seen and the size of the field of view when viewing a specimen under low verses high power. 3. What limits how big a cell can be and how small? 4. What are the differences between a light microscope, a TEM, and an SEM? What are each used for? Be able to tell from a micrograph which type of microscope was the image taken from. 5. Given the diameter of the field of view and a specimen in this field, determine the approximate size of the specimen 6. Be able to identify on a diagram the following: nucleus, nuclear envelope (membrane), nuclear pore, chromatin, nucleolus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, rough er, smooth er, golgi, transport vesicles, central vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondrion, lysosome, perioxisome, cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, cell wall, plasma membrane, centrioles 7. Describe (match) the functions of the structures listed in #6 8. Identify which structures in #6 are found in prokaryotic cells. Identify which are found in eukaryotic cells. Identify those found in plants and those found in animal cells 9. Describe the different types of cell/cell junctions and give examples of where they are found (tight junctions, gap junctions, anchoring junctions, plasmodesmata 10. List organelles that are “membrane bound” 11. Describe the components of the endomembrane system that would be involved in secreting a protein hormone into the blood. (what are they and how do they play a role in this process)