test#1
advertisement

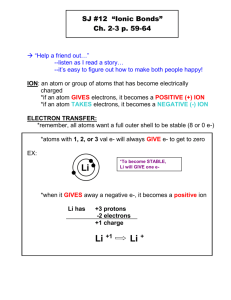
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY – Test#1 REVIEW, chapter 7, sections 7.1 & 7.2 (20 Qu’s) Please note: Section 7.3 Metallic Bonding will be presented on test#2 and not this test. Topic: Ionic Bonding 1. Complete the following table: Element: # valence e- # core e- Ionic charge: # e- lost by atom to form the ion beryllium nitrogen indium cesium 2. Name the element in period 5 that has 4 valence electrons. ___________ 3. Draw the electron dot structure of: a. an atom of fluorine, b. an atom sodium, c. an ion of aluminum, d. an ion of selenium. 4. When the following ions form they follow either the octet rule or the duet rule. State which rule is followed in each of the following ions form: Circle the correct answer in each case. (i) lithium ion, octet rule / duet rule (ii) calcium ion, octet rule / duet rule (iii) carbide ion, octet rule / duet rule (iv) beryllium ion, octet rule / duet rule (v) hydride ion, octet rule / duet rule 5. What is meant by the coordination number of an ion in a crystal structure of an ionic compound? 6. What is the coordination number for each ion in the three compounds, NaCl, CsCl, and rutile? 7. Explain how any ionic compound can be made to conduct electricity. 8. Consider the combination reaction between barium and iodine. Write the two REDOX half reactions (label which one is oxidation and which one is reduction) and then write the overall balanced chemical equation for this chemical reaction. 9. Answer each of the following with either cathode or anode. In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride… 1. …the sodium ions migrate towards the ___________ . b. …electrons travel through the external circuit (wires) from the ___________ to the ___________ . c. …the charge on the ___________ is negative. d. …reduction occurs at the ___________. e. …bubbles of chlorine gas are produced at the ___________. 10. Complete the table of formula units that form between elements shown: sulfur phosphorus carbon bromide calcium lithium gallium 11. Write the equation (using symbols/formulas) to represent the change from… a. …an atom to ion for magnesium: ______________________________ b. …an atom to ion for oxygen: ______________________________ c. …an atom to ion for indium: ______________________________ d. …an atom to ion for arsenic: ______________________________ e. …an atom to ion for lead: ______________________________ 12. Complete Bohr models for a. silicon, b. calcium, c. neon. 13. Complete FULL written configurations for, a. zinc ion, _______________________________________________ b. chloride ion, _______________________________________________ c. rubidium ion, _______________________________________________ d. radon atom, _______________________________________________ 14. Write the equation (using Lewis dot structures) to represent the change from… a. …an atom to ion for nitrogen: ______________________________ b. …an atom to ion for iodine: ______________________________ c. …an atom to cation for hydrogen: ______________________________ 15. Use orbital diagrams to show how the following atoms may change into their common ions: a. beryllium, b. carbon, 16. What is meant by the ‘duet rule’ and ‘octet rule’? 17. Describe the general properties associated with ‘ionic compounds’. 18. What happens when table salt, NaCl, dissolves in water. Explain fully. 19. How is a pseudo noble gas configuration different from a noble gas configuration? Explain fully using examples. 20. Define the following and include examples: a. ionic bond, b. formula unit, c. chemical formula, d. cation, e. anion, f. oxidation, g. reduction, h. “OIL RIG”.