Cell Diversity Lab

Cell Diversity Lab
Objectives:
To become familiar with the cellular characteristics of Eukaryotic organisms
To identify and compare organelles and other cellular structures between different types of cells
To relate the differences in cellular structure to the function of cells
Materials:
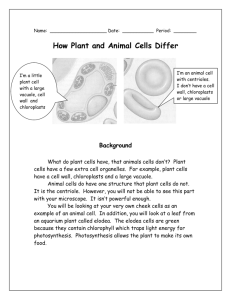
Compound light microscope
Cellular structures handout featuring the Plant and Animal cell, and their organelles
Elodea leaf, pipette, slide (these are glass – be careful), and coverslip
Prepared slides
Hints:
1) Cells are 3-dimensional structures (like you), but the view that you get with a light microscope is only 2D (flat, like a drawing). Try to deep in mind that some of the cell’s structures may not be visible because they were (or are) above or below the flat slice that you have focused on.
2) Organelles are not always easy to see, even when they’re in your plane of view! Try hard…you may have to use a little imagination at first. With practice, it gets easier to discern structures in the blurry cellular environment.
Procedure :
Plants : Obtain a small piece of Elodea leaf and place it in the center of a slide. If the leaf isn’t already sitting in a drop of water, use the pipette to wet the slide – just one drop is plenty!
Stand the cover slip on the edge next to the leaf sample and let it fall onto the leaf. Gently tap the coverslip to reduce air bubbles, and you’re ready to look at in under the ‘scope.
Try to find the following structures: chloroplast cell wall nucleus cell membrane
Sketch the Elodea leaf below, labeling the structures you’ve found: vacuole cytoplasm
Low power*
_______x
High power*
_______x
* The eyepiece itself is 10x magnification. To get the total magnification, multiply the magnification of the lens you have
Selected by 10. For example, the 40x lens gives a total magnification of 400x, or 10x (eyepiece) X 40x lens = 400x total.
QUESTION: What patterns do you observe, if any, in the arrangement of chloroplasts in the cell?
Elodea under attack with SALT WATER!
Now, remove the cover slip from your Elodea specimen, and add a drop of salt water.
Replace the coverslip, observe and draw again.
Low power High power
_______x _______x
QUESTION: How was the plant cell affected by the salt water?
Protists:
Obtain a prepared slide of the single-celled organisms below, one at a time:
Draw one of each in the spaces below, labeling all structures that you can see.
Paramecium (para-ME-see-um) Euglena (you-GLEEN-uh)
Low power Low power
_______x _______x
High power
_______x
High power
_______x
QUESTION: What are three (3) challenges that a Paramecium might face, but an Elodea probably would not?
QUESTION: Select one of the challenges above, and state how it relates to structural differences between the cells
Animal:
Obtain one slide of human blood, frog blood, and frog skin. Sketch a section of each of these below.
Human Blood
Low power High power
_______x _______x
Frog Blood
Low power
_______x
High power
_______x
Frog Skin
Low power
_______x
High power
_______x
QUESTION: Of the three cell types you examined from vertebrates (human blood, frog blood and frog skin), which is suited to carry oxygen from one place to another? What structural characteristics make these cells ideal for the job?
Bonus QUESTION: Obtain a different slide from your teacher featuring an organism not studied above. Describe how you think the structure of the cell or organism relates to its function.