Utilitarianism and Kant answers to mark

What are we looking for?
What are the key features of consequentialist ethics? 5ku
This is when consequences are considered.
Actions are based on what the consequences of actions are.
This is a theory based on the consequences of actions. An act is morally right or wrong based on the consequences of the action.
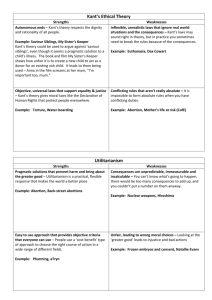
Consequentalism is a theory which looks at the consequences of actions. An act is morally right or wrong depending on the outcome of the action. An act would be right if it produces the greatest amount of happiness for the greatest amount of people.
Consequentialist ethics is more commonly referred to as utilitarianism. It is referred to consequentialist ethics because it is a theory which decides the morality of an action based upon the consequences of actions. A utilitarian would deem an action morally right if it maximises the greatest amount of happiness for the greatest amount of people.
Consequentialist ethics is more commonly referred to as utilitarianism. It is referred to as consequentialist ethics because it is a theory which decides the morality of an action based upon the consequences of actions. A utilitarian would deem an action morally right if it maximises the greatest amount of happiness for the greatest amount of people. The two main proponents of utilitarianism are Jeremy
Bentham and John Stuart Mill. Utilitarianism has been divided into two types: Act and Rule utilitarianism. Act Utilitarians consider every action as a new action, basing morality on maximising happiness for the greatest amount of people, or failing this minimising pain for the greatest amount of people. While rule
Utilitarians take into account general rules and moral laws which they believe would contribute to happiness in the long term.
What are the main features of Kantian ethics?
5ku
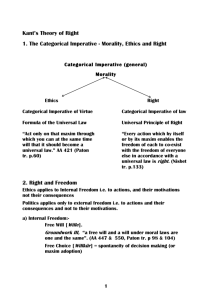
Kant said we need to follow laws that we know are true, to be good. This is the categorical imperative.
Kant thought we needed reason. We need to follow laws to be morally good.
Kant believed we should act out of duty. We should follow moral laws. We use reason to know what our duty is. He believed we should act in such a way that what we do should be a moral law. This is the categorical imperative.
Kant aimed to establish a system of ethics based upon reason. For Kant we should act out of duty, we have an innate duty to follow the moral law. He believed as individuals we should act in such a way that our actions could become universal. An action is right if it can be applied to everyone in all circumstances, with no exceptions. Cant believed stealing could be a categorical imperative; ‘if stealing is wrong for me it is wrong for everyone’.
Kant believed the Categorical imperative is a priori, meaning we can see that it is true without having to experience it first.