Review for Quiz 2 - LaGuardia Community College
advertisement

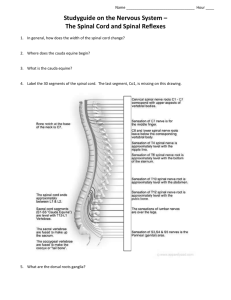
SCB 204.1738, 1739 Quiz 2 Robyn O’Kane, Ph.D. Spring I 2008 FORM A Name__________________________________________________________________ 1. The hypothalamus functions in so many ways partly because it A. is a circumventricular organ. B. lacks a blood-brain barrier in certain areas. C. contains the fourth ventricle. D. All of the above are correct. E. A and B are correct only. 2. All meninges surrounding the spinal cord are structurally the same as the meninges surrounding the brain EXCEPT A. the pia mater. B. the dura mater. C. the arachnoid mater. 3. Equilibrium and balance are the primary functions of the A. premotor area. B. cerebellum. C. thalamus. 4. Spinal nerves are surrounded by a(n) A. epineurium. B. endoneurium. D. prefrontal cortex. C. perineurium. 5. Muscle movements are coordinated partly by information from the cerebellum and the primary motor cortex communicating (synapsing) in the A. superior colliculi. B. red nuclei. C. medulla oblongata. D. reticular formation. 6. All of the following are correct regarding the flexor/withdrawal reflex EXCEPT A. reciprocal inhibition is keeping the stretch reflex from occurring. B. the flexors of the ipsilateral leg are stimulated. C. the reflex is monosynaptic. D. the crossed extensor reflex is typically activated at the same time. 7. Parkinson’s disease is caused in part by a disruption of the communication of the ________________ with the ________________. A. midbrain; basal ganglia. B. substantia nigra; midbrain. C. midbrain; substantia nigra. D. dopamine; norepinephrine. 8. Which part of the brain contains the nuclei for the accessory, glossopharyngeal, vagus, hypoglossal, and vestibulocochlear nerves? A. Thalamus B. Medulla C. Pons D. Midbrain 1 9. If your doctor taps your patellar tendon, trying to elicit the patellar reflex, why might the reflex NOT work? A. The stimulus may not have been strong enough to trigger an action potential in the sensory neuron. B. The synapse between the sensory neuron and the interneuron is not working. C. You have a defect in your cervical spinal cord. D. The axons crossing in the gray commissure are broken. 10. The brain is protected by the ______________ and the spinal cord is protected by the _________________. A. skull; skull B. vertebrae; skull C. skull; vertebrae D. vertebrae; vertebrae 11. The neuroglial cell that is closely associated with the blood-brain barrier is the A. oligodendrocyte. B. microglial cell. C. ependymal cell. D. astrocyte. 12. Cerebrospinal fluid is found in the A. subdural space. B. epidural space. C. subarachnoid space. D. pia mater. 13. Spinal nerves L3-L5 and S1-S5 form the A. conus medullaris. B. filum terminale. C. cauda equina. D. lower part of the vertebral column. 14. Which part of the brain is the bridge that connects the cerebellum, spinal cord, and parts of the brain stem with each other and with the cerebrum? A. Pons B. Hypothalamus C. Infundibulum D. Cerebellum 15. A person suffering from nonfluent aphasia A. probably had his Wernicke’s area damaged. B. cannot speak (or has very limited speaking ability). C. has a changed speech pattern due to uncoordinated speech muscles. D. has a damaged prefrontal cortex. 2 16. While walking down the street, you get startled by a passing car that honks its horn right next to you. Your response is to jump away from the noise. What part of the brain was the primary center involved in this reflex motion? A. Medulla oblongata B. Limbic lobe C. Inferior colliculi D. Superior colliculi 17. The diencephalon A. includes the hypothalamus, epithalamus, and thalamus. B. is superior to the brain stem. C. includes the midbrain, corpora quadrigemina, and cerebral peduncles. D. A and B are correct only. E. B and C are correct only. 18. The cell bodies for somatic motor neurons are located in the A. anterior gray horn. B. posterior gray horn. C. posterior root ganglion. D. anterior root ganaglion. 19. The major relay center in the brain is the A. midbrain. B. basal ganglia. C. thalamus. D. hypothalamus. 20. What structure is important for keeping unwanted hydrophilic materials from entering the brain but allowing necessary nutrients into the brain? A. The spinal cord. B. The blood-brain barrier. C. The circumventricular organs. D. The arachnoid villi. 21. Oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone are A. released by the hypothalamus via the pituitary gland. B. released from the thalamus. C. produced by the infundibulum. D. neurotransmitters. 22. The mechanical process of digestion is accomplished in part by inputs from the A. primary sensory area. B. superior colliculus. C. epithalamus. D. hypothalamus. 3 23. The anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts A. are located in the anterior and posterior gray horns. B. propagate information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. C. contain motor information. D. All of the above are correct. 24. The limbic system is involved in all of the following EXCEPT A. emotions. B. pain. C. vision. D. olfaction. 25. When you fall asleep in class, your ____________________ isn’t working well. A. primary visual area B. basal ganglia C. sensory association area D. reticular activating system 26. The premotor area A. is the motor association area. B. allows you to perform previously learned complex movements more fluidly. C. is located in the frontal cortex. D. All of the above are correct. E. A and B are correct only. 27. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced A. by the arachnoid villi. B. in the lateral ventricles. C. by the astrocytes surrounding capillaries. D. at a rate significantly faster than the rate of reabsorption. 4