LIST OF CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION with CHA4
advertisement

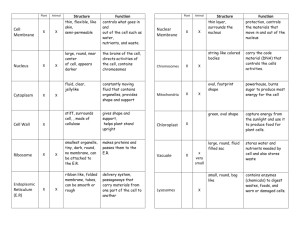
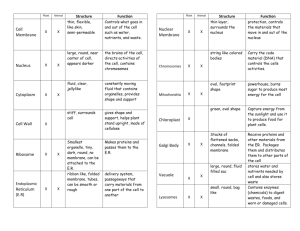
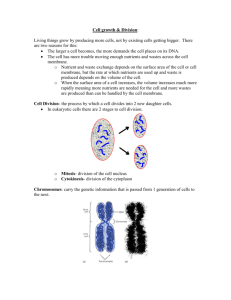
LIST OF CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION Cell Wall : provides shape and support for plants (rigid) Fence Cell Membrane : movement in and out; controls what enters and leaves Gate Cytoplasm : gel-like fluid Environment (Atmosphere) Nucleus : control center; directs cell activities; contains DNA Brain (Computer) Mitochondria : produce most of the energy (power) Powerhouse Chloroplasts : photosynthesis; captures energy in sunlight Farm PROKARYOTE : cell without a nucleus Bacteria EUKARYOTE : cell with a nucleus Plant and Animal PRODUCER : an organism that makes its own food Plants CONSUMER : cannot make its own food Animals ALL CELLS HAVE - - CELL MEMBRANE, CYTOPLASM, & DNA !!! CHPTR 4 – THE CELL IN ACTION (Pg. 90) Big Idea : Cells carry out important life functions including taking in nutrients and releasing materials, obtaining energy, and growing. I. Exchange with the Environment A. What is diffusion? The movement of particles from high to low density. 1. Diffusion of Water 2. The Cell and Osmosis --- The diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. B. Moving Small Particles 1. Passive Transport --- The movement of subst. across a cell membrane w/o the use of energy by the cell. 2. Active Transport --- Requires the cell to use energy. C. Moving Large Particles 1. Endocytosis --- A cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell. 2. Exocytosis --- A cell releases a particle … II. Cell Energy A. From Sun to Cell: Photosynthesis --- The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make food. B. Getting Energy from Food: Cellular Respiration --- The process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food. C. Fermentation --- The breakdown of food without the use of oxygen. III. The Cell Cycle A. The Life of a Cell: Chromosome --Structures in the nucleus that are made up of DNA and protein. B. Mitosis --- A process of cell division that forms two new nuclei with the same number of chromosomes. 1. Interphase – Chromosomes are copied & each becomes two chromatids. 2. Prophase – Chromosomes condense into rodlike structures. 3. Metaphase – Paired chromatids align at the cell’s equator (center). 4. Anaphase – The chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. 5. Telophase – A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes unwind. 6. Cytokinesis – The cytoplasm divides and the cell pinches in two.