Economic Systems: Capitalists vs. Communists
advertisement

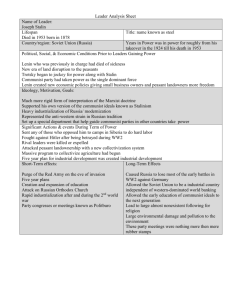
Applications of Option Theory Comm 423 Professor: Jing Chen Date: November 27, 2002 From: Fiona Chan Option Theory of different forms of Government: Communist and Capitalist Our world is roughly classified into two types of governments, Communist and Capitalist. Examples of Democratic capitalist forms of government are the United States and the countries of Western Europe. Examples of Communist societies are the former USSR, China, and North Korea. This is a call option. Stock price = GDP, K= the initial investment of the government. d GDP GDP = r dt + σdz r = expected growth rate σ= volatility According to the relative level of fixed and variable costs, Socialist countries, like the USSR had in Soviet times, have high fixed costs, and low uncertainty. Their expected rate of return is high and volatility is low. Yet, high fixed costs which have lower variable costs in production need higher output volume to breakeven. (Figure 1) Capitalist countries like the United States have low fixed cost with high volatility. Communist Society In a socialist society, the fixed costs are high, but with low uncertainty. These countries prosper in stable environments because of their low marginal cost. However, they have difficulty adjusting when the environment changes quickly. The Communist societies invested large amounts of money in their industry development. Communist systems rely on a centrally planned economy, also called a command economy. They have high fixed costs because of the heavy investment for the countries. For example: At the end of the 1920s Stalin revoked the New Economic Policy and inaugurated the first of a series of Five-Year Plans, committing the regime to a program of high paced industrial development and forced collectivization of agriculture. The result was a radical transformation of Soviet society. The government built hundreds of factories to produce machine tools, automobiles, agricultural machinery, motors, aircraft, generators, chemicals, iron and steel, coal, oil, and armaments.1 During the stable environment between the 1950s and 1970s, communist economies did achieve some success. Studies of growth trends from the 1950s to the early 1970s showed the centrally planned economies equaling and in some cases exceeding the growth rates of the capitalist economies. They also attained high literacy rates, made basic health care available to the population, eliminated extreme poverty, and avoided unemployment.2 Capitalist Society Capitalism is an economic system in which private individuals and business firms carry on the production and exchange of goods and services through a complex network of prices and markets. They have low fixed costs because their economies are based on demand and supply of the market. number of private-owned companies. 1 The economies consisted of a large Under this system, a minimum of government Smith, A. 1993 Russia and the world economy: Problems of integration. London: Routlege. P.20-23 Boswell,T. and Chase-Dunn, C. 2000 The Spiral of Capitalism and Socialism: Toward Global Democracy. London: Lynn Rienner Publishers. P.85-95 2 supervision is required; if competition is present, economic activity will be self-regulating.3 The economies of these societies are very flexible. Changes in the economic environment During the 1980s and 1990s, the world economy was divided between expansion and stagnation. In order to foster renewed economic growth and development, firms, industry, and the state must develop extensive sociopolitical accumulation innovation. A world economic divide was taking place between high-skilled flexible production, such as biotechnical, electronic, and information processing, and on the other side, low-skilled mass production, such as textiles, toys, appliance, and other assembly-line work. State-socialist societies experienced extremely difficult economic reactions to the world divide because they had concentrated so heavily on low-skill mass production in the postwar period.4 For the capitalist societies like the United States, various accumulation innovations were adopted; the most important factor for successful adaptations has been “flexibility”. Flexible organizations included decentralized management with much more cooperative participation from below, higher-skilled and relatively more-autonomous workers, increased scientific and technical labor, variable-batch production runs, and rapid adoption of new technology.5 Conclusions 3 Mandel, E. 1973 An introduction to Marxist economy theory. New York: Pathfinder Press p .47-51 Teeple, G. 2000. Globalization and the decline of social reform: Into the twenty-first Century. Aurora: Garamond press 5 Teeple, G. 2000. Globalization and the decline of social reform: Into the twenty-first Century. Aurora: Garamond press. p.105 4 Communist Societies prosper in a stable environment because of their low marginal cost. However, in a volatile environment they can hardly survive. The capitalist societies prosper in a volatile environment as low fixed costs make them flexible; they can adjust the environment quickly. As a result, the capitalist structured societies are dominated the world. The communist leaders in the surviving communist countries like China, have held out against political reform but welcomed economic reform. Figure 1: Output and return with different level of fixed costs Rate of return Low Fixed Cost High Fixed Cost Output Figure 2: Uncertainty and variable cost 1 Variable Cost High Volatility Low Volatility 0 5 10 15 Level of fixed Cost Reference 20 Boswell,T. and Chase-Dunn, C. 2000 The Spiral of Capitalism and Socialism: Toward Global Democracy. London: Lynn Rienner Publishers. Mandel, E. 1973. An introduction to Marxist economy theory. New York: Pathfinder Press Smith, A. 1993 Russia and the world economy: Problems of integration. London: Routlege. Teeple, G. 2000. Globalization and the decline of social reform: Into the twenty-first Century. Aurora: Garamond press Hull, J.C. 2000. Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives. New Jersey: Prentice Hall