Adult Patients with Depression and Insomnia is Trazodone vs Other
advertisement

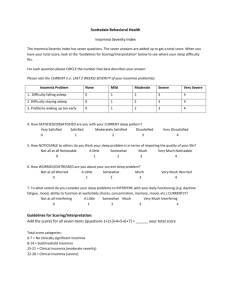
PAGE 2 Running Head: TRAZODONE EFFECTIVENESS IN DEPRESSION AND INSOMNIA Evidenced Based Critically Appraised Topic Adult Patients with Depression and Insomnia is Trazodone vs Other Medications Effective in Reducing Insomnia March 9, 2014 MaKayla Vaughan BSN, RN, FNP-S University of Mary PAGE 2 Running Head: TRAZODONE EFFECTIVENESS IN DEPRESSION AND INSOMNIA Adult Patients with Depression and Insomnia is Trazodone vs Other Medications Effective in Reducing Insomnia Evidenced Based Critically Appraised Topic Case Presentation: A 48 year old female with a new diagnose of mild depression is experiencing an increase in stress in home life. Patient reports feeling anxious and “more stressed out.” The patient reports additional stresses due to recent hospitalizations from her husband and sister. Both are requiring more assistance from patient financially and physically. Patient is describing trouble sleeping over last couple weeks. Patient was prescribed 50mg trazodone po every HS. Clinical Question: In adult patients with depression and insomnia is trazodone vs other medications effective in reducing insomnia? Articles: Wiegand, M. (2008). Antidepressants for the treatment of insomnia: a suitable approach. Drugs, 68(17), 2411-2417. Level of Evidence: IV Thaler, K., Morgan, L., Van Noord, M., Gaynes, B., Hansen, R., Lux, L., & ... Gartlehner, G. (2012). Comparative effectiveness of second-generation antidepressants for accompanying anxiety, insomnia, and pain in depressed patients: a systematic review. Depression and Anxiety, 29(6), 495-505. doi:10.1002/da.21951. Level of Evidence: I Summary and Appraisal of Article 1: Using an antidepressant for insomnia is effective with patients who are also needing treatment for mood disorders or depression. An antidepressant may potentially positively influence these patients (Wiegand, 2008). Wiegand (2008), conducted a large-scale multicentered study (n=589) in which Trazodone 50mg was tested against zolpidem 10mg and placebo for 2 weeks. The effects were measure by subjective estimations of self-reported sleep onset and duration, from morning questionnaires. One week after both active treatments, the study concluded zolpidem significantly reduced sleep latency more than trazodone. After two weeks zolpidem showed a shorter sleep onset than the other groups, but both drugs significantly prolonged subjective sleep duration. There were 12 patients who did withdraw from the study due to adverse events, such as excessive sleepiness, dizziness, headache, etc. Trazodone is effective for short term insomnia when there is some amount of associated depressive symptoms or history of depression. Also noted trazodone is effective in long term insomnia use if needed also, but the study also notes that in long term insomnia treatment trazodone could be combined with zolpidem low dose and low as possible dose of trazodone preferably 50mg for effective treatment of insomnia. Wiegand does note that advantages of using an antidepressant for insomnia tolerance does not develop, or no abuse of addiction potential is not expected. He also notes some disadvantages are there is a broader spectrum of adverse effects, interactions and contraindications. PAGE 2 Running Head: TRAZODONE EFFECTIVENESS IN DEPRESSION AND INSOMNIA Summary and Appraisal of Article 2: Thaler, et. al. (2012) reports 2 different studies on effectiveness of trazodone vs other treatments. Study one was a 6 week trial comparing 126 patients with depression received fluozetine 2060mg or trazodone 100-400mg. The study showed improved sleep disturbances in the trazodone group using the Hamilton depression rating scale (HAM-D). Study two that was a 6 week trial comparing 227 patients who received venlafaxine 75-200mg or trazodone 150-400mg. At the end of the six week trail the HAM-D scores also revealed improved sleep disturbances in the patients that received trazodone. Thaler, et. al. (2012) did indicate that trials that had with a placebo control would provide clinicians with more data for indirect meta-analysis and provider better quality evidence. Results: Wiegand, 2008, does note trazodone effective for short term insomnia when there is some amount of associated depressive symptoms or history of depression. Trazodone does take some build up in body before becoming effective as was noted not as effective in week one study vs zolpidem. Week two demonstrated zolpidem to have a quicker onset of sleep, but trazodone was as effective in sleep duration. Thaler, K, et. al., 2012, reported that trazodone was more effective than fluozetine and venlafazine for treating insomnia with depression. As with both studies trazodone improved HAM-D scores in relation to sleep disturbances. Clinical Bottom Line: 1. Trazodone is effective for short term insomnia when there is some amount of associated depressive symptoms or history of depression. 2. Trazodone is more effective than fluozetine and venlafazine for treating insomnia with depression. Trazodone results in improved HAM-D scores. 3. Practicing providers should base their decision of appropriate antidepressant for their individual patient. As trazodone is an effective antidepressant to control insomnia, more effective in lower doses for this Implications for Practice: I would consider trazodone 50mg po every HS for insomnia for a patient with depression, if indicated as appropriate. If this is not effective I may consider a different antidepressant or zolpidem as indicated in the above study as this was found to be effective also, but with this medication to monitor closely for side effects especially in elderly. Patient should begin trazodone at bedtime and follow-up in 1 month to evaluate effectiveness. References: Thaler, K., Morgan, L., Van Noord, M., Gaynes, B., Hansen, R., Lux, L., & ... Gartlehner, G. (2012). Comparative effectiveness of second-generation antidepressants for accompanying anxiety, insomnia, and pain in depressed patients: a systematic review. Depression and Anxiety, 29(6), 495-505. doi:10.1002/da.21951 PAGE 2 Running Head: TRAZODONE EFFECTIVENESS IN DEPRESSION AND INSOMNIA Wiegand, M. (2008). Antidepressants for the treatment of insomnia: a suitable approach. Drugs, 68(17), 2411-2417