ADAM Dissection
advertisement

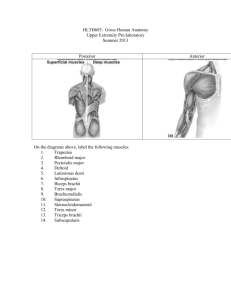
ADAM Dissection - Packet 1 Name: The Muscular System: Muscles of the Abdomen, Chest & Back Refer to this packet while you complete the ADAM computer dissection. Make sure you answer all questions asked and identify all structures listed. Once you have identified a structure in one view you should be able to recognize it thereafter (even if its not in the list). You may have to scroll up/down in each view to identify all muscles listed. 1. Open ADAM Interactive Anatomy from the ADAM folder in the Anatomy and Physiology folder in the hard drive. 2. Choose "Dissectible Anatomy" select the gender and the Anterior view. Then click "open" 3. Click on the depth bar until your reach layer 20. While looking at that view, identify the following: • external oblique • linea alba • serratus anterior • external oblique aponeurosis • pectoralis major (layer 20 ADAM anatomy) Answer the following questions: 1. List two actions of the external oblique: & . 1 4. Next, scroll deeper to layer 26. Watch the screen as you scroll. You are simulating dissection of the superficial structures. Identify the following structures (you will probably have to scroll up/down to view all muscles). • internal oblique • internal oblique aponeurosis • external intercostals • rectus abdominis • serratus anterior (layer 26 ADAM anatomy) 2. Which abdominal muscles cannot rotate the trunk? . 3. The external intercostals assist with & . 2 5. Continue on to layer 29 to view and identify the following muscles. You will have to scroll up to view all muscles and may want to print that graphic. • rectus abdominis • internal oblique (cut) • linea alba • pectoralis minor • transverse abdominis • external oblique (cut) • external intercostals • serratus anterior (layer 29 ADAM Anatomy) 4. Which abdominal muscle is most superficial? Which abdominal muscle is the deepest? . _______ . 3 6. Next change the view to a lateral view. Drag the depth bar to layer 10 and identify the following muscles in this view. You will have to scroll up to view all the muscles listed. • external oblique • pectoralis major • serratus anterior • latissimus dorsi • pectoralis minor (tendon) • teres minor • teres major (layer 10 - lateral view ADAM Anatomy) 5. Why does the latissimus dorsi cause medial rotation not lateral rotation? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4 7. Drag the depth bar to layer 61 and identify the following muscles in this view. • internal oblique • rectus abdominis • internal oblique aponeurosis • external intercostals • erector spinae (longissimus) • serratus anterior (layer 61 - lateral view ADAM Anatomy) 8. Next, drag the depth bar to layer 67 and identify the following muscles in this view (note no graphic has been provided, you may print it if you wish). • transverse abdominis • transverse abdominis aponeurosis • erector spinae (longissimus) • rectus abdominis • internal intercostals 5 Dissection of the Chest and Back 1. Choose "Dissectible Anatomy" select the gender and the Anterior view. Then click "open" 2. Click on the depth bar until your reach layer 19. While looking at that view, identify the following: • pectoralis major • sternocleidomastoid • serratus anterior • trapezius (upper portion) • external oblique • anterior & medial deltoid (use your text to distinguish parts of the deltoid) (layer 19 - ADAM Anatomy) Answer the following questions: 6. List three actions of the pectoralis major: _________________ 7. ________________, & _______ . Observe the two head of the sternocleidomastoid. Based on this, what are the origins of this muscle? & . 6 3. Click on the depth bar until your reach layer 53. While looking at that view, identify the following: • pectoralis minor • serratus anterior • external intercostals • long & short heads of biceps brachii (layer 53 - ADAM Anatomy) Answer the following questions: 8. What are the origin and insertion of the pectoralis minor? origin: _______ insertion: _____ 9. What is an action of the serratus anterior? . 4. Click on the depth bar until your reach layer 91. Observe the location of the tendons of the latissimus dorsi, teres major and subscapularis muscles. 10. What action do all three muscles share? ____________ . 7 5. Next change the view to a posterior view. Drag the depth bar to layer 9 and identify the following muscles in this view. • trapezius • long & lateral heads of triceps brachii • infraspinatus • teres minor • posterior & medial deltoid • latissimus dorsi • teres major (layer 9 - posterior view ADAM) Answer the following: 11. List 4 actions of the trapezius: ___, & ____, , . 8 6. Now, scroll to layer 11 and identify the deeper muscles of the back. • infraspinatus • teres major • supraspinatus • latissimus dorsi • rhomboideus major • levator scapulae • long & lateral heads of triceps brachii • erector spinae muscles (spinalis & longissimus) • teres minor • rhomboideus minor (layer 11 - posterior view ADAM Anatomy) Answer the following: 12. What is the main action of the rhomboids? 13. List 2 muscles that medially rotate the shoulder (humerus): 1. . 2. 9 7. Next change the view to a lateral view. Drag the depth bar to layer 8 and identify the following muscles in this view. • pectoralis major • trapezius • sternocleidomastoid • infraspinatus • teres major • teres minor • supraspinatus • latissimus dorsi • coracobrachialis • posterior, medial & anterior deltoid • serratus anterior (layer 8 - lateral view ADAM Anatomy) Answer the following: 13. List 2 muscles that laterally rotate the shoulder (humerus): 1. 2. 10 8. Next drag the depth bar to layer 13 and identify the following muscles in this view. • pectoralis minor • sternocleidomastoid • infraspinatus • teres major • long head of triceps brachii • supraspinatus • teres minor • coracobrachialis (layer 13 - lateral view ADAM Anatomy) 15. What are the four muscles that form the rotator cuff muscle group? 1) _________, 2) ____________, 3) _________, 4) ____________ 11