Unit 32, P5, M3 19-05
advertisement

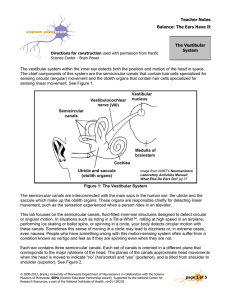
Victoria Bello Unit 32, P5, M3 Matt Hopton Proprioception Proprioception is the way our bodies detect subtle changes in movement, position, tension and force within the body enabling the muscles to contract quickly protecting us from injury. Specialised sensory receptors called Proprioceptors are found on nerve endings in muscles, tendons, the inner ear and joints. These Proprioceptors relay information about the bodies position and it’s movement in space. (http://sportsmedicine.about.com/b/2009/01/18/what-is-proprioception.htm) Proprioception is the ‘memory’ of our muscles; training them to work simultaneously after practicing and repeating the same exercise. Locomotion Fell running is a sport which involves running up and down hills, which takes a large amount of ability and training. One necessary attribute of a fell runner is the ability to change their stride quickly as the surface changes, while ensuring the length of the stride is appropriate for the incline; controlling the stride length to offset the build up of lactic acid. ‘There is no better way of developing the ability to climb than running on the fells or doing specific hill repetitions in training’ (http://www.brianmac.co.uk/fell/fcoach.htm) Repetition of a certain exercise allows the muscles to practice and become used to the procedure and remember how to work together most efficiently. (http://www.runnersworld.co.uk/news/images/hill-descent250x195.jpg) Victoria Bello Unit 32, P5, M3 Matt Hopton Balance Ours ears help keep us balanced; there are three sections of the ear, the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. It is the inner ear which is responsible for balance; composed of three main parts, the cochlea, the semicircular canals and the vestibule. While the cochlea is responsible for hearing, the semicircular canals are associated with balance. Three semicircular canals are positioned at right angles to each other in the inner ear similar to a gyroscope. This enables them to sense changes in movement in the body which causes endolymph waves; this moves hair cells within the canals enabling them to sense the position of the head. This is stimulated when the head moves changing the relationship to gravity. The vestibule connects both the cochlea and the semicircular canals while containing two more balance and equilibrium related strucutures, the utride and the saccule. (http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=21685) Posture Rugby players often practice a ‘scrum’ which involves each team crouching side by side with locked arms engaging the opposite team so that the heads are interlocked. Each rugby player works together to make their team more powerful. They use a isotonic contraction in their legs providing them with lots of tension and force but no movement. There are two types of isotonic contractions; concentric and eccentric. Concentric – The muscle shortens as the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance and stay at that level. Eccentric- The muscle lengthens as the resistance is greater than the force being produced by the muscle. Victoria Bello Unit 32, P5, M3 Matt Hopton (http://newsimg.bbc.co.uk/media/images/44181000/jpg/_44181384_eng_sa_scrum416.jpg) Bibliography http://sportsmedicine.about.com/b/2009/01/18/what-is-proprioception.htm http://www.brianmac.co.uk/fell/fcoach.htm http://www.runnersworld.co.uk/news/images/hill-descent250x195.jpg http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=21685 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isotonic_(exercise_physiology) http://newsimg.bbc.co.uk/media/images/44181000/jpg/_44181384_eng_sa_s crum416.jpg