Chapter 1 - Oxford University Press
advertisement

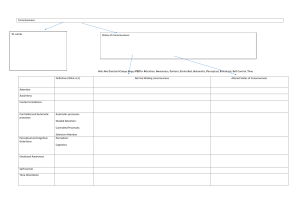
Chapter 3 Suggested Answers Investigate 3.1 1 fedabgc Investigate 3.2 Students’ own responses. Investigate 3.3 Students’ own responses. Review 3.1 1 Normal Waking Consciousness (NWC) occupies the awake to alert zone on the continuum. Altered States of Consciousness (ASC) occupies the reduced awareness and heightened awareness on the continuum. 2 3 4 5 a. NWC is the state of consciousness you experience when you are awake and aware of your thoughts, feelings and perceptions from internal events and the surrounding environment. b. Yes. There are different states of consciousness or more correctly awareness within normal waking consciousness. Students’ own responses. During normal waking consciousness, our ability to maintain self-control is usually maintained. We can plan and monitor what we say and do. We tend to be quite reserved and avoid doing anything that we think is risky or embarrassing. Learning how to drive provides an example of how an activity can become automatic. At first, operating the car requires full attention because it is a controlled process. As skills develop with supervised driving time, it is easier to steer, indicate, check the rear-view mirror and change gears. After practice, these things are done automatically and the basic skills of driving the car are now automatic processes. Investigate 3.4 Students’ own responses. Investigate 3.5 Students’ own responses. Review 3.2 1 Being sick with a high fever: low level of awareness, difficulty performing controlled and automatic processes, reduced ability to process information, cognitive and perceptual distortions may be present, less control over emotions, less self-control and unaware of passing of time. Oxford Psychology Units 3 & 4 ISBN 978 0 19 556717 5 © Oxford University Press Australia 2 3 Being at a party with lots of people, loud music and flashing lights: heightened awareness, difficulty performing controlled and automatic processes, reduced ability to process information, cognitive and perceptual distortions may be present, less control over emotions, less self-control and distorted sense of time. Examples of ASC because the characteristics are consistent with someone who is experiencing heightened or reduced awareness. Review 3.3 1 2 3 4 Daydreaming is a shift in attention to our own private thoughts, feelings and imagined scenarios. Daydreaming occurs often and an enormous amount of our waking time is spent daydreaming. Daydreaming occurs at any time, but we are more likely to daydream when we are alone. Daydreaming affects our awareness by shifting our awareness from the external world to our internal world. We experience a lowered level of awareness of our surrounding environment. Daydreams can also change our emotional awareness by increasing or depressing our mood. Review 3.4 1 2 3 4 Meditation is in an Altered State of Consciousness where a person uses mental exercises to become highly focused on a single thought to the exclusion of others. Meditation has become more popular in our society because it is seen as a way to achieve a state of serenity and promote good psychological and physical health. It is viewed as a way of managing stress. Meditation affects our awareness by lowering it despite the heightened awareness of a single thought. People who meditate become unaware of other stimuli. Meditation is used for pain control because it can lower a person’s perceptions. Investigate 3.6 Students’ own responses. Investigate 3.7 1 2 a. Lower level of awareness. b. Difficulty performing controlled and automatic processes and unable to focus on two tasks at once. c. Little control of content and shorter concentration span. d. Perceptual and cognitive distortions. e. Unstable emotions and can be more confident and risk-taking. f. Little self-control with inhibitions reduced. g. Lack of time orientation. People are more confident than usual and are more likely to take risks. They can be euphoric and more relaxed. Oxford Psychology Units 3 & 4 ISBN 978 0 19 556717 5 © Oxford University Press Australia 3 An alcohol-induced state is considered to be an ASC because people experience lowered awareness, loss of self-control, changes in perceptions and cognition, and experience difficulty performing controlled and automatic processes. Review 3.5 1 Alcohol affects the nervous system by depressing the brain and its functions. Thoughts are distorted and reflexes are slowed which affects motor coordination. Perception is dulled and vision may be blurred. A person will also have difficulty making judgments and focusing attention. 2 Characteristic Daydreaming Meditation Alcohol-induced state Levels of awareness Content limitations Lower awareness Fewer content limitations Difficulty performing controlled processes Lower awareness More or less content limitations Difficulty performing controlled processes Likely perceptual and cognitive distortions Changes in emotional awareness Less self-control Likely perceptual and cognitive distortions Changes in emotional awareness Increased selfcontrol Diminishing time orientation Lower awareness More or less content limitations Difficulty performing controlled and automatic processes Likely perceptual and cognitive distortions Changes in emotional awareness Decreased selfcontrol Diminishing time orientation Controlled and automatic processes Perceptual and cognitive distortions Emotional awareness Self-control Time orientation Diminishing time orientation TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 c d a d a d d b a d When first learning juggling it was a controlled process where she needed selective attention. Now that the she is more comfortable with juggling it has Oxford Psychology Units 3 & 4 ISBN 978 0 19 556717 5 © Oxford University Press Australia become an automatic process where she can divide her attention and thus carry out a conversation. 12 When first learning a new skill it is difficult and thus a controlled process requiring high awareness. When someone becomes more experienced the skill becomes easier requiring less awareness and attention. 13 Level of awareness, Content limitations, Controlled and automatic processes, Perceptual and cognitive distortions, Emotional awareness, Self-control, Time orientation. 14 a. A range going from deep unconsciousness to heightened awareness. b. Normal Waking Consciousness fits in between the awake to alert zone. 15 We experience one state of consciousness but different levels of awareness. 16 Daydreaming, mediation and alcohol-induced all experience the following characteristics: Levels of awareness, Content limitations, Controlled and automatic processes, Perceptual and cognitive distortions, Emotional awareness, Self-control, Time orientation. 17 Content limitations may diminish, he may experience difficulty concentrating (cognitions) and he may become unaware of time orientation. Oxford Psychology Units 3 & 4 ISBN 978 0 19 556717 5 © Oxford University Press Australia