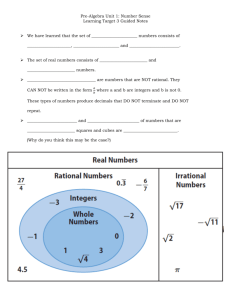
Math 5 Course Guide 2013-2014
advertisement

Palm Springs Unified School District Math 5 Course Guide Traditional and Modified Calendars 2013 - 2014 MATH 5 Table of Contents Preface - Important Note to Teachers……………………………………………………...3 Using the Released Test Questions......................................................................................4 Purpose and Use of Pacing Guide…………………………………………………………5 National Educational Technology Standards Grades Pre-K - 12.........................................6 California Standards Test (CST) Blueprint………………………………………………..8 California Content Standards at a Glance………………………………………………...12 California Content Standards Unpacked…………………………………………………13 Instructional Segments…………………………………………………………….……..19 CST Blueprint Color-Coded by Instructional Segments………......................…….….....25 Trimester 1 Assessment at a Glance………………………….…………………………..28 Vocabulary by Instructional Segments……………….……………………………….….29 Vocabulary in Spanish by Instructional Segments…………………………………….…30 Pacing Guide………………………………………………………………………….….31 Please direct any questions or comments to: Cinthia Ruiz K-12 Math Specialist cruiz@psusd.us (760) 285-5528 Sandi Enochs Coordinator, Assessment and Data Analysis senochs@psusd.us (760) 416-6066 2 IMPORTANT! . THIS PACING GUIDE IS INTENDED TO BE FLEXIBLE!!!! Although a Pacing Guide has been created with a suggested order for teaching the textbook lessons, site grade level teams may change the order of the lessons being taught WITHIN an Instructional Segment. The only requirement is that all lessons within each Instructional Segment be completed (and standards mastered) prior to that Instructional Segment’s Closing Date. The Instructional Segment’s Closing Date is the absolute last date by which the Segment’s Assessment must be administered and results entered into OARS. These are OARS deadline dates, not just dates by which the exams must be administered to your students. Feel free to administer the Assessment any time prior to this date. Throughout this document, the standards that have been designated Key Standards by the California Department of Education are highlighted in bold print and with an asterisk (*) following the standard number. These represent the high impact standards and comprise a minimum of 70% of the California Standards Test (CST). This Course Guide highlights the Key Standards, unpacks the standards, and can be very helpful to teachers in making instructional decisions about focus areas. All teachers need to keep track of whatever is and is not working, for consideration during the next revision of this Course Guide. This is critical, if we are to make useful changes in the future. Please note: Benchmark Exam #2 has been replaced with a CST Mirror Test. During the time between the administration of the CST Mirror Test and the administration of the actual CST teachers will continue to teach new content while providing interventions as indicated by the results of the CST Mirror Test. This Course Guide is NOT suggesting that all content be taught prior to the CST Mirror Test administration date. A Scope and Sequence of the National Educational Technology Standards, Grades Pre-K - 12, has been added to all Course Guides. It clearly identifies the Technology Standards that should be integrated into all subject areas at the appropriate grade levels. The Textbook column of the Pacing Guide refers to our adopted textbook; enVision, by Pearson Scott, Foresman. The two far right columns (Other Resources and # of Days) on the Pacing Guide have been intentionally left blank. These columns are intended to be used by teachers when planning individually or collaboratively. A column, entitled RTQ’s, has been added to the Pacing Guide. It references the specific Released Test Question(s) that align to the lesson being taught at that point in time. If you need a copy of the Grade 5 Mathematics STAR Released Test Questions, you may download them from the CDE website: http://www.cde.ca.gov/ta/tg/sr/documents/cstrtqmath5.pdf Please see the following page for some suggestions of how to use the RTQ’s. 3 Using the Released Test Questions throughout the School Year It is highly recommended that you use the Released Test Questions as a wrap-up of instruction on a particular standard. Close the lesson with “Now let’s see how the state might test this concept (or standard)”. After the students have answered the question(s) and selected their responses, thoroughly review the question and answer choices with them. Discover how many (and which) students answered the question(s) correctly. Then have a frank and open discussion about the distracters and why each student chose a particular distracter Did they totally not understand the concept (standard)? Did they not know a particular vocabulary word (academic or content-specific)? Did they miss a step in the process of solving the problem? Did they not finish solving the problem, because one of the distracters was the answer they received when they were only part-way through solving the problem? Did they arrive at a perfectly good answer, but it was not the answer to the problem? Try and discover all errors and misconceptions now, so that they can be corrected immediately and not continue throughout the school year. Please keep in mind that most standards encompass several (if not many) concepts, as evidenced by the Unpacked Standards in your Course Guide. These Released Test Questions may only assess some of these concepts. That does not mean that these are the only aspects of the standard that will be tested on the CST. These are the questions that CDE chose to release at this point in time. This is not necessarily an indication of which concepts to stress or an indication of which part of the standard will be tested. You may need to generate or find additional questions to assess the other portions of the standard. These questions (and the students’ responses to the questions) should be a focus of your PLC collaborative discussions. They will generate a wealth of information to be shared by the team. Here are some facts quoted from Robert Marzano’s book Classroom Assessment and Grading that Work (pp.5 – 6): When students receive feedback on a classroom assessment that simply tells them whether their answers are correct or incorrect, learning is negatively influenced. When students are provided with the correct answer, learning is influenced in a positive direction. This practice is associated with a gain of 8.5 percentile points in student achievement. Providing students with explanations as to why their responses are correct or incorrect is associated with a gain of 20 percentile points in student achievement. Asking students to continue responding to an assessment until they correctly answer the items is associated with a gain of 20 percentile points. Displaying assessment results graphically can go a long way to helping students take control of their own learning. However, this practice can also help teachers more accurately judge students’ levels of understanding and skill. It is associated with a gain of 26 percentile points in student achievement. Teachers within a school or a district should have rigorous and uniform ways of interpreting the results of classroom assessments. If the interpretation of assessment results is done by a set of rules, student achievement is enhanced by 32 percentile points. 4 Purpose and Use of this Pacing Guide 1. Emphasis for 2013-2014: a. More emphasis is being placed on the Key Standards. b. There are three common Instructional Segment Closing Dates. c. Instructional Segment Assessment data will provide teachers with information to improve and drive instruction through team and department collaboration. d. Instructional Segment Assessment data may be used to provide information to assist with grading, but should not be the only data used in determining grades. 2. Course Guide Format: a. A scope and sequence of the National Educational Technology Standards has been included to assist with the integration of the appropriate technology standards into 5th grade math lessons. b. The actual CST Blueprint from the California Department of Education has been reproduced for this document. It lists all the fifth grade math standards and the number of items per standard that are on the CST. It also identifies with an asterisk the Key Standards (high impact standards) which comprise a minimum of 70% of the test. c. Immediately following this official document is an “At a Glance” version of the standards, which provides a one-page abbreviated summary of the standards. d. The next section, CA Content Standards Unpacked, restates the standards, followed by a listing of the individual skills and/or objectives encompassed by each standard. This may be utilized as a checklist, to check off all components of each standard as they are mastered. Teachers may even reproduce this section as a checklist for students to keep in their notebook to keep track of their individual progress. e. The Pacing Guide is separated into three Instructional Segments. An overview of the three Instructional Segments is placed at the beginning of the next section. Each Instructional Segment summary includes the Main Topics and Standards that must be taught prior to the end of that Instructional Segment, with a space to record the sitespecific Essential Standards. f. The next section contains a color-coded version of the CST Blueprint, aligning each standard with the Instructional Segment where it is taught. g. This is followed by a Benchmark Exam at a Glance page. This chart lists the CA content standards tested on the first Instructional Segment Assessment, along with the number of questions per standard on this assessment. h. The CA content standards (with correlated textbook sections) to be mastered before the end of each Instructional Segment are clearly shown on the Pacing Guide. This pacing guide focuses on the textbook lessons needed to teach the fifth grade CA content standards for mathematics and includes an alignment to the Released Test Questions. 5 National Educational Technology Standards Grades Pre-K - 12 Scope and Sequence (H = Help / I = Introduce / D = Develop / IU = Independent Use) Integration and Projects PK K 1 2 3 4 5 Create developmentally appropriate multimedia products with support from teachers or student H partners Use technology resources for problem solving, communication, & illustration of thoughts, ideas H & stories Work responsibly, independently & as part of a group in developing projects Use teacher-created rubric for assessment of project Use technology for individual & collaborative writing, communication & publishing activities to create knowledge products for audiences inside & outside the classroom. Determine when technology is useful & select the appropriate tools & technology resources to address a variety of tasks & problems Use information literacy skills to research & evaluate the accuracy, relevance, appropriateness, comprehensiveness & bias of information sources concerning real-world problems Save, find & retrieve work in different formats via email, network & online sources for project work Develop & use student-created rubrics for assessment Take on specific role & manage different group activities & rotation strategies as part of a project Develop essential & subsidiary questions as part of projects Properly cite all information sources Design, develop, publish & present real-world products using technology resources that demonstrate & communicate curriculum concepts to audiences inside & outside the classroom Select appropriate technology tools for research, information analysis, problem-solving & decision-making in content learning as part of project-based learning Compile projects in electronic portfolio 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H I D D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H I D D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU H H H I D D D D IU H H H I D D D D IU H H H I D D D D 6 National Educational Technology Standards Grades Pre-K - 12 Scope and Sequence ( H = Help / I = Introduce / D = Develop / IU = Independent Use) Social & Ethical Use Understand and follow rules & procedures for technology use Work cooperatively & collaboratively with others when using technology in the classroom Demonstrate positive social & ethical behaviors when using technology Practice responsible use of technology systems & software Discuss responsible use of technology & information & describe consequences of inappropriate use Demonstrate knowledge of current changes in information technologies & the effect those changes have on the workplace & society Exhibit legal & ethical behaviors when using information & technology & discuss consequences of misuse Understand & follow proper use of copyrighted material & use netiquette when using email Cite resources properly Identify capabilities & limitations of emerging technology resources & assess the potential of these systems & services to address personal, lifelong learning, & workplace needs Access & use primary & secondary sources of information for an activity Demonstrate & advocate for legal & ethical behaviors among peers, family & community regarding the use of technology & information PK K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU IU H H H H I D D D IU IU IU IU H H H H I D D D IU IU IU H H H H I D D D IU IU IU H H H H I D D D IU IU H H H I D D D IU IU H H H I D D D IU 7 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02) CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 # of Items % By the end of grade five, students increase their facility with the four basic arithmetic operations applied to fractions, decimals, and positive and negative numbers. They know and use common measuring units to determine length and area and know and use formulas to determine the volume of simple geometric figures. Students know the concept of angle measurement and use a protractor and compass to solve problems. They use grids, tables, graphs, and charts to record and analyze data. Number Sense Standard Set 1.0 Students compute with very large and very small numbers, positive integers, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship between decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers: 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. 1.2* Interpret percents as a part of a hundred; find decimal and percent equivalents for common fractions and explain why they represent the same value; compute a given percent of a whole number. 1.3 Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. 1.4* Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 and write the numbers as the product of their prime factors by using exponents to show multiples of a factor (e.g., 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 23 × 3). 1.5* Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. Standard Set 2.0 Students perform calculations and solve problems involving addition, subtraction, and simple multiplication and division of fractions and decimals: 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. 2.2* Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format Embedded: Content of standard is embedded within items in other strands. © California Department of Education 29 45% 1 5 1 3 2 7 3 8 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02) CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 2.3* 2.4 2.5 Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems. # of Items 5 1 1 Algebra and Functions Standard Set 1.0 Students use variables in simple expressions, compute the value of the expression for specific values of the variable, and plot and interpret the results: 1.1 Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. 1.2* Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. 1.3 Know and use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables. 1.4* Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. 1.5* Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. 17 Measurement and Geometry Standard Set 1.0 Students understand and compute the volumes and areas of simple objects: 1.1* Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle (i.e., two of the same triangles make a parallelogram with twice the area; a parallelogram is compared with a rectangle of the same area by cutting and pasting a right triangle on the parallelogram). 1.2* Construct a cube and rectangular box from twodimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. 15 * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format Embedded: Content of standard is embedded within items in other strands. © California Department of Education % 26% 1 6 1 4 5 23% 2 1/2** 1/2** 9 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02) CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common measuring systems (i.e., cubic centimeter[cm3], cubic meter[m3], cubic inch[in3], cubic yard[yd3]) to compute the volume of rectangular solids. 1.4 Differentiate between and use appropriate units of measures for, two- and three- dimensional objects (i.e., find perimeter, area, volume). Standard Set 2.0 Students identify, describe, and classify the properties of, and the relationships between, plane and solid geometric figures: 2.1* Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software). 2.2* Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° and the sum of the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° and use this information to solve problems. 2.3 Visualize and draw two-dimensional views of threedimensional objects made from rectangular solids. # of Items % 1.3* Statistics, Data Analysis, and Probability Standard Set 1.0 Students display, analyze, compare, and interpret different data sets, including data sets of different sizes: 1.1 Know the concepts of mean, median, and mode; compute and compare simple examples to show that they may differ. 1.2 Organize and display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) and explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets. 1.3 Use fractions and percentages to compare data sets of different sizes. 1.4* Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. 1.5* Know how to write ordered pairs correctly; for example, (x, y). * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format Embedded: Content of standard is embedded within items in other strands. © California Department of Education 3 1 3 4 1 4 6% 1/3** 1/3** 1/3** 2 1/2** 1/2** 10 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02) CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 Mathematical Reasoning Standard Set 1.0 Students make decisions about how to approach problems: 1.1 Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. 1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. Standard Set 2.0 Students use strategies, skills, and concepts in finding solutions: 2.1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results. 2.2 Apply strategies and results from simpler problems to more complex problems. 2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. 2.4 Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work. 2.5 Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy. 2.6 Make precise calculations and check the validity of the results from the context of the problem. Standard Set 3.0 Students move beyond a particular problem by generalizing to other situations: 3.1 Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the original situation. 3.2 Note the method of deriving the solution and demonstrate a conceptual understanding of the derivation by solving similar problems. 3.3 Develop generalizations of the results obtained and apply them in other circumstances. GRADE 5 TOTAL * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format Embedded: Content of standard is embedded within items in other strands. © California Department of Education # of Items % Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded Embedded 65 100% 11 # CST Items 65 STD 29 45% 1 NS1.1 5 NS1.2* 1 NS1.3 3 NS1.4* 2 NS1.5* 7 NS2.1* 3 NS2.2* 5 NS2.3* 1 NS2.4 1 NS2.5 17 26% 1 AF1.1 6 AF1.2* 1 AF1.3 4 AF1.4* 5 AF1.5* 15 23% 2 1/2 MG1.1* 1/2 MG1.2* 3 MG1.3* 1 MG1.4 3 MG2.1* 4 MG2.2* 1 MG2.3 4 6% 1/3 SP1.1 1/3 SP1.2 1/3 SP1.3 2 1/2 SP1.4* 1/2 SP1.5* Embedded MR1.1 MR1.2 MR2.1 MR2.2 MR2.3 MR2.4 MR2.5 MR2.6 MR3.1 MR3.2 MR3.3 * ** Math 5 Standards at a Glance Standard NUMBER SENSE Estimate and Round Very Large and Very Small Numbers Percents Exponents Prime Factorization of Numbers through 50 Number Line Operations with Decimals, Positive and Negative Integers Division, including Decimals and Long Division Solve Problems: Addition and Subtraction of Fractions and Mixed Numbers Understand Multiplication and Division of Fractions Multiply and Divide Fractions ALGEBRA and FUNCTIONS Interpret Graphs and Equations Write and Evaluate Simple Algebraic Expressions Distributive Property Identify and Graph Ordered Pairs Solve and Graph Simple Linear Equations MEASUREMENT and GEOMETRY Area of Triangle and Parallelogram Surface Area of Cube and Rectangular Box Volume of Rectangular Solids Appropriate Units of Measures for Two- and Three-Dimensional Objects Measure, Identify and Draw Geometric Figures Sum of the Angles of a Triangle and Quadrilateral Draw Two-Dimensional Views of Three-Dimensional Rectangular Solids STATISTICS, DATA ANALYSIS, AND PROBABILITY Mean, median and mode Histograms and Circle Graphs Compare Data Sets using Fractions and Percentages Interpret Data from a Graph Write Ordered Pairs MATHEMATICAL REASONING Analyze Problems Break a Problem into Simpler Parts Estimation to Verify Reasonableness Use Simpler Problems to Solve Complex Problems Variety of Methods to Explain Mathematical Reasoning Appropriate Mathematical Notation and Terms Advantages of Exact and Approximate Solutions Precise Calculations and Check Validity of Results Reasonableness of Solution Methods of Deriving a Solution to Solve Similar Problems Generalize Results and Apply to Other Circumstances Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 12 STD # CST Items Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked STANDARD 45% NS1.1 65 29 NUMBER SENSE Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. 1 Estimate very large numbers Estimate very small numbers Round very large numbers Round very small numbers Manipulate very large numbers Manipulate very small numbers Interpret percents as a part of a hundred; find decimal and percent equivalents for NS1.2* common fractions and explain why they represent the same value; compute a given percent of a whole number. 5 Interpret percents as a part of a hundred Find decimal equivalents for common fractions Find percent equivalents for common fractions Explain why decimal and percent equivalents represent the same value as fraction Compute a given percent of a whole number NS1.3 Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. 1 Understand positive integer powers of nonnegative integers Compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers Compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers as repeated multiplication Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 and write the numbers as NS1.4* the product of their prime factors by using exponents to show multiples of a factor (e.g., 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 23 × 3). 3 Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 Write the numbers through 50 as the product of their prime factors using exponents NS1.5* Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. 2 Identify decimals on a number line Identify fractions on a number line Identify mixed numbers on a number line Identify positive integers on a number line Identify negative integers on a number line Represent decimals on a number line Represent fractions on a number line Represent mixed numbers on a number line Represent positive integers on a number line Represent negative integers on a number line Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; NS2.1* subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 7 13 STD # CST Items Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked Add decimals and verify reasonableness of results Subtract decimals and verify reasonableness of results Multiply decimals and verify reasonableness of results Divide decimals and verify reasonableness of results Add with negative integers and verify reasonableness of results Subtract positive integers from negative integers and verify reasonableness of results NS2.2* Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. 3 Demonstrate proficiency with division Demonstrate proficiency with division using positive decimals Demonstrate proficiency with long division using multi-digit divisors Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the NS2.3* addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. 5 Solve word problems involving addition of fractions with like denominators and simplify Solve word problems involving addition of fractions with unlike denominators of 20 or less and simplify Solve word problems involving subtraction of fractions with like denominators and simplify Solve word problems involving subtraction of fractions with unlike denominators of 20 or less and simplify Solve word problems involving addition of mixed numbers with like denominators and simplify Solve word problems involving addition of mixed numbers with unlike denominators of 20 or less and simplify Solve word problems involving subtraction of mixed numbers with like denominators and simplify Solve word problems involving subtraction of mixed numbers with unlike denominators of 20 or less and simplify NS2.4 1 Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. Understand the concept of multiplication of fractions Understand the concept of division of fractions NS2.5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems. 1 Compute and perform simple multiplication of fractions Compute and perform simple division of fractions Solve word problems involving simple multiplication of fractions Solve word problems involving simple division of fractions 26% AF1.1 ALGEBRA and FUNCTIONS Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. 17 1 Use information taken from a graph to answer questions about a problem situation Use information taken from an equation to answer questions about a problem situation AF1.2* * ** Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. Use a letter to represent an unknown number Write simple algebraic expressions in one variable Evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 6 14 STD Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked # CST Items AF1.3 Know and use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables. 1 Know the distributive property Use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables AF1.4* Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. 4 Identify ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane Graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane AF1.5* Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. 5 Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values Write the equation for problems involving linear functions Graph ordered pairs of linear functions on the coordinate plane 23% MEASUREMENT and GEOMETRY Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle (i.e., two of the same MG1.1* triangles make a parallelogram with twice the area; a parallelogram is compared with a rectangle of the same area by cutting and pasting a right triangle on the parallelogram). 15 2 1/2 Derive the formula for the area of a triangle by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle Derive the formula for the area of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle Use the formula for the area of a triangle Use the formula for the area of a parallelogram MG1.2* Construct a cube and rectangular box from two-dimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. 1/2 Construct a cube from two-dimensional patterns Compute the surface area of a cube using the two-dimensional patterns Construct a rectangular box from two-dimensional patterns Compute the surface area of a rectangular box using the two-dimensional patterns Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common MG1.3* measuring systems (i.e., cubic centimeter[cm3], cubic meter[m3], cubic inch[in3], cubic yard[yd3]) to compute the volume of rectangular solids. 3 Understand the concept of volume Use appropriate units in common measuring systems to compute the volume of rectangular solids MG1.4 Differentiate between and use appropriate units of measures for, two- and threedimensional objects (i.e., find perimeter, area, volume). 1 Differentiate between appropriate units of measures for two- and three- dimensional objects Use appropriate units of measures for two- and three- dimensional objects Find perimeter Find area Find volume * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 15 STD # CST Items Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, rectangles, and MG2.1* triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software). 3 Identify angles Identify perpendicular lines Identify parallel lines Identify rectangles Identify triangles Measure angles using appropriate tools Measure rectangles using appropriate tools Measure triangles using appropriate tools Draw angles using appropriate tools Draw perpendicular lines using appropriate tools Draw parallel lines using appropriate tools Draw rectangles using appropriate tools Draw triangles using appropriate tools MG2.2* Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° and the sum of the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° and use this information to solve problems. 4 Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° Know that the sum of the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° Solve problems using the sum of the angles of a triangle Solve problems using the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral MG2.3 Visualize and draw two-dimensional views of three-dimensional objects made from rectangular solids. 1 Visualize two-dimensional views of three-dimensional objects made from rectangular solids Draw two-dimensional views of three-dimensional objects made from rectangular solids 6% SP1.1 STATISTICS, DATA ANALYSIS, AND PROBABILITY Know the concepts of mean, median, and mode; compute and compare simple examples to show that they may differ. 4 1/3 Know the concept of mean Compute mean Know the concept of median Compute median Know the concept of mode Compute mode Compare simple examples to show that mean, median and mode may differ SP1.2 * ** Organize and display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) and explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets. Organize single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) Display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) Explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 16 1/3 STD SP1.3 # CST Items Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked 1/3 Use fractions and percentages to compare data sets of different sizes. Use fractions to compare data sets of different sizes Use percentages to compare data sets of different sizes SP1.4* Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. 2 1/2 Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph Interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by a graph SP1.5* Know how to write ordered pairs correctly; for example, (x, y). 1/2 Write ordered pairs correctly; for example (x, y) MR1.1 MATHEMATICAL REASONING Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Embed Analyze problems by identifying relationships Analyze problems by distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information Analyze problems by sequencing and prioritizing information Analyze problems by observing patterns MR1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. Determine when to break a problem into simpler parts Determine how to break a problem into simpler parts MR2.1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results. Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results MR2.2 Apply strategies and results from simpler problems to more complex problems. Apply strategies from simpler problems to more complex problems Apply results from simpler problems to more complex problems MR2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, Use words to explain mathematical reasoning Use numbers to explain mathematical reasoning Use symbols to explain mathematical reasoning Use charts to explain mathematical reasoning Use graphs to explain mathematical reasoning Use tables to explain mathematical reasoning Use diagrams to explain mathematical reasoning Use models to explain mathematical reasoning MR2.4 Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work. Express solutions clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms Express solutions clearly and logically by using clear language Support solutions with evidence in verbal work * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 17 STD # CST Items Math 5 CA Content Standards Unpacked Support solutions with evidence in symbolic work MR2.5 Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy. Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems Give answers to a specified degree of accuracy MR2.6 Make precise calculations and check the validity of the results from the context of the problem. Make precise calculations Check the validity of results from the context of the problem MR3.1 Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the original situation. Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the original situation MR3.2 Note the method of deriving the solution and demonstrate a conceptual understanding of the derivation by solving similar problems. Note the method of deriving the solution Demonstrate a conceptual understanding of the derivation of a solution by solving similar problems MR3.3 Develop generalizations of the results obtained and apply them in other circumstances. Develop generalizations of the results obtained Apply generalizations of the results in other circumstances * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 18 INSRTUCTIONAL SEGMENT 1 – Math 5 Benchmark Exam #1 Closing Dates Traditional: November 22, 2013 Modified: November 1, 2013 Main Topics Numeration (Topic 1) Addition and Subtraction Number Sense (Topic 2) Multiplication (Topics 3, 6) Division (Topics 4, 7) Standards Topic 1 Numeration NS 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. Topic 2 Addition and Subtraction Number Sense NS 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. NS 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Topic 3 Multiplication of Whole Numbers NS 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. NS 1.3 Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. Topic 6 Multiplying Decimals NS 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Topic 4 Division of Whole Numbers NS 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. NS 2.2* Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 19 Topic 7 Dividing Decimals NS 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. NS 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. NS 2.2* Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. Essential Standards * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 20 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 2 – Math 5 CST Mirror Test Closing Dates Traditional: March 7, 2014 Modified: February 28, 2014 Please Note: This entire Instructional Segment should be completed before the administration of the CST Mirror Test. Topics 8 and 14 from the next Instructional Segment should be completed before the administration of the actual CST. Main Topics Factors and Multiples (Topic 9) Fractions, Mixed Numbers, and Decimals (Topic 10) Adding and Subtracting Fractions and Mixed Numbers (Topic 11) Percents (Topic 17) Integers (Topic 15) Variables and Expressions (Topic 5) Equations (Topic 16) Equations and Graphs (Topic 18) Graphs and Data (Topic 19) Standards Topic 9 Factors and Multiples NS 1.4* Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 and write the numbers as the product of their prime factors by using exponents to show multiples of a factor (e.g., 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 23 × 3). Topic 10 Fractions, Mixed Numbers, and Decimals NS 1.5* Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. Topic 11 Adding and Subtracting Fractions and Mixed Numbers NS 2.3* Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. Topic 17 Percents NS 1.2* Interpret percents as a part of a hundred; find decimal and percent equivalents for common fractions and explain why they represent the same value; compute a given percent of a whole number. Topic 15 Integers NS 1.5* Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. NS 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 21 AF 1.2* Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. Topic 5 Variables and Expressions AF 1.1 Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. AF 1.2* Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. AF 1.3 Know and use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables. Topic 16 Solving and Writing Equations AF 1.2* Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. AF 1.5* Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. Topic 18 Equations and Graphs AF1.4* Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. AF 1.5* Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. SDP1.4* Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. SDP1.5* Know how to write ordered pairs correctly; for example, (x, y). Topic 19 Graphs and Data AF 1.1 Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. SDP1.1 Know the concepts of mean, median, and mode; compute and compare simple examples to show that they may differ. SDP1.2 Organize and display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) and explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets. SDP1.3 Use fractions and percentages to compare data sets of different sizes. SDP1.4* Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. Essential Standards * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 22 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 3 - Math 5 Site-Based End of Year Assessments Closing Dates Traditional: June 13, 2014 Modified: June 26, 2014 PLEASE COMPLETE TOPICS 8 AND 14 BEFORE THE ADMINISTRATION OF THE CST. Main Topics Shapes (Topic 8) Solids (Topic 14) CST Review and Administration Construction (Topic 20) Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers (Topic 12) Length, Perimeter and Area (Topic 13) Standards Topic 8 Shapes MG2.1* Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software). MG2.2* Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° and the sum of the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° and use this information to solve problems. Topic 14 Solids MG1.2* Construct a cube and rectangular box from two-dimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. MG1.3* Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common measuring systems (i.e., cubic centimeter[cm3], cubic meter[m3], cubic inch[in3], cubic yard[yd3]) to compute the volume of rectangular solids. MG 2.3 Visualize and draw two-dimensional views of three-dimensional objects made from rectangular solids. Topic 20 Constructions MG2.1* Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software). Topic 12 Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers NS 2.4 Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. NS 2.5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems. * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 23 Topic 13 Length, Perimeter and Area MG1.1* Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle (i.e., two of the same triangles make a parallelogram with twice the area; a parallelogram is compared with a rectangle of the same area by cutting and pasting a right triangle on the parallelogram). MG 1.4 Differentiate between and use appropriate units of measures for, two- and three- dimensional objects (i.e., find perimeter, area, volume). Essential Standards * ** Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) 24 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST - GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 1 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 2 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 3 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 # of Items % By the end of grade five, students increase their facility with the four basic arithmetic operations applied to fractions, decimals, and positive and negative numbers. They know and use common measuring units to determine length and area and know and use formulas to determine the volume of simple geometric figures. Students know the concept of angle measurement and use a protractor and compass to solve problems. They use grids, tables, graphs, and charts to record and analyze data. Number Sense Standard Set 1.0 Students compute with very large and very small numbers, positive integers, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship between decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers: 1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. 1.2* Interpret percents as a part of a hundred; find decimal and percent equivalents for common fractions and explain why they represent the same value; compute a given percent of a whole number. 1.3 Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. 1.4* Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 and write the numbers as the product of their prime factors by using exponents to show multiples of a factor (e.g., 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 23 × 3). 1.5* Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. Standard Set 2.0 Students perform calculations and solve problems involving addition, subtraction, and simple multiplication and division of fractions and decimals: 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. 2.1* Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. 2.2* Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format © California Department of Education 29 45% 1 5 1 3 2 7 7 3 25 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST - GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 1 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 2 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 3 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 2.3* 2.4 2.5 Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems. # of Items 5 1 1 Algebra and Functions Standard Set 1.0 Students use variables in simple expressions, compute the value of the expression for specific values of the variable, and plot and interpret the results: 1.1 Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. 1.2* Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. 1.3 Know and use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables. 1.4* Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. 1.5* Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. 17 Measurement and Geometry Standard Set 1.0 Students understand and compute the volumes and areas of simple objects: 1.1* Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle (i.e., two of the same triangles make a parallelogram with twice the area; a parallelogram is compared with a rectangle of the same area by cutting and pasting a right triangle on the parallelogram). 1.2* Construct a cube and rectangular box from twodimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. 15 * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format © California Department of Education % 26% 1 6 1 4 5 23% 2 1/2** 1/2** 26 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST - GRADE 5 MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 1 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 2 INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 3 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: GRADE 5 Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common measuring systems (i.e., cubic centimeter[cm3], cubic meter[m3], cubic inch[in3], cubic yard[yd3]) to compute the volume of rectangular solids. 1.4 Differentiate between and use appropriate units of measures for, two- and three- dimensional objects (i.e., find perimeter, area, volume). Standard Set 2.0 Students identify, describe, and classify the properties of, and the relationships between, plane and solid geometric figures: 2.1* Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software). 2.2* Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° and the sum of the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° and use this information to solve problems. 2.3 Visualize and draw two-dimensional views of threedimensional objects made from rectangular solids. # of Items % 1.3* Statistics, Data Analysis, and Probability Standard Set 1.0 Students display, analyze, compare, and interpret different data sets, including data sets of different sizes: 1.1 Know the concepts of mean, median, and mode; compute and compare simple examples to show that they may differ. 1.2 Organize and display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) and explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets. 1.3 Use fractions and percentages to compare data sets of different sizes. 1.4* Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. 1.5* Know how to write ordered pairs correctly; for example, (x, y). GRADE 5 TOTAL * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format © California Department of Education 3 1 3 4 1 4 6% 1/3** 1/3** 1/3** 2 1/2** 1/2** 65 100% 27 MATH 5 BENCHMARK EXAM #1 AT A GLANCE Benchmark Exam #1 Closing Dates: Traditional: November 22, 2013 Modified: November 1, 2013 # Items STD 4 NS1.1 4 NS1.3 6 NS2.1* 7+ NS2.2* +One STANDARD Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. of the questions for this standard is an open-ended, constructed response question. * Key standards comprise a minimum of 70% of the test ** Fractional values indicate rotated standards (e.g., 1/2 = rotated every two years) *** Not assessable in a multiple-choice format © California Department of Education 28 MATH 5 VOCABULARY Instructional Segment 1 Instructional Segment 2 Instructional Segment 3 Topic 1: digits, value, standard form, expanded form, word form, equivalent decimals Topic 9: factor pair, divisible, prime number, composite number, prime factorization, common factor, greatest common factor Topic 10: Common Factor, Greatest Common Factor (GCF), Fraction, mixed number, simplest form, improper fraction, benchmark fraction Topic 11: common denominator, denominator, numerator, common multiple, least common multiple, least common denominator Topic 8: algebraic expression, line, ray, parallel lines, intersecting lines, point, line segment, plane , angle, acute angle, right angle, obtuse angle, straight angle, vertex, protractor, degrees, polygon, regular polygon, triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, octagon, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, scalene triangle, right triangle, acute triangle, obtuse triangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, rectangle, square, generalization Topic 2: Commutative Property, Associative Property, compensation, compatible numbers, rounding Topic 3: equation, factors, product, Commutative Property of Multiplication, Associative Property of Multiplication, Identity Property of Multiplication, Zero Property of Topic 17: ratio, equal ratios, Multiplication, overestimate, percent underestimate, power, base, Topic 15: inverse, integers exponent, exponential notation, standard form, expanded form Topic 5: compatible numbers, algebraic expression, variable, Distributive Property, order of operations Topic 6: equivalent fractions, Topic 16: equality, inverse factors, mixed numbers operations, equation, Addition Property of Equality, Subtraction Property of Equality, Multiplication Property of Equality, Division Property of Equality Topic 4: Dividend, divisor, Topic 18: coordinate grid, quotient, remainder ordered pair, coordinate plane, x-axis, y-axis, origin, xcoordinate, y-coordinate, trend, data, line graph, table of values, linear equations Topic 7: tenths, thousandths Topic 19: bar graph, picture graph, scale, interval, histogram, circle graph, mean, median, mode, range, tree diagram, sample space, probability, equally likely Topic 14: solid figure, face, edge, vertex, cube, prism, cylinder, cone, pyramid, net, surface area, volume, cubic unit Topic 20: mean, median, mode, construction Topic 12: improper fraction, reciprocal, multiplicative inverse Topic 13: perimeter, formula, area, base, height 29 MATH 5 VOCABULRY IN SPANISH Instructional Segment 1 Instructional Segment 2 Instructional Segment 3 Topic 1: dígitos, valor, forma estándar, forma ampliada, forma escrita, decimales equivalentes Topic 9: par de factores, divisible, número primo, número compuesto, factorización prima, factor común, el más grande factor común Topic 2: Propiedad Comutativa, Propiedad Associativa, compensación, números compatibles, redondear Topic 10: factor común, el más grande factor común, fracción, número mixto, forma simple, fracción impropia, fracción de Topic 8: expreción algebráica, linea, rayo, lineas paralelas, lineas intersectantes, punto, segmento linear, plano, ángulo, ángulo agudo, ángulo recto, ángulo obtuso, ángulo llano, vértice, transportador, grados, polígono, polígono regular, triángulo, cuadrilátero, pentágono, hexágono, octágono, triángulo equilátero, triángulo isósceles, triángulo escaleno, triángulo recto, triángulo agudo, triángulo obtuso, paralelogramo, trapezoide, rectángulo, cuadrado, referencia Topic 3: ecuación, factores, producto, Propiedad Comutativa de la Multiplicación, Propiedad Associativa de la Multiplicación, Propiedad de Identidad de la Multiplicación, Propiedad de Cero de la Multiplicación, sobreestimar, subestimar, potencia, base, exponente, notación exponencial, forma estándar, forma ampliada Topic 6: fracciones equivalentes, factores, números mixtos Topic 4: dividendo, divisor, cociente, resto Topic 7: décimos, milésimos Topic 11: denominador común, denominador, numerador, común múltiplo, mínimo común múltiplo, mínimo común denominador Topic 17: razón, razones equivalentes, porciento Topic 15: inverso, numeros enteros Topic 5: números compatibles, expreción algebráica, variable, propiedad distributiva, orden de operación Topic 16: igualdad, operaciones inversas, ecuación, Propiedad Aditiva de Igualdad, Propiedad de Resta de Igualdad, Propiedad Multiplicativa de Igualdad, Propiedad de División de Igualdad Topic 18: rejilla coordenada, par ordenado, plano coordenado, eje de la x, eje de la y, origen, coordenada de la x, coordenada de la y, tendencia, datos, diagrama de linea, cuadro de los valores, ecuaciones lineales Topic 19: gráfica de barra, pictografia, escala, intervalo, histogramo, gráfica circular, promedio, media, moda, gama, diagrama de árbol, muestra, probabilidad, probabilidad generalización Topic 14: figura sólida, cara, borde, vértice, cubo, prisma, cilíndro, cono, pirámide, red, área superficial, volumen, unidad cúbica Topic 20: promedio, media, moda, construcción Topic 12: fracción impropia, recíproco, inverso multiplicativo Topic 13: perímetro, fórmula, área, base, altura equivalente 30 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 1 RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days VOCABULARY LIST 1 Grade level teams may determine order of topics taught WITHIN each Instructional Segment. Focus on word problems and problem solving strategies throughout this Instructional Segment TOPIC 1 NUMERATION Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. Place value 1.1 Comparing and ordering whole numbers 1.2 Decimal place value 1.3 Comparing and ordering decimals Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Problem Solving: Look for a pattern 1.4 1 NS 1.1 Review/reteach/enrich/assess 1.5 pp. 18-20 TOPIC 2 ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION NUMBER SENSE Review 1 NS 1.1 Review Mental math (optional) Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. Rounding whole numbers and decimals 2.1 Estimating sums and differences 2.3 Adding and subtracting 2.4 2.2 Grade 4 Standard 1, 2 Grade 4 Standard 31 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative NS 2.1* integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Embed MR 2.1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results. 7 Adding decimals 2.5 Subtracting decimals Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Draw a picture and write an equation 2.6 Review/reteach/enrich/assess 23, 26 2.7 pp. 46-48 TOPIC 3 REVIEWING MULTIPLICATION OF WHOLE NUMBERS 6th Grade 1 Embed 1 Multiplication properties (optional) Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers Estimating products 3.1 Review Multiplying by 1-digit numbers (optional) 3.3 Grade 4 Standard Review Multiplying by 2-digit numbers (optional) 3.4 Grade 4 Standard NS 1.1 Grade 6 Standard 3.2 MR 2.1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results. Estimating and multiplying with greater numbers Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; NS 1.3 compute examples as repeated multiplication. Exponents Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. MR 1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. 3.5 Problem Solving: Multiple step problems 3.7 3.6 10 32 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Review/reteach/enrich/assess Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days pp. 72-74 TOPIC 6 MULTIPLYING DECIMALS Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative NS 2.1* integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Multiplying decimals by 10, 100, 1000 6.1 Multiplying a whole number and a decimal 6.2 Estimating the product of a whole number and a decimal 6.3 Multiplying two decimals 6.4 MR 2.1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results. Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to Embed MR 2.5 problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy. Make precise calculations and check the validity of the results from the Embed MR2.6 context of the problem. Problem Solving: Reasonableness 6.6 7 22, 25 20, 24, 27 Embed Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 148-150 TOPIC 4 DIVISION OF WHOLE NUMBERS 3 1 3 Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. Using patterns to divide Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small NS 1.1 (e.g., thousandths) numbers Estimating quotients Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive NS 2.2* decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. Connecting models and symbols NS 2.2* 4.1 4.2 4.3 33 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Dividing by one digit divisors 4.4 Zeros in the quotients 4.5 Dividing by two digit divisors 4.6 30, 31 More dividing by two digit advisors Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small 1 NS 1.1 (e.g., thousandths) numbers Estimating and dividing with greater numbers Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Draw a picture and write an equation 4.7 29 Other Resources # of Days 4.8 4.9 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 106-108 TOPIC 7 DIVIDING DECIMALS Estimate, round, and manipulate very large (e.g., millions) and very small (e.g., thousandths) numbers. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative NS 2.1* integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive NS 2.2* decimals and long division with multi-digit divisors. Dividing decimals by 10, 100, 1000 7.1 Dividing a decimal by a whole number 7.2 Estimation: Decimals divided by whole numbers 7.3 Dividing a decimal by a decimal 7.4 MR 1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Multi-step problems 7.5 1 7 3 NS 1.1 21 28 Embed 34 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 168-170 BENCHMARK EXAM #1 CLOSING DATES Traditional: November 22, 2013 Modified: November 1, 2013 VOCABULARY LIST 1 BENCHAMRK EXAM #1 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERVENTIONS INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 2 VOCABULARY LIST 2 Please Note: This entire Instructional Segment should be completed before the administration of the CST Mirror Test. Topics 8 and 14 from the next Instructional Segment should be completed before the administration of the actual CST. TOPIC 9 FACTORS AND MULTIPLES Review Understanding factors (optional) 9.1 Grade 4 Standard Prime and composite numbers (optional) Determine the prime factors of all numbers through 50 and write the NS 1.4* numbers as the product of their prime factors by using exponents to show multiples of a factor (e.g., 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 23 × 3). Finding prime factors 9.2 Grade 4 Standard Review 3 th 6 Grade Common factors and greatest common factor (optional) Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Problem Solving: Try/check/revise 9.3 9.4 11 - 16 Grade 6 Standard 9.5 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 208-210 35 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days TOPIC 10 FRACTIONS, MIXED NUMBERS, AND DECIMALS Review Meanings of fractions Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed NS 1.5* numbers, and positive and negative integers. Fractions and division 10.1 Mixed numbers and improper fractions 10.3 Equivalent fractions (optional) 10.4 Grade 4 Standard 6 Grade Comparing and ordering fractions and mixed numbers (optional) 10.5 Grade 6 Standard 6th Grade Fractions in simplest form (optional) Students compute with very large and very small numbers, positive integers, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship between decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers. Tenths and hundredths 10.6 Grade 6 Standard Thousandths Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed 2 NS 1.5* numbers, and positive and negative integers. Fractions and decimals on the number line Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Writing to explain 10.8 2 Review th NS 1.0 Grade 4 Standard 10.2 10.7 10.9 18, 19 10.10 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 240-242 36 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons Other Resources RTQ’s # of Days TOPIC 11 ADDING & SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS & MIXED NUMBERS 5 Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed NS 2.3* numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. Adding and subtracting fractions with like denominators th 6 Grade 11.1 Common multiples and LCM (optional) Solve simple problems, including ones arising in concrete situations, involving the addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed NS 2.3* numbers (like and unlike denominators of 20 or less), and express answers in the simplest form. Adding fractions with unlike denominators 11.2 Subtracting fractions with unlike denominators 11.4 Adding mixed numbers 11.5 33, 37 Subtracting mixed numbers Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Problem Solving: Look for a pattern 11.6 35, 36 5 11.3 Grade 6 Standard 32, 34 11.7 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 264-266 Note: You may want to briefly teach 12.1 through 12.4 here (multiply and divide fractions). TOPIC 17 PERCENT 6th Grade 5 Understanding ratios (optional) Interpret percents as a part of a hundred; find decimal and percent NS 1.2* equivalents for common fractions and explain why they represent the same value; compute a given percent of a whole number. 17.1 Grade 6 Standard 37 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Understanding percent 17.2 Percents, fractions, and decimals 17.3 4-8 Finding percents of a whole number Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Make a table and look for a pattern 17.4 3, 9 Other Resources # of Days 17.5 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 396-398 TOPIC 15 INTEGERS Identify and represent on a number line decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, and positive and negative integers. Understanding integers 15.1 Comparing and ordering integers 15.2 Integers and the number line Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative NS 2.1* integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Adding integers 15.3 Subtracting integers Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate 6 AF 1.2* simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution Simplifying expressions Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Work backward 15.5 2 7 NS 1.5* 17 15.4 15.6 15.7 38 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 358-360 TOPIC 5 VARIABLES AND EXPRESSIONS 1 6 Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate AF 1.2* simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution AF 1.1 43, 45, 47, 48, 50, 53 Variables and expressions 5.1 Patterns and expressions 5.2 More patterns and expressions Know and use the distributive property in equations and expressions with variables. Distributive property 5.3 46, 49, 52 5.4 54 - 56 Order of operations (optional) Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Act it out and use reasoning 5.5 1 AF 1.3 th 6 Grade Grade 6 Standard 5.6 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 130-132 TOPIC 16 SOLVING AND WRITING EQUATIONS 6th Grade th 6 Grade Solving addition and subtraction equations (optional) Solving multiplication and division equations (optional) Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the Embed MR 3.1 original situation. 16.1 Grade 6 Standard 16.2 Grade 6 Standard 39 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Problem Solving: Use reasoning Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate AF 1.2* simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write AF 1.5* the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. Patterns and equations 16.3 16.4 63, 65 More patterns and equations Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Draw a picture and write an equation 16.5 66 16.6 51, 67 6 5 Other Resources # of Days Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 380-382 TOPIC 18 EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. 1/2 SDP 1.5* Know how to write ordered pairs correctly; for example, (x, y). 4 AF 1.4* 2 1/2 SDP 1.4* 4 AF 1.4* 5 AF 1.5* Embed MR 1.1 Ordered pairs Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. Line graphs Identify and graph ordered pairs in the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. Graphing equations Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and 18.1 57 – 62, 96 18.2 94 18.3 64 40 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days observing patterns. Problem Solving: Work backwards 18.4 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 414-416 TOPIC 19 GRAPHS AND DATA Use information taken from a graph or equation to answer questions about a problem situation. Organize and display single-variable data in appropriate graphs and 1/3 SDP 1.2 representations (e.g., histogram, circle graphs) and explain which types of graphs are appropriate for various data sets. Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning 2 1/2 SDP 1.4* of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. Bar graphs and picture graphs 19.1 Histograms 19.2 1 AF 1.1 Circle graphs Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, Embed MR 2.3 graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Make a graph Know the concepts of mean, median, and mode; compute and compare 1/3 SDP 1.1 simple examples to show that they may differ Mean 6th Grade 19.3 44, 95 92 19.4 19.5 Median, mode and range 19.6 Outcomes (optional) 19.7 91 Grade 6 Standard 1/3 SDP 1.3 Use fractions and percentages to compare data sets of different sizes. Writing probability as a fraction 19.8 93 MR 1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. Apply strategies and results from simpler problems to more complex Embed MR 2.2 problems. Embed 41 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Problem Solving: Solve a simpler problem Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days 19.9 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 444-446 CST MIRROR TEST CLOSING DATES Traditional: March 7, 2014 Modified: February 28, 2014 CST MIRROR TEST DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERVENTIONS CST RELEASED TEST QUESTIONS and any or all of the following: 65 ALL Multiple-choice test to assess students' understanding of the concepts and skills taught in each Topic 65 ALL Additional assessment options in Form A and B format for each Topic 65 ALL Item Analysis for Diagnosis and Intervention chart for each Topic Student text – end of each Topic Teacher Resource Masters Teacher Edition - end of each Topic PLEASE COMPLETE TOPICS 8 AND 14 BEFORE THE ADMINISTRATION OF THE CST. INSTRUCTIONAL SEGMENT 3 Vocabulary List 3 TOPIC 8 SHAPES 3 Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, MG 2.1* rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software Basic geometric ideas 8.1 83 Measuring and classifying angles 8.2 80 – 82 42 # CST Items 4 Embed Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Know that the sum of the angles of any triangle is 180° and the sum of MG 2.2* the angles of any quadrilateral is 360° and use this information to solve problems. Polygons 8.3 84 Triangles 8.4 85 – 88 Quadrilaterals 8.5 89 STD MR 3.3 MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Other Resources # of Days Develop generalizations of the results obtained and apply them in other circumstances. Problem Solving: Make and test generalizations 8.6 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 188-190 TOPIC 14 SOLIDS Review Solids (optional) 14.1 Grade 4 Standard Review Relating shapes and solids (optional) 14.2 Grade 4 Standard Construct a cube and rectangular box from two-dimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. Surface area 14.3 73 Views of solids 14.4 90 Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common measuring systems (i.e., cubic centimeter [cm3], cubic meter MG 1.3* [m3], cubic inch [in3], cubic yard [yd3]) to compute the volume of rectangular solids. Models and Volume 14.5 Volume 14.6 1/2 MG 1.2* 1 3 MG 2.3 Visualize and draw two-dimensional views of three-dimensional objects made from rectangular solids. 74 - 77 43 # CST Items Embed STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Other Resources # of Days MR 1.2 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. Problem Solving: Use objects and solve a simpler problem 14.7 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 336-338 CST ADMINISTRATION TOPIC 20 CONSTRUCTIONS 3 Embed Measure, identify, and draw angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, MG 2.1* rectangles, and triangles by using appropriate tools (e.g., straightedge, ruler, compass, protractor, drawing software Constructing angles 20.1 Constructing lines 20.2 Constructing shapes 20.3 MR 2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Use objects 20.4 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 464-466 TOPIC 12 MULTIPLYING & DIVIDING FRACTIONS & MIXED NUMBERS 1 NS 2.4 Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. 1 NS 2.5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems Multiplying fractions and whole numbers 12.1 42 Multiplying two fractions 12.2 40, 41 Dividing a whole number by a fraction 12.3 39 44 # CST Items STD MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s 12.4 38 Dividing two fractions Other Resources # of Days Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant Embed MR 1.1 from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Problem Solving: Missing or extra information 1 NS 2.4 Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. 1 NS 2.5 Embed MR 2.3 12.5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems Multiplying mixed numbers 12.6 Dividing mixed numbers 12.7 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Draw a picture and write an equation 12.8 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 290-292 TOPIC 13 LENGTH, PERIMETER AND AREA 1 MG 1.4 Differentiate between and use appropriate units of measures for, two- and three- dimensional objects (i.e., find perimeter, area, volume). Using customary units of length 13.1 Using metric units of length 13.2 Perimeter 13.3 79 78 Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a 2 1/2 MG 1.1* rectangle (i.e., two of the same triangles make a parallelogram with twice the area; a parallelogram is compared with a rectangle of the same area by cutting and pasting a right triangle on the parallelogram. 45 # CST Items Embed STD MR 2.3 MATH 5 PACING GUIDE 2013 - 2014 Textbook Lessons RTQ’s Area of squares and rectangles 13.4 Area of parallelograms 13.5 68, 69, 72 Area of triangles 13.6 70, 71 Other Resources # of Days Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Problem Solving: Draw a picture and make an organized list 13.7 Review/reteach/enrich/assess pp. 312-314 SITE-BASED END OF YEAR ASSESSMENT CLOSING DATES Traditional: June 13, 2014 Modified: June 26, 2014 END OF YEAR ASSESSMENT DATA ANALYSIS 46