Final Report - Networked Software Systems Laboratory
advertisement

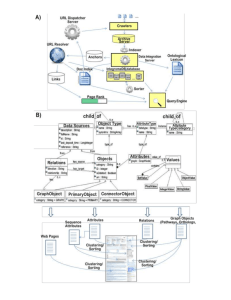
Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Spring 2010 Software System Laboratory Employing Web Search indexing for fast creation of filtered view of large text files Requirements & Design Document Students: Mostafa Agbaria 301154100 Ahmad Atamlh 300423530 Supervisor: Oved Itzhak Lab Chief Engineer: Dr. Ilana David 1 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Table of Contents Table of Contents ...................................................................................................................... 2 Abstract ........................................................................................................................................ 3 Terms and Definitions................................................................................................................... 4 Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 5 General Approach ........................................................................................................................ 6 Architecture .................................................................................................................................. 7 Multi-Threaded Indexing ............................................................................................................... 8 Class Overview........................................................................................................................... 10 Sequence Overview ................................................................................................................... 13 References ................................................................................................................................. 17 Appendix .................................................................................................................................... 18 2 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Abstract In today’s Internet-scale services it’s not uncommon to have logs that contain huge amounts of data. Inspecting such logs can easily overwhelm a human. Therefore, specialized tools that make it easier to manage all the data are essential. In this project we implement a Plug-in to the existing VLTF1 application which takes the text file and creates an Index that enables very fast search in the file, using inverted indexing. The VLTF provides the GUI for searching and quickly navigating to the found locations in the text file. 1 Very Large Text File Viewer 3 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Terms and Definitions Inverse indexing: Much like the well-known back-of-the-book index, reverse indexes help users find information using a variety of keywords and gathering similar information under a single topic. Instead of page numbers, web indexes are hypertext-linked directly to the content within the website itself. VLTF: very large text file viewer. 4 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Introduction Event logging and log files are playing an increasingly important role in system and network management. Over the past two decades, the BSD syslog protocol has become a widely accepted standard that is supported on many operating systems and is implemented in a wide range of system devices. Well-written system applications either use the sys log. Protocol or produce log files in custom format. While many devices like routers, switches, laser printers, etc … are able to log their events to remote host using the syslog protocol, normally, events are logged as single-line textual messages. Since log files are an excellent source for determining the health status of the system, many sites have built a centralized logging and log file monitoring infrastructure. Due to the importance of log files as the source of system health information, a number of tools have been developed for monitoring log files, e.g., Swatch Log surfer and SEC.[2] Log requires human inspection for analyzing incidents as well as getting insight into the server operation for tuning. Inspecting very large log files verbatim by humans is impractical .Simplistic filtering (a-la grep) requires going over the entire file for every filter, which is a time consuming operation. In a previous work done in the lab a VLTF viewer was designed. A VLTF viewer is an application that scales well with the file size, the application takes the input file that the user loads and creates an index that is easier and faster to access. This index maps lines to their containing segment; when the VLTF needs to display a certain line, it loads only the segment that contains it. The VLTF makes it easier to inspect the log files but doesn't support searching in a file without going over the entire text, and our project was intended to add a plug-in to support searching using VLTF without going over the entire text file every time we search. 5 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty General Approach The main goal is to create a search plug-in that uses the VLTF [5] and displays the search results withstanding time. The conventional approach previously used requires going over the entire text file to perform the search, which is time consuming and not practical. The main idea was to develop a pattern that enables us to perform a search in less time and more practice, a preprocessing for the text file can enable us to perform a search in a faster and more reliable way. First we go through the entire file and create an Index that enables a faster search in the text file Index that we save for later use for the text file, a time consuming process because it need to go through the entire Text file but a price that we are willing to pay once for faster search in the later searches,. Such index will save the power and process of making the index again every time we perform a search and would solve the naïve way of going over the entire file for a search. , Therefore, once the Index is created every time we search in the text file the same index will be used and the performance of the search will be faster and more practical way. Since the index requires pre-processing of the Text file , a problem arises with the growth of it ; pre-processing the file starts to take non linear time to the growth, so dealing with Text files with the size of 1GB – 4GB became impractical because it was hard to know and estimate the time of the pre-processing it . In many cases it was hard to know if the VLTF is not responding or it is still processing and the Index is being made , either way lead us to develop a more advanced pattern that is faster in creating the Index and also utilize the use of the CPU more , by multithreading , the file was divided into parts according to the size and the thread number and for every part there was a different thread, by this the threads could run in parallel and the time for creating the index was lower , nonetheless the CPU functionality was more utilized . 6 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Architecture In order to address our objectives we decided to divide the search engine into units, each unit is responsible for delivering the job it is meant to do not withstanding other unit she main function of the search engine that is provided is to create an easier interface for search, and its mains function is among the data layers . The architecture consists of several units: File parser – parsing data from the text file Indexer – processing what was received from the parser. Web Technique Searcher – a user interface that perform the search and responsible for storing the Indexer for later use. The reasons for preferring this architecture are: Development Stage – it's intuitive to look at our objectives as three parts problem: (1) parsing the file, (2) processing the Indexer, and (3) search interface for the indexer. These parts are hardly interconnected and we may implement a separate solution to everyone. Maintenance Stage - It has a good modularity that makes it easier to understand the implementation nonetheless perform debugging. 7 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Multi-Threaded Indexing Motivation: After implementation, running the test on the system using large files consumed a huge amount of time. A thorough investigation of the problem has shown that the major time consumed was due to a lot of I/O requests and not CPU time. A suggested solution was the use of multithreaded indexing: a number of threads are created and each one would be responsible for indexing a portion of the file. Meaning that each thread creates a sub-database, which is a part of the whole database. Hence, when one thread is waiting for the I/O request, another thread can use the CPU for indexing, resulting in a faster process for the indexing. 8 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Determining the amount of threads: A maximum amount of allowed threads is set in the system (which can be changed if needed). Also, a default chunk size (A "chunk", is the amount of data a threads is to process) was chosen to be 1MB. When a file is chosen for indexing, the system divides its size (in bytes) by 1Mb. Resulting in the amount of needed threads, assuming each one handles 1Mb. If the amount of needed threads for processing is lower (or equal) to the amount of maximum allowed threads, the threads will be created and each thread would process 1Mb. However, if the amount of threads needed exceeds the maximum amount, the maximum number of allowed threads would be created, and each one would handle data, so that the full file is processed by the threads. Tests and Results: The system was tested using a 100Mb file, each time using a different amount of threads. As can be seen from the previous graph, when using multithreading the system performs faster. 9 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Class Overview This section contains the system class relation diagram. A detailed design of each class is specified in the next subsections. 11 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty In order to separate between functionality and implementation in the previous project, it encapsulated all the functionality of the Business Logic Layer in an abstract class. Abstract Controller provides the functionality of the Business Logic Layer in the VLTF viewer. Our implementation to it , is the Web Technique Controller class. In the Web Technique Controller we connect between the VLTF and the search technique that we have developed. The Web Technique Controller gets the data base from the indexer and through it we can do the search , the Web Technique Controller inherit from a base class called Abstract Controller that belongs to VLTF which is used for search and the result we fire to the VLTF Web Technique Searcher Class: this class is responsible for gathering the Indexes from the Indexer to shape the entire DataBase. The Indexer, which is responsible for building the Index for the part it gets, delivers all the indexes for the Web Technique searcher. Creating the DateBase is done once only and then saved through serialization into the disk to enable later use for search. Getting the database from the created one is done Through De-serialization; every add-on for the end of the file is dealt by creating an Index for the new data and as so to the entire Datebase which lead to a change in the Serialized version. 11 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Indexer Class: This class receives the data for building the index from the file parser, building the Index using inverse indexing for the words it get. Each Index is sent to Web Technique Searcher that uses every Index it gets to shape the entire DataBase. File Parser Class: This class is responsible for opening the stream file and send every word in the file with its line number to the Indexer so the Index could be built. DataBase Class : This class uses as inner class to the Indexer , each Index that we create have a built-in DataBase class that includes all the data. It uses the Dictionary class to save the relevant data using the basic methods and fields of the class and it considered the data layer in the search engine. 12 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Sequence Overview Sequence Diagram (init file) Web Technique File Stream File Parser Indexer Thread constructor(FileName) constructor(FileName) constructor start Read AddWord Write Parse Serialize When loading the file, web Indexer object that is responsible for getting the data base is created. When first loading the file, the data base does not exist and therefore, the web indexer creates a new indexer object that creates a file parser object. An interaction between the indexer and the file parser leads to creation of data base in the indexer while the file parser does the parsing of the file and sends the words to the indexer to add each word to the data base. At the end of processing the data, the file parser sends the indexer a finished signal, and at this stage a serialized data base appears on the disk for future use, leading to reduction of efforts in creating data base each time. 13 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Sequence Diagram (Dispose) Indexer Web Technique Dispose File Parser Dispose() Thread Cancel() Join() In the process of creating the data base if we try to load another file, we stop creating the new data base and dispose of the created web indexer. When the running thread that creates the data base finishes, we join the existing thread with the new thread of the data base and start making the data base of the new loaded file. 14 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Sequence Diagram (Search Pattern) VLTFV Indexer Web Techniqe SearchPattern() Thread constructor() Start() SearchPattern() FireOnAddSearchResultLine() FireOnAddSearchResultLine() When the user sends a search request through the VLTF, it sends the search to web indexer. The latter runs a thread that looks for the appearance of the search object in the whole file, at the end of the searching operation the web indexer gets the lines of the search results from the indexer and sends them to the GUI of the VLTF. 15 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Sequence Diagram (Cancel Search) Thread Web Techniqe Cancel Search() Stop Search() Join() The web indexer sends a cancellation request to the indexer. It stops the search, waits till the thread ends and informs the web indexer. 16 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty References [1] "C# for C++ developers", Appendix D. p. 1253-1305. Media Wiley. [2] James H. Andrews. Testing using Log File Analysis: Tools, Methods, and Issues. ase, pp.157, 13th IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE'98), 1998. [3] Risto Vaarand. A Data Clustering Algorithm for Mining Patterns From Event Logs. Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Workshop on IP Operations and Management [4] Donald E. Knuth. The Art of Computer Programming, 3rd edition, 1973. [5] Zobel, Justin; Moffat, Alistair; Ramamohanarao, Kotagiri. Inverted files versus signature files for text indexing. ACM Transactions on Database Systems. 1998, 23 (4): pp. 453–490 [6] Baeza-Yates, Ricardo; Ribeiro-Neto, Berthier .Modern information retrieval. Addison-Wesley Longman. p. 192, 1999. [5] Amitay Svetlit and David Nasi. VLTF Viewr manual. EE Department Technion. 2009 17 Technion – Electrical Engineering Faculty Appendix User Interface: Our graphic interface is optimized for viewing large text files. In this section we provide the manual for the functionality to be implemented in the VLTF viewer application according to the project requirements: [5] Basic Layout: 3.1. Open File 3.2. Go to Line 3.3. Search 3.6. Line Numbers 3.4. Conventional Scroll Bar 3.5. Scroll Knob 3.7. Search Results Pane 3.10 Text view area 3.8. File lines counter 3.9. Progress Bar 18