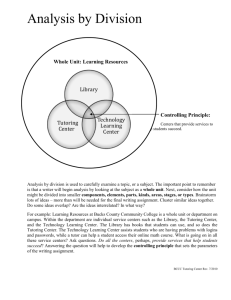
Neil T Heffernan - Computer Science
advertisement

Professor Neil T. Heffernan III CV Note: An electronic version of this document with working links to all papers is at all papers is at http://nth.wpi.edu/pubs_and_grants/papers/index-home.html Education Ph. D. Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, 2001. M.S. Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, 1997. B.A. Computer Science and History, Amherst College, Summa cum laude,1993. Appointments Associate Professor July 2008 to present. Assistant Professor, WPI, July, 2002 to 2008. Post-Doctoral Researcher, Human-Computer Interaction Institute, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, 2001 to 2002. Awards & Honors A14Massachusetts Association of School Committee’s Annual Award for “Community Leader for Public Education”. The citation reads “Since coming to Worcester in 2002, Neil and Cristina Heffernan have generously dedicated their time, talent and boundless energy to building ASSISTments, an online math tutoring system, for Worcester middle and high school students and their teachers. This program is a magnificent tool that is distinguished by, among other facets, its clarity and easy of access and use.” A132008 Sigma Xi Research Award for Outstanding Junior Faculty Researcher. A12Honored for meritorious achievement as an advisor to best Major Qualifying Project in the department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, 2007 A11Best 3-page "Poster" Award (with my student Jason Walonoski), International Intelligent Tutoring System Conference. 2006. A10US Patent Filed by WPI for technology used in the ASSISTment intelligent tutoring system. A9 Nominated for Best Paper First Authored by a student (with Mingyu Feng) a conference with an 11% acceptance rate ;World Wed Web Conference (WWW'06). A8 I was invited to serve on the NSF/CRA CyberLearning Workshop focused on Technology-Enabled Assessment to help shape a research agenda for NSF's EHR Directorate. A7 National Science Foundation's most prestigious award for young researchers. A6 Nominated for the Massachusetts Teacher Associations “Friend of Education” award by Forest Grove Middle School for my ASSISTment project work. A5 Nominated by my department for WPI's Ambassador Award for doing a outstanding job of representing WPI to the community. A4 Best 3-page "Poster" Award (with my student Leena Razzaq), International Intelligent 1 Tutoring System Conference. 2004. A3 US Patent #6,634,887: Methods and systems for tutoring using a tutorial model with interactive dialog (with Ken Koedinger). A2 National Academy of Education/Spencer Foundation Post-Doctoral Fellowship Award. 2002. A1 The David Marr Award for Best Student Paper Award, (with Ken Koedinger), Cognitive Science Conference. 1997. Grants Awarded My research was benefited from about 9 million dollars from the National Science Foundation, U.S. Department of Education, the Office of Naval Research, the Spencer Foundation, the US Army and the Massachusetts Technology Transfer Council. GA18US Department of Education: Institute for Education Sciences. ASSISTments Meets Science Learning. PI Janice Gobert. CoPI’s Heffernan and Beck. $1.2 million. 3/093/2012 GA17NSF: GK12 ““Partnership Implementing Math and Science Education: Assisting Middle School Use of Tutoring Technology. PIMSE. $2 million. 2008-13 GA16NSF: Research Experience for Teachers Supplement. $19,500 . GA15NSF: DRK-12. “ASSISTments Meets Inquiry” PI: Gobert. Co-PI’s Heffernan, Ruiz & Kim. Anticipated start date is 2007-Sept, 1. Five years. $1.5 million. GA14NSF Supplement Research Experience for Undergraduates. $13,500. GA13Massachusetts Technology Transfer Center: "Scaling up a Web-Based Formative Assessment System: Testing the Replicability of Deploying ASSISTment beyond its 'Home Town'". PI Heffernan. $40,000. (Awarded Jan 24th, 2007 ) GA12US Department of Education: "Making Longitudinal Web-Based Assessments Give Cognitively Diagnostic Reports to Teachers, Parents & Students While Employing Mastery Learning." PI Heffernan. Co-PIs Ken Koedinger (CMU), Brian Junker (CMU), George T. Heineman (WPI), Murali Mani (WPI) & Cristina Heffernan (WPS). $2 million over 4 years commencing in 2007. GA11National Science Foundation: CAREER Grant. "Learning About Learning" PIHeffernan. $900,000. 2005-2010 GA10Office of Naval Research: "Demonstrating Affordable Behavior Modeling with CTAT through Machine Learning and Human Computer Interaction Techniques." PIHeffernan. $275,000 2005-08. GA9 US Department of Education: "Fellowships in CS to Support the Learning Sciences and Security." Awarded approximately $800,000 to support 5 PhD per year. 20062009. PI Matt Ward. Co-PIs Heffernan, Agu and Mani. GA8 US Dept of Education: Institute of Education Sciences: “Using Web-Based Cognitive Assessment Systems for Predicting Student Performance on State Exams” PIKoedinger. Co-PIs Heffernan, Junker and Ritter. $1.4 million over 4 years. 2003-07. 2 GA7 National Science Foundation: “Research Experience for K12”. $99,457. PIRundensteiner. Co-PI Heffernan. 2006-08 GA6 US Army: Phase 2: STTR $500,000 with Sonalysts Inc GA5 US Army: Phase 1: STTR Grant to explain to the Army how to incorporate intelligent tutoring into their warrior simulation systems. $100,000 with Sonalysts Inc. GA4 Research Advancement Program at WPI: “Programming by Demonstration for Intelligent Tutoring Systems.” PI-Heffernan. $7,500. 2003. GA3 Office of Naval Research: "Affordable Cognitive Modeling Authoring Tools using HCI Methods". PI-Heffernan. $203,304 2003-06 GA2 Office of Naval Research: "Cognitive Tutor Tools for Advanced Instructional Strategies." PI-Koedinger. Co-PI's Heffernan & Aleven. April -Sept, 30th 2002. $200,000. GA1 National Academy of Education/ Spencer Foundation: "A Comparison of Student Learning Under Multiple Conditions: Classroom Instruction, One-on-one Human Tutoring, and Different types of Computer Tutoring". PI-Heffernan. $50,000. 20022004 3 Press Newspaper Articles PRESS15Worcester Telgrem citation for award from School Committee. PRESS14“U.S. gives $1.5 million for science tutoring” by Boston Globe. January 10, 2008. PRESS13“New WPI System” by Worcester Telegram & Gazette. January 10, 2008. “WPI projects win NSF grants: Work on science education, tiny sensors receive PRESS12 funding” by Jacqueline Reis. Worcester Telegram & Gazette. August 23, 2007. IEEE Intelligent System “In the News” article called “Intelligence Tutors Make PRESS11the Grade” that talked about ASSISTments and other Intelligent tutoring systems. By reporter Mark Ingebretsen. “WPI Tutor Program is Money in the Bank” by Matthew Brown. Worcester PRESS10 Business Journal. June 2007. http://nth.wpi.edu/press/WorBus/WBJ.htm “WPI receives $2M ‘assist’ for tutoring.” by Telegram & Gazette Staff. Telegram PRESS9 & Gazette. May 26, 2007. “WPI Receives $2 Million Award to Develop an Intelligent Tutoring System That PRESS8 Can Improve Math Education” ACM TechNews. May 23, 2007. PRESS7 “Assessing the Odds.” by Michael W. Dorsey. Transformations. Fall 2006. “Professor’s preparation program adds up to better MCAS math scores.” by PRESS6 Gretchen Weber. The Worcester Educator. Spring 2006. “Enter the Computer Tutor: PCs Can Help Kids Pass No Child Left Behind PRESS5 Tests.” by Angie C. Marek. U.S. News & World Report. November 11, 2005. “Schools, sponsors teaming up for TV ads.” by Jacqueline Reis Telegram & PRESS4 Gazette. December, 2005. “WPI asst. profs awarded grants.” by Mallary Jean Tenore. Telegram & Gazette. PRESS3 August 11, 2005 “‘Assistment’ makes the grade.” by Jacqueline Reis. Telegram & Gazette. May PRESS2 23, 2005. “Pupils to get online help with MCAS.” by Clive McFarlane. Telegram & PRESS1 Gazette. January 14, 2004. Radio and Television RT3 "Prof. Neil Heffernan gets coverage by WPI": A short clip by WPI's TEAM Worcester featuring the ASSISTment system. Archived at: http://web.cs.wpi.edu/Research/trg/public/project/videos/asst_wmv.wmv RT2 580 AM, WTAG interview by Greg Byrne, August 11th, 2005: This 55 second audio clip is from Worcester's local radio station, 580 AM. In it, Prof Heffernan is interviewed about how his $900,000, NSF CAREER award is going to impact Massachusetts 8th and 10th grade math students. Archived at: http://web.cs.wpi.edu/Research/trg/public/project/audio/Neil_interview.mp3 4 RT1 "Prof. Neil Heffernan makes huge impact", NECN Nightly News, May 23rd, 2005: A two minute clip showing students at Forest Grove Middle School, and their math teacher, using and talking about the Assistment System. Archived at: http://web.cs.wpi.edu/Research/trg/public/project/videos/NECN_MCAS_story_5-232005.wmv 5 Publications Note: In the following sections all coauthors who are WPI students are italicized. Book Chapters BC3Pardos, Z. A., Heffernan, N. T., Anderson, B., Heffernan, L. C. (In Submission) Using Fine-Grained Skill Models to Fit Student Performance with Bayesian Networks. Chapter in C. Romero, S. Ventura, S. R. Viola, M. Pechenizkiy and R. S. J. Baker. Handbook of Educational Data Mining. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press. BC2Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T., & Koedinger, K.R. (in press). Student Modeling in an Intelligent Tutoring System. Submitted to Stankov, Glavinc, Rosic. (Eds.) Intelligent Tutoring Systems in E-learning Environments: Design, Implementation and Evaluation. IGI Global. early 2010 (anticipated) (Based on W10, W11 and W12) BC1Razzaq, Feng, Heffernan, Koedinger, Nuzzo-Jones, Junker, Macasek, Rasmussen, Turner & Walonoski. (2007). A Web-based authoring tool for intelligent tutors: Assessment and instructional assistance. In Nadia Nedjah, Luiza deMacedo Mourelle, Mario Neto Borges and Nival Nunesde Almeida (Eds). Intelligent Educational Machines. Intelligent Systems Engineering Book Series. pp.23-49. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. http://www.springerlink.com/content/m2g23834641m858n/fulltext.pdf Journal Articles J10Feng , M, Heffernan, N., Heffernan, C. & Mani, M. (accepted) Using Mixed-Effects Modeling to Analyze Different Grain-Sized Skill Models. IEEE Transaction on Learning Technologies. Expected publication date of Fall 2009. (Based on PP8 and WP15) J9 Razzaq, L., Patvarczki, J., Almeida, S.F., Vartak, M., Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T. and Koedinger, K. (accepted). The ASSISTment builder: Supporting the Life-cycle of ITS Content Creation. Submitted to the IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies Special Issue on Real-World Applications of Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Expected publication date of Fall 2009. (Based on YRP5) J8 Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T., & Koedinger, K.R. (in press). Addressing the assessment challenge in an Intelligent Tutoring System that tutors as it assesses. Accepted by The Journal of User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction. (Based on CP15) J7 Mendicino, M., Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N. T. (accepted- In Press) Improving Learning from Homework Using Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Journal of Research on Technology in Education (JRTE). Published by the International Society For Technology in Education (ISTE). Scheduled to appear in the Spring 2009 issue. J6 Razzaq, L., Heffernan, N., Feng, M., Pardos Z. (2007). Developing Fine-Grained Transfer Models in the ASSISTment System. Journal of Technology, Instruction, 6 J5 J4 J3 J2 J1 Cognition, and Learning, Vol. 5. Number 3. Old City Publishing, Philadelphia, PA. 2007. pp. 289-304. Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T. (2007). Towards live informing and automatic analyzing of student learning: Reporting in the Assistment system. Journal of Interactive Learning Research (JILR) 18(2) pp. 207-230. Chesapeake, VA: AACE. (Based on W12) Baker, R., Walonoski, J., Heffernan, T., Roll, I., Corbett, A. & Koedinger, K. (2008) Why students engage in "Gaming the System" behavior in interactive learning environments Journal of Interactive Learning Research (JILR). Chesapeake, VA: AACE. 19(2), 185-224 (Based on CP12 and PP5) Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T. (2006). Informing teachers live about student learning: Reporting in the Assistment system Technology, Instruction, Cognition, and Learning Journal Vol. 3. Number 1-2. Old City Publishing, Philadelphia, PA. 2007. (Based on W12) Heffernan, Koedinger & Razzaq (2008) Expanding the model-tracing architecture: A 3rd generation intelligent tutor for Algebra symbolization. The International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education. 18(2). 153-178 (Builds upon CP8 and CP1-4) . Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2002). Results from a Web-Based Tutor for Writing Algebra Expressions for Word-Problems Sciences et Techniques Educatives Volume 9:1-2. (This French language journal has translated our paper into French. My translation of this Journal's title is "Educational Sciences and Technology.") http://www.inrp.fr/atief/ste/ste-res-vol9.htm (Based on D1) Journal Articles in Submission: Strictly Reviewed Conferences (Percent acceptance rate in the 30s or below) ; CP29Razzaq, L., Heffernan, N.T., Shrestha, P., Wei, X., Maharjan, A., Heffernan, C. (Submitted) Are Worked Examples an Effective Feedback Mechanism During Problem Solving? Submitted to the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, 2009. CP28Kim, R, Weitz, R., Heffernan, N. & Krach, N. (submitted) Tutored Problem Solving vs. “Pure”: Worked Examples Submitted to Cognitive Science Society Annual 2009 Conference CP27Sao Pedro, M., Gobert, J. Heffernan, N. & Beck, J. (submitted) Can an Intelligent Tutor Teach the Control Variables Strategy for Scientific Inquiry? Submitted to Cognitive Science Society Annual Conference CP26Pardos, Z. & Heffernan, N. (accepted) Detecting the Learning Value of Items in a Randomized Problem Set. AIED 2009. CP25Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N. (accepted) To Tutor or Not to Tutor: That is the Question. AIED 2009 CP24Feng, M. & Heffernan, N. (accepted) Using Learning Decomposition to Analyze Instructional Effectiveness in the ASSISTment System. AIED 2009 CP23Feng, M., Beck, J,. Heffernan, N. & Koedinger, K. (2008) Can an Intelligent Tutoring 7 System Predict Math Proficiency as Well as a Standardized Test? In Baker & Beck (Eds.). Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Education Data Mining. pp.107-116. CP22Feng, M., Heffernan, N., Beck, J, & Koedinger, K. (2008) Can we predict which groups of questions students will learn from? In Baker & Beck (Eds.). Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Education Data Mining. pp.218-225. CP21 CP20Razzaq, L., Mendicino, M. & Heffernan, N. (2008) Comparing classroom problemsolving with no feedback to web-based homework assistance. In Woolf, Aimeur, Nkambou and Lajoie (Eds.) Proceeding of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. pp. 426 -437. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. CP19Razzaq, L., Heffernan, N. T., Lindeman, R. W. (2007). What Level of Tutor Interaction is Best? In Luckin & Koedinger (Eds.) Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. IOS Press. pp 222-229. CP18Pardos, Z. A., Heffernan, N. T., Anderson, B. & Heffernan, C. (2007). The effect of model granularity on student performance prediction using Bayesian networks. The International User Modeling Conference 2007. (Based on W14 and W18) CP17Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., Mani, M., & Heffernan, C. (2007). Assessing students’ performance longitudinally: Item difficulty parameter vs. skill learning tracking. The National Council on Educational Measurement 2007 Annual Conference, Chicago. (Based upon WP15) CP16Feng, M., Heffernan, N. & Koedinger, K.R. (2006a). Predicting state test scores better with intelligent tutoring systems: developing metrics to measure assistance required. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 31-40. CP15Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2006b). Addressing the testing challenge with a Web-based e-assessment system that tutors as it assesses. Proceedings of the Fifteenth International World Wide Web Conference (WWW-06). New York, NY: ACM Press. ISBN:1-59593-332-9. pp. 307-316. [Nominated for Best Student Paper] CP14Heffernan N.T., Turner T. E., Lourenco A.L.N., Macasek M.A., Nuzzo-Jones G., & Koedinger K.R. (2006). The ASSISTment builder: Towards an analysis of cost effectiveness of ITS creation. Proceedings of the 19th International FLAIRS Conference, Melbourne Beach, Florida, USA. pp. 515-520. (Based on W10) CP13Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N.T. (2006). Scaffolding vs. hints in the Assistment system. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 635-644. CP12Walonoski, J. & Heffernan, N.T. (2006a). Detection and analysis of off-task gaming behavior in intelligent tutoring systems. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. SpringerVerlag: Berlin. pp. 382-391. 2006. CP11Razzaq, L., Feng, M., Nuzzo-Jones, G., Heffernan, N.T., Koedinger, K. R., Junker, B., Ritter, S., Knight, A., Aniszczyk, C., Choksey, S., Livak, T., Mercado, E., Turner, T.E., Upalekar. R, Walonoski, J.A., Macasek. M.A. & Rasmussen, K.P. (2005). The Assistment project: Blending assessment and assisting. In C.K. Looi, G. McCalla, B. Bredeweg, & J. Breuker (Eds.) Proceedings of the 12th Artificial Intelligence in 8 Education, Amsterdam: ISO Press. pp. 555-562. CP10Rose C., Donmez P., Gweon G., Knight A., Junker B., Cohen W., Koedinger K., Heffernan N.T. (2005). Automatic and semi-automatic skill coding with a view towards supporting on-line Assessment. In Looi, McCalla, Bredeweg, & Breuker (Eds.) The 12th Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2005, Amsterdam. ISO Press. pp. 571-578. CP9 Croteau, E., Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K. R. (2004). Why are Algebra word problems difficult? Using tutorial log files and the power law of learning to select the best fitting cognitive model. In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 240-250. CP8 Heffernan, N. T. & Croteau, E. (2004). Web-Based Evaluations Showing Differential Learning for Tutorial Strategies Employed by the Ms. Lindquist Tutor. In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 491-500. CP7 Jarivs, M., Nuzzo-Jones, G. & Heffernan. N. T. (2004). Applying machine learning techniques to rule generation in intelligent tutoring systems. In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 541-553. CP6 Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., Heffernan. T., McLaren, B. & Hockenberry, M. (2004). Opening the door to non-programmers: Authoring intelligent tutor behavior by demonstration. In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference,e, Maceio, Brazil. pp.162-173. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. CP5 Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Web-based evaluations showing both cognitive and motivational benefits of the Ms. Lindquist tutor In F. Verdejo and U. Hoppe (Eds) 11th International Conference Artificial Intelligence in Education. Sydney, Australia. IOS Press. pp.115-122. CP4 Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R.(2002). An intelligent tutoring system incorporating a model of an experienced human tutor In Stefano A. Cerri, Guy Gouardères, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.): 6th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring System. Biarritz, France. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science: pp. 596-608. CP3 Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2000) Intelligent tutoring systems are missing the tutor: Building a more strategic dialog-based tutor. In C.P. Rose & R. Freedman (Eds.) Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium on Building Dialogue Systems for Tutorial Applications. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press. ISBN 978-1-57735-124-5. pp. 14- 19 CP2 Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K. R. (1998). A developmental model for algebra symbolization: The results of a difficulty factors assessment. In M. Gernsbacher & S. Derry (Eds.) Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. pp. 484-489. CP1 Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K.R. (1997). The composition effect in symbolizing: The role of symbol production vs. text comprehension. In Proceedings of the 9 Nineteenth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. pp. 307-312. [Marr prize winner for best student paper.] Published 3-4 Page Papers (aka "Poster") in Prestigious Conferences (Percent acceptance rate in the 50-60s%) PP10Jozsef Patvarczki, Shane F. Almeida, Joseph E. Beck, and Neil T. Heffernan.( 2008 Note- this is not the final version linked yet ) Lessons Learned from Scaling Up a WebBased Intelligent Tutoring System. In Woolf & Aimeur (Eds.) Proceeding of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. PP9 Yu Guo , Neil T.Heffernan, Joseph E. Beck.(2008) Trying to Reduce Bottom-out hinting: Will telling student how many hints they have left help?. In Woolf & Aimeur (Eds.) Proceeding of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. PP8 Pardos, Z., Feng, M. & Heffernan, N. T. & Heffernan-Lindquist, C. (2007) Analyzing fine-grained skill models using bayesian and mixed effect methods. In Luckin & Koedinger (Eds.) Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. IOS Press. pp. 626-628. (Based on W17) PP7 Wietz, R., Heffernan, N. T., Kodaganallur, V. & Rosenthal, D. (2007). The distribution of student errors across schools: An initial study. In Luckin & Koedinger (Eds.) Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. IOS Press. pp 671-673. PP6 Kardian, K. & Heffernan, N.T. (2006). Knowledge engineering for intelligent tutoring systems: Assessing semi-automatic skill encoding methods. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.) Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 735-737. A longer version was published as WPI-CS-TR-06-06 (pdf) PP5 Walonoski, J. & Heffernan, N. (2006b). Prevention of off-task gaming behavior in intelligent tutoring systems. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 722-724. [Winner of the Best 3-page Paper Award out of 40 such papers]. A longer version is here. PP4 Nuzzo-Jones, G., Walonoski, J.A., Heffernan, N.T. & Livak, T. (2005). The eXtensible tutor architecture: A new foundation for ITS. In Looi, McCalla, Bredeweg, & Breuker (Eds.) Proceedings of the 12th Artificial Intelligence in Education, 555-562. Amsterdam: ISO Press. pp. 902-904. (Based on W11) PP3 Turner, T.E., Macasek, M.A., Nuzzo-Jones, G., Heffernan, N..T & Koedinger, K. (2005). The Assistment builder: A rapid development tool for ITS. In Looi, McCalla, Bredeweg, & Breuker (Eds.) Proceedings of the 12th Artificial Intelligence in Education, Amsterdam: ISO Press. pp. 929-931. A longer version appears in Hefferan et al. 2006. (Based on W10) PP2 Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., & Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Toward a rapid development environment for cognitive tutors. In F. Verdejo and U. Hoppe (Eds) 11th International Conference Artificial Intelligence in Education. Sydney, Australia. IOS Press. pp. 455457. PP1 Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N. T (2004) Tutorial dialog in an equation solving intelligent 10 tutoring system . In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual International Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Berlin: SpringerVerlag. pp. 851-853. [Winner of the Best Poster Award] Less Stringently Reviewed Venues WP19Razzaq, L., Heffernan, N.T. (2008). Towards Designing a User-Adaptive Web-Based E-Learning System. In Mary Czerwinski, Arnold M. Lund, Desney S. Tan (Eds.): Extended Abstracts Proceedings of the 2008 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. pp. 3525-3530. Florence, Italy: ACM 2008 WP18Pardos, Z., Heffernan, N. T., Anderson, B., & Heffernan-Lindquist, C. (2007). The effect of model granularity on student performance prediction using Bayesian networks. The Educational Data Mining Workshop held at the International User Modeling Conference 2007. Corfu, Greece. (Work later led to CP18) WP17Pardos, Z., Feng, M. Heffernan, N. T., Heffernan-Lindquist, C. & Ruiz, C. (2007) Analyzing fine-grained skill models using Bayesian and mixed effect methods. In the Educational Data Mining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. This is a longer version of CP18. WP16Lllyod, N., Heffernan, N. & Ruiz, C. (2007). Predicting student engagement in intelligent tutoring systems using teacher expert knowledge. In the Educational DataMining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. WP15Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., Mani, M., & Heffernan, C. (2006). Using mixed-effects modeling to compare different grain-sized skill models. In Beck, J., Aimeur, E., & Barnes, T. (Eds). Educational Data Mining: Papers from the AAAI Workshop. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press. pp. 57-66. Technical Report WS-06-05. (Work later led to PP8) WP14Pardos, Z. A., Heffernan, N. T., Anderson, B., & Heffernan C. (2006). Using finegrained skill models to fit student performance with Bayesian networks. Workshop in Educational Data Mining held at the Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Taiwan. 2006. (Work later led to PP8) WP13Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Looking for sources of error in predicting student's knowledge. In Beck. J. (Eds). Educational Data Mining: Papers from the 2005 AAAI Workshop. Menlo Park, California: AAAI Press. pp. 5461. Technical Report WS-05-02. WP12Feng, M., & Heffernan, N. (2005). Informing teachers live about student learning: Reporting in the Assistment system. Workshop on Usage Analysis in Learning Systems held at the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam. (Work later led to J3 and J5) WP11Nuzzo-Jones, G., Walonoski, J.A., Heffernan, N.T. & Livak, T. (2005). The eXtensible tutor architecture: A new foundation for ITS. Workshop on Adaptive Systems for Web-Based Education: Tools and Reusability held at the 12th Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam. pp. 1-7. (Work later led to BC1 and PP4) WP10Turner, T.E., Macasek, M.A., Nuzzo-Jones, G., Heffernan, N..T & Koedinger, K. (2005). The Assistment builder: A Rapid development tool for ITS. In a workshop on 11 WP9 WP8 WP7 WP6 WP5 WP4 WP3 WP2 WP1 on Adaptive Systems for Web-Based Education: Tools and Reusability, held at the 12th Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education Amsterdam. (Work later led to BC1, PP4 and CP14) Freyberger, J., Heffernan, N., & Ruiz, C. (2004). Using association rules to guide a search for best fitting transfer models of student learning.ing. In Beck, Baker, Corbett, Kay, Litman, Mitrovic & Rigger (Eds.) Workshop on Analyzing Student-Tutor Interaction Logs to Improve Educational Outcomes. Held at the 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. ISBN 978-3-540-22948-3. Livak, T., Heffernan, N. T., Moyer, D. (2004). Using cognitive models for computer generated forces and human tutoring. 13th Annual Conference on (BRIMS) Behavior Representation in Modeling and Simulation. Simulation Interoperability Standards Organization. Arlington, VA. Summer 2004. Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N. T (2004). Tutorial dialog in an equation solving intelligent tutoring system. Workshop on “Dialog-based Intelligent Tutoring Systems: State of the art and new research directions” at the 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. pp. 33-42. Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., & Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Toward a rapid development environment for cognitive tutors. The 12th Annual Conference on Behavior Representation in Modeling and Simulation. Simulation Interoperability Standards Organization. (Work later led to CP7) Heffernan, N. T., (2002). Web-based evaluation showing both motivational and cognitive benefits of the Ms. Lindquist tutor. SIGdial endorsed Workshop on Empirical Methods for Tutorial Dialogue Systems which was part of the International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring System 2002. pp. 1-8. Also appeared in a NSFDFG sponsored workshop on Collaboration between German and American researchers in instructional technology. Tampa, Florida, May 5-7, 2002. (Work later led to CP8) Heffernan, N. T, Koedinger, K. (2001). The design and formative analysis of a dialog-based tutor. Workshop on Tutorial Dialogue Systems held as part of the 2001 Artificial Intelligence in Education. pp. 23-34. (Work later led to CP8) Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2000). Building a 3rd generation ITS for symbolization: Adding a tutorial model with multiple tutorial strategies. Workshop entitled "Learning Algebra with the computer, a transdisciplinary workshop". Held at Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2000 Conference. (pp. 12-22). Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1839, Berlin: Springer. (Work later led to CP8) Heffernan, N. T. (2000). Adding a cognitive model of human tutor to an intelligent tutoring systems. Intelligent Tutoring System Conference- Young Researchers Track. (Work later led to D1) Heffernan, N. T. (1998). Intelligent tutoring systems have forgotten the tutor: Adding a cognitive model of human tutors. Abstract at the 1998 Computer Human Interaction Conference's Doctoral Consortium. (Work later led to D1) My Young Researchers Track Papers YRP5 Almeida, S., 12 YRP4 YRP3 Vartak, M & Heffernan, N. (2008) Supporting the Generation of Isomorphic Tutoring Content Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2008 - Young Researchers Track Guo, Yu, Beck, J. & Heffernan, N. (2008) Trying to Reduce Bottom-out hinting: Will telling student how many hints they have left help? Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2008 - Young Researchers Track Feng, M., Heffernan, N., Beck, J. & Koedinger, K. (2008) Can we predict which groups of questions students will learn from? 13 YRP2 YRP1 Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2008 - Young Researchers Track Pardos, Z., Heffernan, N., Ruiz, C., Beck, J. (2008) Effective Skill Assessment Using Expectation Maximization in a Multi Network Temporal Bayesian Network Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2008 - Young Researchers Track Heffernan, N. T. (2000). Adding a cognitive model of human tutor to an intelligent tutoring systems. Intelligent Tutoring System ConferenceYoung Researchers 14 Track. (Work later led to D1) Papers in Preparation PIP 2 WPI-CS-TR-08-07 is assigned to NTH on Mon Aug 25, 2008 Title: "An Analysis of Middle-School Math Errors Across Schools" Authors: Weitz, Neil T. Heffernan, Rosenthal, and Mingyu Feng Rob Weitz, Neil Heffernan, David Rosenthal & Mingyu Feng An Analysis of Middle-School Math Errors Across Schools. PIP 1 Pardos, Z. A., Heffernan, N. T., Ruiz, C. Effective skill assessment using expectation maximization in a multi network temporal Bayesian network. Tech Reports WPI-CS-TR-08-08 – waiting for link to website WPI-CS-TR-08-06 The International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education Special Issue on Authoring Tools. (Submitted) WPI-CS-TR-08-03 (pdf) Cost-Effective Content Creation with Variabilization (March 2008) Manasi P. Vartak, Shane F. Almeida & Neil T. Heffernan WPI-CS-TR-08-02 (pdf) Lessons Learned from Scaling Up a Web-Based Intelligent Tutoring System (March 2008) Jozsef Patvarczki, Shane F. Almeida, Joseph E. Beck & Neil T. Heffernan WPI-CS-TR-07-04 (pdf) Measuring Student Engagement in an Intelligent Tutoring System (May 2007) Nicholas M. Lloyd WPI-CS-TR-06-12 (pdf) Scaling up the Server-based ASSISTment ITS: Speed and Reliability (Jun 2006) Kai Rasmussen, Jozsef Patvarczki & Neil T. Heffernan. WPI-CS-TR-06-08 (pdf) Common Tutor Object Platform: an e-Learning Software Development Strategy (May 2006) Goss Nuzzo-Jones, Michael Macasek, Jason Walonoski, Kai Rasmussen & Neil T. Heffernan. WPI-CS-TR-06-07 (pdf) Towards Enabling Collaboration in Intelligent Tutoring Systems (May 2006) Michael A. Macasek & Neil T. Heffernan. WPI-CS-TR-06-06 (pdf) Knowledge Engineering for Intelligent Tutoring Systems: Using machine learning assistance to help humans tag questions to skills based upon the words in the questions (May 2006) Kevin Kardian & Neil T. Heffernan. WPI-CS-TR-06-05 (pdf) Prevention of Off-Task Gaming Behavior in Intelligent Tutoring Systems (May 2006) Jason Walonoski & Neil T. Heffernan. WPI-CS-TR-03-31 (pdf) An Evaluation of the Run-Time Performance of the Model-Tracing Algorithm of Two Different Production Systems: JESS and TDK (August 2003). Sanket Choksey and Neil Heffernan. 15 Dissertation D1Heffernan, N. T (2001) Intelligent tutoring systems have forgotten the tutor: Adding a cognitive model of human tutors. Dissertation. Computer Science Department, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. Technical Report CMU-CS-01-127. (Pieces published as J1, CP8, CP5, CP4, and CP3) Teaching Teaching Experience Department of Computer Science, Worcester Polytechnic Institute 2002 - present Teaching Assistant Human Computer Interaction, Carnegie Mello University 2001 Math and Science Teacher Ephraim Curtis Middle School, Sudbury Public Schools, 1998-99 Teaching Assistant Data Structures (1996), Artificial Intelligence (1997), Human Computer Interaction (2001), Carnegie Mellon University Math and Science Teacher Holy Sprit Catholic School, Baltimore, MD 1994-95 Science Teacher Booker T. Washington Middle School, Baltimore Public Schools, Baltimore, MD Teach For America Placement, 1993-1994 Amherst College Helped run Student for Educational Equality. Ran a one-on-one tutoring program pairing up Amherst College students with inner-city children in Holyoke. MA 1989-1993 Courses Taught at WPI Undergraduate Courses 2002 Fall B-Term: CS4341: Artificial Intelligence. 2005 Spring: D-term: CS4341: Artificial Intelligence. 2006 Fall: A-term: CS4341: Artificial Intelligence. 16 2007 Spring D-Term: CS2102: Object Oriented Design (the first Java class students take at WPI.) 2008 Spring D-Term: CS2102: Object Oriented Design (the first Java class students take at WPI.) Graduate Courses 2002 Fall: CS534: Artificial Intelligence. 2003 Spring: CS525: Intelligent Tutoring Systems and Cognitive Modeling. 2004 Spring: CS538: Expert Systems. 2004 Spring: CS525: Intelligent Tutoring Systems and Cognitive Modeling. 2004 Fall: CS534 : Artificial Intelligence. 2006 Spring: CS525: Intelligent Tutoring System and Cognitive Modeling. 2006 Fall: CS525: Advanced Intelligent Tutoring Systems: Web-based Technologies and Knowledge Tracing. 2007 Fall: CS525: Pedagogical Agents. 2008 Fall: CS525 Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2009 Fall: CS525: Empirical methods for CS student. (Assisted Joe Beck in teaching this class). Graduate Theses and Dissertations Advisor of Ph.D. Dissertations Leena Razzaq, in progress, 2004-present. Dissertation Proposal Accepted by Department. Mingyu Feng, in progress, 2004-present. Dissertation Proposal Accepted by Department. Jozsef Parvarczki, in progress, 2005-present. Planning a dissertation proposal Spring 2008. Michael Sao Pedro, in progress, 2007-present. Currently past master degree. Zachary Pardos, in progress, 2006-07. Currently pursuing Master Degree Yue Gong, in progress, 2008-present. Currently researching a topic. Dovan Rai, in progress, 2008-present. Currently researching a topic. Advisor of Master Theses Vilmos Csizmadia: Constructing an Authoring Tool for Intelligent Tutoring Systems with Hierarchical Domain Models, 2003 Leena Razzaq, Tutorial Dialog in an Equation Solving Intelligent Tutoring System, 2003. Ethan Croteau, Evaluating Predictions of Transfer and Analyzing Student Motivation, 2004 Jon Freyberger, Using Association Rules to Guide a Search for Best Fitting Transfer Models of Student Learning, 2004 Matt Jarvis, Applying Machine Learning Techniques to Rule Generation in Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 2004 17 Tom Livak, Collaborative Warrior Tutoring, 2004 Sanket Choksey, Developing an Affordable Authoring Tool For Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 2004 Michael Macasek, Towards Teachers Quickly Creating Tutoring Systems, 2005 Terrence Turner, The Assistment Builder: A tool for rapid tutor development, 2005 Jason Walonowski, Visual Feedback for Gaming Prevention in Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 2005 Ruta Upalekar, Tools to help build models that predict student learning, 2005 Goss Nuzzo-Jones, The Common Tutor Object Platform, 2005 Kai Rasmussen, Developing a Cognitive Rule-Based Tutor for the ASSISTment System, 2007 Nick Lloyd, Measuring Student Engagement in an Intelligent Tutoring System, 2007 Yu Gao, TBA, 2009 Elijah Forbes Summer, TBA, 2009 Member of Ph.D. Dissertation Committee Leena Razzaq (2007) Mingyu Feng (2007) Aparna Varde, Graphical Data Mining for Computational Estimation in Materials Science Applications, 2006 Undergraduate Projects (MQPs, IQPs, Sufficiency) Advised Advisor of Major Qualifying Projects Derek Radkte, ? 2008 Pardos, Zach A., Using Bayesian Networks to Predict Test Scores, 2006 Kardian, Kevin R., Knowledge Engineering for Intelligent Tutoring, 2006 Schafer, Roger James & Walsh, Jonathan B., Curriculum Tools in the ASSISTment Project, 2006 Fusaro, Michael Vincent, Peltier, Brandon Geoffrey & Runcie, Jason Michael, Latent Semantic Analysis Use in a Museau Exhibit, 2004 Nuzzo-Jones, Goss F., Machine Learning in Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 2004 Moyer, Dale Christopher, Warrior Tutoring:Intelligent Tutoring Sys for US Army, 2004 Advisor of Interactive Qualifying Projects Aniszczyk, Christopher Richard, Analysis of an ITS: The Assistments Project, 2004 Haines, Charles Allen, Analysis of 8th Grade MCAS ITS: Assistment Project, 2005 Pardos, Zach A. & Quinn, Patrick J, Improving Online Tutoring Content, 2006 Lourenco, Abraao N., Methods of Teaching Mathematics in Middle School, 2006 Ushakov, Igor, Intellignet Tutoring System Project, 2006 Radtke, Derek B. & Spetla, Hattie, Scaffolding in Computer Aided Learning, 2006 Paduroiu, Andrei & Potter, Emily June, Effective Teaching Methods, 2006 Petrova, Olga Petrovna, Role of Multimedia in Tutoring Systems, 2006 18 Sader, Paul M., Enhancing Web-Based Tutoring with Scaffolding, 2007 Christopher Freeman, Roderick Talyor, Cosmin Tutor, & Michael Zhang , The ASSISTment Project, 2007 Ramon Harrington & Aaron Holroyd, Hints versus Scaffolding, 2007 Loren Gjata, David Curran & David Lamoureux, Intelligent Tutoring Content for 10th Grade Math, 2007 Denis Vadimovich, Mihai Tiberiu Luca & Antoniya Toneva Statelova; Which Works Better: Worked Examples or Hint Messages? 2008 Jeslin J Wu & Boris Svirchuk; the Assistment Project 2008 Ashish Maharjan, Prawal Shrestha & Xing Wei; Comparison Between Scaffolding and Worked Example in ASSISTment Tutoring System 2008 Service International Steering Committee: The Second International Conference on Educational Data Mining 2009 Program Committee: The Second International Conference on Educational Data Mining 2009 Program Committee: Artificial Intelligent in Education Conference 2009. Poster Co-Chair for Artificial Intelligent in Education Conference 2009. Program Committee: Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference 2008. Demonstrations: Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference 2008. Program Committee: First International Conference on Educational Data Mining 2008 http://www.educationaldatamining.org/EDM2008CFP.htm Senior Program Committee: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2007. Program Committee: American Association for Artificial Intelligence 2007 (AAAI'07). Co-Chair of “Educational Data Mining Workshop” to be held at the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2007. Reviewed for IEEE Intelligent Systems Journal. 2007. Reviewer for User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction: The Journal of Personalization Research 2007. Reviewer for Cognitive Science Conference 2007. Program Committee: International Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2006. Program Committee: FLAIRS-2006 Special Track on Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2006. Program Committee: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2005 Workshops Co-Chair International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2005. Reviewer for International Intelligent Tutoring System Conference 2004. 19 Chair of workshop on Dialog-Based Intelligent Tutoring Systems: State of the art and new research directions held at the Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference 2004. Reviewer for International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education 2002. Reviewed for International Journal of Computers for Mathematical Learning. On the program committee for numerous workshops held in conjunction with AIED and ITS conferences. National Service Reviewed on Multiple NSF Panels I was invited to serve on the NSF/CRA CyberLearning Workshop focused on Technology-Enabled Assessment to help shape a research agenda for NSF's EHR Directorate. National Science Foundation Reviewer. ROLE. 2005. National Science Foundation Reviewer. In CISE, the Computer Science directorate, in the Human Computer Interaction program. 2003 Worcester Polytechnic Service I and my graduate student helped bring the GRID Portal here to WPI. WPI is now the only grid portal that connects the major scientific supercomputing grid in Europe with the GRID in the United States, giving WPI increased recognition. Graduate Research Committee (4 years), Colloquium Committee (2 years, one year as chair) Invited Talks 2008-09 Harvard Computer Science Department 2007-08 IT5 International Mind, Brain and Education Society 2007 conference. http://www.imbes.org/conference/conf07.html IT4 Presented at EDUCASE http://www.educause.edu/e07 2006-07 IT3 I was invited to serve on a Boston University panel on making recommendations about how the No Child Left Behind act should be changed as it is up for re-authorization this year in Congress. 2005-06 20 Tufts University. UMASS Amherst. Due to my work on authoring tools for intelligent tutoring systems, I was selected as one of 15 fully-funded invited speakers for the “Authoring Tools for Advanced Learning Systems with Standards” workshop held by The Institute for Intelligent Systems and the Advanced Distributed Learning Workforce Co-Lab at the University of Memphis. The University of Georgia paid for me to give a invited talk at their Education school October 2005. American Education Research Association (AERA) annual meeting in Montreal. (with Feng) Informing Teachers Live about Student Learning: Reporting in the ASSISTment System. 2004-05 Boston University. Intel Foundation. Mass Insight Education, a business-funded "not-for-profit organization focused on improving student achievement in Massachusetts' public schools". See also my dissemination efforts with the CIRCLE Summer School. I served on the Concord Consortium's advisor board meeting for a IERI grant Aug 29, 2005. IT2 Invited talk: October 2004, NASA Houston Space Center : " Training For Tomorrow." IT1 Invited talk: March 2005, NASA Langley: " Advances in Learning Technologies." 2003-04 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Charles River Analytics. Citation Index for Neil Heffernan’s Tenure Package (Compiled June 2007- Last updated Sept 1, 2007) In this citation index I have attempted to collect the references to my work that I happen to know of. I filtered out papers where I was one of the authors. This list has over 150 citations in total. I have included URLs to the papers so you could see how they cited my work, but I am sure the URLs are liable to “break” over time so expect some broken links. More Unusual Citation Zucker’s book Woolf’s Book Martha Evans Book 21 [J5] Feng, M., Heffernan, N.T. (2007). Towards live informing and automatic analyzing of student learning: Reporting in the Assistment system. Journal of Interactive Learning Research (JILR) 18(2) pp. 207-230. Chesapeake, VA: AACE. 1. Scheuer, O. & Zinn, C. (2007) How did the e-learning session go? : The Student Inspector. In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, IOS Press. pp 487-494. [CP1] Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K.R. (1997). The composition effect in symbolizing: The role of symbol production vs. text comprehension. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. pp. 307-312. 1. Corbett, A. (2002). Cognitive Tutor Algebra I: Adaptive Student Modeling in Widespread Classroom Use. In a book edited by the National Research Council entitled Technology and assessment: Thinking ahead: Proceedings of a workshop. Board on Testing and Assessment, Center for Education, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. http://books.nap.edu/booksearch.php?record_id=10297&term=heffernan&cha pter=50-62 2. Graesser, A.C., Person, N., Harter, D., & TRG (June, 2000). Teaching tactics in AutoTutor. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education (2001), 12, 257-279. http://aied.inf.ed.ac.uk/abstracts/Vol_12/graesser.html 3. The portions of above paper also seem to have first appeared in a workshop before appearing in the journal list above. Graesser, A.C., Person, N., Harter, D., & TRG (June, 2000). Teaching tactics in AutoTutor. Paper presented at the workshop on tutorial dialogue at the Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2000 Conference, Montreal, Canada. http://www.cs.pitt.edu/~litman/courses/cs3710/graesser.pdf 4. Koedinger, (1998) Intelligent Cognitive Tutors as Modeling Tool and Instructional Model. A Position Paper for the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) Standards 2000 Technology Conference. June 5-6, 1998. http://mathforum.org/technology/papers/papers/koeding/koeding2.htm 5. Koedinger, K.R. (2001). Cognitive Tutors as Modeling Tool and Instructional Model. In Forbus, K.D. & Feltovich, P.J. (Eds.) Smart Machines in Education: The Coming Revolution in Educational Technology, (pp. 145-168). Menlo Park, CA: AAAI/MIT Press. http://www.psychology.nottingham.ac.uk/staff/com/c8clat/resources/Koedinge r2002.pdf 6. Mark, M. A., & Koedinger, K. R. (1999). Strategic support of algebraic expression writing. In Kay, J. (Ed.) Proceedings of the Seventh International 22 Conference on User Modeling, (pp. 149-158). SpringerWein, New York. http://bistrica.usask.ca/um/UM99/Proc/mark.pdf 7. Nathan, M. & Koedinger, K. (2000) An Investigation of Teachers' Beliefs of Students' Algebra Development. Cognition and Instruction, Vol. 18, No. 2. pp. 209-237. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=07370008%282000%2918%3A2%3C209%3AAIOTBO%3E2.0.CO%3B2-P [CP2] Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K. R. (1998). A developmental model for algebra symbolization: The results of a difficulty factors assessment. In M. Gernsbacher & S. Derry (Eds.) Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.pp. 484-489. 1. Baker, R. S., Corbett, A. T., Koedinger, K. R. & Schneider, M. P. (2003). A formative evaluation of a tutor for scatterplot generation: Evidence on difficulty factors. In U. Hoppe, F. Verdejo, & J. Kay (Eds.), Artificial Intelligence in Education: Shaping the Future of Learning through Intelligent Technologies, Proceedings of AI-ED 2003 (pp. 107-114). Amsterdam, IOS Press. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~rsbaker/BCKSAIED2003Final.pdf 2. Baker, R.S., Corbett, A.T., Koedinger, K.R., Wagner, A.Z. (2004) Off-Task Behavior in the Cognitive Tutor Classroom: When Students "Game The System". Proceedings of ACM CHI 2004: Computer-Human Interaction, 383390. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~rsbaker/p383-baker-rev.pdf 3. Corbett, A. (2002). Cognitive Tutor Algebra I: Adaptive Student Modeling in Widespread Classroom Use. In a book edited by the National Research Council entitled Technology and assessment: Thinking ahead: Proceedings of a workshop. Board on Testing and Assessment, Center for Education, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. http://books.nap.edu/booksearch.php?record_id=10297&term=heffernan&cha pter=50-62 4. Gama, Claudia. PAL Tool: uma ferramenta cognitiva para organização e representação de problemas algébricos. Anais do XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação SBIE, Novembro. NCE/UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2003. http://www.nce.ufrj.br/sbie2003/publicacoes/paper22.pdf 5. Graesser, A.C., Lu, S., Jackson, G.T., Mitchell, H., Ventura, M., Olney, A., & Louwerse, M.M. (2004). AutoTutor: A tutor with dialogue in natural language. Behavioral Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36, 180-193. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=15990616 6. Khan, J., Hardas, M., Ma, Y., Analyzing Question Difficulty Using Course Ontology Based Semantic Knowledge Maps for Test-ware Standardization, 2005, Proceedings of WSEAS, Corfu, Greece. http://www.cs.kent.edu/~mhardas/papers/final(WSEAS-DL-2005-Greece).pdf 7. Koedinger, (1998) Intelligent Cognitive Tutors as Modeling Tool and Instructional Model. A Position Paper for the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) Standards 2000 Technology Conference. June 5-6, 23 1998. http://mathforum.org/technology/papers/papers/koeding/koeding2.htm 8. Koedinger, K.R. (2001). Cognitive Tutors as Modeling Tool and Instructional Model. In Forbus, K.D. & Feltovich, P.J. (Eds.) Smart Machines in Education: The Coming Revolution in Educational Technology, (pp. 145-168). Menlo Park, CA: AAAI/MIT Press. http://www.psychology.nottingham.ac.uk/staff/com/c8clat/resources/Koedinge r2002.pdf 9. Koedinger, K. R. (2002). Toward evidence for instructional design principles: Examples from Cognitive Tutor Math 6. Invited paper in Proceedings of PMENA XXXIII (the North American Chapter of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education). http://nth.wpi.edu/PapersByOthers/Koedinger_PME_paper_dissem2.pdf 10. Koedinger, K. R. & Mathan, S. (2004). Distinguishing qualitatively different kinds of learning using log files and learning curves. In the Working Notes of the ITS2004 Workshop on Analyzing Student-Tutor Interaction Logs to Improve Educational Outcomes. http://www.andrew.cmu.edu/user/jb8n/its2004/koedinger.pdf 11. Leszczenskil, J. & Beck, J. E. (2007) What’s in a Word?: Extending Learning Factors Analysis to Model Reading Transfer. In the Educational Datamining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Los Angeles. pp 31-39. [CP3] Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2000) Intelligent tutoring systems are missing the tutor: Building a more strategic dialog-based tutor. In C.P. Rose & R. Freedman (Eds.) Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium on Building Dialogue Systems for Tutorial Applications. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press. ISBN 978-1-57735-124-5. pp. 14- 19 1. Aleven, V., Popescu, O., & Koedinger, K.R. (2001). Pedagogical Content Knowledge in a Tutorial Dialogue System to Support Self-Examination. Workshop on Tutorial Dialogue Systems held as part of the 2001 Artificial Intelligence in Education. pp. 59-70. http://www.hcrc.ed.ac.uk/aied2001/workshops.html 2. Aleven, V., Popescu, O., & Koedinger, K. R. (2001). Towards tutorial dialog to support self-explanation: Adding natural language understanding to a cognitive tutor. In J. D. Moore, C. L. Redfield, & W. L. Johnson (Eds.), Artificial Intelligence in Education: AI-ED in the Wired and Wireless Future, Proceedings of AI-ED 2001 (pp. 246-255). Amsterdam, IOS Press. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/People/aleven/AlevenEtAlAIED2001.pdf 3. Aleven V., Popescu, O. , & Koedinger, K. R. (2001). A Tutorial Dialogue System with Knowledge-Based Understanding and Classification of Student Explanations. In Working Notes of the 2nd IJCAI Workshop on Knowledge and Reasoning in Practical Dialogue Systems, August 5, 2001, Seattle. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/People/aleven/AlevenEtAlIJCAI2001WS.pdf 24 4. Benzmuller, C., Fiedler, A., Gabsdil, M., Horacek, H., Kruijff-Korbayova, I., Pinkal, M., Siekmann, J., Tsovaltzi, D. Vo, B.Q., Wolska, M. (2003). Discourse Phenomena in Tutorial Dialogs on Mathematical Proofs. In Ivana Kruijff-Korbayová and Claudia Kosny (eds.), Proceedings of DiaBruck'03, the 7th Workshop on the Semantics and Pragmatics of Language, pp. 165--166, Saarbruecken, Germany. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~tsovaltzi/SB1.pdf 5. Benzmuller, C., Fiedler, A., Gabsdil, M., Horacek, H., Kruijff-Korbayova, I., Pinkal, M., Siekmann, J., Tsovaltzi, D. Vo, B.Q., Wolska, M. (2003). Towards a Principled Approach to Tutoring Mathematical Proofs. In Andreas Harrer and Katrin Gaßner (eds.), Proceedings of the KI-03 Workshop on Expressive Media and Intelligent Tools for Learning, Hamburg, Germany. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~tsovaltzi/KI-03.pdf 6. Benzmuller, C., Fiedler, A., Gabsdil, M., Horacek, H., Kruijff-Korbayova, I., Pinkal, M., Siekmann, J., Tsovaltzi, D. Vo, B.Q., Wolska, M. (2003). Tutorial Dialogs on Mathematical Proofs. In Peter Baumgartner, Paul A. Cairns, Michael Kohlhase, and Erica Melis (eds.), pp. 12-22, Acapulco, Mexico, 2003. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~chris/papers/W20.pdf 7. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 83 & 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-One-Tutoring-HumansComputers/dp/0805843612 8. Fiedler, A., Gabsdil, M. (2002). Supporting Progressive Refinement of Wizard-of-Oz Experiments. In Carolyn Penstein Rose and Vincent Aleven (eds.), , pp. 62-69, San Sebastian, Spain, 2002. http://www.ags.unisb.de/~afiedler/pubs/papers/its-02-ws.pdf 9. Fiedler, A., Tsovaltzi. D. (2003). Automating Hinting in an Intelligent Tutorial Dialog System. In Proceedings of the IJCAI workshop on Knowledge Representation and Automated Reasoning for E-Learning Systems, Acapulco, Mexico, pp. 23-35. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~tsovaltzi/collective.pdf 10. Freedman, Reva. 2001. An Approach to Increasing Programming Efficiency in Plan-Based Dialogue Systems. Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on AI in Education (AI-ED 2001), San Antonio. http://www.cs.niu.edu/~freedman/papers/aied2001.pdf 11. Popescu, O. (2005). Logic-Based Natural Language Understanding in Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Dissertation. Language Technologies Institute, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. 12. Ramachandran, S. & Stottler, R. (2003). A Meta-Cognitive Computer-based Tutor for High-School Algebra. In Proceedings of World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia and Telecommunications 2003 (pp. 911914). Chesapeake, VA: AACE. http://www.stottlerhenke.com/papers/ramachandran_algebra_tutor.pdf 13. D. Rasseneur, E. Delozanne , P. Jacoboni et B. Grugeon (2002), Learning with virtual agents: Competition and Cooperation in AMICO, Proceedings of ITS’ 2002, Lectures Notes in Computer Sciences 2363, Springer, 61-70. http://pepite.univ-lemans.fr/Telechargement/anglais/3-ITS-2002Rasseneureal.pdf 25 14. Scarlatos, L. (2002). TICLE: using multimedia multimodal guidance to enhance learning. Information Sciences—Informatics and Computer Science: An International Journal 140(1) pp. 85-103. New York, NY. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6V0C44B4J7R1&_user=74021&_coverDate=01%2F31%2F2002&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=s earch&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000005878&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_ userid=74021&md5=8b6e80a5bfe71840bfc7ee100391a03c 15. Scarlatos, L., Landy, S.S., Breban, J., Horowitz, R., Sandberg, C. On the Effectiveness of Tangible Interfaces in Collaborative Learning Environments. http://www.cs.gc.cuny.edu/tr/files/TR-2002004.pdf 16. Tsovaltzi, D., Fiedler, A. (2003). An Approach to Facilitating Reflection in a Mathematics Tutoring System. In aied2003 (Artificial Intelligence in Education) Supplementary Proceedings,Vol.V. workshop on Learner Modelling for Reflection, Sydney, Australia, pp. 278-287, 2003. http://www.it.usyd.edu.au/~aied/vol5/vol5_tsovaltzi.pdf 17. Tsovaltzi, D., Fiedler, A. (2003). Enhancement and Use of a Mathematical Ontology in a Tutorial Dialogue System. In Proceedings of the IJCAI Workshop on Knowledge and Reasoning in Practical Dialogue Systems, Acapulco, Mexico, pp. 19-28. http://www.ida.liu.se/labs/nlplab/ijcai-ws03/papers/Tsovaltzi.pdf [CP4] Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R.(2002). An intelligent tutoring system incorporating a model of an experienced human tutor. In Stefano A. Cerri, Guy Gouardères, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.): 6th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring System. Biarritz, France. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science: pp. 596-608. 1. Aleven, V., Stahl, E., Schworm, S., Fischer, F., & Wallace, R. M. (2003). Help seeking and help design in interactive learning environments. Review of Educational Research, 73(2), 277-320. http://www.msu.edu/user/mccrory/pubs/Alevenetal.pdf 2. Barnes, T., D. Bitzer & M. Vouk. (2005). The q-matrix method: Mining student response data for knowledge. Proceedings of the AAAI 20th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence Educational Data Mining Workshop (AAAI2005), Pittsburgh, PA, July 9-13. http://nth.wpi.edu/classes/cs525t_tutoring_systems/PaperForClass/WS205Barn esT.pdf 3. Cox, R, & Pang, J. (2007) VL-PATSy: Facilitating Vicarious Learning via Intelligent Resource Provision. In R. Luckin, Koedinger & Greer (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Education: Building Technology Rich Learning Contexts that Work. IOS Press. pp. 85-92. 4. Crowley, R.S., Medvedeva, O. (2005) An Intelligent Tutoring System for Visual Classification Problem Solving. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. http://slidetutor.upmc.edu/papers/Crowley%20AIM%20828.pdf 26 5. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 6. Horacek, H. & Wolska, M. (2007) Generating Responses to Formally Flawed Problem-Solving Statements. In R. Luckin, Koedinger & Greer (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Education: Building Technology Rich Learning Contexts that Work. IOS Press. pp. 17-24. 7. Kim, Jung Hee, Reva Freedman, Michael Glass, and Martha W. Evens. Annotation of Tutorial Dialogue Goals for Natural Language Generation. Discourse Processes vol. 42 no. 1 (2006), pp. 37--74. http://www.csam.iit.edu/~circsim/documents/kfgedp06.pdf 8. Kodaganallur, V., Weitz, R., Rosenthal, D. (2006). Tools for Building Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (2), p. 46.2 http://csdl2.computer.org/comp/proceedings/hicss/2006/2507/02/250720046b. pdf 9. Litman, D.J., Rose, C.P., Forbes-Riley, K., VanLehn, K., Bhembe, D., Silliman, S. (2006). Spoken Versus Typed Human and Computer Dialogue Tutoring. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education 16(2). pp. 145-170. http://www.cs.pitt.edu/~litman/ijaied06.pdf 10. Martens, A., Harrer, A. (2004). Lehr-/Lernsysteme – Welche Rolle spielt die Kunstliche Intelligenz gestern, heute und morgen? In Teaching and Training Systems – the role of intelligence in past, present, and future. pp. 396-409 http://www.informatik.uni-rostock.de/~martens/Papers/MaHa_gi_ki04.pdf 11. Patel, N., Glass, M., Kim, J.H. (2003). Data Collection Application for the North Carolina A&T State University Algebra Tutoring Dialogue (Wooz Tutor) Project. Fourteenth Midwest Cognitive Science and AI Conference (MAICS03), Cincinnati http://www.comp.ncat.edu/itsLab/docs/maics03-v2.2.pdf 12. Peters, S., Bratt, E.O., Clark, B., Pon-Barry, H., Schultz, K. (2004) Intelligent Systems for Training Damage Control Assistants. In Proceedings of I/ITSEC 2004. Orlando FL, USA. http://www-csli.stanford.edu/semlabhold/muri/papers/1908.PDF 13. Pon-Barry, H., Clark, B., Bratt, E.O., Schultz, K., & Peters, S. (2004). Evaluating the Effectiveness of SCoT: a Spoken Conversational Tutor. In Proceedings of ITS 2004 Workshop on Dialogue-based Intelligent Tutoring Systems: State of the Art and New Research Directions. Maceio, Brazil. 23-32. http://godel.stanford.edu/old/muri/papers/ITS_2004_Workshop.pdf 14. Rose, C. P., Aleven, V. & Torrey, C. (2004). CycleTalk: Supporting Reflection in Design Scenarios with Negotiation Dialogue, Proceedings of the CHI 2004 Workshop on Designing for Reflective Practitioners: Sharing and Assessing Progress by Diverse Communities http://www.ics.uci.edu/~redmiles/chiworkshop/papers/Rose.pdf 15. Rose, C.P., Gaydos, A., Hall, B.S., Roque, A., VanLehn, K. (2003). Overcoming the Knowledge Engineering Bottleneck for Understanding Student Language Input. In Ulrich Hoppe, Felisa Verdejo, and Judy Kay (eds.) 27 Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam: IOS Press. 315-322. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~cprose/tools.pdf 16. Rose, C.P., Litman, D., Bhembe, D., Forbes, K., Silliman, S., Srivastava, R., VanLehn, K. (2003). A comparison of tutor and student behavior in speech versus text based tutoring. Proceedings of the HLT-NAACL 03 Workshop on Building educational applications using natural language processing – Volume 2. pp. 30-37 http://acl.ldc.upenn.edu/W/W03/W03-0205.pdf 17. Rosé, C. P., & VanLehn, K. (2005). An Evaluation of a Hybrid Language Understanding Approach for Robust Selection of Tutoring Goals. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 15(4), 325-355. http://iospress.metapress.com/app/home/contribution.asp?referrer=parent&bac kto=issue,4,4;journal,7,15;linkingpublicationresults,1:110564,1 18. Tchetagni, J., Nkambou, R. and Bourdeau, J. (2007). Explicit Reflection in Prolog-Tutor. 17, 169-215. http://aied.inf.ed.ac.uk/abstract/Vol_17/Tchetagni07.html 19. Thomsen-Gray, Z., Schultz, K., Clark, B., Bratt, E.O., Peters, S. (2003). Intelligent Tutoring for Non-Deterministic and Dynamic Domains. In Ulrich Hoppe, Felisa Verdejo, and Judy Kay (eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam: IOS Press. 506-508. http://godel.stanford.edu/old/muri/papers/aied-final.pdf 20. Wiemer-Hastings,P. et al. (2000). Research Methods Tutoring in the Classroom. De Paul University. Chicago,IL. USA http://reed.cs.depaul.edu/peterwh/papers/Wiemer-Hastings2003rmt.pdf 21. Woolf, B. A draft version of a text book called Building Intelligent Tutors, to be published by Elsevier, gives two pages to this work. [CP5] Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Web-based evaluations showing both cognitive and motivational benefits of the Ms. Lindquist tutor In F. Verdejo and U. Hoppe (Eds) 11th International Conference Artificial Intelligence in Education. Sydney, Australia. IOS Press. pp.115-122. 1. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 2. Lundy, M.P. An Analysis of the Effectiveness of an Interactive Educational Game. Interactive Qualifying Project. Worcester Polytechnic Institute Library http://web.cs.wpi.edu/~claypool/iqp/massbalance/iqp.pdf [CP6] Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., Heffernan. T., McLaren, B. & Hockenberry, M. (2004). Opening the door to non-programmers: Authoring intelligent tutor behavior by demonstration. In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. pp.162-173. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1. Aleven, V., McLaren, B.M., Sewall, J., Koedinger, K.R. (2006). The Cognitive Tutor Authoring Tools (CTAT): Preliminary Evaluation of Efficiency Gains. 28 In the proceedings of 8th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Jhongli, Taiwan. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/CTAT-ITS2006.pdf 2. Aleven, V., Rose, C.P. (2005). Authoring plug-in tutor agents by demonstration: Rapid, rapid tutor development. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 735-737. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://shamash.cycletalk.cs.cmu.edu/CycleTalkAIED2005.pdf 3. Barnes, T. & Stamper, J. (2007) Toward the extraction of production rules for solving logic proofs. In the Educational Datamining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Los Angeles. pp. 11-20. 4. Blessing, S., Gilbert, S., Ourada, S. & Ritter, S. (2007) Lowering the Bar for Creating Model-tracing Intelligent Tutoring Systems . In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, IOS Press. pp. 443-450. 5. Bollen, Lars. (2005). Generating reports of graphical modelling processes for authoring and presentation. In Proccedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Young Researcher's Track, p. 954. Amsterdam, The Netherlands http://www.rhodes.aegean.gr/ltee/kaleidoscopeia/Publications/bollen_Generating_Reports.pdf 6. Brough J.E, Schwartz M., Guptal S.K., Anand D.K. , Clark C., Peterson R., Yeager C. (2006). Virtual Training Studio: a Step Towards Virtual Environment Assisted Training. In Workshop Proceedings of 1st International Virtual Manufacturing Workshop (VirMan 06), Alexandria, Virginia 7. Brown, J. (2004). Integrating Tools for the Creation of Speech-Enabled Tutors. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jonbrown/publications/Brown_TechReport.pdf 8. Harrer, A., McLaren, B. M., Walker, E., Bollen, L., and Sewall, J. (2005). Collaboration and Cognitive Tutoring: Integration, Empirical Results, and Future Directions. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://ctat.pact.cs.cmu.edu/pubs/CollaborationAIED05.pdf 9. Harrer, A., McLaren, B. M., Walker, E., Bollen, L., and Sewall, J. (2006). Collaboration and Cognitive Tutoring: steps toward realization. In User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction 16(3-4), pp.175-209. http://www.springerlink.com/content/p45v8q6m53184717/?p=cbeacb9177424 c7d929dd851d9364f25&pi=1 10. Harrer, A., McLaren, B. M., Walker, E., Bollen, L., and Sewall, J. (2005) Collaboration and Cognitive Tutoring: Integration, Empirical Results, and Future Directions. In The Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.pitt.edu/%7Ebmclaren/AIED2005-Collaboration.pdf 11. Herrmann, K., Hoppe, U. (2005). Making an Unintelligent Checker Smarter. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 282-289. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. 29 12. Hockenberry, M. (2005) Simple tutors for hard problems: understanding the role of pseudo-tutors. In Extended Abstracts Proceedings of the 2005 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI 2005, Edited by Gerrit C. van der Veer and Carolyn Gale. p. 459-1462 http://www.informatik.unitrier.de/~ley/db/conf/chi/chi2005a.html#Hockenberry05 13. Kumar, R., Rose, C., Aleven, V., Iglesias, A., Robinson, A. (2006) Evaluating the Effectiveness of Tutorial Dialogue in an Exploratory Learning Context. Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) 2006, Taipei, Taiwan http://ctat.pact.cs.cmu.edu/pubs/kumar-dialogue.pdf 14. Kumar, R., Rose, C., Wang, Y., Joshi, M. & Robinson, A. (2007) Tutorial Dialogue as Adaptive Collaborative Learning Support. In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, IOS Press. pp. 383-390. 15. Mavrikis, M., Hunn, C. (2005). Interoperability Issues in Authoring Interactive Activities. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 869-871. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.booksonline.iospress.com/Content/View.aspx?piid=55 16. Matsuda, N, Cohen, W.W., Jonathan Sewall, and Kenneth R. Koedinger (2006). Applying Machine Learning to Cognitive Modeling for Cognitive Tutors, Technical report CMU-ML-06-105, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. http://reportsarchive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/usr/ftp/ml/CMU-ML-06-105.pdf 17. McLaren, B.M. (2005) Lessons in Machine Ethics from the Perspective of Two Computational Models of Ethical Reasoning. Presented at the AAAI Fall 2005 Symposium, Washington, D. C. In Papers from the AAAI Fall Symposium, Technical Report FS-05-06, pp. 70-77. 18. McLaren, B. M., Koedinger, K. R., Schneider, M., Harrer, A., and Bollen, L. (2004). Bootstrapping Novice Data: Semi-Automated Tutor Authoring Using Student Log Files. In the Proceedings of the Workshop on Analyzing StudentTutor Interaction Logs to Improve Educational Outcomes, Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS-2004), August 2004. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/AAAI-05-MachineEthics.pdf 19. McLaren, B. M., Koedinger, K. R., Schneider, M., Harrer, A., and Bollen, L. (2004). Toward Cognitive Tutoring in a Collaborative, Web-Based Environment. In Engineering Advanced Web Applications, From the Proceedings in Connection with the 4th International Conference on Web Engineering (ICWE 2004), Munich, Germany, 28-30 July, 2004. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/AHCW-04-Publication1.pdf 20. McLaren, B. M., Lim, S. Yaron, D. & Koedinger, K. (2007) Can a Polite Intelligent Tutoring System lead to Improved Learning Outside of the Lab? . In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, IOS Press. pp 433-440. 30 21. Mitrovic, A., Suraweera, P., Martin, B., Zakharov, K., Milik, N., Holland, J. (2006). Authoring Constraint-Based Tutors in ASPIRE. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (4053). pp. 41-50. www.cosc.canterbury.ac.nz/tanja.mitrovic/ASPIRE-ITS06.pdf 22. Suraweera, P., Mitrovic, A., Martin, B. (2005). A Knowledge Acquisition System for Constraint-based Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 638-645. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.cosc.canterbury.ac.nz/tanja.mitrovic/ASPIRE-ITS06.pdf 23. Tollinger, I., Lewis, R.L., McCurdy, M., Tollinger, P., Vera, A., Howes, A., Pelton, L. (2005). Supporting efficient development of cognitive models at multiple skill levels: exploring recent advances in constraint-based modeling. Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, April 02-07, 2005, Portland, Oregon, USA http://www.cf.ac.uk/psych/howesa/ccm/docs/Tollinger2005chi.pdf 24. Wyle, R. (2007) Are we asking the right questions? Understanding which tasks lead to robust learning of the English Article System. In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, IOS Press. pp 709-711. [CP7] Jarvis, M., Nuzzo-Jones, G. & Heffernan. N. T. (2004). Applying machine learning techniques to rule generation in intelligent tutoring systems. In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 541-553. 1. Fiedler, A., Tsovaltzi. D. (2003). Automating Hinting in an Intelligent Tutorial Dialog System. In Proceedings of the IJCAI workshop on Knowledge Representation and Automated Reasoning for E-Learning Systems, Acapulco, Mexico, pp. 23-35. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~tsovaltzi/collective.pdf 2. Kuno, H & Lemon, M. (2001) A Lightweight Dynamic Conversation Controller for E-Services. International Workshop on Advanced Issues of ECommerce and Web-Based Information Systems (WECWIS) 2001. June 2122, 2001, San Jose, CA. Also published as HP Techincal Resport HPL-2001-25R1 http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/2001/HPL-2001-25R1.html 3. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W.W., Sewall, J., and Koedinger K.R. (2006). Applying Machine Learning to Cognitive Modeling for Cognitive Tutors, Technical report CMU-ML-06-105, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. http://reports-archive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/usr/ftp/ml/CMUML-06-105.pdf 4. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W. W., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Applying Programming by Demonstration in an Intelligent Authoring Tool for Cognitive Tutors. In AAAI Workshop on Human Comprehensible Machine Learning (Technical Report WS-05-04) (pp. 1-8). Menlo Park, CA: AAAI association. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mazda/Doc/AAAI05/Matsuda05b.pdf 31 5. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W. W., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Building Cognitive Tutors with Programming by Demonstration. In S. Kramer & B. Pfahringer (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Inductive Logic Programming (Technical report, TUM-I0510) (pp. 41-46): Institut fur Informatik, Technische Universitat Munchen. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mazda/Doc/ILP2005/Matsuda05c.pdf 6. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W.W., Sewall, J., and Koedinger K.R. (2006). What characterizes a better demonstration for cognitive modeling by demonstration? Technical report CMU-ML-06-106, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. http://reports-archive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/ml/CMUML-06-106.pdf 7. Mitrovic, A., Suraweera, P., Martin, B., Zakharov, K., Milik, N., Holland, J. (2006). Authoring Constraint-Based Tutors in ASPIRE. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (4053). pp. 41-50. http://www.cosc.canterbury.ac.nz/tanja.mitrovic/ASPIRE-ITS06.pdf 8. Suraweera, P., Mitrovic, A., Martin, B. (2005). A Knowledge Acquisition System for Constraint-based Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 638-645. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.cosc.canterbury.ac.nz/tanja.mitrovic/SuraweeraAIED05.pdf 9. Tchetagni, J. and R. Nkambou. A framework for diagnosis and epistemological remediation in learning logic programming. In International Conference on Computer Aided Learning in Engineering Education. 2004 http://www-clips.imag.fr/calie04/actes/Tchetagni_final.pdf [CP8] Heffernan, N. T. & Croteau, E. (2004). Web-Based Evaluations Showing Differential Learning for Tutorial Strategies Employed by the Ms. Lindquist Tutor. In James C. Lester, Rosa Maria Vicari, Fábio Paraguaçu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 491-500. 1. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 [CP9] Croteau, E., Heffernan, N. T. & Koedinger, K. R. (2004). Why are Algebra word problems difficult? Using tutorial log files and the power law of learning to select the best fitting cognitive model. In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 240-250. 1. Cen, H., Koedinger, K. R., & Junker, B. (2005). Automating Cognitive Model Improvement by A* Search and Logistic Regression. In Proceedings of AAAI'05 workshop on Educational Data Mining. http://www.learnlab.org/uploads/mypslc/publications/ws205cenh.pdf 32 2. Cen, H., Koedinger, K. R., & Junker, B. (2006). Learning Factors Analysis: A general method for cognitive model evaluation and improvement. In M. Ikeda, K. D. Ashley, T.-W. Chan (Eds.) Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 164-175. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. http://www.learnlab.org/uploads/mypslc/publications/learning_factor_analysis _5.2.pdf 3. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 4. Khan, J., Hardas, M., Ma, Y., A Study of Problem Difficulty Evaluation for Semantic Network Ontology Based Intelligent Courseware Sharing. WI, pp. 426-429, the 2005 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI'05), 2005. http://www.medianet.kent.edu/publications/WI05DL-problemcmplexityKHM.pdf 5. Khan, J., Hardas, M., Ma, Y., Analyzing Question Difficulty Using Course Ontology Based Semantic Knowledge Maps for Test-ware Standardization, 2005, Proceedings of WSEAS, Corfu, Greece. http://www.cs.kent.edu/~mhardas/papers/final(WSEAS-DL-2005-Greece).pdf 6. Koedinger, K. R. & Mathan, S. (2004). Distinguishing qualitatively different kinds of learning using log files and learning curves. In the Working Notes of the ITS2004 Workshop on Analyzing Student-Tutor Interaction Logs to Improve Educational Outcomes. http://www.andrew.cmu.edu/user/jb8n/its2004/koedinger.pdf 7. Leszczenskil, J. & Beck, J. E. (2007) What’s in a Word?: Extending Learning Factors Analysis to Model Reading Transfer. In the Educational Datamining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Los Angeles. pp 31-39. 8. Manske, M., Conati, C. (2005) Modeling Learning in Educational Games. Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, 411-418. http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~conati/mypapers/aied05FinalMM2.pdf [CP11] Razzaq, L., Feng, M., Nuzzo-Jones, G., Heffernan, N.T., Koedinger, K. R., Junker, B., Ritter, S., Knight, A., Aniszczyk, C., Choksey, S., Livak, T., Mercado, E., Turner, T.E., Upalekar. R, Walonoski, J.A., Macasek. M.A. & Rasmussen, K.P. (2005). The Assistment project: Blending assessment and assisting. In C.K. Looi, G. McCalla, B. Bredeweg, & J. Breuker (Eds.) Proceedings of the 12th Artificial Intelligence in Education, Amsterdam: ISO Press. pp. 555-562. 1. Aleven, V., McLaren, B.M., Sewall, J., Koedinger, K.R. (2006). The Cognitive Tutor Authoring Tools (CTAT): Preliminary Evaluation of Efficiency Gains. In the proceedings of 8th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Jhongli, Taiwan. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/CTAT-ITS2006.pdf 2. David Yaron, Gaea Leinhardt, Karen Evans, Jordi Cuadros, Michael Karabinos, William McCue and David Dennis, "Creation of an online stoichiometry 33 course that melds scenario based leaning with virtual labs and problem-solving tutors", Paper Presented on CONFCHEM. Online Conference, Spring 2006. http://iry.chem.cmu.edu/about/paper/confchem06/cc06.pdf [CP12] Walonoski, J. & Heffernan, N.T. (2006). Detection and analysis of off-task gaming behavior in intelligent tutoring systems. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 382-391. 2006. 1. Rodrigo, M.M.T., Baker, R.S.J.d., Lagud, M.C.V., Lim, S.A.L., Macapanpan, A.F., Pascua, S.A.M.S., Santillano, J.Q., Sevilla, L.R.S., Sugay, J.O., Tep, S., Viehland, N.J.B. (in press) Affect and Usage Choices in Simulation Problem Solving Environments. To appear in Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence in Education 2007. http://www.psychology.nottingham.ac.uk/staff/lpzrsb/RodrigoBakeretal2006Fi nal.pdf 2. This paper was cited in a official web-based guide to research put out by the American Advance of Artificial Intelligence. I have archived a copy of the web page here and highlighted the relevant section. [CP15] Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K.R. (2006). Addressing the testing challenge with a Web-based e-assessment system that tutors as it assesses. Proceedings of the Fifteenth International World Wide Web Conference (WWW-06). New York, NY: ACM Press. ISBN:1-59593-332-9. pp. 307-316. 1. Anozie, N., Junker, B. (2006). Predicting end-of-year accountability assessment scores from monthly student records in an online tutoring system. AAAI'06 workshop on Educational Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/anozie-aaai06.pdf 2. Ayers E. & Junker B. (2006). Do skills combine additively to predict task difficulty in eighth grade mathematics? AAAI'06 workshop on Educational Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/WS0606AyersE.pdf [CP16] Feng, M., Heffernan, N. & Koedinger, K. (2006a). Predicting state test scores better with intelligent tutoring systems: developing metrics to measure assistance required. In Ikeda, Ashley & Chan (Eds.). Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 31-40. 1. Anozie, N., Junker, B. (2006). Predicting end-of-year accountability assessment scores from monthly student records in an online tutoring system. AAAI'06 workshop on Educational Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/anozie-aaai06.pdf 2. Ayers E. & Junker B. (2006). Do skills combine additively to predict task difficulty in eighth grade mathematics? AAAI'06 workshop on Educational 34 Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/WS0606AyersE.pdf [PP1] Razzaq, L. & Heffernan, N. T (2004) Tutorial dialog in an equation solving intelligent tutoring system . In J.C. Lester, R.M. Vicari, & F. Parguacu (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th Annual International Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 851-853. 1. Kafkas, S., Bayram, Z., Yaratan, H. Implementation Strategies for “Equation Guru,” A User Friendly Intelligent Algebra Tutor. 8th International Conference on Enterprice Information Systems (ICEIS'06), 23-27 May 2006, Paphos, Cyprus. http://cmpe.emu.edu.tr/bayram/Papers/EG_ICEIS_4.pdf [PP2] Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., & Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Toward a rapid development environment for cognitive tutors. In F. Verdejo and U. Hoppe (Eds) 11th International Conference Artificial Intelligence in Education. Sydney, Australia. IOS Press. pp. 455-457. 1. Aleven, V., McLaren, B.M., Sewall, J., Koedinger, K.R. (2006). The Cognitive Tutor Authoring Tools (CTAT): Preliminary Evaluation of Efficiency Gains. In the proceedings of 8th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Jhongli, Taiwan. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/CTAT-ITS2006.pdf 2. Ayala, A.P., Azuela, J.H.S. Educacion Basada en Web: un Estado del Arte http://www.somece.org.mx/simposio2004/memorias/grupos/archivos/069.doc 3. Brown, J. (2004). Integrating Tools for the Creation of Speech-Enabled Tutors http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jonbrown/publications/Brown_TechReport.pdf 4. Chepegin V., Aroyo, L., De Bra, P., Houben, G.J. (2003). CHIME: serviceoriented framework for adaptive web-based systems. In Proceedings of Dutch National Conference InfWet, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, November 20, 2003, 29-35. http://wwwis.win.tue.nl/infwet03/proceedings/3/ 5. Di Eugenio, B., Lu, X., Kershaw, T.C., Corrigan-Halpern, A., Ohlsson, S. (2005). Positive and Negative Verbal Feedback for Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 798-800. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.cs.uic.edu/~bdieugen/PSpapers/AIED05p.pdf 6. Herrmann, K., Hoppe, U., Kuhn, M. (2005). Help in Modeling with Visual Languages. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 830-832. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. 7. Hockenberry, M. (2005). Simple tutors for hard problems: understanding the role of pseudo-tutors. Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Portland, Oregon. pp. 1459-1462 http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1056941 35 8. Hunn, C., Mavrikis, M. (2004). Improving Knowledge Representation, Tutoring, and Authoring in a Component-based ILE. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science: pp. 827-829. 9. John, B.E., Prevas, K., Salvucci, D.D., Koedinger, K.R. (2004). Predictive Human Performance Modeling Made Easy. Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, Vienna, Austria, pp. 455462. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bej/cogtool/p466-john.pdf 10. John, B.E., Salvucci, D.D. (2005). Multipurpose prototypes for assessing user interfaces in pervasive computing systems. In Pervasive Computing, IEEE 4(4). pp. 27-34 http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~mariah/hci/CogTool.pdf 11. John, B.E., Salvucci, D.D., Centgraf, P., Prevas, K. (2004). Predictive Human Performance Modeling Made Easy. Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Cognitive Modeling, Mahwah, New Jersey, pp.130-135. http://portal.acm.org/ft_gateway.cfm?id=985750&type=pdf&coll=GUIDE&dl =GUIDE&CFID=22383924&CFTOKEN=84183877 12. Luo, L., John, B.E. (2005). Predicting task execution time on handheld devices using the keystroke-level model. Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Portland, Oregon. pp. 1605-1608 http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1056808.1056977 13. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W.W., Sewall, J., and Koedinger K.R. (2006). Applying Machine Learning to Cognitive Modeling for Cognitive Tutors, Technical report CMU-ML-06-105, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. http://reports-archive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/usr/ftp/ml/CMUML-06-105.pdf 14. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W. W., Sewall, J., Lacerda, G., & Koedinger, K. R. (2007; in press). Predicting students performance with SimStudent that learns cognitive skills from observation. In Proceedings of the international conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mazda/Doc/AIED2007/MatsudaN07b-toAppear.pdf 15. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W. W., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Applying Programming by Demonstration in an Intelligent Authoring Tool for Cognitive Tutors. In AAAI Workshop on Human Comprehensible Machine Learning (Technical Report WS-05-04) (pp. 1-8). Menlo Park, CA: AAAI association. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mazda/Doc/AAAI05/Matsuda05b.pdf 16. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W. W., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Building Cognitive Tutors with Programming by Demonstration. In S. Kramer & B. Pfahringer (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Inductive Logic Programming (Technical report, TUM-I0510) (pp. 41-46): Institut fur Informatik, Technische Universitat Munchen. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mazda/Doc/ILP2005/Matsuda05c.pdf 17. Matsuda, N., Cohen, W.W., Sewall, J., and Koedinger K.R. (2006). What characterizes a better demonstration for cognitive modeling by demonstration? Technical report CMU-ML-06-106, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. http://reports-archive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/ml/CMUML-06-106.pdf 36 18. Mavrikis, M., Hunn, C. (2005). Interoperability Issues in Authoring Interactive Activities. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 869-871. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 2005. [PP3] Turner, T.E., Macasek, M.A., Nuzzo-Jones, G., Heffernan, N..T & Koedinger, K. (2005). The Assistment builder: A rapid development tool for ITS. In Looi, McCalla, Bredeweg, & Breuker (Eds.) Proceedings of the 12th Artificial Intelligence in Education, Amsterdam: ISO Press. pp. 929-931. A longer version appears in Hefferan et al. 2006. (Based on W10) 1. Core, M. G., J. D. Moore, and C. Zinn, 2000. Supporting Constructive Learning with a Feedback Planner. In Building Dialogue Systems for Tutorial Applications, Papers of the 2000 AAAI Fall Symposium, edited by C. P. Rose and R. Freedman, 1-9. Technical Report FS-00-01. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press. http://people.ict.usc.edu/~traum/cs599f05/core00supporting.pdf 2. Le, V. “Learning and Tutoring Agent Shell: A New Approach to Building Intelligent Tutoring System for Expert Problem Solving Knowledge.” Thesis Defense http://lac.gmu.edu/publications/data/2006/Vu-Proposal-Defense.pdf [WP3] Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2000). Building a 3rd generation ITS for symbolization: Adding a tutorial model with multiple tutorial strategies. Workshop entitled "Learning Algebra with the computer, a transdisciplinary workshop". Held at Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2000 Conference. (pp. 12-22). Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1839, Berlin: Springer. 1. Core, M. G., J. D. Moore, and C. Zinn, 2000. Supporting Constructive Learning with a Feedback Planner. In Building Dialogue Systems for Tutorial Applications, Papers of the 2000 AAAI Fall Symposium, edited by C. P. Rose and R. Freedman, 1-9. Technical Report FS-00-01. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press. http://people.ict.usc.edu/~traum/cs599f05/core00supporting.pdf 2. Dietrich, D., Buckley, M. Verification of Proof Steps for Tutoring Mathematical Proofs. In Rose Luckin and Ken Koedinger, editors, Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Los Angeles, USA, 2007. http://www.coli.unisaarland.de/~buckley/content/DietrichBuckleyAIED07.pdf 3. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 83 & 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-One-Tutoring-HumansComputers/dp/0805843612 4. Fiedler, A. and D. Tsovaltzi, Automating hinting in an intelligent tutorial system, in: Proceedings of the IJCAI Workshop on Knowledge Representation and Automated Reasoning for E-Learning Systems, Acapulco, 2003, pp. 23-35. http://www.ags.uni-sb.de/~tsovaltzi/collective.pdf 37 5. Freedman, Reva. 2001. An Approach to Increasing Programming Efficiency in Plan-Based Dialogue Systems. Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on AI in Education (AI-ED 2001), San Antonio http://www.cs.niu.edu/~freedman/papers/aied2001.pdf 6. Tsovaltzi, D., Fiedler, A., Horacek, H. (2004). A Multi-Dimensional Taxonomy for Automating Hinting. Intelligent Tutoring Systems: 7th Annual Conference, ITS 2004, pp. 772-781 7. Tsovaltzi, D., Horacek, H., Fiedler, A. (2004). In Valerie Barr and Zdravko Markov (eds.), Proceedings of the Seventeenth Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference (FLAIRS 2004), pp. 929-934, Menlo Park, CA, AAAI Press, 2004 [WP4] Heffernan, N. T, Koedinger, K. (2001). The design and formative analysis of a dialog-based tutor. Workshop on Tutorial Dialogue Systems held as part of the 2001 Artificial Intelligence in Education. pp. 23-34. 1. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2006) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 [WP5] Heffernan, N. T., (2002). Web-based evaluation showing both motivational and cognitive benefits of the Ms. Lindquist tutor. SIGdial endorsed Workshop on Empirical Methods for Tutorial Dialogue Systems which was part of the International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring System 2002. pp. 1-8. Also appeared in a NSF-DFG sponsored workshop on Collaboration between German and American researchers in instructional technology. Tampa, Florida, May 5-7, 2002 1. Kaklauskas, A., Ditkevicius, R., Gargasaite, L. (2006). Intelligent Tutoring System for all Real Estate Management. International Journal of Strategic Property Management (2006) 10, pp. 113-130. http://www.vgtu.lt/upload/property_zurn/ijspm_2006_vol_10_no_2_p_113130.pdf [WP6] Koedinger, K. R., Aleven, V., & Heffernan, N. T. (2003). Toward a rapid development environment for cognitive tutors. The 12th Annual Conference on Behavior Representation in Modeling and Simulation. Simulation Interoperability Standards Organization. (Work later led to CP7) 1. Heinath, M., Dzaack, J., Wiesner, A. & Ubas, L. (2007) Applications for cognitive user modeling. In C. Conati, K. McCoy & G. Paliouras (Eds.) User Modeling 2007. Springer. Pp., 127-136. 2. Mavrikis, M., Hunn, C. (2005). Interoperability Issues in Authoring Interactive Activities. In the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (AIED-05), pp. 869-871. Amsterdam, the 38 Netherlands, July 2005. http://www.booksonline.iospress.com/Content/View.aspx?piid=55 [WP9] Freyberger, J., Heffernan, N., & Ruiz, C. (2004). Using association rules to guide a search for best fitting transfer models of student learning.ing. In Beck, Baker, Corbett, Kay, Litman, Mitrovic & Rigger (Eds.) Workshop on Analyzing StudentTutor Interaction Logs to Improve Educational Outcomes. Held at the 7th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Maceio, Brazil. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. ISBN 978-3-540-22948-3. 1. Jaroszewicz, S. (2006). Polynomial association rules with applications to logistic regression. Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. pp. 586-591 http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1150472 2. Leszczenskil, J. & Beck, J. E. (2007) What’s in a Word?: Extending Learning Factors Analysis to Model Reading Transfer. In the Educational Datamining Workshop held at the 13th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Los Angeles. pp 31-39. 3. Morales, C.M., Soto, S.V., Martinez, C.H. (2005). Estado actual de la aplicacion de la mineria de datos a los sistemas de ensenanza basada en web. Actas del III Taller Nacional de Mineria de Datos y Aprendizaje, TAMIDA2005. pp. 49-56 http://www.lsi.us.es/redmidas/CEDI/papers/189.pdf 4. Winters, T. (2006) Educational Data Mining: Collection and Analysis of Score Matrices for Outcomes-Based Assessment. Dissertation. Doctor of Philosophy, Computer Science, University of California Riverside. June 2006 [WP11] Nuzzo-Jones, G., Walonoski, J.A., Heffernan, N.T. & Livak, T. (2005). The eXtensible tutor architecture: A new foundation for ITS. Workshop on Adaptive Systems for Web-Based Education: Tools and Reusability held at the 12th Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam. pp. 1-7. 1. Aleven, V., McLaren, B.M., Sewall, J., Koedinger, K.R. (2006). The Cognitive Tutor Authoring Tools (CTAT): Preliminary Evaluation of Efficiency Gains. In the proceedings of 8th Annual Intelligent Tutoring Systems Conference, Jhongli, Taiwan. http://www.pitt.edu/~bmclaren/CTAT-ITS2006.pdf [WP13] Feng, M., Heffernan, N. T., & Koedinger, K. R. (2005). Looking for sources of error in predicting student's knowledge. In Beck. J. (Eds). Educational Data Mining: Papers from the 2005 AAAI Workshop. Menlo Park, California: AAAI Press. pp. 5461. Technical Report WS-05-02. 1. Romero, C., Ventura, S. (2007). Educational data mining: A survey from 1995 to 2005. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal 33(1) pp. 135-146. Tarrytown, NY http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6V03- 39 4JW10WR2&_user=10&_coverDate=07%2F31%2F2007&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=searc h&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_user id=10&md5=f46e1fe62b7d3422a81f1999604158cf 2. Winters, T. (2006) Educational Data Mining: Collection and Analysis of Score Matrices for Outcomes-Based Assessment. Dissertation. Doctor of Philosophy, Computer Science, University of California Riverside. June 2006 [WP14]Pardos, Z. A., Heffernan, N. T., Anderson, B., & Heffernan C. (2006). Using finegrained skill models to fit student performance with Bayesian networks. Workshop in Educational Data Mining held at the Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Taiwan. 2006. 1. Anozie, N., Junker, B. (2006). Predicting end-of-year accountability assessment scores from monthly student records in an online tutoring system. AAAI'06 workshop on Educational Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/anozie-aaai06.pdf 2. Ayers E. & Junker B. (2006). Do skills combine additively to predict task difficulty in eighth grade mathematics? AAAI'06 workshop on Educational Data Mining, Boston, 2006. http://www.assistment.org/project/papers/aaai06/WS0606AyersE.pdf [D1] Heffernan, N. T (2001) Intelligent tutoring systems have forgotten the tutor: Adding a cognitive model of human tutors. Dissertation. Computer Science Department, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. Technical Report CMUCS-01-127. 1. Baker, R.S. (2005) Designing Intelligent Tutors That Adapt to When Students Game the System. Doctoral Dissertation. CMU Technical Report CMU-HCII-05-104. http://reportsarchive.adm.cs.cmu.edu/anon/anon/usr0/ftp/hcii/CMU-HCII-05104.pdf 2. Beal, C. R., & Lee, H. (2005). Creating a pedagogical model that uses student self reports of motivation and mood to adapt ITS instruction. Workshop on Motivation and Affect in Educational Software, July 18-22, 2005, Amsterdam. 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education. http://wayangoutpost.net/paper/Beal&LeeCRC.pdf 3. Bruno, A., Gonzalez, C., Moreno, L., Noda, M., Aguilar, R., Munoz, V. Teaching Mathematics to Children with Down’s Syndrome. http://www.it.usyd.edu.au/~aied/vol8/vol8_Bruno.pdf 4. Chiu-Chen Hsieh, Tzong-Han Tsai, David Wible, Wen-Lian Hsu: Exploiting Knowledge Representation in an Intelligent Tutoring System for English Lexical Errors. ICCE 2002: 115-116 http://csdl2.computer.org/comp/proceedings/icce/2002/1509/00/15090115.pdf 40 5. Evens, M. & Michael, J. (2000) One-on-One Tutoring by Humans and Computers. Erlbaum: New Jersey pp. 388. http://www.amazon.com/One-OneTutoring-Humans-Computers/dp/0805843612 6. Gama, Claudia. PAL Tool: uma ferramenta cognitiva para organização e representação de problemas algébricos. Anais do XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação SBIE, Novembro. NCE/UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2003. PAL Tool: uma ferramenta cognitiva para organização e representação de problemas algébricos 7. Grubisic, A., Stankov, S., Zitko, B. (2002). Evaluating the Educational Influence of an E-Learning System. http://www.pmfst.hr/~ani/radovi/2005CEEPUS.pdf 8. Ibraheem, A.M., Shaalan, K., Riad, M.B., Darwish, M.G. (2003). A Model and Supporting Mechanism for Item Evaluation in Distance-Learning Based Environment. Egyptian Informatics Journal 4(2), 169-188 http://www.claes.sci.eg/publication/document_view.asp?doc_id=160&File_Na me=item_evalutaion_fci.pdf 9. Kim, Jung Hee, Reva Freedman, Michael Glass, and Martha W. Evens. Annotation of Tutorial Dialogue Goals for Natural Language Generation. Discourse Processes vol. 42 no. 1 (2006), pp. 37--74. http://www.csam.iit.edu/~circsim/documents/kfgedp06.pdf 10. Kim, J.H., Glass, M. (2004). Evaluating Dialogue Schemata with the Wizard of Oz Computer-Assisted Algebra Tutor. Intelligent Tutoring Systems: 7th Annual Conference, ITS 2004, pp. 358-367 11. Kodaganallur, V., Weitz, R., Rosenthal, D. (2006). Tools for Building Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (2), p. 46.2 http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/HICSS.2006.490 12. Padilla Franco Jávitt Higmar Nahitt, Lara Rodríguez Amado, Márquez Gutiérrez Pedro Rafael. (2001). Sistema Inteligente para la Ensenanze de las Matematicas. Electro 2001. pp. 99-104 http://www.depi.itchihuahua.edu.mx/electro/archivo/electro2001/mem2001/art iculos/cmp6.pdf 13. Patel, N., Glass, M., Kim, J.H. (2003). Data Collection Application for the North Carolina A&T State University Algebra Tutoring Dialogue (Wooz Tutor) Project. Fourteenth Midwest Cognitive Science and AI Conference (MAICS03), Cincinnati http://www.comp.ncat.edu/itsLab/docs/maics03-v2.2.pdf 14. Pon-Barry, H., Clark, B., Schultz, K., Bratt, E.O., Peters, S. (2004). Advantages of Spoken Language Interaction in Dialogue-Based Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In Intelligent Tutoring Systems (3220) pp. 390-400. http://godel.stanford.edu/old/muri/papers/ITS_2004.pdf 15. Sarrafzadeh, A., Page, C., Overmyer, S.P., Fan, C., Messom, C.H. (2003). The Next Generation Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In Ulrich Hoppe, Felisa Verdejo, and Judy Kay (eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Education. Amsterdam: IOS Press. 500-502. 16. Stamey, J.W. (2006). A Comparison of the Performance of Undergraduate Statistics Students Using Intelligent Learning Objects Versus those Receiving 41 Traditional Classroom Instruction. Dissertation. Technology Education, North Carolina State University. http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/theses/available/etd07102006-075902/ 17. VanLehn, K., Siler, S., Murray, C, Yamauchi, T., & Baggett, W. B. (2003). Why do only some events cause learning during human tutoring? Cognition and Instruction, 21 (3), 209-249. http://www.pitt.edu/~vanlehn/distrib/Papers/TutorialEvents.pdf 18. Woolf, B. A draft version of a text book called Building Intelligent Tutors, to be published by Elsevier, gives two pages to this work. 19. Zeferino, L.H., Rapkiewicz, C.E., Morales, G. (2003). Construindo o Modulo do Dominio de um Assitente Inteligente Utilizando a Ferramenta Java Expert System Shell. XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação - NCE IM/UFRJ 2003 42