WHMIS Test - Pembina Trails School Division
advertisement
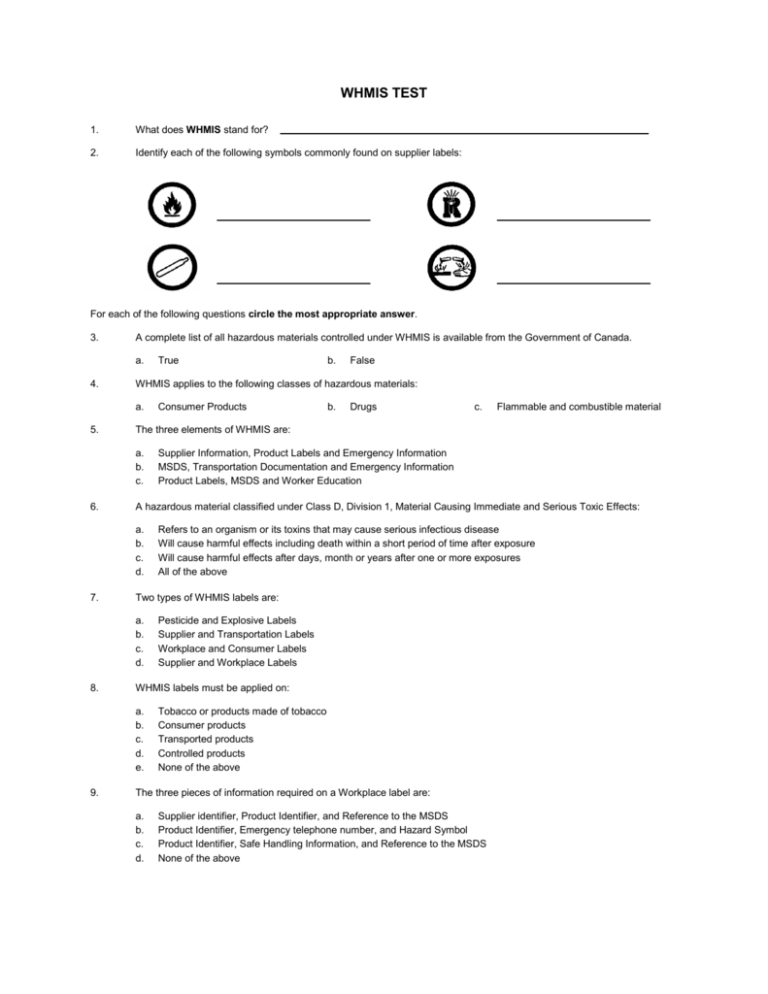
WHMIS TEST 1. What does WHMIS stand for? 2. Identify each of the following symbols commonly found on supplier labels: For each of the following questions circle the most appropriate answer. 3. A complete list of all hazardous materials controlled under WHMIS is available from the Government of Canada. a. 4. Drugs c. Flammable and combustible material Supplier Information, Product Labels and Emergency Information MSDS, Transportation Documentation and Emergency Information Product Labels, MSDS and Worker Education Refers to an organism or its toxins that may cause serious infectious disease Will cause harmful effects including death within a short period of time after exposure Will cause harmful effects after days, month or years after one or more exposures All of the above Pesticide and Explosive Labels Supplier and Transportation Labels Workplace and Consumer Labels Supplier and Workplace Labels WHMIS labels must be applied on: a. b. c. d. e. 9. b. Two types of WHMIS labels are: a. b. c. d. 8. Consumer Products A hazardous material classified under Class D, Division 1, Material Causing Immediate and Serious Toxic Effects: a. b. c. d. 7. False The three elements of WHMIS are: a. b. c. 6. b. WHMIS applies to the following classes of hazardous materials: a. 5. True Tobacco or products made of tobacco Consumer products Transported products Controlled products None of the above The three pieces of information required on a Workplace label are: a. b. c. d. Supplier identifier, Product Identifier, and Reference to the MSDS Product Identifier, Emergency telephone number, and Hazard Symbol Product Identifier, Safe Handling Information, and Reference to the MSDS None of the above 10. A controlled product may fall under more than one hazard classes and therefore the supplier label for that product will have more than one hazard symbol on it. a. 11. True b. False True b. False True b. False True b. False If the vapour of a flammable substance with a flash point of 4 °C kept in a room at 23 °C comes into contact with a flame, a. b. c. 21. Only by safety professionals Only in emergency situations Before you use a controlled product Occasionally to review hazard and precautionary information a and d c and d For flammable materials, the lower the flash point, the greater is the fire hazard. a. 20. False Oxidizers and Flammable materials are incompatible and should not be stored together. a. 19. b. The larger the LD50, the more lethal the substance. a. 18. True The LC50 and the LD50 of a material gives an indication of lethality. a. 17. Assist the purchasing department in buying chemicals Describe to you the nature of the processes in the work place Provide detailed hazard and safety information about the material None of the above An MSDS should be consulted: a. b. c. d. e. f. 16. Manufacturers Safety Data Sheets Materials Safety Diagnostic Sheets Mines Safety Direction Sheets Material Safety Data Sheets None of the above For a controlled product, the greater the evaporation rate, the more quickly it will create a vapour hazard. a. 15. A Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) label No label because the original container has a supplier label A workplace label A supplier label None of the above An MSDS is available in the work place to: a. b. c. d. 14. False The acronym MSDS stands for: a. b. c. d. e. 13. b. A container into which you transferred a hazardous product from the original supplier container requires: a. b. c. d. e. 12. True The vapour will ignite and cause an explosion The vapour will not ignite because the flash point is lower than 20 °C The vapour will ignite if its concentration in air is within the specific upper and lower flammability limits An odour threshold above the exposure limit means: a. b. c. If you cannot smell the material, you are not at risk of exposure There is no danger of exposure and you can work with the material If you can smell the material, you will be overexposed to the chemical






![WHMIS training for Elearning 2013 new template [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008888286_1-330ea65d2b07dfe4eb34b09a7f76579d-300x300.png)
