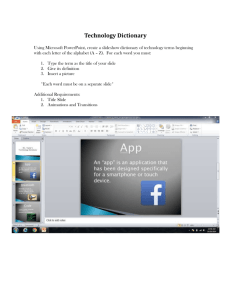
Option 3 Database design
advertisement
INFORMATION AND SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGY 7 - 10 SAMPLE OPTION TOPIC PROGRAM BASED ON IST: WARE ET AL OPTION 3: DATABASE DESIGN TEXT: Chapter 3 Database design Suggested time: 80 periods Syllabus outcomes: 5.2.1 describes and applies problem-solving processes when creating solutions 5.2.2 designs, produces and evaluates appropriate solutions to a range of challenging problems 5.2.3 critically analyses decision-making processes in a range of information and software solutions. Students learn about: Students learn to: Core content Option content 10.1 : define the terms data and information. identify the different forms that data can take (e.g. text, images, numbers). describe how data can be turned into information by organising, analysing (sorting and searching), editing and displaying. explain the importance of both data and information. 3.1: define the term database and describe the purpose of a database. define the term DBMS and describe what it does Option activities Syllabus Outcomes Database development purpose of a database define and describe a database explain the purpose of a database 1 see how data can be managed using a variety of application software. use search and sort functions in a word document and/or a spreadsheet. Students learn about: Students learn to: Database development components of a database inputs of a database validation and verification checks of data Core content Option content describe the relationships between a database, file, record, field and data character 10.4: data types list input data 10.4: original and second hand data 12.3: data ownership - copyright 12.4: appropriate use of collected data and codes of practice and conduct use validation and verification checks on the data for a database 12.4: accuracy, validity and bias of data 2 Option activities 3.2: hierarchy of data structures identify data types commonly used in databases define the term data dictionary and describe its importance. 3.3: Importance of identifying and acknowledging sources of data Identify the sources and types of data that would have to be collected for sample databases. 3.3: define the terms validation and verification giving examples of each. designing tests for entered data explain the importance of accurate data Syllabus Outcomes design paper or WP based data dictionaries. start a simple database by designing and entering a data dictionary for a database of students in the class, their ages, postcodes, star signs, gender add data input rules to the class data dictionary enter data into the database outputs of a database distinguish between data forms, data tables, reports identify the required outputs when designing a database 10.1: review differences between data and information and how organising the display of data can turn it into information 3 3.4: the different data views available in a DBMS, their uses and advantages/disadvantages. choosing an output view. perform basic sorts and filter searches using class database create a basic form view create a basic report Students learn about: Students learn to: Core content Option content Collecting, organising and storing data data types create a data required to solve dictionary to a problem illustrate and describe data types sources of data to solve a problem database storage on a storage medium 3.5: identifying a sample problem designing a possible solution designing data validation tests creating a data dictionary to help solve the problem document and acknowledge data sources 3.6: identify data source or sources for movie database review ethical and legal implications when using collected data input and store data for a given problem consider file size, portability and updatability issues 3.6: collect and enter data examine possible methods of automating the data collection process in general (e.g. bar codes, RFID) discuss issues of file size, data portability, data security and the need to update the data 4 Option activities Syllabus Outcomes students work through the sample project to construct a data dictionary for the movie database students design a suitable acknowledgment for their data source to be added to the database form view students work through the sample project to collect and enter data for the movie database students examine physical size of database Students learn about: Students learn to: Methods of processing and analysing data editing, construct query searching and searches and sorts sorting records on given data edit existing fields and records within a database Core content Option content 10.3: how ASCII affects search and sort results Methods of presenting information forms and create an effective reports design for a database form identify and use header, footer and body text in reports prepare a range of report and form layouts for presentation 3.7: problems of sorting and filtering different types of data using relational (e.g. “>=”) and logical (e.g. “AND”) operators using queries to automate search/sort tasks 3.8: the basics of designing a report the basics of designing data display forms 5 Option activities Syllabus Outcomes students edit the data to fix data collection or entry errors. students work through the sample project to perform basic sorting and searching operations on the data and to create queries. students work through the sample project to design and create alternative report and form layouts. Methods of processing and analysing data mathematical design and calculations perform calculations on data create macros to perform repetitive tasks 3.9: calculation fields in a database automating tasks by using macros 6 students work through the sample project to add calculated fields and macros to the database. Students learn about: Integration importing from existing electronic data exporting data for other uses Students learn to: import data, such as a graphic element, from a different source create a mail merge from stored data export data from the database to other applications Core content Option content 3.10: importing data through the clipboard (copy and paste) importing data files (e.g. graphic images) 3.10: exporting the results of searches and queries to other applications Option activities Syllabus Outcomes students work through the sample project to import prepared graphics into their database forms and/or reports. students work through the sample project to export selected records from their database into other applications such as spreadsheets or word processed documents. students create a mail-merged document using data from their database Assignment design and produce a simple database to solve a specified problem research and report on a database system incorporating an expert system students design and develop their own database based on solving a specific data management problem students use a web based expert system to solve a specific problem students investigate how databases are used in expert systems Additional content expert systems 3.11 CD-ROM: databases are at the core of expert systems using expert systems 7