Content and course structure –Core Course Basel
advertisement
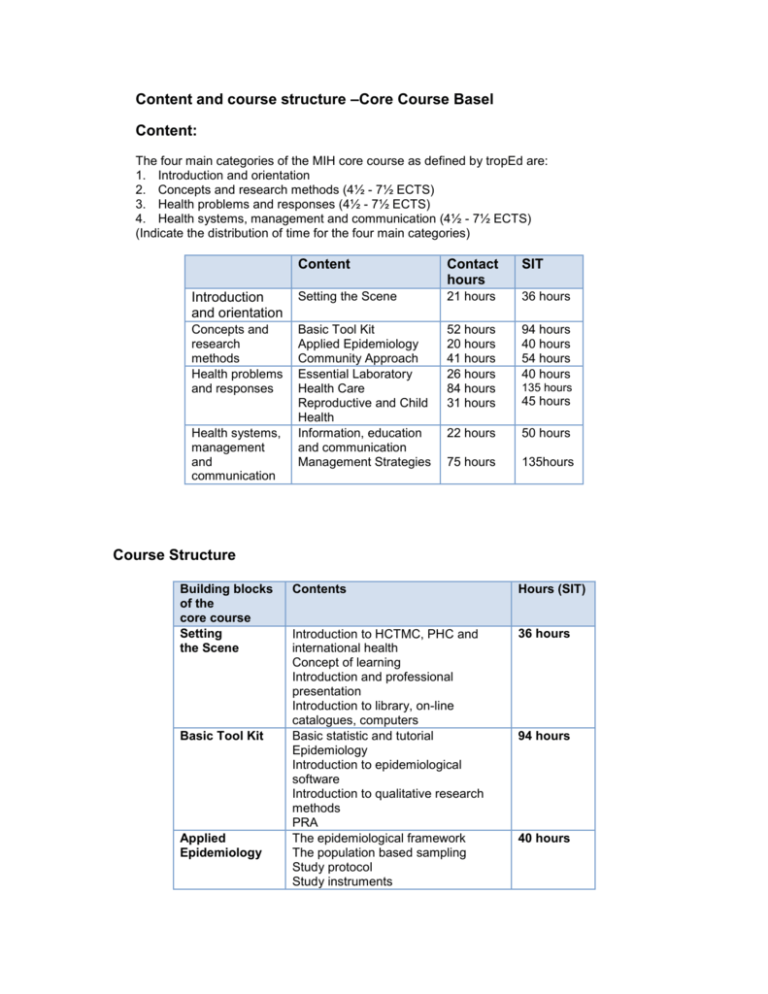
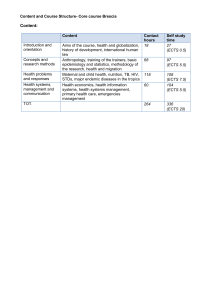
Content and course structure –Core Course Basel Content: The four main categories of the MIH core course as defined by tropEd are: 1. Introduction and orientation 2. Concepts and research methods (4½ - 7½ ECTS) 3. Health problems and responses (4½ - 7½ ECTS) 4. Health systems, management and communication (4½ - 7½ ECTS) (Indicate the distribution of time for the four main categories) Content Contact hours SIT Introduction and orientation Setting the Scene 21 hours 36 hours Concepts and research methods Health problems and responses Basic Tool Kit Applied Epidemiology Community Approach Essential Laboratory Health Care Reproductive and Child Health Information, education and communication Management Strategies 52 hours 20 hours 41 hours 26 hours 84 hours 31 hours 94 hours 40 hours 54 hours 40 hours 22 hours 50 hours 75 hours 135hours Health systems, management and communication 135 hours 45 hours Course Structure Building blocks of the core course Setting the Scene Basic Tool Kit Applied Epidemiology Contents Hours (SIT) Introduction to HCTMC, PHC and international health Concept of learning Introduction and professional presentation Introduction to library, on-line catalogues, computers Basic statistic and tutorial Epidemiology Introduction to epidemiological software Introduction to qualitative research methods PRA The epidemiological framework The population based sampling Study protocol Study instruments 36 hours 94 hours 40 hours Community Approach Essential Laboratory and Parasitology Health Care Reproductive and Child Health Information, Education and Communication Management Strategies The analytical plan Presenting the study Field study in a rural part of Switzerland Introduction to medical parasitology Essential laboratory Integrated vector management Gender and Health Malaria, Filariasis, Viruses-HepatitisHepatopathies, Schistosomiasis STI, Respiratory Infections, TB, Diarrhoea, HIV/AIDS North-South Contrast Primary Oral Health Care IMCI, EPI, Growth and Nutrition Mental Health, Neglected Tropical diseases, Non communicable diseases, public health in prisons, one medicine Water, Sanitation / climate change, Accidents due to Venomous and Poisonous Animals, Visit to WHO and ICRC Introduction to reproductive health FP, Safe motherhood Neonatology and Paediatrics incl. AIDS HIV/AIDS Reproductive rights Socio – economic mediators of sexual and reproductive health Working in groups Culture’s consequence Communicating effectively about rational drug use Writing in international health Introduction to health systems Health Sector Reform SWAP HIS Monitoring and Evaluation The role of cost-effectiveness analysis Financing and payment of health services Human Resource Management Technologies in health service provision Project cycle management Health promotion strategies Social marketing Access to essential drugs Health in humanitarian assistance Quality assurance Social marketing 54 hours 40 hours 135 hours 45 hours 50 hours 135 hours