Final Program
advertisement
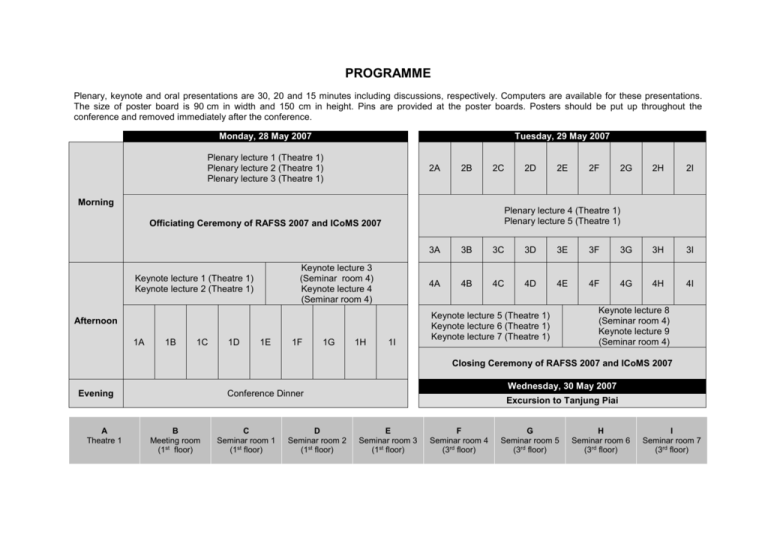
PROGRAMME
Plenary, keynote and oral presentations are 30, 20 and 15 minutes including discussions, respectively. Computers are available for these presentations.
The size of poster board is 90 cm in width and 150 cm in height. Pins are provided at the poster boards. Posters should be put up throughout the
conference and removed immediately after the conference.
Monday, 28 May 2007
Tuesday, 29 May 2007
Plenary lecture 1 (Theatre 1)
Plenary lecture 2 (Theatre 1)
Plenary lecture 3 (Theatre 1)
2A
2B
2C
2D
2E
2F
2G
2H
2I
Morning
Plenary lecture 4 (Theatre 1)
Plenary lecture 5 (Theatre 1)
Officiating Ceremony of RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
Keynote lecture 3
(Seminar room 4)
Keynote lecture 4
(Seminar room 4)
Keynote lecture 1 (Theatre 1)
Keynote lecture 2 (Theatre 1)
Afternoon
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
1G
1H
1I
3A
3B
3C
3D
3E
3F
3G
3H
3I
4A
4B
4C
4D
4E
4F
4G
4H
4I
Keynote lecture 5 (Theatre 1)
Keynote lecture 6 (Theatre 1)
Keynote lecture 7 (Theatre 1)
Keynote lecture 8
(Seminar room 4)
Keynote lecture 9
(Seminar room 4)
Closing Ceremony of RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
Evening
A
Theatre 1
Wednesday, 30 May 2007
Conference Dinner
B
Meeting room
(1st floor)
C
Seminar room 1
(1st floor)
D
Seminar room 2
(1st floor)
Excursion to Tanjung Piai
E
Seminar room 3
(1st floor)
F
Seminar room 4
(3rd floor)
G
Seminar room 5
(3rd floor)
H
Seminar room 6
(3rd floor)
I
Seminar room 7
(3rd floor)
2
Monday, 28 May 2007
0800
REGISTRATION AND BREAKFAST
PLENARY LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Zainal Abdul Aziz
Venue: Theatre 1
0900
0935
1010
1040
1100
1230
Nanoelectronics: a challenge for sustainable development (Plenary lecture 1)
Prof. Dr. Moehammad Barmawi (Department of Physics, Institut Teknologi Bandung,
Indonesia)
Newton Polyhedron and Estimation of Exponential Sums (Plenary lecture 2)
Prof. Dato' Dr Hj Kamel Ariffin Mohd. Atan (INSPEM, Universiti Putra Malaysia)
National Strategic Framework of Thailand's Nanotechnology and Her NANOTEC Center
(Plenary lecture 3)
Prof. Dr. Wiwut Tanthapanichakoon (National Nanotechnology Center, NSTDA , Thailand)
COFFEE BREAK
OPENING CEREMONY
Welcoming Speech by Prof. Dr. Samsudi Sakrani, Director of Ibnu Sina Institute for
Fundamental Science Studies
Opening Speech by Datuk Prof. Ir. Dr. Mohd. Zulkifli B. Tan Sri Mohd. Ghazali, Vice
Chancellor of Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Speech and officiation of RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007 by the Minister of
Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia, YB Dato’ Mustapa Mohamed
LUNCH
KEYNOTE LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Norsarahaida Amin
Venue: Theatre 1
1400
1430
1500
A Systematic Approach to Filtration Modeling (Keynote lecture 1)
Keynote lecture by Prof. Dr. Ali J Chamkha (College of Technical Studies, PAAET, Kuwait)
The Role of Statistics in Biological and Medical Sciences in Developing Countries
(Keynote lecture 2)
Asep Saefuddin (Institut Pertanian Bogor Indonesia)
COFFEE BREAK
KEYNOTE LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Hadi Nur
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
1400
1430
1500
Recent Progresses in Membrane Gas Separation Technology (Keynote lecture 3)
Prof. Dr. Takeshi Matsuura (University of Ottawa, Canada)
Fabrication of Platinum Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Shell
as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrogenation Reactions (Keynote lecture 4)
Prof. Dr. Shigeru Ikeda (Osaka University, Japan)
COFFEE BREAK
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
3
RO = Oral presentation for RAFSS 2007
RP = Poster presentation for RAFSS 2007
IO = Oral presentation for ICoMS 2007
IP = Poster presentation for ICoMS 2007
SESSION 1A
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wan Muhamad Saridan Wan Hassan
Venue: Theatre 1
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Resistivity of Nanocrystals (RO1)
Hasan Abu Kassim. Norhasliza Yusof and Keshav N. Shrivastava
Local distributions of electric fields and percolation in layered systems under Quantum Hall
Effect conditions (RO2)
V.E.Arkhincheev
Improvement of Power Output by Selecting The Appropriate Material Under Various
Conditions (RO3)
Javed Sami and M. A. K. Lodhi
Single Electron Transistor Structure Characterization Using Scanning Probe Microscopy
(RO4)
U. Hashim, Sutikno, Z.A.Z. Jamal and Y. Wahab
Earth’s Atmosphere Link to Solar Activity (RO5)
Jahanzeb Qureshi, Benjamin Noll and M.A.K.Lodhi
EM Wave Scattering from an Infinitely Long Cylinder (RO6)
Ithnin Abdul Jalil and Rio Hirowati Sharifudin
Affective Computing on Mathematics Learning (RO7)
Panimalar a/p Manoharan,Geraldine David
Thermal Symmetry of Markovian Master Equation (RO8)
B. A. Tay
SESSION 1B
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Abdul Rahim Yacob
Venue: Meeting room (1st floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Si and SiGe Based Materials for Microelectronic and Photonics Applications (RO9)
Md Roslan Hashim
Thermal Diffusivity Determination of CuSe Metal Chalcogenide Semiconductor Using
Photoacoustic and Photoflash Technique (RO10)
L.Y.C. Josephine, Z. A. Talib, W.M.M. Yunus, Z, Zainal, W.D.W. Yusoff, and M.M. Moksin
The Thermoluminescence Response of Ge-Doped Optical Fibres to X-Ray Photon
Irradiation (RO11)
Suhairul Hashim, Ahmad Termizi Ramli, D.A. Bradley and Husin Wagiran
Generation of QSAR Models for Cancer Treatment and Its Application to Grouping the
Photosensitizer Agents (RO12)
Sharifuddin M. Zain, Noorsaadah Abdul Rahman, Neni Frimayanti
Conductivity and Dielectric studies of a polyvinyl alcohol blended with zeolite – Technology
in membrane fuel for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC) (RO13)
Sharifah Zuraiha S.M.Zain, Elias Saion, Muhammad Zaki A.R.
Fuzzy Classification of Mountains Extracted from Multiscale Digital Elevation Models
(RO14)
Dinesh Sathyamoorthy
Studies on Carbon Dioxide Laser-Malaysian Light Hardwood (Shorea Uliginosa, Dyera
Costulata) and Plywood Interactions Using Ultrasound, Scanning Electron Microscope and
Energy Dispersive X-Ray (RO15)
Izyani Karudin, Mohamad Suhaimi Jaafar, Khalid M.Omar Al-Hadithi and Nor Fadhlin
Jaafar
Effect of Temperature on DC Conductivity of CdSe (RO16)
Amalina N. M , Z. A. Talib , W. M. D. W. Yusoff, Josephine L. Y. C., Norfazlinayati O.,
Emma Z.M.T
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
4
SESSION 1C
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Zaitul Marlizawati Zainuddin
Venue: Seminar room 1 (1st floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
A 2-D Analysis of the Stability and Convergence of a Nonlinear Optimal Control Algorithm
(IO1)
Rohanin Ahmad, Mohd Ismail Abdul Aziz
Using Genetic Algorithm (GA) for Solving Integer Linear Programming Problem (ILpp)
(IO2)
Shamsollah Ghanbari
Look Ahead Heuristics for Modeling Solid Waste Collection Problems (IO3)
Irhamah Nurhadi, Zuhaimy Ismail, L.S.Lee
The PSB-SD’s Method for the Unconstrained Optimization Problem (IO4)
Mustafa Mamat, Yosza Dasril, Ismail Mohd
Optimization of Crude Palm Oil Transportation for Northern Peninsular Malaysia (IO5)
Shamsudin Ibrahim, F.M. Abbas Al-Karkhi, Omar A. Kadir
A Review on Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Solving Facility Layout Problems
formulated as Quadratic Assignment Problems (IO6)
Phen Chiak See, Kuan Yew Wong
A Genetic Algorithm for Solving Vehicle Routing Problem with Stochastic Demands (IO7)
Zuhaimy Ismail, Irhamah Nurhadi
Mixed Integer Programming Model for the Portfolio Selection with Minimum Transaction
Lots (IO8)
Lucy K. Basar, Fajriana, Maryana, Putra B.J. Bangun, Rustam Sinaga, Zainal Azis,
Herman Mawengkang.
SESSION 1D
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ismail Mohamad
Venue: Seminar room 2 (1st floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Statistical Modeling of the Incidence of Breast Cancer in NWFP, Pakistan (IO9)
Salahuddin Khan
An Overview of Evaluation Criteria in Logistic Regression Models (IO10)
Hussain Jassim N., Low Heng Chin, F.M. Abbas Alkarkhi
Projection Pursuit Regression A Method of Statistical Downscaling (IO11)
A.H. Wigena, Aunuddin
The Determinants of Breast Feeding: Quantiles Regression Approach (IO12)
Mahdiyah, Wan Norsiah Mohamed & Kamarulzaman Ibrahim
The Use of Logistic Regression Model to Indentify the Risk Factor of H5N1 Avian Influenza
Virus at Native Chicken in Sumatera and Kalimantan Island, Indonesia (IO13)
Etih Sudarnika, Asep Saefuddin , Abdul Zahid, Chaerul Basri
Sensitivity Analysis for Survival Regression Models (IO14)
Hussain Jassim N., Low Heng Chin, F.M. Abbas Alkarkhi
Applying Robust M-Regression in Modeling Oil Palm Yield (IO15)
Zuhaimy Ismail & Azme Khamis
Using Logistic Regression to Determine the Sex of Spiderhunters (Family: Nectariniidae)
(IO16)
Charlie J.M. Laman, Siti Nurlydia binti Sazali, Mustafa Abdul Rahman
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
5
SESSION 1E
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Zuhaimy Ismail
Venue: Seminar room 3 (1st floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Reliability Assessment of Corroding Pipeline – A Statistical and Probabilistic Approach
(IO17)
Norhazilan Md Noor
Estimating the Intensity of Point Processes Models for Earthquake Occurrences (IO18)
Nurtiti Sunusi, Sutawanir Darwis, & Wahyu Triyoso
Statistical Profiling of Low Employability Graduates in Malaysia: Feasible? (IO19)
Lim Hock-Eam
The Effect of Imputing Missing SDs (IO20)
Nik Ruzni Nik Idris
The Modified Spatial Interpolation Methods for Missing Rainfall Data in Malaysia (IO21)
Shariffah Suhaila Syed Jamaludin, M.D. Sayang & Abdul Aziz Jemain
Cross – Sectional and Longitudinal Approaches in a Survival Mixture Model (IO22)
Zarina Mohd Khalid
Pipe Failure Probabilities of Water Distribution Systems (IO23)
Syarifah Hidayah Syed Harun, Ismail bin Mohd
Correction And Preparation Of Continuously Measured Rain Gauge Data In Malaysia
(IO24)
Marlinda Abd. Malek, Ismail Mohamad, Sobri Harun
SESSION 1F
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ali H. M. Murid
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Numerical Modelling of the 2004 Indonesian Tsunami along Peninsular Malaysia and
North Sumatra due to a Time Dependent Source (IO25)
Ahmad Izani Md. Ismail
Half-Sweep Geometric Mean Method for Solution of Linear Fredholm Equation (IO26)
M.S. Muthuvalu, Jumat Sulaiman
Numerical Solution to Simulation of Time-Multiplexing Cellular Neural Network (IO27)
S. Senthilkumar, R. Ponalagusamy
Edge Detection of Long Bone X-Ray Images using Cubic B-Spline Wavelet (IO28)
Nor Ashikin Mohamad Kamal, Arsmah Ibrahim
Finite Elements Model of Shape Memory Alloy Anti-Symmetric Angle-Ply Composite
Beams for Active Shape Control (IO29)
Z. A. Rasid, N.A Nik Mohamad, A.K.A Mohd Ihsan
Convergence Monte Carlo Simulation to the Black-Scholes Formula in Pricing Warrants
(IO30)
Benny Yong
Finite Elements Model of Shape Memory Alloy Anti-Symmetric Angle-Ply Composite
Plates for Active Modal Modifications (IO31)
Z.A. Rasid, S. Sarip & M.Z. Hassan
A Preconditioning Technique for Elliptic Problems in Two Dimensions (IO32)
Sarah Flora Samson Juan
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
6
SESSION 1G
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Nor’aini Aris
Venue: Seminar room 5 (3rd floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Magnetic Contour Plane As A Historical Framework For Brainstorm (IO33)
Tahir Ahmad, Rashdi Shah Ahmad, Liau Li Yun
Two-Generator Two-groups of Class Two of Order 32 and Their Application in
Crystallography (IO34)
Norashiqin Mohd Idrus, Nor Haniza Sarmin, Shahrizal Shamsuddin
The Graph of Relative Diagram Groups from Relative Diagram Groups
Zn | t1, t2 | xt1 t1x, xt2 t2 x, x Zn (IO35)
Sri Gemawati, Abd. Ghafur Bin Ahmad
Exterior Squares of Infinite Non-Abelian 2-Generator Groups of Nilpotency Class 2 (IO36)
Nor Haniza Sarmin, Nor Muhainiah Mohd Ali, Luise-Charlotte Kappe
On Counting the Conjugacy Classes of 2-Generator p-Group of Class 2 (IO37)
Azhana Ahmad, Robert F. Morse, Nor Haniza Sarmin, Satapah Ahmad
Capability of Infinite 2-Generator Groups of Nilpotency Class Two (IO38)
Nor Muhainiah Mohd Ali, Nor Haniza Sarmin, Luise-Charlotte Kappe
On the Rosenberger Monster II (IO39)
Robert Fitzgerald Morse
Group Theoretical Approach in Determining the Molecular Vibration of the Square Pyramid
Molecule (IO40)
Rohaidah Hj. Masri, Nor’aini Aris, Nor Haniza Sarmin, Satapah Ahmad
SESSION 1H
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Maslan Osman
Venue: Seminar room 6 (3rd floor)
1530
Some Numerical Algorithms for Parallel Multigrid Method on Distributed Parallel Computer
Systems (IO41)
Norma Alias, Tan Sui Chin, Shalela Mohd Mahali
1545
On The L Boundedness Of Certain Rough Singular Integral Operators (IO42)
Hussain M. AI-Qassem
A Note on the Partial Differential Equations and Convolutions (IO43)
Adem Kiliçman, Hassan Eltayeb
A Study of Two Space Dimensions Generalized Order Partial Differential Equations of the
Parabolic Type (IO44)
Rio Hirowati Shariffudin, Ithnin Abdul Jalil
A Solution of Boundary Value Problem By Using the Double Laplace Transform Technique
(IO45)
Adem Kiliçman
Application of Similarity Solution to Film Cooling for Flat Plate (IO46)
Kahar Osman, Lee Tuck Kuen, Jamaluddin Md. Sheriff
A Study of the Supercritical Solution of the Stationary Forced KdV Equation (sfkdv) (IO47)
Abdelaziz Hamad Elawad, Mukheta
Nonlinear Waves & Soliton Applications (IO48)
Ong Chee Tiong, Mohd Nor Mohamad,Tay Kim Gaik, Tiong Wei King, Chew Yee Ming,
Anny Hii
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
p
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
7
SESSION 1I
CHAIRMAN: Assoc Prof. Dr. Shaharuddin Salleh
Venue: Seminar room 7 (3rd floor)
1530
1545
1600
1615
1630
1645
1700
1715
Application of Taguchi Method to Investigate Several Network Parameters Affecting the
Performance of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol in a Self-Organizing Network (IO49)
Mazalan Sarahintu, Muhammad Hisyam Lee, Hazura Mohamed
Simulation of the Growth of Complex Geometric Patterns in Polymer Membrane (IO50)
S. Amir, N.S. Mohamed, S. A. Hashim Ali
Identifying Factors Affecting on Data Delivery Performance in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
Routing Protocol using a Systematic Approach (IO51)
Hazura Mohamed, Muhammad Hisyam Lee, Mazalan Sarahintu
Modeling of an Agent Based Schedule: Preliminary Study (IO52)
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
A Heuristic Algorithm for Solving Airline Crew Scheduling with Side Constraints (IO53)
Ani Minarni, Faridawaty, Marlina Setia Sinaga, Pasukat Sembiring, Robinson Sitepu,
Herman Mawengkang.
A Simulation-based Simulated Annealing for Stochastic Job Shop Scheduling Problem
(IO54)
Rashidah Ahmad, Sutinah Salim
Preliminary Analysis for Data Collection on Vehicle Inspection (IO55)
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
An Effective Modelling and Solution Approach for the Hamiltonian p-Median Problem
(IO56)
M. Zohrehbandian
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
8
Tuesday, 29 May 2007
SESSION 2A
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Sugeng Triwahyono
Venue: Theatre 1
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Theoretical Analysis of Left-Handed Metamaterials using Adomian Decomposition Method
(RO17)
Mohd Rafie Johan
On the Expression of Exoticity of A Slowly Rotating Wormhole (RO18)
Anuar Alias, Ithnin Abdul Jalil and Hasan Abu Kassim
A Study of One Space Dimension Generalised Order Partial Differential Equations of
the Parabolic Type (RO19)
Ithnin Abdul Jalil and Rio Hirowati Shariffudin
Core Calculation of 1 MW Reactor Triga Puspati (RTP) Using Continuous Energy Method
of Monte Carlo MYP Code System (RO20)
Julia Abdul Karim and Adnan Bokhari
DC Conductivity Studies in Conducting PPy Polymer with Applied Temperature (RO21)
Norfazlinayati O., Z. A. Talib, A. Kassim, Josephine L.Y.C., and A. H Shaari
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2B
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Zainab Ramli
Venue: Meeting room (1st floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
The Synthesis, Characterization and DC Electrical Conductivity of Poly[di(2,5-dimercapto1,3,4-thiadiazole)-Metal] Complexes (RO22)
Ali G. El-Shekeil , Hussein M. Al-Maydama and Omar M. Al-Shuja'a
Inductively Coupled Plasma Reactive Ion Etching on GaN in Cl2 Containing Plasmas
(RO23)
Siti Azlina Rosli and Azlan Abdul Aziz
Interactions and Characterizations of Shorea Collina Spp. and Parashorea Sp. using CO2
Laser (RO24)
Nor Fadhlin Jaafar, Mohamad Suhaimi Jaafar, Khalid M. Omar and Izyani Karudin
Plasmid Library Production From Local Medicinal Plant, Gardenia jasminoides (RO25)
Zaidah Rahmat, Nor Kamila Kamaruzaman and Siti Intan Rosdianah Damis
Engineering the Maltose Binding Protein For Biosensing Application (RO26)
Shafinaz Shahir, Tony Cass
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2C
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mohd Ismail Abd Aziz
Venue: Seminar room 1 (1st floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
A Simulated Annealing Approach for Uncapacitated Continuous Location-Allocation
Problem with Zone Dependent Fixed Cost (IO57)
Tolhah Abdullah, Zaitul Marlizawati Zainuddin & Sutinah Salim
Uncertainty Model for Solving Water Supply Problem in Agriculture Irrigation (IO58)
Gayus Simarmata, Herman Mawengkang
Stochastic Programming Model for Portfolio Optimization Problems (IO59)
Nerli Khairani, Herman Mawengkang
Discrete-Time Linear Optimal Control with a Random Input Study (IO60)
Kek Sie Long
Assessment of Point Process Models Following the Neyman-Scott Process (IO61)
Fadhilah Y, Zalina MD, Nguyen V-T-V, Maizah Hura A, Zulkifli Y
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
9
0930
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2D
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Azme Khamis
Venue: Seminar room 2 (1st floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Statistical Approach on Grading the Students Achievement via Mixture Modeling (IO62)
Zairul Nor Deana Md Desa, Ismail Mohamad, Zarina Mohd Khalid, Md Hanafiah Mad Zin
Estimation of Skewness and Kurtosis for Muscat Stock Market Data (IO63)
Muhammad Idrees Ahmad
On The Asymptotic Variance of Sample Vector Variance (IO64)
Erna T. Herdiani, Maman A. Djauhari
Generalized Addictive Mixed Models for Small Area Estimation (IO65)
Anang Kunia, Khairil A. Notodiputro
The Impacts of Age-Related Hearing Loss (IO66)
Azmin Azliza Aziz
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2E
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Salahuddin Khan
Venue: Seminar room 3 (1st floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Practical Forecasting Approach for Malaysia Electricity Load Forecasting (IO67)
Zuhaimy Ismail, Mohd Fuad Jamaludin
Analysis Effect of Terrorism toward Tourism by Intervention Model (IO68)
Riswan Effendi, Suhartono
Generalization of a Stochastic Model for Analysis of Multivariate Longitudinal
Measurements (IO69)
Khalid Ali Salah
Stochastic Logistic Model for Fermentation Process (IO70)
Arifah Bahar, Madihah Salleh
ARPS Hyperbolic Decline Model (IO71)
Sri Wahyuningsih, Sutawanir Darwis, Agus Yodi Gunawan & Asep Kurnia Permadi
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2F
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Siti Mariyam Shamsuddin
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Primary Hip Stem Stability: The Effect of Bone Pathology on Micromotion (IO72)
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq, K. Nazri
Matrix Transfer and Coupled Mode Equation for Nonlinear Photonic Bandgap as Optical
Signal Processing (IO73)
Ayi Bahtiar, Irwan Ary Dharmawan
Influence of Occlusal Loads on Stress Distribution of Dental Implants (IO74)
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq, M. I. Mohd Norshahid
Doppler Frequency Model for Sea Surface Current Simulation from RADARSAT-1 SAR
Images (IO75)
Maged Marghany, Mohamed Miyas, Mazlan Hashim
Performance of Glenoid Prostheses in a Conventional Glenohumeral Joint Arthroplasty
(IO76)
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq, I. Alhamzee
COFFEE BREAK
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
10
SESSION 2G
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Mohd Salmi Md Noorani
Venue: Seminar room 5 (3rd floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Tricritical domination (IO77)
Doost Ali Modjeh, Parisa Firoozi
The Total Edge-Irregular Strengths of Gears (IO78)
Nurdin
Graphs with Exponent 3 (IO79)
Didi Febrian, Saib Suwilo
On The Basis Number and the Minimum Cycle Bases of the Wreath Product of Some
Graphs (IO80)
M.M.M. Jaradat, M.K. Al-Qeyyam
2-Exponents of Two-Colored Lollipops (IO81)
Saib Suwilo
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2H
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Ali J. Chamkha
Venue: Seminar room 6 (3rd floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Modeling of Concentration and Capacity Profile of Solid Diffusion in Lithium-Ion Cell
(IO150)
Siti Aishah Hashim Ali
Lattice Boltzmann Simulation for the Permeability of Reconstructed Porous Media (IO83)
Irwan Ary Dharmawan
The Unsteady Power Law Blood Flow through a Multi-Irregular Stenosed Artery (IO84)
Norzieha Mustapha & Norsarahaida Amin
Mathematical Modeling of Boundary Layer Flow over a Moving Thin Needle with
Prescribed Wall Temperature (IO85)
Syakila Ahmad, Norihan Md Arifin, Roslinda Mohd Nazar, Abdul Aziz Jaafar & Ioan Pop
Effect of Body Acceleration on a Micropolar Blood Flow through a Mild Stenosed Artery
(IO86)
Ilyani Abdullah & Norsarahaida Amin
COFFEE BREAK
SESSION 2I
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Siti Aishah Hashim Ali
Venue: Seminar room 7 (3rd floor)
0815
0830
0845
0900
0915
0930
Wireless Sensor Network Deployment in Water Retention Problem (IO87)
Shaharuddin Salleh Ruzana Ishak, and Shazirawati Muhd Puzi
Verification of Mathematical Model of A Splicing System (IO88)
Nor Haniza Sarmin , Noor Aini Abdul Rashid, Fong Wan Heng & Mohd Firdaus Abdul
Wahab
2-Dimensional Fuzzy Number in Multi-Stage Dynamical System: An Improved Algorithm
(IO89)
Normah Maan, Tahir Ahmad
An Introduction to Mathematical Models of Linguistic Theories (IO90)
Tengku Muhammad Andri
Stable Self Similar and Locally Self Similar Processes (IO91)
S. Rezakhah
COFFEE BREAK
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
11
PLENARY LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Bahrom Sanugi
Venue: Theatre 1
1000
1035
1230
The Future of Statistical Process Control In Supply Chain Management: The Case at
Indonesian-Aerospace Industry (Plenary lecture 4)
Prof. Maman Abdulrachman Djauhari (Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia)
Singapore Synchrotron Light Source – a regional platform for multidisciplinary crossborder research (Plenary lecture 5)
Prof. Dr Herbert O. Moser (Singapore Synchrotron Light Source, National University of
Singapore)
LUNCH
SESSION 3A
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salasiah Endud
Venue: Theatre 1
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Photocatalytic Degradation of Dye Pollutants using SiO 2/TiO2 Catalyst (RO27)
Nazwin Ahmad
Optical Characterization of Au Thin Film Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Technique
(RO28)
I. Nurul Izrini, M.Y.W.Mahmood, A.T. Zainal, A.W. Zaidan
Acidity Study of Mesoporous Alumina Containing para-toluenesulfonic Acid Stabilized by
n-octadecyltrichlorosilane (RO29)
Sheela Chandren, Zainab Ramli, Hadi Nur
The effect of Attachment of Polyaniline on Stannic Oxide-Titanium Dioxide Coupled
Semiconductor in Photocatalytic Oxidation of 1-Octene (RO30)
Hadi Nur, Izan Izwan Misnon, Lim Kheng Wei
15N Nitroxide Free Radicals Imaged by Field-Cycled Proton-Electron Double-Resonance
Imaging (FC-PEDRI) at Low Magnetic Field (RO31)
Chittakorn Polyon, David J. Lurie, Wiwat Youngdee, Chunpen Thomas and Ian Thomas
Synthesis of Zeolites from Low Grade Kaolin (RO32)
Shamsul Kamal Sulaiman
SESSION 3B
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Md Roslan Hashim
Venue: Meeting room (1st floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Stress Variations due to Different in Stem Length on TKR (RO33)
M.I.Z. Ridzwan, M.S. Mohidin, Solehuddin Shuib, and A.A. Shokri
Supported SnO2-Based Ion Exchange Systems for the Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals
From Industrial Effluent (RO34)
Chin Kee Chin, Jamaludin Karim, Ismail Ibrahim and Hamdan Yahya
Refractory Castable for Ladle Lining in Ferronickel Mining Industries (RO35)
Hendra Wijayanto, Faisal Alkadrie
Selective Oxidation of Hydrocarbon by Heterogeneous Catalysis (RO36)
Taufiq Yap Yun Hin
Characteristic of AC Conductivity in Ternary Zinc Oxide Calcium Oxide Phosphate Glasses
(RO37)
Zainal Abidin Talib, S.F. Khor, E.Z.M. Tarmizi, H.A.A. Sidek, W.D.W. Yusoff, W.M.M
Yunus and A.H. Shaari
Multistate Survival Analysis on The Presence of Diabetes Related Complications (RO38)
Yuhaniz Hj Ahmad, M. Ataharul Islam and Noorani Ahmad
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
12
SESSION 3C
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Ismail Mohd
Venue: Seminar room 1 (1st floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Metaheuristics for Solving Facility Layout Problems: Concepts and Trends (IO92)
Nadia Nurul Nordin, Zaitul Marlizawati Zainuddin & Kuan Yew Wong
Optimization Investment Models With a Single Stochastic Factor (IO93)
Sugiyarto Surono & Ismail Mohd
A Solution of Optimal Control Problem of Continuous Interconnected Nonlinear System
using DISOPE Approach (IO94)
Nor Hazadura Hamzah, Hazadura Hamzah & Mohd Ismail Mohd Aziz
Thermal Performance of a Microchannel with Entropy Generation Minimization (IO95)
Ummikalsom Abidin & Normah Mohd. Ghazali
Agent’s Coordination and Cooperation in the Water Resources Reallocation Project under
Uncertainties (IO96)
Sharmila Karim & Mohd Ismail Abdul Aziz
Modelling and Controlling of a Human-Like Arm with Muscle Flexibility (IO97)
Musa Mailah, Suhail Kazy, Hossein Jahan Abadi, Mohd Zarhamdy Mohd Zain
SESSION 3D
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Asep Saefuddin
Venue: Seminar room 2 (1st floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Hybrid Model for Subdistribution of Competing Risks (IO98)
Abdul Kudus, Noor Akma Ibrahim, Isa Daud & Mohd Rizam Abu Bakar
Statistical Analysis of The Wireless Internet Usage Among Students In Universiti Malaysia
Sabah (IO99)
Darmesah Gabda, Suriani Hassan, Sathissan a/l Ragavan
Bootstrapping Nonlinear Regression (IO100)
Sutawanir Darwis, Agus Yodi Gunawan, M. Ali Ashat, Sri Wahyuningsih, Nurtiti Sanusi,
Rian Febtrian Umbara & Elis Nurzannah
Small Area Estimation: A Review and Comparison on Various Methods (IO101)
Dian Handayani & Noor Akma Ibrahim
Permutational Tests of Interaction Effects in Multi-Factorial Experiments (IO102)
Bidin Yatim
A Heuristic Method of Scenario Generation in Multi-Stage Decision Problem under
Uncertainty (IO103)
Suherman, Herman Mawengkang
SESSION 3E
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tahir Ahmad
Venue: Seminar room 3 (1st floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
Error Estimation in the Charge Simulation Method for Two and Three Dimensional
Potential Problems (IO104)
Dai Okano, Li Tao, Kaname & Amano
A Weighted Ostrowski Type Inequality for Twice Differentiable Mappings and Applications.
(IO105)
Ather Qayyum
Asymptotic of Finite Difference Time Domain Method (IO106)
Otong Nurhilal, Irwan Ary Dharmawan & Ayi Bahtiar
The application of homotopy analysis method for Lotka-Volterra equations (IO107)
A. Sami Bataineh & M.S.M. Noorani
The Computation of the Comrade Matrix and the Greatest Common Divisor of Polynomials
(IO108)
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
13
1230
Nor’aini Aris
Variability issues in manufacturing process: A perspective from industrial practitioners
(IO109)
Jafri Mohd Rohani, Sha’ri Mohd Yusof & Ismail Mohammad
SESSION 3F
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Izani Md. Ismail
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Convexity – Preserving Scattered Data Interpolation (IO110)
Abd. Rahni Mt. Piah, Azizan Saaban & Ahmad Abd. Majid
Automatic Reading of Node Values in a Numerical Model (IO111)
Rudi Heriansyah & S. A. R. Abu Bakar
Improving Parallel Pipeline Algorithm using Message Passing Interface for Time
Dependent Problem (IO112)
Ng Kok Fu & Norhashidah Mohd Ali
Approximate Analytical Solution of the El Nino – Southern Oscillation Model (IO113)
Noor Fadiya Mohd Noor & Ishak Hashim
Fuzzy Edge Connectivity Relates the Variables in Clinical Waste Incineration Process
(IO114)
Sabariah Baharun, Tahir Ahmad & M Rashid M Yusof
An Integral Equation Method For Conformal Mapping Of Doubly Connected Regions
Involving The Kerzman-Stein Kernel (IO115)
Ali H. M. Murid, Laey-Nee Hu, Mohd Nor Mohamad
SESSION 3G
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Adem Kilicman
Venue: Seminar room 5 (3rd floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
An Optimization Problem in Ergodic Theory (IO116)
Mohd Salmi Md Noorani
Subclass of Function Close-to-Convex with respect to Symmetric Points (IO117)
Aini Janteng, Suzeini Abdul Halim & Maslina Darus
On Sufficient Condition and Angular Estimation for -like Function (IO118)
Saibah Siregar & Maslina Darus
Improved Boundary Integral Equation for Dirichlet Problem on Region with Corners
(IO119)
Munira Ismail, Ali Hassan Mohammed Murid & Bahrom Sanugi
An Application of a Fractional Calculus Operator to a Subclass of p-Valently Analytic
Functions with Negative Coefficients of Complex Order (IO120)
Ajab Akbarally & Maslina Darus
Recent Results on Ruscheweyh Operators (IO121)
Maslina Darus
SESSION 3H
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Shamsuddin Ahmad
Venue: Seminar room 6 (3rd floor)
1115
1130
1145
The Boundary Layer Flow past a Moving Wall with Mass Transfer (IO122)
Anuar Ishak, Roslinda Nazar & Ion Pop
3D Numerical Simulation of Tsunami Runup from QUICKBIRD Satellite Data (IO123)
Maged Marghany & Mazlan Hashim
Effect of Magnetic Field and Conduction on Natural Convection Flow along a Vertical Flat
Plate in the Presence of Heat Generation (IO124)
A. A. Mamun, Z.R.Chowdhury & M.A.Azim
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
14
1200
1215
1230
Numerical Modeling of Inviscid Acoustic Waves in a Closed Chamber (IO125)
Mah T.C and Normah Mohd Ghazali
Development of 2D and 3D Double Population Thermal Lattice Boltzmann Models (IO126)
Nor Azwadi Che Sidik & T. Tanahashi
Unsteady Boundary Layer Flow of a Micropolar Fluid near the Stagnation Points of a
Plane Semi-Infinite Wall (IO127)
Anati Ali, Norsarahaida Amin, Ioan Pop
SESSION 3I
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jamalludin Talib
Venue: Seminar room 7 (3rd floor)
1115
1130
1145
1200
1215
1230
Quasistationary Approximation for One Phase Stefan Problem (IO128)
Halijah Osman, Choong Ai Mei & Khairil Anuar Arshad
Comparative Analysis for Jukes-Cantor and Kimura Evolutionary Model (IO129)
Ivonne Martin
Modeling of the PDE’s in a Silver Substrate using Finite Difference Method (IO130)
Noraini Abdullah
Using Delay Time Analysis To Study Palm Oil Mills Maintenance Problem (IO131)
Abd Samad Hasan Basari
On the Performance of Group Krylov Iterative Methods on Systems Arising from a TwoDimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations (IO132)
Sam Teek Ling, Norhashidah Hj. Mohd Ali
Modeling of the Spread of HFMD (Exteroviral Vesicular Stomatitis with Exanthem) using
Stochastic Differential Equations (IO133)
Noraini Abdullah
SESSION 4A
CHAIRMAN: Dr. Sugeng Triwahyono
Venue: Theatre 1
1400
1415
1430
The quality analysis of polycrystalline diamond coated Si3N4 using Raman Spectra: the
effect of chamber pressure and microwave power (RO39)
A. Purniawan, E. Hamzah, M. R. M. Toff
Ice point blackbody cavity for checking the performance of an infrared radiation
thermometer operating near 0 °C (RO40)
Irene Safinaz Hassan, Hafidzah Othman , Md. Nor Md. Chik
Measurement and Calibration of Frost Point and Dew Point Meter (RO41)
Faridah Hussain, Hafidzah Othman, Md Nor Md Chik
SESSION 4B
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Abdul Rahim Yacob
Venue: Meeting room (1st floor)
1400
1430
1415
Identification and Characterization of A Marine Pseudoalteromonas Sp from
Fish Mucus (RO42)
Wan Siti Nur Atirah Wan Mohd Azemin, Mohd Shahir Shamsir Omar, Azmi Rani
Biolistic-Transformation of Impatiens Balsamina Using hph Gene for Hygromycin Resistant
(RO43)
Aishah Mohd Taha, Alina Wagiran, Zaidah Rahmat and Fahrul Zaman Huyop
Preparation and Conductivity Studies on Poly(Methyl Metacrylate)-Epoxidised Natural
Rubber Blend Solid Electrolytes (RO44)
Madzlan Aziz and Famiza Abdul Latif
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
15
SESSION 4C
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Bidin Yatim
Venue: Seminar room 1 (1st floor)
1400
1415
1430
Branch and Bound Approach for Solving Two-Stage Mixed-Integer Stochastic
Programming Problems (IO134)
Jafaruddin Harahap and Herman Mawengkang
Revisiting Missingness Mechanism (IO135)
Ismail Mohamad
Characteristics of Deterministic Equivalent Model for Multi-Stage Mixed Integer Stochastic
Programs (IO136)
Irvan & Herman Mawengkang
SESSION 4D
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Robiah Adnan
Venue: Seminar room 2 (1st floor)
1400
1415
1430
Comparing the Accuracy of Density Forecast from Competing Models: An Application to
KLCI Returns (IO137)
Abu Hassan Shaari Mohd Nor, A. Shamiri & Fauziah Maarof
Development of Small Area Estimation Research in Indonesia (IO138)
Khairil A. Notodiputro & Anang Kurnia
The Performance of MM-Estimators on Simple Mediation Analysis (IO139)
Anwar Fitrianto & Habsah Midi
SESSION 4E
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Yudariah Mohamad Yusof
Venue: Seminar room 3 (1st floor)
1400
1415
1430
Computers-Assisted Student Learning in Engineering Mathematics (IO82)
Maya Pundoor & Ramadas Narayanan
Dynamic Geometry: Theory and Practice (IO142)
Robert L. Pour
Computer Based Assessment in Engineering Mathematics: A Case Study (IO155)
Maya Pundoor & Ramadas Narayanan
SESSION 4F
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Kaname Amano
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
1400
1415
1430
Biomechanical Analyses of Two Lumbar Vertebrae Implanted with an Artificial Disc (IVD)
(IO143)
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq & W.H. Wan Mohd Musyris
Biological Classifiers for Problem Solving (IO144)
Siti Maryam Shamsuddin
Newton-Kaczmarz Methods for Reconstruction of Electrical Impedance Tomography with
Multiple Measurement Data: A Numerical Result (IO145)
Agah D. Garnadi
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
16
SESSION 4G
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nor Haniza Sarmin
Venue: Seminar room 5 (3rd floor)
1400
1415
1430
Students’ Approach on Delivering A Simple and Alternative Euclidean Division Algorithm
(IO146)
Mohd Sulhi, Azniah, Noraishiyah, Tuan Salwani & Siti Mistima
Cardinality of the Sets of Solution to Congruence Equation Associated with a Seventh
Degree Form (IO147)
Siti Hasana Sapar & K.A Mohd Atan
On Higher Order Analogues of the RSA Cryptosystem (IO148)
Mohamad Rushdan Md. Said
SESSION 4H
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Roslinda Mohd Nazar
Venue: Seminar room 6 (3rd floor)
1400
1415
1430
1445
Effect of Control on the Onset of Marangoni-Bénard Convection with Uniform Internal Heat
Generation (IO149)
Norfifah Bachok, Norihan Md Ariffin & Fadzillah Md. Ali
Maximum Density Effects on G-Jitter Induced Free Convection between Vertical Plates
Heated and Asymmetrically (IO151)
Sharidan Shafie, Norsarahaida Amin & Ioan Pop
An Efficient Parallel Numerical Integration Algorithm for Multilayer Layer Raster CNN for
Simulation (IO140)
R. Ponalagusamy & S. Senthilkumar
Sliding Mode Tracking Controller For Hydraulic Robot Manipulators With Numerical
Analysis (IO141)
Syarifah Zyurina Nordin, Haszuraidah Ishak & J.H.S Osman
SESSION 4I
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Dai Okano
Venue: Seminar room 7 (3rd floor)
1400
1415
1430
Analysis of a Dengue Disease Transmission Model without Immunity (IO152)
Yusuf Yaacob
Time-Dependent Generation Of Fluid Motion Along A Channel By A Traveling Magnetic
Field (IO153)
Mohd Noor Saad
Numerical Solutions of The One-Dimensional Shallow Water Equations (IO154)
Salemah Ismail, Zainal Abd. Aziz, Mohd Nor Mohamad & Nazeeruddin Yaacob
KEYNOTE LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Zainal Abd. Aziz
Venue: Theatre 1
1500
1530
1600
Revenue Management: Applying Optimization Concept in Business
(Keynote lecture 5)
Prof. Dr. Bahrom Sanugi (Universiti Teknologi Malaysia)
Numerical Conformal Mapping by the charge simulation method (Keynote lecture 6)
Prof. Dr. Kaname Amano (Ehime University, Japan)
Symbolic computing for the working scientist
(Keynote lecture 7)
Prof. Dr. Robert Fitzgerald Morse (University of Evansville, USA)
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
17
KEYNOTE LECTURES SESSION
CHAIRMAN: Prof. Dr. Moehammad Barmawi
Venue: Seminar room 4 (3rd floor)
1500
1530
Nanomaterials for Energy Conversion (Keynote lecture 8)
Prof. Dr. Muhammad Yahaya (Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia)
Organic-less Separations: Let the Pressure and Temperature Work on
(Keynote lecture 9)
Prof. Dr. Marsin Sanagi (Universiti Teknologi Malaysia)
CLOSING CEREMONY
Venue: Theatre 1
1645
Closing Speech by Prof. Dr. Norsarahaida Amin, Chairman of ICoMS 2007
Closing Speech by Assoc Prof. Dr. Zainal Abdul Aziz, Chairman of RAFSS 2007
Closing Speech by Prof. Ir. Dr. Siti Hamisah Tapsir, Deputy Vice Chancellor (Academic &
International), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
18
LIST OF POSTERS
RP1
RP2
RP3
RP4
RP5
RP6
RP7
RP8
RP9
RP10
RP11
RP12
RP13
RP14
RP15
RP16
RP17
RP18
RP19
RP20
Theoretical and Empirical Comparison of Coupling Coefficient and Refractive Index
Estimation for Coupled Waveguide Fiber
Saktioto, Jalil Ali, Jasman Zainal, Rosly Abdul Rahman, Bashir Ahmed Tahir
Characterization of Low Pump Power Nd:YAG Laser
Abd Rahman Tamuri, Wan Rashidah Wan Majid, Noriah Bidin and Yaacob Mat Daud.
Epitaxial Method Of Quantum Devices Growth
Rosnita Muhammad, Zulkafli Othaman,Samsudi Sakrani
Process Development and Optimization of Laser Diode to Single-Mode Fiber Coupling
and Packaging Using Laser Welding Technique
Fadhali M. A., Zinal J., Munajat Y., and Rahman R.
Preliminary Analysis for Data Collection on Vehicle Inspection
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Taylor Series Expansion Model for Optical Free Space Feedforward Linearization System
A. B. Maiteeg, S. M. Idrus, H. Harun
Morphology and Optical Properties of Silicon Nanocrystals embedded in Silicon oxide
Yussof Bin Wahab, Yeong Wai Woon, Karim Bin Deraman
Tabletting of Morinda citrifolia Powder
Yus Aniza Yusof, Che Rodiziah Md. Noor
Fracture mechanisms of natural fiber reinforced composites at high temperatures
Al Emran Ismail
Harmonic Balance Analysis of the Downconversion Optoelectronic Mixer in HBT
Photodetector
S.M.Idrus, A.Hussain, H.Harun, A.B. Mohammad
Algorithm for Magnetic Field Visualization of a Flat Plane Induced by Finite Dipole
Segment Using GCC and Gnuplot
Rashdi Shah Ahmad, Chew Teong Han
Synthesis of Zeolite A by Ultrasound Irradiation Technique
H. M. Razif, N. H. N. Hadzuin, T. Sugeng and A. J. Aishah
Modeling of An Agent Based Schedule: Preliminary Study
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Preparation of Pt/Carbon Nanocomposites with Hollow Structure Using TiO2
Photocatalytic Reaction
Yun Hau Ng, Takashi Harada, Shigeru Ikeda and Michio Matsumura
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography determination of high explosives residues in post
blast water samples following solid phase extraction
Umi K. Ahmad and Sumathy Rajendran
An ESR Study of Trapped Electron on High Surface Area Carbon
from Palm Kernel Shells
Abdul Rahim Yacob, Ratna Sari Dewi Dasril, Mohd. Khairul Asyraf A.M., and Vicnisvarri
Inderan
Effect of Substrate Temperature and Deposition Time on the Sizes of Silicon Nanodots
Grown on Corning Glass (7059) Substrate
Imam Sumpono , Lim Qiao Jie and Samsudi Sakrani
Electrosynthesis of benzoic acid from chlorobenzene by carbon dioxide fixation method
Aishah Abdul Jalil, Hartini Mohd Aris, Normala Suliman, Norhuda Abdul Manaf, Nur
Hanis Hayati Hairom, Mohd Razif Harun and Sugeng Triwahyono
Influence of Surfactant Types on Correlation of Retention Factor and Hydrophobicity of
Selected Triazole Fungicides in Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography
Wan Aini Wan Ibrahim, Dadan Hermawan, Mohamed oor Hasan and Mohd Marsin
Sanagi
Design and Characterization of Resistance Heating for Czochralski Crystal Growth
Hamdan H.K and Mohammad Radzi Sudin
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
19
RP21
RP22
RP23
RP24
RP25
RP26
RP27
RP28
RP29
RP30
RP31
RP32
RP33
RP34
RP35
RP36
RP37
IP1
IP2
IP3
IP4
IP5
IP6
AC Conductivity of Ca0.8Ba0.2Cu3TiO4O12 Ceramic Sample
M. Mazni, W. D. W. Yusoff, C. P. Walter, S. A. Halim, Z. A. Talib
The Study of Precipitated Cu-Zn-Al Catalyst via pH Titration Analysis
Nur Fadhilah Idrisa, Salamiah Zakariaa, Nurain Nasrudinb, Robert Schlöglc and Sharifah
Bee Abd Hamid
Mo-V-Te-Nb-Mn-O Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Propane to Acrylic Acid: Effect
Promoter Loadings to Surface Modification
Rosliza Mohd Salim, Fazliana Abd Hamid, Noor Azeerah Abas, Looi Ming Hoong and
Sharifah Bee Abd Hamid
Effect of Platinum and Tungsten Oxide Metal Loading on n-Pentane Isomerization over
HZSM-5 Based Catalyst
Mohd Razif Harun, Mohd Zamry Jamaludin, Sugeng Triwahyono and Aishah Abdul Jalil
Modified effects of LDPE/EVA blends by electron beam irradiation
Mazyiar Sabet, Azman Hassan, Mat Uzir Wahit
Nanometer Scale of Silicon Oxide Pattern using Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
Teguh Darsono, Sabar Derita Hutagalung, Zainal Arifin Amad, Cheong Kuan Yew,
Khatijah Aisha Yaacob
The Role of IgE antibodies in protection against P.falciparum
Reem Bairam, Marita Troye Bloomberg, Muntasir Eltayeb, Ibrahim Elhassan
Physicochemical Studies of CdS Nanoparticles -Titanosilicate Hybrid
Mustaffa Shamsuddin, Ng Yew Choo
Catalytic Properties of Metallosalen supported on MCM-41 in Oxidation of Benzene
Salasiah Endud, Chin Tian Kae, Shajarahtunnur bt. Jamil and Wong Ka Lun
μ-Oxo Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complex Incorporated in MCM-48 as Efficient Catalyst
for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohol
Salasiah Endud, Lau Su Chien, Wong Ka Lun
MCNP for Neutron Radiography Simulation
Sumilah Marto, Wan Muhamad Saridan Wan Hassan and Azali Muhamad
Measurement of Diamagnetic Susceptibility of Crude Oils
Abd. Aziz Abd. Kadir, Hasrul Afendi Ahmad Khonif, Rashdi Shan Ahmad
Growth and Characterization of Gallium Oxide Thin Films Deposited By DC Magnetron
Sputtering
Mechanical Properties of Talc and Calcium Carbonate Filled PVC
Bee Soo Tueen, Azman Hassan and Aznziam Abu Bakar
Effect of Na loading on the properties of catalysts and n-heptane isomerization over
Pt/SO42--ZrO2 catalyst.
Sugeng Triwahyono and Aishah Abdul Jalil
A Supported Titanium and Copper Based Catalyst For Desulphurization Reaction
Junaidi Mohamad Nasir, Wan Azelee Wan Abu Bakar and Mohd Yusuf Othman
Photonic Devices Pigtailing and Packaging Using Laser Welding Technique
Fadhali M. A., Saktioto, Zainal J., Munajat Y. and Rahman R.
Oblique Stagnation Slips Flow of a Micropolar Fluid
Lok Yian Yian, Norsarahaida Amin, Ioan Pop
The Important of Statistical Orientation for Quality Improvement in Automotive Parts
Manufacturing and Supply in Malaysia
Muzalwana Abdul Mutalib
Comparison of Two Algorithms for Production Layout Improvement – The Application
Syed Ahmad Helmi bin Syed Hassan
Identifying Statistically Significant Protein Spots in 2-DE Protein Expression Data
Norhaiza Ahmad & J. Zhang
Regression Model for Forecasting Malaysian Electricity Load Demand
Zuhaimy Ismail & Faridatul Azna Jamaluddin
Least cost and Highest Demand Procedure as Feasible Solution for Dedicated Vehicle
Routing Problem
Zuhaimy Ismail & Mohammad Fadzli Ramli
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
20
IP7
IP8
IP9
IP10
Selected Heuristic Algorithms for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
Zuhaimy Ismail & Wan Rohaizad Wan Ibrahim
An Electricity Load Demand Analysis Based on Day-Type using Exponential Smoothing
Zuhaimy Ismail & Rosnalini Mansor
Mixed Convection Boundary Layer of a Viscoelastic Fluid near a Stagnation Point
Nur Ilyana Anwar Apandi, Norsarahaida Amin & Sharidan Shafie
The Parallel AGE Method For Solving Incomplete Blow-Up Problem Using Heterogeneous
Multiprocessor Systems
Norma Alias, Nurul Ain Zhafarina Muhamad
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
21
Plenary lecture 1
Nanoelectronics: a challenge for sustainable development
Moehammad Barmawi
Professor Emeritus in Physics, Institut Teknologi Bandung and
Member of Akademi Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia
Nano-science explores the possibility of creating nano-structures. It is of great interest, because these
sructures have unique properties, leading to new and high functionality, and to various applications. A
general overview on the Nano-science is presented emphasizing on the nano-fabrication and the
basic science aspects. Then the presentation is concentrated in one of the high functionality, namely
the functional nano scale devices, the socalled Nano electronics, which could be a challenge for the
sustainable development. In this presentation the areas of nano electronics considered are: The
Single Electron Transistor and its extension into I.C., and the Spintronics, the spin based electronics.
The problem of spin injection is discussed as an illustration of the problem encountered in spintronics.
It was found that, spin transport is fundamentally different from charge transport. Spintronics offers the
possibility of further miniaturization and of lowering power consumption than the present, charge
based, electronics could afford. The presentation is concluded with a suggestion on a possible
regional cooperation and on how we should meet the challenge.
Plenary Lecture 2
Newton Polyhedron and Estimation of Exponential Sums
Kamel Ariffin Mohd Atan
Laboratory of Theoretical Mathematics, Institute for Mathematical Research
Universiti Putra Malaysia
A p-adic Newton polygon associated with a polynomial
f ( x) ai x i is defined to be the convex
i
hull of the set of points (i, or dpai). Such a Newton polygon yields information on the number of roots
of f with certain p-adic sizes. This information is useful in the determination of the estimate of onevariable exponential sums. An analogue of the polygon is the Newton polyhedron. It is the lower
convex hull of the points (i, j, or dpaij) associated with a two-variable polynomial f ( x, y )
a x y
i
ij
j
.
i, j
The Newton polyhedron yields information on the p-adic properties of the zeros of the associated
polynomial. The indicator diagram is a device in the Euclidean plane that provides descriptions of the
properties of a Newton polyhedron. It is useful in the determination of p-adic sizes of common roots
of a pair of polynomials in Zp[x,y]. This is done by examining the combination of indicator diagrams of
the Newton polyhedrons associated with both polynomials. Information on the p-adic sizes of
common zeros of partial derivative polynomials associated with a two-variable polynomial in Zp[x,y]
obtained is used to determine the estimate of an exponential sum associated with the polynomial.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
22
Plenary lecture 3
National Strategic Framework of Thailand’s Nanotechnology and
Her NANOTEC Center
Wiwut Tanthapanichakoon and Weeraya Pakawech
National Nanotechnology Center, NSTDA, Thailand
The presentation gives an overview of the National Strategic Framework for Nanotechnology in
Thailand as well as an introduction of the 5-year Master Plan of the National Nanotechnology Center
(NANOTEC) under the National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA), Ministry of
Science and Technology. It concludes with a brief description of the current situation and future trend
of the platform technologies recently adopted by NANOTEC: nano-coating, nano-encapsulation,
nano-devices and computational nanoscience.
Plenary lecture 4
The Future of Statistical Process Control In Supply Chain Management: The Case At
Indonesian-Aerospace Industry
Maman A. Djauhari1 and Sutarno2
1Institut
Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
Industry (IAe)
2Indonesia-Aerospace
Indonesian-Aerospace Industry (IAe), initiated in 1948, produces many types of airplanes and
helicopters and is also a supplier of Airbus and many other international aircraft industries. As an
aircraft industry, IAe has also its own suppliers. Thus, IAe is part of a large supply chain management
(SCM) system and simultaneously it has its own system. All suppliers in those SCM systems are to
fulfill the requirements, which are multivariate in nature, of principal customer. In this paper we
present some multivariate setting problems faced by IAe, as a part of the SCM system at Airbus, that
we define as our future research direction in order to improve quality and productivity and reduce
costs.
Keywords: multivariate capability analysis, multivariate statistical process control, quality and
productivity improvement, supply chain management.
Plenary lecture 5
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
23
Singapore Synchrotron Light Source – A Regional Platform for Multidisciplinary Cross-Border
Research
Herbert O. Moser
Singapore Synchrotron Light Source,
National University of Singapore, 5 Research Link, Singapore 117603
Synchrotron radiation has become one of the premier experimental tools not only for research across
a great many of science fields, but also for widespread commercial applications. Funded by the
Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), the Ministry of Education (MOE) and the
National University of Singapore (NUS), SSLS is operated as a university-level research institute of
NUS.
Five beamlines and experimental facilities are operational including the
LiMiNT facility (Lithography for Micro/Nanotechnology) for micro/nanofabrication based on the
LIGA process network with the primary pattern generation being performed by means of electron
beam or laser beam writing, the
PCIT phase contrast imaging and tomography beamline that enables white light microimaging of
opaque samples, in particular, soft matter and tissue, the
SINS beamline (Surface, interface and nanostructure science) for the characterisation of electronic
and magnetic properties of advanced materials by means of X-ray photoemission (XPS), X-ray
absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS) and magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) in the soft
X-ray range from 50 eV to 1.2 keV, the
ISMI facility (Infrared spectro/microscopy) to characterise molecules and low energy electron
excitations in gases, liquids, solids and engineered materials, and the
hard X-ray beamline XDD (X-ray demonstration and development) that features the main common
X-ray methods such as diffraction (XRD), reflectometry (XRR), topography (XRT), absorption fine
structure spectroscopy (XAFS), and fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF).
One more beamline for electron and photon beam diagnostics (EPD) is nearing completion.
This portfolio of experimental facilities caters for a wide variety of disciplines including artwork
characterization, biomedical engineering, chemical engineering and catalysis, data storage,
environmental science and engineering, life sciences, materials science and engineering,
micro/nanotechnology, physics, semiconductor manufacturing, water technology, and zoology. SSLS’
userbase stands at more than 350 researchers, 83% local and 17% from abroad, and is steadily
growing.
SSLS’ own R&D programme comprises
micro/nanomanufacturing of devices, engineered materials, and 10 nm nanolithography, the
analytical characterization of materials and processes, and
work towards new synchrotron light sources using superconducting miniundulators.
In these fields, SSLS is providing both, research and commercial service.
A selection of recent achievements includes the development of the first electromagnetic
metamaterials in the THz spectral range up to a record frequency of 216 THz, the study of charge
transfer processes between organic molecules and metal surfaces by means of core hole clock
spectroscopy in the soft X-ray spectral range, and the characterisation of thin multilayer systems
for optical and magnetic data storage by means of X-ray reflectometry and grazing incidence
XAFS.
SSLS is inviting Malaysian and, specifically, Johor-based researchers to consider the wealth of
opportunities that wait for exploitation in the framework of a cross-border cooperation.
Keynote lecture 1
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
24
A Systematic Approach to Filtration Modeling
Ali J. Chamkha
Manufacturing Engineering Department, The Public Authority for Applied Education and Training,
P.O.Box 42325, Shuweikh, 70654 Kuwait
The work reported in this presentation represents a systematic development of a multiphase, multidimensional, continuum filtration model. General multi-dimensional mixture theory is discussed first.
This is followed by a systematic reduction of the general equations to the accepted deep-bed filter
formulation. Consequently, the assumptions inherent in that formulation are made clear. Next, a way
to derive the shallow filter equations from the deep-bed filter equations for idealized pressure and
mass transfer functions are reported. Then, attention is returned to the general deep-bed filter
equations and numerical results for various physical conditions are reported. Finally, important results
are summarized and suggestions for future research are given.
Keynote lecture 2
The Role of Statistics in Biological and Medical Sciences in Developing Countries
Asep Saefuddin
Department of Statistics, Faculty of Mathematics and Science, IPB, Bogor, Indonesia
Statistics is unavoidable in biology and medical research. It is due to the complexity of these areas
involving large population, many factors related to outcome variables, measurement aspect, clustering,
and other things that invite statistics to play its role in biology and medical sciences. This paper
describes briefly statistical method in these areas encompassing basic/standard statistics, modelling
application in estimating/predicting parameters, statistical conclusion, and recommendation. Due to
biology and medical research characteristics, statistics plays significant role mixed effect models both
linear and generalized linear models. Additionally, the experience of IPB (Bogor Agricultural
University) in statistical education and research is presented. IPB is the oldest Dept. of Statistics in
Indonesia has been contributing statistical concept originally in animal/plant breeding/quantitative
genetics and now expanding to other biological sciences, epidemiology, and medical sciences.
However, its contribution to molecular biology and geosciences is still limited. Hence, international
collaboration in the area of geo and bioinformatics is required.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
25
Keynote lecture 3
Recent Progresses in Membrane Gas Separation Technology
Takeshi Matsuura
Department of Chemical Engineering
University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
This paper gives a historic overview of the membrane gas separation technology. It was the discovery
of the asymmetric structure of the membrane in nineteen sixties that triggered industrial membrane
applications, in general, and membrane gas separation technology, in particular. Since then, many
efforts have been made to search for superior polymeric materials for further improvement of
membrane performance.
In 1991 Robeson set upper bounds in the selectivity-permeability plots of several gas-pairs by
compiling experimental data for a large number of polymeric materials. It was then realized that
although the boundary lines had been shifted to the desirable direction after nearly twenty years’
research efforts, the achievement had not been truly spectacular. Attention of membrane research
community was then focussed on inorganic materials, such as silica, zeolite and carbon, which
exhibited molecular sieving properties. Remarkable improvements have been made in terms of the
selectivity-permeability plot but the exploitation of these materials for practical applications remains
underachieved primarily due to their poor processibility.
In order to combine the superb molecular sieving effects of inorganic materials and the desirable
mechanical and processing properties of polymers, considerable efforts have been made recently to
fabricate composite membranes, also called mixed matrix membranes (MMMs), in which inorganic
particles are incorporated in host polymeric membranes. With respect to carbon material, attempts to
fabricate MMMs were further encouraged by the recent progress in nano-technology in general and
carbon nano-tubes in particular. Major performance achievements of MMMs are reviewed in this
paper.
Another attempt was to facilitate reactions by combining reactor and membrane separator in one unit.
These membrane reactors were developed for dehydrogenation, oxidative coupling, steam reforming
etc, i.e. for the reactions that had relevance for the petrochemical industry. Although industrial
applications of the membrane reactor are not fully explored for a number of reasons, this still remains
a very attractive concept.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
26
Keynote lecture 4
Fabrication of Platinum Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Shell as
Efficient Catalysts for Hydrogenation Reactions
Shigeru Ikeda, Takashi Harada, Natsumi Okamoto, Tsukasa Torimoto,2 and Michio Matsumura
Research Center for Solar Energy Chemistry, Osaka University, Toyonaka, 560-8531, Japan &
of Crystalline Materials Science, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University,
Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8603, Japan
2Department
Studies on catalysis of metal nanoparticles (MNPs) have attracted much attention because their
specific properties lead to inducing unique organic reactions. These MNP catalysts are usually
preserved by organic ligands to prevent coalescence and used in homogeneous systems. One of the
interests in designing practical catalysts is the heterogenization of MNPs by fixing on solid surfaces.
Although numerous supported MNPs have been proved to catalyze a variety of reactions, these are
still encountered by inevitable propensity of coalescence. In this study, we fabricated a ligand-free Pt
nanoparticle (2.2 nm) encapsulated in a hollow porous carbon shell of ca. 30 nm (Pt@hmC) as a
typical catalyst. Since the carbon shell not only acts as a barrier to prevent coalescence between Pt
nanoparticles but also provides a void space where organic transformation occurs on the naked
surface of the Pt nanoparticle, the Pt@hmC particle works as a robust and reusable heterogeneous
catalyst for hydrogenation reactions.
Keynote lecture 5
Revenue Management: Applying Optimization Concept in Business
Bahrom Sanugi
Department of Mathematics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Revenue management is considered to be one of the most successful applications of operations
research. It originated as a relatively obscure practice among a handful of major airlines and has
grown to its status today as a mainstream business practice with a growing supporting industry of
software and consulting firms. This presentation aims to provide an overview of its theory and
practice as it is carried out today, and to demonstrate the basic concepts used to enhance firm
revenues while selling the same quantities of products. Some of the major tools of revenue
management will be reviewed and the underlying concepts discussed. Opportunities to contribute to
research and practice in Revenue Management will also be highlighted.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
27
Keynote lecture 6
Numerical Conformal Mapping by the Charge Simulation Method
Kaname Amano, Dai Okano, Hidenori Ogata & Masaaki Sugihara
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Computer Science,
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Ehime University,
Department of Computer Science,
The University of Electro-Communications,
Department of Mathematical Informatics,
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo
Conformal mapping of multiply connected domains are familiar in the problem of potential flow past
obstacles. However, no simple method has been available for their computation till recently. We
have proposed a numerical method for the conformal mapping of an unbounded multiply connected
domain D exterior to closed Jordan curves onto the three types of canonical slit domains (Nehari,
1952), i.e., onto the parallel slit domain, the circular slit domain and the radial slit domain, subject to
the condition . These conformal mapping are applicable to the problem of the uniform flow, a vortex
flow and a point source flow, respectively. We here propose a numerical method for the same
domains subject to the different condition. These conformal mappings are applicable to the problem
of a dipole source flow, a vortex pair flow and a point source and sink flow. In the method, we
express the mapping functions in terms of a pair of conjugate harmonic functions and approximate
them, using the charge simulation method, by a linear combination of complex logarithmic functions.
The method is simple without integration and suited for domains with curved boundaries.
Keynote lecture 7
Symbolic Computing for the Working Scientist
Robert Fitzgerald Morse
University of Evansville, Evansville, IN 47722 USA
Since the first computers were built researchers have been interested in having these machines do
symbol manipulations and make exact calculations. Early examples include computing the cosets of
finitely presented group (1953) and symbolic integration (1961). It is clear that what we do formally as
scientists and mathematicians is manipulate symbols and make exact calculations. Essentially
factoring a polynomial is an exercise in symbol manipulation. Donald Knuth and Peter Bendix in their
seminal paper from 1967 formalize algebraic symbol manipulation in a precise manner such that it
can be done on the computer. In this talk we will consider symbolic computations within the context of
applications from engineering and science. In particular, aspect from computational group theory will
be highlighted
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
28
Keynote lecture 8
Nanomaterials for Energy Conversion
Muhamad Yahaya1, Muhamad Mat Salleh2
1School
of Applied Physics, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
43600 UKM, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
2Institute of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 UKM,
Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
A great challenge for material scientists is to provide clean, affordable and sustainable energy. Most
laboratories across the world continue to search for new materials and technique to generate energy.
It is believed that a solution to the global energy problem will require revolutionary new technology,
new approach as well as conserving the existing natural resources. Breakthroughs in nanotechnology
can be utilized in solving the energy problem and this will introduce new technology, which is more
efficient and environmentally friendly. In solar energy conversion, silicon based solar cell is still
leading the market demand. However, the efficiency of the cell is low and prohibits the industrial scale
application. The low cost solar cells are underdevelopment but the efficiency is not comparable with
silicon. In this context, nanotechnology can play an important role in the development of organic solar
cell, and in dye-sensitized solar cell, which shows a strong potential for commercialization. Solar
energy group at UKM has been actively involved in these areas, and in this seminar, we will present
a review works on nanomaterials for energy conversion.
Keynote lecture 9
Organic-less Separations: Let the Pressure and Temperature Work on
Mohd Marsin Sanagi, See Hong Heng and Wan Aini Wan Ibrahim
Separation Science Research Group, Department of Chemistry
Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Solvent polarity (dielectric constant) of a solvent varies with changing temperature. At elevated
temperature, pure water exhibits solvating power comparable to organic solvents such as methanolor acetonitrile-water mixtures at room temperature and ambient pressure. This can be used to great
advantage in separation techniques such as pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) and liquid
chromatography (LC). Good separations with acceptable column efficiencies are achievable at high
temperature (100C-200C) using water-rich and superheated water as the eluent. For example, high
temperature LC technique has been successfully applied to the separation of selected barbiturates
using 100% pure water as the eluent. High temperature PLE has been demonstrated to offer
outstanding extraction performance with a total of 4-fold reduction in total organic solvent
consumption and up to 16-fold reduction in the total extraction time required against the Soxhlet
extraction without significant loss in extraction efficiency. This paper elaborates on these potentials
and possibilities of creating efficient separation techniques with less dependence on organic solvents
while exploiting the power of temperature and pressure.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
29
RO1
Resistivity of Nanocrystals
Hasan Abu Kassim. Norhasliza Yusof and Keshav N. Shrivastava
Department of Physics, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur 50603, Malaysia
We find that the usual temperature dependence of the resistivity is considerably modified in going
from crystals to nanocrystals. The usual T 5 dependence is completely changed to the exponential of
negative inverse temperature. The quantized resistivity of h/2e 2, because of two electrons travelling
in opposite directions, acquires temperature dependence and the value for four electrons, h/4e 2, is
also expected to appear. The experimental data of resistivity of nanometer size Ag crystals has been
examined and found to be in agreement with the theory. The experimental data of single-walled
carbon nanotubes has also been examined to find how it depends on the length when tube diameter
is very small compared with the length. It is found that electrons are scattered along the cylindrical
length due to oscillations (phonons) in the tube. In the case of a thin nanocrystal the electrons exhibit
flux quantization. Although the phenomenon of flux quantization is usually discussed in the
superconductors, it does not require superconductivity. The single electrons can exhibit flux
quantization with unit charge as e and pairing with charge 2e is not necessary. In some experiments,
two electrons travel in opposite directions so that the unit charge 2e appears without
superconductivity.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
30
RO2
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
31
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
32
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
33
RO3
Improvement of Power Output by Selecting the Appropriate Material under Various Conditions
Javed Samia and M. A. K. Lodhib
a Department
b Department
of Space Science, University of The Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
of Physics, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX 79409, USA
Alkali metal thermal to electric converter (AMTEC) is device that converts the thermal energy into
electrical energy. Basically, it consists of two major parts electrolyte and electrodes. Beta alumina ((//
Alumina) solid electrolytes (BASE) is used as electrolyte and materials like Molybdenum (M 0),
titanium-nitride (TIN) rhodium-tungsten (RhW), Platinum-tungsten (PtW) etc. are used for electrodes.
Life’s time of electrode is defined as the time required to grow the grains of electrode to a diameter of
1 m . During operation of AMTEC electrode and keeping the efficiency higher it is necessary grain
growth should be minimal. The smaller grains combine with together to produce large grains and large
grains combine with large grains and produces another grain of large diameter. As a result area
spacing between the grains open and total grains decreases. The surface contact among the
electrode grain reduces. This in turn affect the power output pf AMTEC. In this work we present the
power dependence on the grain growth model parameters and look for the parameters of AMTEC
power output and its electrode materials.
RO4
Single Electron Transistor Structure Characterization Using Scanning Probe Microscopy
U. Hashim1, Sutikno2, Z.A.Z. Jamal3 and Y. Wahab4
1,2,3 School
of Microelectronic Engineering
Universiti Malaysia Perlis
4Physics Department, Faculty of Sciences
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Single electron transistor is able to be fabricated through either top down or bottom up method. Top
down fabricated single electron transistors have still been attracting a lot of interests of many
researchers at recent years. Most essential steps in top down fabrication of single electron transistors
such as nano structure etching and pattern dependent oxidation for nano structure shrinking. Both
those steps need surface morphology characterization and profile analysis. Three dimensions profile
analysis of nano structures is characterized by scanning probe microscopy. Variations of etching time
ranges from 55 s to 85 s and oxygen flow rate of 10 sccm up to 50 sccm are made to control nano
structure dimensions such as height, width, distance and gradient. Such controllable dimensions are
to provide established single electron transistor fabrication.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
34
RO5
Earth’s Atmosphere Link to Solar Activity
Jahanzeb Qureshi a, Benjamin Noll b and M.A.K.Lodhi a,b
aDepartment
of Space Science, University of The Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
of Physics, Texas Tech University, Lubbock TX 79409 USA.
bDepartment
The solar activity in the form of appearance of sunspots on its surface varies periodically on average
of eleven year cycle. As a consequence of this activity or independently there are other solar
phenomenon which vary with the same periodicity for example, the emission of radio waves,
ultraviolet, X-rays and high energy particles increases substantially during the solar maximum.
However, the total solar luminosity barely increases (0.1%) from solar minimum to solar maximum. If
solar activity does affect the Earth’s climate, it must be through some very subtle mechanism.
Perhaps the expansion of the Earth’s atmosphere with solar maximum may somehow cause changes
in the Earth’s weather. In this paper the effect of solar activity studied on the air density of Earth’s
upper atmosphere is presented. The Earth’s atmospheric density fluctuates by far more during the
maximum solar activity than what it is during the minimum solar activity on monthly and daily basis.
RO6
EM Wave Scattering from an Infinitely Long Cylinder
Ithnin Abdul Jalila and Rio Hirowati Sharifudinb
aDepartment
of Physics and bInstitute of Mathematical Sciences
University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
The scattering of electromagnetic(EM) plane waves, with TM and TE modes, from an infinitely long
cylinder has been considered. We used the T-matrix method and the repetitive summation of the
partial waves, Bessel and Hankel functions have been performed computationally. The quantities of
interest calculated are the scattering coefficients, extinction and scattering cross-sections and the
Mueller scattering matrix. We studied the variation of the quantities with the radius, refractive index
and the tilt angle of the cylider.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
35
RO7
Affective Computing on Mathematics Learning
Panimalar a/p Manoharan, Geraldine David
Faculty of Information and Technology
Multimedia University (Malacca Campus),75450 Ayer Keroh
Melaka
Mathematics as a subject has remained mysteriously difficult and unpopular for most university
students. This is despite the fact that no one is in doubt of its importance in almost all careers,
especially in the science and technological fields. Studies have shown that students that have positive
attitude toward mathematics tend to do well in the subject, and students that have negative attitude
toward mathematics tend to perform badly in the subject As a result, intensive research has been
done to determine students’ attitude towards mathematics in relation to different variables. The
method used to develop this system is a combination between 3D system model, affective computing
and three important topics in mathematics, to show the differences to learn mathematics in a very
easy way & user friendly manner as well as it will enhance the use of the Multimedia Learning System
(MMLS) used by students of Multimedia University (MMU). This way might increase interest among
students to learn mathematics because the system is using emotions and 3D system which is totally a
different way to learn using computer. This 3D system is another solution that will make mathematics
an easier subject to learn because graphs can be plotted in one coordinate system using different
colors and lighting conditions. Besides that the system can plot high quality equation and table based
graphs, zoom them, rotate, view at any angle and even animate. All types of coordinates are
supported for example Cartesian, cylindrical, spherical and many more.
RO8
Thermal Symmetry of Markovian Master Equation
B. A. Tay
Department of Physics, University Putra Malaysia, 43300 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
The Markovian quantum master equation of the reduced dynamics of a harmonic oscillator coupled to
a thermal reservoir is shown to possess a thermal symmetry. This symmetry is a Bogoliubov
transformation that can be represented by a hyperbolic rotation acting in the Liouville space of the
reduced dynamics. The Liouville space is obtained as an extension from the Hilbert space by
introducing tilde variables as carried out in thermo¯eld dynamics formalism. The angle of rotation
depends on the temperature of the reservoir, or the value of Planck's constant. The symmetry
connects the thermal states of the system between any temperature, including absolute zero that
contains a purely quantum effect, or between any value of Planck's constant.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
36
RO9
Si and SiGe Based Materials for Microelectronic and Photonics Applications
Md Roslan Hashim
Nano-Optoelectronics Research Lab, School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia 11800, Penang
Research in Si/SiGe for microelectronic and photonic applications is spurred by the idea of realizing
the integration of both photonic and electronic systems on a single chip. The technology is about
manipulation of the low cost and matured silicon technology while enjoying the benefits of bandgap
engineering to improve performance due to the inclusion of germanium into the silicon. In
microelectronic applications, silicon based technology has been in the market for more than 60 years.
The technology has matured itself to the extent that the low cost of production is always the main
advantage over other technologies. However Si only technology suffers from low operation frequency
compared with GaAs technology. With the introduction of a small percentage of Ge into Si, the
resulting SiGe devices can compete with GaAs technology in terms of device performance and at the
same time benefit from the low production cost of Si technology. With the maturity of Si based
technology in microelectronic applications, any new development on Si and SiGe for photonic
applications will hold the promise of realizing integrated optoelectronics on the same wafer. This
paper will discuss some developments in Si and SiGe based materials for optoelectronics applications
especially in our research lab. This will include fabrication and simulation works on Si/SiGe transistors,
Si/SiGe photodetector, Si/SiGe waveguides and porous silicon.
RO10
Thermal Diffusivity Determination of CuSe Metal Chalcogenide Semiconductor Using
Photoacoustic and Photoflash Technique
L.Y.C. Josephinea, Z.A. Talibb, W.M.M. Yunusb, Z, Zainalc, W.D.W. Yusoffb, and M.M. Moksinb
a
Universiti Pertahanan Nasional Malaysia, Kem Sungai Besi, 57000 Kuala Lumpur.
bDepartment of Physics, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM, Serdang.
c Department of Chemistry, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM, Serdang.
Copper selenide (CuSe) is an interesting semiconductor compound with various applications in solar
cells, super ionic conductors, photo-detectors, photovoltaic cells and Shottky-diodes. Our current
research efforts are directed towards an investigation concerning how to determine the thermal
diffusivity value of the CuSe metal chalcogenide semiconductor using the photoacoustic and
photoflash technique. The thermal diffusivity of CuSe was determined to be at 1.125 x 10-2 cm2/s with
sample thickness in the range of 0.0921 cm to 0.3445 cm using photoflash technique. The thermal
diffusivity obtained from photoacoustic phase fitting technique is 1.126 x 10 -2 cm2/s with sample
thickness in the range of 0.0456 cm - 0.1064 cm. Both techniques show the thermal diffusivity value
yielded good agreement with each other with the experimental error within 0.1%. The measured
results have shown that the thermal diffusivity value can be obtained independent of the sample
thickness. Our studies validates that the photoacoustic techniques is particularly suitable for the
measurements of sample thickness lower than 1 mm while the photoflash technique is suitable for the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
37
sample thickness higher the 1 mm. The PA technique has shown more attractive features as
compare to the photoflash technique. It has been proved to be more convenient, reliable and the
sample size required is very small for thermal diffusivity measurement. In the case of semiconductors,
the photoacoustic signal will provides us the information regarding the carrier-transport properties
besides the thermal parameters.
RO11
The Thermoluminescence Response of Ge-Doped Optical Fibres To X-Ray Photon Irradiation
Suhairul Hashim a, Ahmad Termizi Ramlia, D.A. Bradley b and Husin Wagirana
a
Department of Physics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor Darul Takzim, Malaysia
b Department of Physics, University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH, U.K.
Thermoluminescence dosimetry (TLD) is useful in medical application to determine dose received by
patient in cancer treatment. The interest is to introduce optical fibres as a new thermoluminescence
(TL) material. This paper presents preliminary results on the TL response reproducibility with various
doses and fading of Ge-doped optical fibres to X-ray photon irradiation. The optical fibres investigated
were typical single-mode fibres, with a core diameter of 130 µm. Prior to X-ray photon irradiation, the
calibration of diagnostic X-ray machine doses was made using ionization chamber. Dose rate of 58.31
mGy/s was delivered to the Ge-doped optical fibre using 49.8 kVp and 986µA current setting. During
irradiation, a retort stand was used to hold the plastic container in order to get uniform exposure. TL
response of Ge-doped optical fibre following X-ray irradiations was found to be linear in medical
radiotheraphy dose range up to 10 Gy. In fading studies, a total of 30 samples of Ge-doped optical
fibres were simultaneously irradiated, first to 2 Gy of X-rays and then subsequently to 10 Gy of X-ray
dose. The performance of Ge-doped optical fibres was then compared against the currently available
TL material i.e. TLD-700 (LiF:Mg,Ti). The average reading from five repeated measurements on both
types of TL material were recorded on a daily basis over a period of six days. After irradiation, and
until readout, the samples were kept in the lightproof container at a room temperature. Six days after
irradiation, the Ge-doped optical fibre exposed to 2 Gy showed a 26.2 % loss of signal compared to
the yield obtained 24 hours after irradiation, while at 10 Gy the fibre showed a loss of 19.7 %.
Conversely, for TLD-700 the respective values were 75.9 % and 36.1 %.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
38
RO12
Generation of QSAR Models for Cancer Treatment and Its
Application to Grouping the Photosensitizer Agents
Sharifuddin M. Zain, Noorsaadah Abdul Rahman, Neni Frimayanti
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Malaya
50603 Lembah Pantai, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) sometimes referred to as photo chemotherapy is widely used as a
curative and palliative treatment for a variety of solid malignancies. PDT involves the action of a drug
by visible light, resulting in the generation of cytotoxic oxygen species. In this study, Quantitative
Structure Activity Relationship (QSAR) has been used to develop a model that can correlate the
features of chemical compounds (photosensitizer) with their activity (i.e. inhibition concentration). The
models were constructed by first generating a series of descriptors from three dimensional
representations of the compounds in the data set. In this study, data set consists of 36 compounds
were then divided to a training set (24 compounds) for QSAR model development and a prediction set
(12 compounds) for model validation. Multiple linear regression analysis (MLRA) has been used to
generate the model. The best QSAR model has r2 value of 0.7246 and r2 (CV) value of 0.6419, thus
low predictive power. Removing some outliers (i.e. high residual value) was needed to improve the
model. A new model with r2 value of 0.8697 and r2 (CV) value of 0.7080 was generated. This model is
capable of predicting the inhibition concentration (IC 50) value of the excluded 12 compounds in the
prediction set with r2 value of 0.70. The Euclidean distance concept was applied to measure the
similarity between active compounds in the data set with the external set by using a set of descriptors
in the QSAR models. The validation of QSAR models were also carried out in a cluster analysis. It
can also be used for grouping the compounds base on their main properties in the QSAR models.
RO13
Conductivity and Dielectric Studies of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Lended with Zeolite – Technology in
Membrane Fuel for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC)
Sharifah Zuraiha S.M.Zain 1, Elias Saion 1, Muhammad Zaki A.R.2
Physics Department 1, Chemistry Department 2
Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia,
43400 Serdang, Selangor D.E.
Direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) has a strong potential to be a future source of electrical energy and
equally capable to handle its multiple stationary and mobile applications. The key component in
DMFC is its solid polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) and when DMFC works, PEM conducts
protons. Nafion® at present is the sole membrane among all other commercially available proton
conducting membranes that has the best proton conductivity but when used in DMFC, along with
proton conduction, the methanol fuel also crosses over from anode towards cathode of the cell. This
crossover of the fuel hampers the working of the cell and ultimately its output voltage reduces. This
defect of Nafion® paved way for the other membranes to be developed. In this work, the working
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
39
principle and applications of DMFC will be discussed. Using polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as the polymer
based, the membranes will be incorporated with zeolite dopant that acts as proton carriers. The
conducting property of the new composite materials for DMFC showed that the conductivity increase
as the temperature increase. The concentration of zeolite in this new membrane ranges between 10%
till 50%. Various temperatures ranges between 40°C till 70°C showed the increase of conductivity as
the temperature increase. The developed composite membranes are characterized by using SEM for
microstructure and impedance analyser for their proton conductivity.
RO14
Fuzzy Classification of Mountains Extracted from Multiscale Digital Elevation Models
Dinesh Sathyamoorthy
Science and Technology Research Institute for Defence (STRIDE),
Ministry of Defence, Malaysia.
Mountains are generally viewed as Boolean objects, whereby a terrain can be divided into two
classes: mountain and non-mountain. However, recent studies have shown that mountains are more
suitable to be viewed as fuzzy objects, whereby a mountain is defined as a region in the continuum of
variation of the surface of the earth. In this paper, the fuzzy classification of mountains extracted from
multiscale DEMs is performed. First, the lifting scheme is used to generate multiscale DEMs.
Mountains extraction is implemented on the generated multiscale DEMs. Fuzzy classification is
performed based on by the average of Boolean memberships of the extracted mountains features
over the scales of measurement. The proposed fuzzy classification method is useful for statistical
analyses and determination of sample schemes.
RO15
Studies on Carbon Dioxide Laser-Malaysian Light Hardwood (Shorea uliginosa, Dyera
costulata) and Plywood Interactions using Ultrasound, Scanning Electron Microscope and
Energy Dispersive X-ray
Izyani Karudin, Mohamad Suhaimi Jaafar, Khalid M.Omar Al-Hadithi and Nor Fadhlin Jaafar
Medical Physics Research, School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800, Minden, Penang,
Malaysia
Processing of wood by conventional mechanical tools like saws or planes leaves behind a layer of
squeezed wood only slightly adhering to the solid wood surface. Laser wood cutting could improve
the quality of cutting, obtaining precise and narrow cuts with little or no distortion to the surrounding
base material. The aim of this work is to provide a phenomenological understanding of interactions
between an intense CW CO2 laser with Malaysian light hardwoods. The capability of a 5.2 W low
power CO2 laser in cutting meranti bakau (Shorea uliginosa), plywood and jelutung (Dyera costulata)
has been studied. The woods were irradiated at different incident angles of ranged 0°, 10°, 20°, 30°,
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
40
40° and 50° and distances from laser source from 5 cm up to 30 cm. Surface morphology
observation with SEM as well as element and compounds identification with EDX has also been
carried out on Shorea uliginosa and Dyera costulata. The depth of penetration decreases with the
incident angle from 0° until 50°. The surface diameter of penetration for Shorea uliginosa and
plywood increases with the incident angle from 0° until 20°, after that it remained decreased until 50°,
while the surface diameter of penetration for Dyera costulata remained increases from 0° until 50°.
The degree of depth of penetration and surface diameter of penetration as a function of incident
angles are Shorea uliginosa>plywood>Dyera costulata. The depth of penetration and surface
diameter of penetrations for Shorea uliginosa, plywood and Dyera costulata decrease, as the power
density increases. Shorea uliginosa has the highest depth of penetration as it has produced the
smallest surface diameter of penetration while plywood has produced the depth and surface diameter
between Shorea uliginosa and Dyera costulata. Dyera costulata has the lowest depth as it has
produced the greatest surface diameter of penetration. The depth of penetration decreases with the
distance of wood samples from laser source from 5 cm until 30 cm. The surface diameter of
penetration increases with the distance of wood samples from laser source from 5 cm until 30 cm.
Melting was observed for all components of the wood structure and the breaking of molecular bonds
by direct interaction with a photon seems to be the dominating process. The EDX result shows that
irradiation reduced the percentage of the elements in wood samples. The analysis will assist the
manufacturing industry to choose a suitable laser system for cutting woods. Several chemical
processes contribute to the effect of the far infra red laser radiation especially the amount of absorbed
energy.
RO16
Effect of Temperature on DC Conductivity of CdSe
Amalina N. M , Z. A. Talib , W. M. D. W. Yusoff, Josephine L. Y. C. ,
Norfazlinayati O., Emma Z.M.T
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University Putra Malaysia,
43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
In recent years, much attention has been paid to semiconducting II-VI compounds because of their
optoelectronic properties and application. Among the II-VI semiconductors, Cadmium Selenide, CdSe
has been emerged as potential AIIBVI type candidate in optoelectronic device applications such as
fabrication of a photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells, non-linear optics, gas sensors, photoconductors,
thin film transistors, gamma ray detectors, large-screen liquid crystal display, photoluminescence
response, solar cells and etc. In this paper, effect of temperature on dc conductivity of CdSe is
discussed. The measurements were carried out on bulk samples of CdSe of uniform disc. Sandwich
method was used to determine the dc conductivity of CdSe in temperature range 200K – 500K. From
the experiment, the conductivity increase from 6.06x10-12 S/cm at 200K to 2.73x10-5 S/cm at 500K. So,
CdSe sample showed a semiconducting nature; electrical conductivity increases with increasing
temperature.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
41
RO17
Theoretical Analysis of Left-Handed Metamaterials using Adomian Decomposition Method
Mohd Rafie Johan
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Malaya
50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
In this presentation we review of the current state of the physical properties of the left-handed
metamaterials together with analytical results. This kind of materials has been studied recently due to
some non-intuitive and strange behavior. Using Adomian Decomposition Method, we were able to
solve analytically nonlinear electromagnetic wave equation in left-handed metamaterials.
1. Introduction
Materials with simultaneously negative dielectric permittivity 0 and magnetic permeability
0 in a certain frequency range demonstrate many interesting and unusual physical properties
[1] and are believed to have strong application potential [2]. Some of the properties, such as negative
refraction, were experimentally confirmed [3]. Several recent studies showed that the nonlinear wave
interaction in left-handed materials has peculiar features [4-5].
2. Formulation
In this paper we study coupled nonlinear Schrodinger equations for electromagnetic wave propagation
in nonlinear left-handed materials. For isotropic and homogeneous nonlinear left-handed materials,
the Maxwell’s equation for electric and magnetic fields lead naturally, within the slowly varying
approximation to a system of coupled nonlinear Schrodinger equations. The equations are:
2 E
2 H
2E
t
2
2H
t
2
2P
t
2
.E
2M
t
2
NL H
t
t
.H
NL t E PNL
NL E
t
t
NL t H M NL
(1)
(2)
Eqs.(1) & (2) were solved analytically using Adomian Decomposition Method [6].
3. Conclusion
We found that Adomian Decomposition Method allowed much accurate and more efficient solution
compared to other method like finite element, …etc.
4. References
[1] V. G. Veselago, Sov. Phys. Usp. 10, 509 (1968).
[2] Optics Express, sepecial issue on Negative Refraction and Metamaterials, 11, 639-755 (2003).
[3] D. R. Smith & N. Kroll, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2933 (2000).
[4] I. V. Shadrivov et al., Phys. Rev. E 69, 016617 (2004)
[5] V. M. Agranovich et al., Phys. Rev. B 69,165112 (2004)
[6] G. Adomian, J. Math. Anal. App. 135 (1988) 501-544.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
42
RO18
On The Expression of Exoticity of A Slowly Rotating Wormhole
Anuar Alias, Ithnin Abdul Jalil and Hasan Abu Kassim
Department of Physics, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
For a wormhole to be traversable it is necessary to investigate the effect of a slowly rotating wormhole
on the exoticity of the exotic matter. From the null energy condition we can derive the expression of
exoticity and with the inclusion of the rotating effect we can determine whether it is of any benefit to
reduce the exoticity and thus reduce the requirement of the exotic matter. Having derived the exoticity
expression, we can specifically check the exoticity at the throat and find the relationship between the
flaring out characteristic of the wormhole and the exoticity.
RO19
A Study of One Space Dimension Generalised Order Partial Differential Equations of the
Parabolic Type
1
Ithnin Abdul Jalil and Rio Hirowati Shariffudin
2
1
Department of Physics,Faculty of Science, University of Malaya,
2Institute of Mathematical Sciences ,Faculty of Science, University of Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
The one space dimension generalized order parabolic equation is given by the equation
over a finite interval and with xL < x < xH and t > 0 with 1< a < 2. The space fractional equation above
is approximated by a Riemann fractional derivative. The shifted Grünwald approximation procedure is
used at all time levels. Using the Crank-Nicolson method which is implicit in nature, the resulting
matrix is lower triangular with non-zero elements on the super diagonal. Our work emphasizes on
using even number of simulation points because we observe that on using an even number of interior
points we are able to simulate two unknowns at any one time in a Gauss-Seidel methodology. This
method is chosen because of the ease in dealing with inverses of 2x2 matrices. From the study we
will be able to understand the stability and convergence of the iterative procedure.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
43
RO20
Core Calculation of 1 MW Reactor Triga Puspati (RTP) Using Continuous Energy Method of
Monte Carlo MVP Code System
Julia Abdul Karim and Adnan Bokhari
Reactor Facility Unit, Malaysian Nuclear Agency (Nuclear Malaysia)
43000 Kajang,Selangor, Malaysia
The RTP is a light-water moderated from TRIGA MARK II type with having power capacity of 1MWatt.
It is built in 1979 and attained the first criticality on 28 June 1982. The RTP was designed mainly for
neutron activation analysis, small angle neutron scattering, neutron radiography, radioisotope
production, education and training purposes. It uses standard TRIGA fuel developed by General
Atomic in which the zirconium hydride moderator is homogenously combined with enriched uranium.
It has cylindrical core but not in periodically in its lattice structure, which possibly locates 127 of fuel
elements. Both of the coolant and moderator uses light water system and the reflector was made
from high purity graphite. Because of this research reactor’s power is relatively small compared to the
power reactor; it uses natural convection for its cooling system. To ensure the integrity of the core,
fuel shuffling have been made for several times. Until now, there are 11 configurations of the core
and recently has achieved the 12th configuration. This paper will described the RTP core calculation
using Monte Carlo MVP code system. MVP is a general multi-purpose Monte Carlo codes for neutron
and photon transport calculation based on the continuous energy and multi-group methods. In MVP,
RTP core has been modeled using cylinder along the z-coordinate geometry and its cross section
data has been calculated beforehand. The objectives of the calculation are to calculate the
multiplication factor values (keff), fission density and flux distribution from the tally data.
RO21
DC Conductivity Studies in Conducting PPy Polymer with Applied Temperature
Norfazlinayati O.1, Z. A. Talib1, A. Kassim2, Josephine L.Y.C.1, and A. H Shaari1
Department of Physics1, Department of Chemistry2,
Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia,
43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor
Conductive polymers have generated a great deal of interest towards the applications to produce
simple and faster devices. Polypyrrole (PPy) conducting polymer is the most extensively studied
polymer due to the high conductivity and optimal mechanical properties. In this paper, the PPy
conducting polymer was prepared by chemical reaction method using Iron (III) Chloride
6-hydrate
(FeCl3.6H2O) as a dopant. The effected of temperature on the surface dc conductivity for various mole
ratio of FeCl3/PPy was measure by using four probe method. The voltage was increased with
increasing current for all of measurements in the value range between 10 mA and 50 mA from room
temperature to 380K. This result also indicated that conductivity increased as temperature increased.
However, after the maximum temperature, 340K the conductivity decreased with increasing
temperature. It is observed that both concentration of the dopant and temperature influenced the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
44
conductivity value for PPy conducting polymer. The activation energy for this polymer is also
examined.
RO22
The Synthesis, Characterization and DC Electrical Conductivity of Poly[Di(2,5-Dimercapto1,3,4-Thiadiazole)-Metal] Complexes
Ali G. El-Shekeil , Hussein M. Al-Maydama and Omar M. Al-Shuja'a
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Sana’a University, Yemen.
P. O. Box 12463, Sana’a, Yemen
Poly[di(2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole)]-metal complexes of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) were
synthesized by the reaction of 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole (6.6 mmol) with anhydrous cobalt,
nickel, copper and zinc chlorides (3.3 mmol) in absolute ethanol under reflux for 24 hours. The
products were characterized by elemental analyses, electronic spectra, FTIR spectroscopy, as well as
thermal analyses (TGA and DTA) and X-Ray diffraction. The DC electrical conductivity variation of the
poly[di(2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole)-metal] complexes were studied in the temperature range
300-500 K as annealed for 24 hours at 100 ºC and after doping with 5% I2 for comparison. An attempt
is made to interpret the DC electrical conductivity behavior and thermal properties to doping,
annealing, structure and metal used.
RO23
Inductively Coupled Plasma Reactive Ion Etching on GaN in Cl2 Containing Plasmas
Siti Azlina Rosli and Azlan Abdul Aziz
1Nano
Optoelectronics Research and Technology Laboratory (N.O.R)
School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
In this study, the plasma characteristics and GaN etch properties of inductively coupled Cl 2/Ar
plasmas were investigated. It has shown that the results of a study of inductively coupled plasma
(ICP) etching of gallium nitride by using Cl2/Ar is possible to meet the requirement (anisotropy, high
etch rate and high selectivity, simultaneously. We have investigated the etching rate dependency on
the percentage of Argon in the gas mixture, the total pressure and DC voltage. We found that using a
gas mixture with 40% of Ar, the optimum rate of GaN was achieved. The etch rate were found to
increase with voltage, attaining a maximum rate at -487V. The addition of an inert gas, Ar is found to
barely affect the etch rate. Surface morphology of the etched samples was checked by scanning
electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. It was found that the etched surface was
anisotropic and the smoothness of the etched surface is comparable to that of polished wafer.
Introduction
Group III nitrides have attracted much attention recently because of their wide spectrum of potential
applications ranging from optoelectronic devices for the blue ultraviolet spectral region [1] to high
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
45
temperature devices [2]. The high bond strength of gallium to nitrogen presents a challenge to
achieving good etching characteristics in GaN. A number of methods have been employed to etch
GaN and its related compounds, including photochemical wet etching [3] dry etching utilizing high
density plasmas [4] and conventional reactive ion etching [5]. However, to fabricate GaN-based
optoelectronic devices successfully, reproducible etching processes with high etch rate and vertical
etch profile are required. Recently, dry etching techniques using high density electron cyclotron
resonance (ECR) plasmas or chemically assisted ion beams (CAIBE) have been employed to define
device features with controlled profiles and etch depths [6-8]. While most studies on dry etching are
focused on the etch properties related to the etch equipment and etch process parameters such as
plasma chemistry, source power, bias voltage, etc., detailed studies on the dry etching characteristics
of GaN-based materials based on the plasma diagnostic and surface analysis have been little
reported.
Materials and Methods
The material used here is nominally n-type GaN wafers. Four samples were used and prepared using
similar photolithographic process. Before patterning, the samples were cleaned, dipped in DI water
and dried using N2 gas. Photo resist was spin coated onto all samples, forming ~ 1.5 µm layer. After
that, all of them were etched by inductively coupled plasma etching using various gases in Oxford
Plasma 80 system. The gallium was etched using combination of Cl 2/Ar at operational pressure for 20
mTorr while ICP power, substrates temperature and RF power were fixed at 100 W, 17C and 600 W,
respectively. For this experiment, the Ar flow rate was varied from 0 sccm to 60 sccm meanwhile the
Cl2 flow rates at 60 sccm. After that, an individual sample was loaded into the chamber, centered on
platters with the oxidized side exposed to the upper electrode. Immediately after samples removed
from etching system, they were dipped into acetone to remove the photoresist. The etch rates were
measured from the depth of the etched features with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) after the
removal of the PR layer. Surface morphology, etch anisotropy, wall angle and sidewalls undercutting
of the etched GaN was evaluated with SEM model JSM-6460 LV while ULTRAObjective AFM is used
to measure the surface roughness.
Results and Discussion
For these experiments, etch rates were studied as a function of addition of Ar and DC bias. Prior to
etching patterned samples, a simple set of experiments were conducted to get an understanding of
how changes in Ar affect the etch rate. It was found that the etch rates were found to increase
significantly between 0 sccm to 60 sccm of Ar, peaking around 20 sccm and then dropping off slightly
around 24 sccm. For gas Ar flow rates of 24 sccm and higher, it was found that the etch process
decrease.
Fig. 3
Cross-sectional SEM micrograph of the etched patterns; (a) 20 mTorr. Process condition:
Cl2/Ar = 60/20 sccm, RIE power = 100 W, RF Power = 600 W, electrode temperature = 17 C.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
46
Conclusion
We have shown the effects of Ar to Cl2 interaction in ICP process. The highest etch rate obtained at
20 sccm of Ar. It was explained as if the Ar concentration is high (> 30%) polymerization occurs on all
surfaces and etching stops. We have also shown that DC voltage decreased as the flow rate of Ar
increased. Furthermore, the etched surface is of anisotropic type and has smooth sidewalls.
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted under IRPA RMK8 strategic research grant. The support from Universiti
Sains Malaysia is gratefully acknowledged.
References
1. S. Nakamura and G. Fasol, The Blue Laser Diode: GaN Based Light Emitters and Lasers
(Springer, Berlin, 1997).
2. Q. Chen, M. Gaska, M. Asif Khan, M. S. Shur, A. Ping, I. Adesida, J. Burm, W. J. Schaff, and L. F.
Eastman, (1997), Electron. Lett. 33, 637.
3. C. Youtsey, I. Adesida, and G. Bulman, Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 2151 (1997).
4. R. J. Shul, G. B. McClellan, S. J. Pearton, C. R. Abernathy, C. Constantine, and C. Barratt,
(1996), Electron. Lett. 32, 1408.
5. D. Basak, M. Verdu, M. T. Montojo, M. A. Sanchez-Garcia, F. J.Sanchez, E. Munoz, and E. Callej,
(1997), Semicond. Sci. Technol. 12, 1654.
6. C. Caillat et. al, Solid State Electronics, 46 (2002).
7. P.J Matuso, B.E.E Kasteimeier, J.J. Buelens, and G.S Oehrlein, (1997), J. Vac. Sci. Sci. Technol.
A, 15, 4.
8. I. Hassan, C.A. Pawlowics, L.P Berndt, and N.G. Tarr, (2002), J. Vac. Sci. Sci. Technol. A, 20, 3.
RO24
Interactions and Characterizations of Shorea Collina Spp. and Parashorea Sp. using CO2 Laser
Nor Fadhlin Jaafar, Mohamad Suhaimi Jaafar, Khalid M. Omar and Izyani Karudin
Medical Physics Research, School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia,
11800 Minden, Pulau Pinang
Carbon dioxide laser (CO2 laser) was one of the most efficient infrared lasers. In this study, CO 2 laser
is used to penetrate the balau (Shorea Collina Spp.) and gerutu (Parashorea Sp.).Correlation
between average surface diameter and average depth penetration with time, incident angles and
power density is obtained. Lasing process occurred between 9 to 12 minutes, 0° to 50° incident
angles and power density range from 10 W/cm 2 to 23 W/cm2. After laser exposure, each of the wood
samples is immersed in water and ultrasound technique is used to measure the surface diameter and
depth penetration of the burned portion. For both samples, the time of exposure is varies linearly with
depth penetration non-linearly with surface diameter. Power density of the laser is inversely
proportional to the surface diameter and depth penetration.Layer of charcoal appeared only on
Parashorea Sp. surface. This is due to the fact that Shorea Collina Spp. has a high density of 800-880
kg/m3 compared to Parashorea Sp. with 640-770 kg/m3. The finding shows that the most suitable
angle for fine cutting with smallest surface diameter and deepest depth penetration is 0˚. This is due
to the angular divergence in the laser beam, formed within the near and far zone. In the far zone,
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
47
angular divergence increases with diameter. The findings obtained can be utilized in the selection of
laser parameters for fine cutting of Shorea Collina Spp. and Parashorea Sp.
RO25
Plasmid Library Production from Local Medicinal Plant, Gardenia jasminoides
Zaidah Rahmat, Nor Kamila Kamaruzaman and Siti Intan Rosdianah Damis
Biology Department, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai,
Johor, Malaysia.
Attributing approximately 90% of the newly discovered pharmaceuticals, medicinal plants continue to
be a powerful source of new drugs. One such local medicinal plant, Gardenia jasminoides, is gaining
use in therapeutic aid for alleviating human ailments. Advancement in biotechnological methods of
DNA-based study facilitates the determination of the suitable restriction enzyme for genomic DNA
digestion and comparison of transformation method towards the plasmid library construction and
subsequently, the screening procedure. Partial digestion of genomic DNA was achieved with HindIII
restriction enzyme after 1 hour and 15 minutes digestion. Chemical transformation was a better
method for library construction compared to Magic E.coli transformation method, giving higher
transformation efficiency at 4 x 106 as compared to 8 x 104 for the latter method. PCR was used to
evaluate the library in which 77% clone of various sizes were obtained from the library.
RO26
Engineering the Maltose Binding Protein for Biosensing Application
Shafinaz Shahir1, Tony Cass2
1
Biology Department, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor 2
Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Imperial College London, South Kensington Campus, London
SW7 2AZ, United Kingdom
The aim of this work is to the develop a reagentless fluorescent sensing system for the detection of
metal ions using genetically engineered metal binding variants of the maltose binding protein (MBP)
as the biorecognition element. MBP is a member of the periplasmic binding proteins that typically
adopt two conformations: an open form in the absence of ligand and a closed form upon ligand
binding. This ligand-mediated conformational change forms the basis of the sensing system. In
developing such as sensor system this work will demonstrate the use of rational protein engineering
techniques to (1) adapt the MBP as reagentless fluorescent sensors by coupling the binding
characteristics of the protein to a single environmentally sensitive fluorescent group and (2) change
the specificity of the MBP by introducing metal-binding sites based on the designs previously
described in the literature into the receptor pocket of the protein. Protein engineering is defined as the
ensemble of methods that allow the modification of the gene that codifies for a protein with the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
48
purpose of generating mutants or variants with the desired properties. The immobilisation of
biomolecules is also a crucial aspect in the design and construction of biosensors. Hence, the use of
biotin as a tag will be investigated as a method for site-specific attachment of the proteins onto a solid
support. The resulting tagged metal-binding MBP variants will be assessed for their ligand binding
properties via metal ion dependent fluorescence intensity changes in solution. The possibility of
extending the sensor system to a solid platform will then be examined by site-specifically immobilising
the tagged metal-binding MBP variants onto glass slides in a microarray format.
RO27
Photocatalytic Degradation of Dye Pollutants using SiO 2/TiO2 Catalyst
Nazwin Ahmad
Mineral Research Centre, Department of Mineral and Geosdence,
Jalan Sultan Azlan Shah, 31400 Ipoh. Perak, Malaysia.
The photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) in aqueos solution
with SiO2/TiO2 as catalyst have been carried out using UV light. The SiO 2/TiO2 catalyst was prepared
by deposition of titanium dioxide (TiO2) aver a silica gel as a support by hydrolysis and condensation
reaction of TiO2, There are significant differences in adsorption of dyes on SiO 2/TiO2 catalyst. The
effect of various parameters such as catalyst loading and pH has been determined. The photocatalytic
degradation rate of MB and MO using SiO2/TiO2 catalyst were faster than using pure TiO2. The
effects of the calcination temperature and the TiO2 loading on the phdtooatalytic activity of SiO2/TiO 2
catalyst were also discussed.
RO28
Optical Characterization of Au Thin Film Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Technique
I. Nurul Izrini, M.Y.W.Mahmood, A.T. Zainal, A.W. Zaidan
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang,
Selangor, Malaysia
The optical constant for various thickness of Au thin film was studied using Kretschmann method of
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technique. The optical properties of very thin Au films have been
evaluated by Fresnel analysis with optical boundary condition pertaining to the SPR at the gold-air
interface. It is observed that the optical constants of real part (ε r) not dependent to the Au film. For the
thickness below 45 nm, εr values are at the range of -8.854 to -8.678 while the thickness above 45 nm,
the values of εr is at the range of -10.448 to -10.057. For the imaginary part (εi), the values are
constant with the thickness which is between 1.227 and 2.110. The optimum SPR excitation
conditions and instrumental sensitivity was achieved at a sharply defined thickness of 49.32 nm. With
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
49
decreasing film thickness below 45 nm, the resonance angle starts to shift to larger values. A
substantial increased of the intrinsic resonance broadening parameter is observed below 61nm
associated with an increasingly asymmetric SPR line shape.
RO29
Acidity Study of Mesoporous Alumina containing para-toluenesulfonic Acid Stabilized by noctadecyltrichlorosilane
Sheela Chandren1, Zainab Ramli1 and Hadi Nur2
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
2Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Aluminas are extensively used as catalyst, catalyst support and adsorption applications. With the
development of large molecule hydrocarbon processes, mesoporous alumina which possesses high
surface area with narrow pore size distribution has received a great deal of attention. Although
mesoporous alumina possesses high mechanical and thermal stability, but its acid properties lack
Bronsted acidity and showed only Lewis acid sites. In this study, para-toluenesulfonic acid (TsOH) is
impregnated on mesoporous alumina in order to introduce Bronsted acidity. In order to avoid the
leeching of TsOH from the mesoporous alumina, the surface of the samples were modified by the
alkylsilylation of n-ocatdecyltrichlorosilane (OTS). The acidity of the samples that were coated and not
coated with OTS were then determined using FTIR-Pyridine. The acidity study shows that only the
sample coated with OTS showed the presence of Bronsted acidity, while samples without the surface
modification by OTS displayed only Lewis acid sites. This proved that by modifying the surface of the
TsOH impregnated on mesoporous alumina with OTS, the Bronsted acidity on mesoporous alumina
by impregnation of TsOH is preserved.
RO30
The effect of Attachment of Polyaniline on Stannic Oxide-Titanium Dioxide Coupled
Semiconductor in Photocatalytic Oxidation of 1-Octene
Hadi Nur, Izan Izwan Misnon, Lim Kheng Wei
Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Stannic oxide-titanium dioxide (SnO2-TiO2) coupled semiconductor photocatalyst loaded with
polyaniline (PANI), a conducting polymer, possesses a high photocatalytic activity in oxidation of 1octene to 1,2-epoxyoctane in the presence of aqueous hydrogen peroxide. The photocatalyst was
prepared by impregnation of SnO2 and followed by attachment of PANI onto a TiO2 powder to give
sample PANI-SnO2-TiO2. The electrical conductivity of the system becomes high in the presence of
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
50
PANI. Enhanced photocatalytic activity was observed in the case of PANI-SnO2-TiO2 compared to
PANI-TiO2, SnO2-TiO2 and TiO2. A higher photocatalytic activity in the oxidation of 1-octene on PANISnO2-TiO2 than SnO2-TiO2, PANI-TiO2 and TiO2 can be considered as an evidence of enhanced
charge separation of PANI-SnO2-TiO2 photocatalyst as confirmed by photoluminescence
spectroscopy. It suggests that photoinjected electrons are tunneled from TiO 2 to SnO2 and then to
PANI in order to allow wider separation of excited carriers.
RO31
15
N Nitroxide Free Radicals Imaged by Field-Cycled Proton-Electron
Double-Resonance Imaging (FC-PEDRI) at Low Magnetic Field
Chittakorn Polyon1, David J. Lurie2, Wiwat Youngdee1, Chunpen Thomas1 and Ian Thomas1
1Department
2Bio-Medical
of Physics, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, 40002, Thailand
Physics, School of Medical Sciences, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, AB252ZD, UK
Field-Cycled Proton-Electron Double-Resonance Imaging (FC-PEDRI) was used to indirectly image
15N nitroxide free radicals, from the difference image, by saturation of Electron Paramagnetic
Resonance (EPR) transitions at a lower field and performing proton Magnetic Resonance Imaging
(MRI) at a higher field with and without EPR irradiation. To locate EPR transitions, Field-Cycled
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (FC-DNP) experiments were performed on a 5.5 ml aqueous solution
sample of 1 mM 15N D17 TEMPOL (a 15N nitroxide system) at EPR frequencies between 45 and 133
MHz. FC-PEDRI experiments were performed at low magnetic field (1.1-5.7 mT) for EPR with a
proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) detection field of 59 mT (at 2.495 MHz). For this EPR
frequency range, the lowest EPR power deposited in the sample was taken at a lower frequency of
52.52 MHz, but the image quality was poor. This image could be improved when taken at a higher
frequency of 132.5 MHz but the EPR power deposited in the sample was higher. However, the best
image quality could be obtained at the lower frequency of 123.785 MHz with a lower EPR power
deposition.
RO32
Synthesis of Zeolites from Low Grade Kaolin
Shamsul Kamal Sulaiman
Mineral Research Center Department of Minerals and Geoscience, Jalan Sultan Azlan Shah 31400,
Ipoh, Perak, Malaysia
Low grade kaolin from Bidor area was characterized and used for the synthesis of zeolites. The
synthesis method used was a hydrothermal treatment with NaOH activation at low temperature. The
kaolin was pretreated with thermal treatment to make it more reactive in the hydrothermal process. In
hydrothermal treatment, transformation phenomena involved the dissolution of metakaolinite and
quartz, and subsequent formation of zeolite A which then slowly transformed to zeolite HS. As
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
51
temperature and reaction time increased, zeolite A transformed to more stable zeolite P. The
synthesis product from the material was tested for potential application in removal heavy metal and
ammonium ions from wastewater and preliminary treatment of landfill.
RO33
Stress Variations due to Different in Stem Length on TKR
1
1
1
M.I.Z. Ridzwan , M.S. Mohidin , Solehuddin Shuib , and A.A. Shokri
2
1
School of Mechanical Engineering, Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 14300 Nibong
Tebal, Seberang Perai, Malaysia
2
Department of Orthopedics, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia,
16150 Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia
The purpose of this study was to observe the effect in stress distributions when varying the stem
length in total knee replacement (TKR). The stem was varied between 41 to 58 mm long and it was
respectively similar with the tray size started from number 1 to 6. The implanted model included
cortical and cancellous bones, tibial tray and polyethylene (PE) insert. They were assembled in
SolidWorks, then imported to ANSYS software and analysed using finite element method. The finite
element (FE) models were smart meshed with SOLID92 element type. Compressive load was applied
on top of PE insert at both of its medial and lateral sides with the magnitude was similar as during
standing position. Bones distal end was rigidly fixed from any translations and rotations. Results were
taken along medial, lateral, anterior and posterior regions started from proximal end for both stem and
cancellous bone. In implant, stresses were distributed almost similar for all locations except in anterior
position where it was placed relatively far with the applied load. Thus increased the stress due to
moment rather than in normal stress. For cancellous bone, stresses were shielded at proximal end but
it increased when it reached the distal end. However the maximum stresses for any materials were
lower than its yield strength.
RO34
Supported SnO2-Based Ion Exchange Systems for the Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals From
Industrial Effluent
Chin Kee Chin, Jamaludin Karim, Ismail Ibrahim and Hamdan Yahya
Pusat Penyelidikan Mineral, Jabatan Mineral & Geosains
Jalan Sultan Azlan Shah, 31400 Ipoh, Perak, Malaysia
Malaysian Rice Husk Ash (RHA) has been selected as silica source in synthesis of Zeolite X. Silica
from RHA are found to be very reactive and feasible in producing Zeolite X. Zeolite are known to
exhibit excellent sorptive and ion exchange properties. These properties render the zeolite mineral to
be used as suitable active support materials for making supported SnO 2 - based ion exchange system.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
52
A comparative study between Zeolite X and tin supported Zeolite X by ion-exchange was done for
removing toxic heavy metals from industrial effluents. As a result of tin coated onto Zeolite X, the ionexchange properties to remove heavy metals were not improved.
RO35
Feasibility Study
Refractory Castable for Ladle Lining in Ferronickel Mining Industries
Hendra Wijayanto and Faisal Alkadrie
Processing and Engineering Department Nickel Mining Business Unit,
PT ANTAM Tbk, Indonesia
Ladle is a cylindrical steel container that is used for storing ferronickel crude from smelter to be
transported to refining process. Crude temperature is around 1480 oC and for handling condition like
that, ladle shell must be protected by material which has good ability to hold high heat effect. In ladle
construction, ladle wall consist of shell and lining refractory, where shell is made from SUS 400 and
lining refractory is used refractory brick. Refractory brick has low conductivity which is placed in inner
surface of shell. The main function of refractory brick is to hold high heat effect temperature from
crude to the shell. Refractory brick has an expensive price and need a specific time to install it in ladle,
as we know that we have to always make improvisation to reduce production cost, and one of effort is
changing brick refractory with refractory castable where it has same conductivity even lower than brick
refractory and of course it price is cheaper than brick refractory as well as it need shorter time
installation. For make sure changing process is secure, authors have to make some theoretical
analysis, computational simulation analysis with software. The first step of methodology is theoretical
analysis including chemical and heat transfer analysis. Chemical analysis is done to analyze reaction
that occurred between refractory castable compound and slag of ferronickel crude compound.
Reaction between refractory castable compound and slag of ferronickel crude are influenced by
thermodynamic and kinetic reaction. Heat transfer analysis is done to analyze heat transfer that
occurred between ferronickel crude, refractory castable and shell. The second type of methodology is
computational simulation analysis with software. In this step authors use software to analyze and
simulate chemical reaction and heat transfer process in computer. After both step of methodology are
finished, authors can make comparison between both result, and finally can make conclusion from it.
If from theoretical analysis and computational simulation analysis are obtained good and secure result.
The changing process of refractory brick with refractory castable can be done.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
53
RO36
Selective Oxidation of Hydrocarbon by Heterogeneous Catalysis
Y.H. TaufiqPutra Laboratory for Catalysis Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Selective catalytic oxidation is one of the major areas of industrial petrochemical production. Indeed,
more than 60% of the chemicals and intermediates synthesized via catalytic processes are products
of oxidation. These products made through oxidation mechanism are usually key intermediates for
subsequent processes (eg. monomers, comonomers, or modifiers for polymer). One of the most
important application of selective oxidation catalysis is the functionalization of hydrocarbons. In this
lecture, the synthesis of maleic anhydride from n-butane which is the only commercialized application
of alkane selective oxidation by heterogeneous gas-solid catalytic processes will be discussed.
Vanadium phosphate is almost exclusively used as catalyst for this reaction with the active phase of
vanadyl pyrophosphate. Several fundamental aspects of this catalyst such as the chemistry of
preparation, the nature of the active phase and active centres, the role of different oxygen species,
structural-activity relationships, mechanochemical pretreatment and the role of dopants will also be
described.
RO37
Characteristic of AC Conductivity in Ternary Zinc Oxide Calcium Oxide Phosphate Glasses
Z.A. Talib, S.F. Khor, E.Z.M. Tarmizi, H.A.A. Sidek, W.D.W. Yusoff,
W.M.M Yunus and A.H. Shaari
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Binary calcium phosphate and ternary calcium phosphate containing ZnO glasses have been
synthesized by melt quenching technique over a wide composition range. The electrical properties of
theses glasses were investigated by ac impedance spectroscopy from 10 mHz to 1 MHz for
temperatures ranging from room temperature to 300 oC. In this work, ternary glasses with mole
fraction x = 0.01 to x =0.09 with interval of 0.02 and binary glasses with mole fraction x = 0.05 to
x =0.4 with interval of 0.05 were investigated. The conductivity of both samples show dispersive
behavior at lower temperatures while at higher temperatures the conductivity is almost constant at the
lower end of the frequency, approaching the dc conductivity limit and rises rapidly as the frequency is
increased. We also noted that as the frequency is increased, the conductivity shows a dispersion
which shifted to higher frequencies with the increase in temperature. The dc conductivity ( dc ) was
found to increase with higher temperatures. The impedance plots show only one semicircle indicating
the presence of one type of conduction mechanism. Activation energy, E and E for
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
54
ZnOx CaO0.3 x P2 O5 0.7
were found to be slightly higher than CaOx P2 O5 1 x . Bulk resistivity
( ) decreases with increase in temperature for the both materials. However, bulk resistivity for
ZnOx CaO0.3 x P2O5 0.7 is higher than CaOx P2O5 1 x . Increasing ZnO concentration will
increase ' ' value of ZnO x CaO0.3 x P2 O5 0.7 when compared with the CaOx P2 O5 1 x . The
' values decrease as temperature is increased irrespective of ZnO doping.
RO38
Multistate Survival Analysis on the Presence of Diabetes Related Complications
Yuhaniz Hj Ahmad, M. Ataharul Islam and Noorani Ahmad
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia
This paper illustrates the use of multistate approach to product limit method developed by Islam
(1994) under the competing risk framework for diabetes related complications among diabetic patient.
The method takes into account of the censored and uncensored survivorship functions separately. To
identify the risk factor for the diabetic related complications, an exponential regression model under
the competing risk framework were used. Since more than one complication could occur, thus, only
the incidences of the first complication among the diabetic patient were considered in the study. The
complications are cardiovascular, peripheral vascular, cerebrovascular, ophthalmic, neurologic and
renal disease complication.
RO39
The Quality Analysis Of Polycrystalline Diamond Coated Si3N4 Using Raman Spectra: The
Effect Of Chamber Pressure And Microwave Power
A.Purniawan1, E. Hamzah.1, M. R. M. Toff2.
1
Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor Malaysia
2 Advanced Materials Research Center (AMREC), Lot 34, Jalan Hi-Tech 2/3,
Kulim Hi-Tech Park, 09000 Kulim, Kedah, Malaysia.
Diamond (sp3) is the hardest material and high chemical resistant that is one form of carbon structure.
Another structure namely graphite (sp2), diamond-like carbon (DLC), disordered sp3, and other sp2
that are hopeless the presence on the surface, however non-diamond structure caused decreasing of
diamond properties to identification sp3 or sp2 structure. Raman spectroscopy is a standard tool for
the characterization of carbon materials. In the work, the effects of deposition parameters namely
chamber pressure and microwave power was studied. Furthermore, the characterization of diamond
coating quality was carried out by using Raman spectra and its microstructure was investigated by
Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) in order to study the effect of deposition
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
55
parameters on diamond quality. Based on the SEM images, the chamber pressure has more
significant effect on nucleation and faceting of diamond. Microwave power also affected the facet that
changes cauliflower to octahedral structure. Furthermore Raman spectra analysis found that the
quality of polycrystalline diamond increase with increase both parameters.
RO40
Ice Point Blackbody Cavity for Checking the Performance of an Infrared Radiation
Thermometer Operating Near 0 °C
Irene Safinaz Hassan , Hafidzah Othman , Md. Nor Md. Chik
National Metrology Laboratory,
SIRIM Berhad (NML-SIRIM), 43900 Sepang, Selangor
The usage of infrared radiation thermometers has expanded tremendously in Malaysia. Their distinct
capability of measuring an object’s temperature without contact has boost up its popularity among
industries. For an infrared radiation thermometer that operates near 0 °C, the simplest method to
check if it is working reliably is by using ice point check. The ice point check should be performed at
regular basis and the ice point reading is normally taken as the first impression of the thermometer’s
performance. An ice point blackbody cavity has been designed and constructed at NML-SIRIM,
Malaysia. It is a mean to measure the ice point reading of client’s infrared radiation thermometer that
operates near 0 °C. The ice point check will predict the performance of the thermometer at other
temperature range.
RO41
Measurement and Calibration of Frost Point and Dew Point Meter
Faridah Hussain, Hafidzah Othman, Md Nor Md Chik
National Metrology Laboratory,
SIRIM Berhad (NML-SIRIM), 43900 Sepang, Selangor
Dew point sensors are commonly used in various type of industry to detect the presense of small
amount of water vapour. Industries involved are compressed air, breating air for medical, plastic
processing, natural gas and many others. In certain application such as in medical, dew point of
compressed air used for breathing purposes shall be continously monitored in order to prevent it
exceeds 4 °Cdp. In order to support these industries, National Metrology Laboratory, SIRIM Berhad
has a Two temperature/two pressure frost point generator for range -95 °C to 10 °C used to supply a
test gas for calibrating and validating a wide range of dew point sensors. This paper describes the
measurement technique during the measurement and calibration. The capabilities provide traceability
for Malaysian industries, research organizations and other accredited laboratories.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
56
RO42
Identification and Characterization of a Marine Pseudoalteromonas Sp from
Fish Mucus
Wan Siti Nur Atirah Wan Mohd Azemin1, Mohd Shahir Shamsir Omar1, Azmi Rani2
1Biology Department, Faculty of Science
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia
2Brackishwater Aquaculture Research Centre,
Department of Fisheries, 81550 Gelang Patah, Johor Bahru,Johor.
Marine bacteria have been shown to have symbiosis with fish by living on its skin or mucus. The aim
of this study is to isolate potential symbiotic bacteria from farmed marine fish. Mucus samples were
collected from skin of farmed fish Bawal Emas (Trachinotus blochii) in order to identify and
characterize potential symbiotic marine bacterium. The fish was isolated from Sungai Johor estuary at
Kong Kong, Johor. The sample was investigated by use of a phenotypic approach and a phylogenetic
approach based on genes encoding 16S rRNA. The strain was gram negative rods, motile, aerobic
and grows at optimal temperature 37°C. On the basis of several phenotypic characters and a
phylogenetic analysis of the genes coding for the 16S rRNA, this strain was identified as a possible
Pseudoalteromonas sp. Species of Pseudoalteromonas are generally found in association with
marine eukaryotes and display anti-bacterial,bacteriolytic, agarolytic and algicidal activities. The
production of a range of compounds such as antimicrobial peptides which are active against a variety
of target organisms appears to be a unique characteristic for this genus and may be of potential use in
the future.
RO43
Biolistic-Transformation of Impatiens Balsamina Using Hph Gene for Hygromycin Resistant
Aishah Mohd Taha, Alina Wagiran, Zaidah Rahmat and Fahrul Zaman Huyop
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai ,Johor, Malaysia.
Cotyledon explants of Impatiens balsamina were bombarded with plasmid pRQ6 contained hph gene
encoding hygromycin phosphotransferase for hygromycin resistance and uidA gene encoding for
GUS as reporter gene. Both genes were driven by cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter.
Condition for optimal delivery of DNA to explants was developed based on transient GUS assay within
24 h post-bombardment. Cotyledon explants were cultured on osmoticum solution- containing
medium (0.2 M mannitol and 0.2 M sorbitol) 16 h before bombardment. The bombardment was
carried out at 28 Hg vacuum pressure, a helium pressure of 1100 psi, 9 cm of target distance, the
plasmid DNA of 1.0 µg with one time bombardment. Only 14 of the plants in 75 mg/L hygromycin
were GUS positive. PCR analysis to detect hph gene resulted on 18.3% transformation frequency.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
57
RO44
Preparation and Conductivity Studies on Poly(Methyl Metacrylate)-Epoxidised Natural Rubber
Blend Solid Electrolytes
Madzlan Aziz1 nd Famiza Abdul Latif2
1Jabatan
Kimia, Fakulti Sains, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia and 2Jabatan Kimia, Fakulti Sains
Gunaan, Universiti Teknologi Mara
Employment of solid electrolytes in power sources such as lithium batteries is a challenge. In order to
function well as an electrolyte it has to meet certain criteria. One of the important criteria is a good
ionic conductivity. Poly(methyl metacrylate) (PMMA) has the potential as it has a reasonably good
conductivity value in the order of 10-9 Scm-1. Although it has the conductivity needed but it is brittle
and as such couldn’t provide the interfacial properties to perform as an electrolyte. In order to
increase interfacial contact it has to be more flexible that it can withstand pressure. To introduce
flexibility PMMA is blended with rubber. The type of rubber used is 50% epoxidised natural rubber
(ENR50). The PMMA-ENR blends were prepared with suitable compositions so as to produce free
standing films. Free standing films were obtained when PMMA was blended with 10 and 20% ENR50.
A series of percentage by weight PMMA-ENR50 blends were prepared by solvent casting. The films
cast have a thickness in the order of 0.1 mm. The ionic conductivities were evaluated using the
impedance values obtained using an impedance analyzer. The highest conductivity value obtained
was 6.63 x 10-10 Scm-1. In the presence of lithium salts as used in lithium batteries the conductivity
values increased by three order of magnitude or more to 5.05 x 10 -7 Scm-1 for LiNO3 salts and 5.09 x
10-5 Scm-1 for LiCF3SO3. Temperature dependence studies were also conducted to elucidate the
mechanism of conduction and the Arrhenius behaviour suggests ionic conduction similar to ionic
solids.
RP1
Theoretical and Empirical Comparison of Coupling Coefficient and Refractive Index Estimation
for Coupled Waveguide Fiber
Saktioto, Jalil Ali, Jasman Zainal, Rosly Abdul Rahman, Bashir Ahmed Tahir
Advance Optics and Photonics Technology Center (AOPTC), Physics Department
Science Faculty, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM)
81310 Skudai, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
Power transmission of coupling ratio for coupled waveguide fiber depends on coupling coefficient. The
coupling coefficient obtained in experimental result as a function of separation of fiber axis and
refractive index of core and cladding varies in a wide range. For empirical formula, coupling coefficient
can be calculated from experimental result of coupling ratio distribution 1-75%. Theoretically, it has a
dependence of some parameters resulting sinusoidal curve. Both empirical and theoretical formulae
are compared to obtain new phenomena of refractive index of fibers after fusion.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
58
RP2
Characterization of Low Pump Power Nd:YAG Laser
Abd Rahman Tamuri, Wan Rashidah Wan Majid, Noriah Bidin & Yaacob Mat Daud.
Laser Technology Laboratory,
Physics Department, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor Bharu
Nd:YAG laser is the most commonly used type of solid-state laser in many fields at present because
of its good thermal and mechanical properties and easy maintenance. However the range of output
energy of lasers available in the market is limited. This is also allow very narrow scope of application
either in scientific research or medical used. Hence the aim of this project is to design and construct
Nd:YAG laser with specifically having wide range of energy. This is accomplished by designing
special power supply to power flashlamp. The flashlamp was used to pump Nd:YAG laser rod. The
flashlamp and the laser rod were placed parallelly (for seek of grade pumping) in a ceramic heat sink
chamber. To avoid the temperature gradient due to the heat from pumping process, cooling system
was provided. A plano-concave resonator was set up to amplify the beam and generate laser output.
Capacitor voltage was verified with in 0 to 900 V to get wide range of energy. Infrared sensor card,
powermeter and burn paper were employed to detect the laser output. The maximum output this
designed laser is 250 mJ.
RP3
Epitaxial Method of Quantum Devices Growth
Rosnita Muhammad1, Zulkafli Othaman2,Samsudi Sakrani1
1Ibnu
Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
2Physics Department, Faculty Of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Epitaxy is an affordable method for growing high quality crystalline in quantum devices applications.
The fabrication of the quantum devices is an outstanding challenge in nanostructure materials science.
During last few years, a lot of attention has been devoted to the growth and characterization of
quantum dots by using epitaxy method. In this paper, we present several epitaxy methods in recent
advancement. We then briefly examine MOVPE systems starting with basic chemical reaction
process, gas delivery equipment, reaction and safety. Growth mechanisms and criteria for growth
rate are also described. Lastly, we examine and compare the MOVPE system at our place, Ibnu Sina
Institute University Technology Malaysia.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
59
RP4
Process Development and Optimization of Laser Diode To Single-Mode Fiber Coupling And
Packaging Using Laser Welding Technique
Fadhali M A*, Zinal J, Munajat Y, and Rahman R
Optoelectronic laboratory, Physics Dept., Faculty of Science, UTM,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
The rapid development in optical communications requires stable and high coupling efficiency
optoelectronic devices in high yield, mass quantities at lower costs. Packaging process remains a
bottleneck for the cost-effective manufacturing of the optoelectronic devices. The design parameters
in the process development are numerous. In this work we used discrete lens coupling using two ball
lenses in confocal configuration, result of the obtained coupling efficiency and misalignment
tolerances both theoretically and experimentally are presented. The effect of laser welding beam
parameters such as peck power density, focusing position on the target, pulse duration, and pulse
repetition rate on the spot weld dimensions for two different alloys ( Kovar and stainless steel 304) as
welding tools materials are presented which show that a peak power density of the range of (5*10 5
w/cm2 ) is suitable for laser welding in photonic devices packaging where the heat affected zone
( HAZ) has to be minimized to prevent the damage of sensitive optical components inside the module
package. That value lead to an optimization of the laser weld depth and width ratio. A mathematical
mode has been developed to estimate the penetration depth as a function of the incident power which
shows the linear relation ship between power and penetration depth materials are s work is to study
the respective contribution of each of the many parameters in the process development on coupling
and packaging reliability.
RP5
Preliminary Analysis for Data Collection on Vehicle Inspection
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Centre of Advanced and Software Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia City Campus, Jalan Semarak, 45410 Kuala Lumpur
This paper presents a preliminary analysis of data collection on vehicle inspection centre. From the
original data collected, data was improved by a little adjustment. The average value for every step of
inspection is calculate to get a brief idea on how much time taken by every inspection for each vehicle
before the value approximate into a range of additional maximum five seconds. There is a clash
between two vehicles at some point in this analysis, which it define by two vehicles conflicting in two
same time period at some point in first and second inspecting vehicle process. Knowing that there is a
clash between the two series of same colored points, we tried to resolve the situation by adding a
period of time called ‘waiting time’ to make sure that the conflicting points would be separated into
different time units. In this research, we offer solutions using constraint programming techniques, with
aims to improve the inspection process with greater efficiency and throughput.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
60
RP6
Taylor Series Expansion Model for Optical Free Space Feedforward Linearization System
A. B. Maiteeg, S. M. Idrus, H. Harun
Photonic Technology Centre,
Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Johor Bahru, Malaysia
One primary limitation on the performance of the optical transceiver is the nonlinearity of the laser
transmitter, which produces intermodulation distortions and necessitates various compromises
between modulation depth, channel spacing and types of modulation scheme, leading to degraded
bandwidth efficiency. Nonlinearity of a directly modulated laser diode imposes limitations in the
performance of the optical communication systems. Many laser linearization techniques involve the
use of duplicate lasers or optical modulators, and those, which attempt to create physical structures
within the optical modulators, and lasers can obviously increase the cost relative to ordinary optical
transmitters. Fundamentally, linearization techniques can be divided into one of the following
categories: feedforward, feedback, precorrective distortion. In this paper a new free space optical link
non-linearity correction system has been introduced employing the Feedforward Linearization
technique, so called Optical Free Space Feedforward Linearization System (OFFLS). The system was
modeled by Taylor series and the results of the simulations have shown a significant reduction in the
3th and 5th order intermodulation distortion products (IMD) by 30 dB over 2GHz bandwidth.
RP7
Morphology and Optical Properties of Silicon Nanocrystals embedded in Silicon oxide
Yussof Bin Wahab, Yeong Wai Woon, Karim Bin Deraman
Physics Department, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM, Skudai, Johor
Crystalline Silicon (Si) being dominant in electronic industry has an indirect bandgap, and therefore is
incapable of light emission. The light emission from low dimensional Si, especially nano-scale Si, has
attracted a strong interest since the Canham’s report 1 on the strong visible photoluminescence from
porous Si at room temperature. Among the many types of Si nanostructures, Si nanocrystals (Si-NCs)
embedded in amorphous silica matrix has been extensively studied due to their unique optical
properties, simplicity of producing, and the technological compatibility with present Si integrated
circuits. Here, we report our investigation on the structural and optical properties of Si-rich Si oxide
(SiOx) films with different values of x (x<2), which were deposited by magnetron RF co-sputtering
technique. The SiOx film composition has been controlled by varying the number of Si chips being
placed on the pure SiO2 target during the sputtering process. These films were rapid thermal
annealed in nitrogen gas at high temperature to form Si-NCs embedded in SiO2. The focus of our
study is on the effect of excess Si concentration on the properties of Si-NCs. Light emission from the
Si-NCs is investigated by using photoluminescence (PL). Spectroscopic ellipsometry, UV-Vis-NIR
spectrometer was used to obtain accurate information about film thickness and refractive index of
material. Structural characterization method, such as atomic force microscope (AFM), field emission
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
61
scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and Infra-red spectroscopy, were also used to obtain general
surface characteristics and nanostructure patterns in order to assist in the understanding of the
underlying PL mechanism of the Si-NCs.
RP8
Tabletting of Morinda citrifolia Powder
Yus Aniza Yusof, Che Rodiziah Md. Noor
Department of Process and Food Engineering,
Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia,
43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
This paper presents a study on tabletting of Morinda citrifolia a herb known as Mengkudu in Malaysia
and traditionally used for treating coughs, fever, nausea, and colic. For centuries, this herb was
consumed at home by the method of infusion, and only later that the herb was marketed in the form of
concentrate, tea sachet, capsules and tablets. The tablet is a universal form in the modern medicine
due to its ability to provide uniform product composition, particle size and density distributions, and to
eliminate dust formation; and most importantly, it has a longer shelf life compared to the other forms
of delivery. It is achieved by pressing a blend of ingredients into a tablet. In this study, a 13-mmdiameter cylindrical uniaxial die was used. Pressures ranging from 7.5 to 75 MPa were applied to the
powder. The effect of binder upon tabletting was also investigated using microcrystalline cellulose,
with composition ranging from 10 to 60 % of the blend. The strength of the tabletted herb was then
tested using an indirect tensile strength test, called diametrical compression test. The results were
presented in form of pressure-volume relationship, tensile strength, and stress relaxation. The
experimental data was compared to prediction using a first order model. The results indicated that this
simple approach can be used to understand the tabletting behaviour of the herb.
RP9
Fracture Mechanisms of Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites at High Temperatures
Al Emran Ismail
Faculty of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering,
Tun Hussein Onn University of Malaysia (UTHM),
Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, 86400 Johor, Malaysia
In the last decade, natural-fiber composites of thermoplastics and thermosets have been embraced by
European car makers for door panels, seat backs, headliners, package trays, dashboards, and trunk
liners. Now the trend has reached North America. Natural fibers have benefited from the perception
that they are green or eco-friendly. Exterior automotive parts generally exposed to temperature higher
that ambient temperature. Temperature played an important role in strengthening or weakening the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
62
natural fiber reinforced composites through fiber shrinkage and result interfacial debonding of the
embedded fibers. In this work, extruded composites contained different fiber loadings are stressed at
different temperatures to failure. Stress versus strain curves are recorded and analyzed to study the
effect of temperatures on composite strength. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) is used to
observe the fracture mechanisms of the composites. The results showed that surrounding
temperatures have a significant effect on composite strength and failure mechanisms.
RP10
Harmonic Balance Analysis of the Downconversion Optoelectronic Mixer in HBT
Photodetector
S.M.Idrus, A.Hussain, H.Harun, A.B. Mohammad
Photonic Technology Centre,
Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
University Technology of Malaysia,
81310, Skudai, Johor Darul Takzim.
An optoelectronic mixer (OEM) performs the detection and the frequency conversion of signal
between radio frequency (RF) and intermediate frequency (IF). The RF is converted to an IF to allow
improved selectivity and an easier implementation of low noise and high gain amplification. OEM can
be used in many applications such as in Radio over Fibre Subcarrier Multiplexed (RoF SCM) systems,
where it can down-convert the microwave subcarrier frequency to lower IF in order to recover the
original baseband information. In this paper, we demonstrate an OEM down-converter as the optical
receiver front end configuration for SCM RoF system. A three-terminal InP/InGaAs heterojunction
bipolar transistor (HBT) with optical access has been used in this OEM configuration. In this work we
reported -24.75dB maximum internal mixing efficiency obtained by using the non-linear harmonic
balance simulation technique.
RP11
Algorithm for Magnetic Field Visualization of a Flat Plane Induced by Finite Dipole Segment
Using GCC and Gnuplot
Rashdi Shah Ahmad, Chew Teong Han
Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Magnetic field visualization has been playing an important role in a a wide area of application such as
magnetoencephalography (MEG). In the MEG technique, measurement of magnetic field induced by
the activated region of neurons in human brain is carried out.; an inverse problem approach. An
activated neuron can be simplified into a current carrying finite length segment or wire. By applying
the Biot-Savart Law for a finite length segment, magnetic field induced at any point can be calculated.
In this reseach, the magnetic field induced by such finite length segment on a flat plane is simulated; a
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
63
forward problem approach. Although the real approach used by MEG and in this research is different
but there is still some significance behind. In forward problem approach, the location source is known
and the magnetic field is generated. However, in inverse problem approach, the magnetic field is
detected and the location of source is to be determined. By using forward approach, the magnetic
mapping is obtained and by comparing the results with the MEG’s, the mapping can be re-generated
by reducing the difference bewteen the measured value and calculated value. As a result, when the
mapping match the calculated one, the location of source can be determined. The plane chosen is
divided into grids that acts as measurement point. By using vector analysis, neccessary parameters
were determined and the numerical results is represented in an iso-field plot. An algorithm is written
in C programming laguage using the Gnu Compiler Collection (GCC) which provides some extra
options compared to the standard C programming. For vusualization purpose, a program called
Gnuplot is used. These two softwares are open source and free softwares. Such usage of them will
encourage the contributions from anyone to their respective area of interest without worrying much
about budget in terms of softwares manipulation.
RP12
Synthesis of Zeolite A by Ultrasound Irradiation Technique
1H.
1Faculty
M. Razif, 1N. H. N. Hadzuin, 2 T. Sugeng and 1A. J. Aishah.
of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering, 2Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental
Science Studies, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Zeolite A synthesized from colloidal silica by ultrasound irradiation technique is compared with the
material obtained by hydrothermal technique. The composition is at molar ratio of 1 Al2O3: 0.85 SiO2:
3.0 Na2O: 200 H2O. X-Ray diffraction (XRD) and Scanning Electron Microscope have been used to
characterize the products. Although, XRD pattern of both samples showed typical peaks of zeolite A,
intensity of peaks were higher for ultrasound irradiation technique compared to the hydrothermal
technique. Moreover, SEM analysis indicated the crystal size of zeolite A synthesized by ultrasound
irradiation technique (1.7-5.2µm) is smaller compared to the hydrothermal technique (1.9-5.5 µm).
Thus, ultrasound irradiation has a potential to be applied in synthesizing zeolite A.
RP13
Modeling of an Agent Based Schedule: Preliminary Study
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Centre of Advanced and Software Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia City Campus,
Jalan Semarak, 45410 Kuala Lumpur
Agent is computer program that can do work for the user. They are responsible for doing task on the
behalf of the user and also train the user and monitor event. Therefore we propose an agent based
approach in scheduling reservation system which each person has an agent that negotiates with other
agents to schedule the meeting. The agent should support their associated human user in complex
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
64
process of meeting to be better and faster. In this paper, we also focus on benefit of agent during
handling the problems occur in meeting process. Agent based scheduler system is the system uses a
multi agent paradigm, where independent agent are responsible for deciding how the task is to be
achieved and actually performing the necessary set of action, including handling interaction with other
agent. We offer solutions using agent paradigm in this new application area, with aims to improve the
optimization of scheduling to achieve greater efficiency and throughput. To this end, we described
which agent is more suitable to improve the overall solution.
RP14
Preparation of Pt/Carbon Nanocomposites with Hollow Structure Using TiO 2 Photocatalytic
Reaction
Yun Hau Ng, Takashi Harada, Shigeru Ikeda and Michio Matsumura
Research Center for Solar Energy Chemistry, Osaka University, 1-3 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka 5608531, Osaka, Japan.
Highly dispersed platinum nanoparticles embedded in hollow carbon layers were successfully
prepared by a TiO2 photocatalytic reaction for the first time. By photoirradiating an aqueous TiO 2
suspension containing hexachloroplatinic acid (H 2PtCl6) and phenol, photoexcited electrons and
positive holes which generated on TiO2 were consumed to reduce the Pt4+ and oxidize the phenol
precursor, respectively. This induced the simultaneous photodeposition of Pt and polymerization of
phenol onto TiO2 particle, which eventually resulted in Pt-loaded TiO2 fully covered by phenolic
polymer. Upon carbonization of the phenolic polymer followed by removal of the TiO 2 through
chemical etching, hollow carbon containing Pt nanoparticles were obtained. Transmission electron
microscopy (TEM), N2 adsorption-desorption analysis, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and
thermogravimetry (TG) measurements were used to characterize the nanocomposites synthesized.
The catalytic reactivity of this Pt/Carbon nanocomposite in the liquid-phase hydrogenation of various
linear and cyclic olefins was compared with that of commercially available activated carbon-supported
Pt catalyst.
RP15
Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography Determination of High Explosives Residues In Post
Blast Water Samples Following Solid Phase Extraction
Umi K. Ahmad and Sumathy Rajendran
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
A micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) method was developed for the simultaneous
determination of five common energetic compounds namely octrahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7tetrazocine (HMX), 1,3,5-hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitrotriazine (RDX), 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT),
pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN) and 2,4-dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT). In this preliminary study, an
electrolyte composed of 2.5 mM sodium tetraborate and 12.5 mM boric acid containing 50 mM sodium
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
65
dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was chosen as the running buffer with 5% organic modifier (ACN:MeOH, 1:1).
Separation runs were carried out at positive (anodic injection) at 30 kV with a constant temperature of
25°C and was performed using a fused-silica capillary of total length 112 cm (104 cm effective length)
and 50 µm I.D. The developed MEKC method was coupled with a simple cartridge solid phase
extraction (SPE) system as the off-line extraction and pre-concentration method to enhance the
detection limit of the technique. The SPE cartridges were constructed from SPE material, LiChrolut
EN. In the absence of SPE, the detection limits obtained for the analytes were in the range of 11 – 32
ppm. By coupling the separation with pre-concentration using SPE, the detection limits for detecting
these five explosives in water sample were lowered by more than 1000 times with good percentage
recovery (> 87%). In order to test the possibility to apply the developed method to real cases, postblast water samples were analyzed and their results were compared with those obtained with high
performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The post-blast water samples which were collected from
Baling Bom training range, Ipoh contained RDX in the range of 0.05 – 0.17 ppm with no analytes
detected in some samples.
RP16
An ESR Study of Trapped Electron on High Surface Area Carbon
from Palm Kernel Shells.
Abdul Rahim Yacob, Ratna Sari Dewi Dasril, Mohd. Khairul Asyraf A.M.,
and Vicnisvarri Inderan
Chemistry Department, Science Faculty,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 81310Skudai Johor.
Palm kernel shells, an agricultural by-product, has been found to be a suitable starting material for the
preparation of economical high surface area activated carbon. It was found that the palm kernel
shell’s activated carbon contain a high carbon content of 75% and with low ash content of 1%. Palm
kernel shells were converted to high surface area activated carbon via both physical and chemical
methods. In this study, chemical activation was carried using zinc chloride as the activating agent
while characterization was carried using FTIR, single point BET surface area, FESEM and N 2
adsorption. Due its porosity and high surface area activated carbon, its property in trapping electrons
was studied using ESR. For this study, the sample was first degassed and hydrogen gas was
introduced. The sample was then UV irradiated and the activity observed. A singlet peak which
corresponds to trap free electron with the g-value of 2.0235 was observed throughout the 90 minutes
of UV irradiation. Deviation from the free electron g-value of 2.0023 indicates some contribution of the
p-orbital from carbon. As the irradiation time increases, the peak intensity reduces while the g-value
slightly shifted. The reduction of the singlet peak intensity is most probably due to the pairing out of
the additional electrons, whilst shifted g-value indicates less contribution with the p-orbital of carbon
atom during the hyperfine interaction. No interaction from hydrogen atom was however observed. This
experiment shows that carbon is not capable to trapped electrons at its pores and the cavities, but
continuously pairing them out through time.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
66
RP17
Effect of Substrate Temperature and Deposition Time on the Sizes of Silicon Nanodots Grown
on Corning Glass (7059) Substrate
Imam Sumpono, Lim Qiao Jie and Samsudi Sakrani
Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
The growth of silicon nanodots is investigated using a self-assembly method of deposition, in
particular RF magnetron sputtering. The dots with sizes ranging between 80 - 160 nm were grown on
corning glass (7059) substrate at the following conditions: Fixed setting of 100W RF power and 5
sccm argon flow rate, and varying substrate temperatures and deposition times. The surface
morphology was characterized using a non-contact dynamic mode of AFM (model SPI3800N).
Observation from AFM images revealed the average dot sizes which decreased with increasing
substrate temperatures, except for deposition time 600 s and substrate temperature 200°C. The
average dots sizes were also found to vary in an increasing and decreasing manner with deposition
times for the samples under study. Analysis from photoluminescence measurements gave the band
gap energies around 1.79 eV which was greater than the band gap energy of bulk silicon (1.12 eV).
The results showed strong indication of the nanodot size dependency on both substrate temperature
and deposition time.
RP18
Electrosynthesis of Benzoic Acid from Chlorobenzene by
Carbon Dioxide Fixation Method
Aishah Abdul Jalil1, Hartini Mohd Aris1, Normala Suliman1, Norhuda Abdul Manaf1,
Nur Hanis Hayati Hairom 1, Mohd Razif Harun1and Sugeng Triwahyono2
1Faculty
of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering,
Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
2Ibnu
An alternative dechlorination method of chlorobenzenes by using a simple electrolysis system via
carbon dioxide fixation technique has been developed. Electrolysis of chlorobenzene was carried out
in a one-compartment cell fitted with an aluminium anode and a platinum cathode. Reaction in an
N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solution containing 0.1M of tetrapropylammonium bromide (TPAB) at
0oC, 100 Ncc/min of CO2 flow rate and 120 mA/cm 2 of current density was found to be the optimum
conditions of this electrocarboxylation, which gave 72% yield of benzoic acid. This conditions was
then applied to 1,2-dichlorobenzene and 1,3-dichlorobenzene in order to convert it to their
corresponding benzoic acids.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
67
RP19
Influence of Surfactant Types on Correlation of Retention Factor
and Hydrophobicity of Selected Triazole Fungicides
in Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography
Wan Aini Wan Ibrahim, Dadan Hermawan, Mohamed Noor Hasan and Mohd Marsin Sanagi
Separation Science Research Group (SSRG)
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Application of micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) in quantitative structure-retention
relationship (QSRR) has been studied for selected triazole fungicides. Effect of different surfactant
types and concentrations of bile salts and sodium dodecyl sulfate on the correlation between
logarithm of retention/capacity factor (log k) in MEKC and logarithm of distribution coefficient between
1-octanol and water (log Pow) was investigated. Five standard fungicides (cyproconazole,
bromuconazole, epoxiconazole, bitertanol and difenoconazole) with known log Pow values from 2.9 to
4.3 were used for constructing the calibration curve of log Pow against the MEKC retention factor, log
k. High correlations were observed between hydrophobicity (log Pow) and log k in MEKC using two bile
salt surfactants viz. sodium cholate and sodium deoxycholate and mixed bile salt systems, with
correlation coefficient of linear regression greater than 0.98, due to the similar hydrogen bonding
interaction patterns between bile salts MEKC systems and the 1-octanol-water system.
RP20
Design and Characterization of Resistance Heating for Czochralski Crystal Growth
Hamdan H.K. and Mohammad Radzi Sudin
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
A resistance heating for Czochralski crystal growth system has been constructed. The vertical tube
resistance furnace with outside diameter of 240.00 0.05 mm, inside diameter of 100.00 0.05 mm
and high of 290.00 0.05 mm is placed in the chamber. Wire Super Kanthal A-1 of diameter 2.05
0.05 mm and resistance of 9.70 0.05 is used for resistance furnace. Two thermocouples type- K
are used to control and measure the temperature inside resistance furnace. The temperature control
has been interface to computer for monitoring the crystal growth process. A high alternating current
of 23.71 0.05 ampere is used to resistance furnace for reaching high temperature quickly. The
maximum temperature of the resistance furnace is 1300.00 0.05 °C. The temperature gradient of
resistance furnace are found between 1.00 0.05 °C/cm to 5.00 0.05 °C/cm.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
68
RP21
AC Conductivity of Ca0.8Ba0.2Cu3Ti4O12 Ceramic Sample
M. Mazni, W. D. W. Yusoff, C. P. Walter, S. A. Halim, Z. A. Talib
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Putra Malaysia,
43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor
Ca0.8Ba0.2Cu3Ti4O12 (CBCTO) ceramics has been doped on Ca site with Barium and was prepared
using solid state reaction technique. Dielectric measurement was done from 30 oC to 250oC in
frequency range of 10-2 Hz to 106 Hz. XRD pattern shows single phase with cubic structure. Two
relaxation dispersions of the electrical parameters were found in complex impedance plot and
conductivity plot due to grain boundary at low frequency and bulk at high frequency. It can be seen
that the conductivity, σ is increasing with increasing temperatures. From Arrhenius plot of conductivity
data, the activation energy, Ea for grain boundary region are 0.53 eV and 0.22 eV for bulk region.
RP22
The Study of Precipitated Cu-Zn-Al Catalyst via pH Titration Analysis
Nur Fadhilah Idrisa, Salamiah Zakariaa, Nurain Nasrudinb, Robert Schlöglc and Sharifah Bee Abd
Hamidb.
aNanoC
Sdn Bhd, 29 Jalan PJU 3/47, Sunway Technology Park,
47810 Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia
bCombinatorial Technology and Catalysis Research Centre,
Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia,
cFritz-Haber Institute der Max Planck-Gesselschaft,
Faradayweg 4-6, 14195 Berlin, Germany.
The used of conventionally precipitated Cu-Zn-Al catalyst has been studied to increase the activity for
reaction like methanol synthesis. Controlling the precipitation is crucial in determining the final
dispersion of active sites in catalyst. Thus, the initial understanding of process changes through
precipitation in multi components system is very useful. A series of titration experiment was carried
out in order to gain deeper insight into the precipitation reaction of the complex ternary system by
investigation of single metal, binary and ternary system during pH increment. Samples at relevant pH
plateaus were taken and analyzed using XRD for phase identification and the content of Cu in solution
was inspected by in-situ UV-Vis method. Spontaneous nucleation at pH increment was observed for
single Cu and Zn systems exhibited crystalline precursors and oxolation to crystalline metal oxide at
higher pH. The Al showed a partial oxolation to bayerite because the molecular species was unstable
at higher concentration. The binary and ternary systems showed a complicated mixture of phase
formation at respective pH plateaus. Nevertheless, it is clearly observed that Cu species was less
soluble allowing it to be first precipitated leaving other elements to buffer the system. The final
conclusion can be made that the precipitation has substantially occurred step-wise and not by coprecipitation. Therefore, the fast precipitation is essential to improve the system preventing sequential
precipitation in order to control the process and finding the correct nucleation and growth kinetics.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
69
RP23
Mo-V-Te-Nb-Mn-O Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Propane to Acrylic Acid: Effect Promoter
Loadings to Surface Modification
aRosliza
Mohd Salim, aFazliana Abd Hamid, bNoor Azeerah Abas,
Ming Hoong and aSharifah Bee Abd Hamid
aLooi
aCombinatorial
Technology and Catalysis Research Centre (COMBICAT),
University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
bNanoC Sdn Bhd, 29 Jalan PJU 3/47, Sunway Technology Park, 47810 Petaling Jaya, Selangor,
Malaysia
Manganese promoted catalysts were prepared at a fixed composition of Mo1V0.3Te0.23Nb0.125Mn≤nOx
(n =0.0005, 0.005, 0.05) by slurry method and tested for the selective oxidation of propane to acrylic
acid. The catalysts with moderate metal loading shows better activity than the rest with up to 49%
yield to acrylic acid. By dispersing the active material onto SiO 2, the catalysts become more selective
but less active whereas without SiO2 the catalyst turn out to be more active but less selective to
acrylic acid. The leaching treatment does affect the catalyst activity but the bulk structure remained
unchanged. The systems have been investigated by XRD, SEM, IR, TG and DSC to further
understand the relationship between the physical-chemical properties of the catalysts to their
corresponding catalytic performance.
RP24
Effect of Platinum and Tungsten Oxide Metal Loading on
n-Pentane Isomerization over HZSM-5 Based Catalyst
Mohd Razif Harun1, Mohd Zamry Jamaludin1, Sugeng Triwahyono2 and Aishah Abdul Jalil1
1Faculty
of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering,
Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
2Ibnu
Effect of Pt and WO3 metal loading on the skeletal isomerization of n-pentane to isopentane over
HZSM-5 based catalyst were studied. HZSM-5, WO3/HZSM-5, Pt/HZSM-5 and Pt/WO3/HZSM-5 were
synthesized by impregnation method. The catalysts were characterized by using XRD and FTIR. XRD
and FTIR results showed that incorporation of metals into HZSM-5 zeolite does not significantly alter
the natural structure of HZSM-5 zeolite. Catalytic isomerization of n-pentane over the prepared
catalysts was carried out in a packed bed micro-reactor under hydrogen atmosphere. HZSM-5 and
WO3/HZSM-5 exhibited low catalytic activity and selectivity towards isopentane. Promotion of HZSM-5
with Pt dramatically improved its catalytic activity and the isomerization selectivity in n-pentane
conversion. Pt is required to generate hydrogen atoms from hydrogen molecules, which are needed to
provide hydrogenation-dehydrogenation capability for structural rearrangement of n-pentane and
stabilize the catalyst. In addition, WO3 increased the acidity of catalyst, which enhanced the selectivity
of catalyst towards isopentane.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
70
RP25
Modified Effects of LDPE/EVA Blends By Electron Beam Irradiation
Mazyiar Sabet, Azman Hassan, Mat Uzir Wahit
Faculty of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering, University technology Malaysia (UTM),
81310 Skudai, Johor bahru, Malaysia
The effect of electron beam irradiation on the properties of low density polyethylene (LDPE, LH0075),
ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA, with 18 %VA) and blends were investigated. The improvement of the
measured gel content, hot set, tensile strength at break, elongation at break, density changes,
temperature of melting and degradation of LDPE, EVA and blends vs. absorbed doses have been
investigated. In this research a significant improvement in the tensile strength of the neat EVA
samples was obtained upon electron beam radiation up to 210 KGy. It was also found that The
irradiation LDPE/EVA blends showed improvements in tensile strength and elongation at break when
compared with LDPE.
RP26
Nanometer Scale of Silicon Oxide Pattern using Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
Teguh Darsono, Sabar Derita Hutagalung, Zainal Arifin Amad, Cheong Kuan Yew,
Khatijah Aisha Yaacob
School of Materials and Mineral Resources Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia,
14300 Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Local oxidation of semiconductor by a scanning probe microscopy (SPM) is a promising approach for
nano electronics devices prototyping. The local anodic oxidation by SPM tips allows for the
lithography of the smallest semiconductor structures among a variety of top down processing methods.
In the anodic oxidation process an electrically conducting Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) tip that is
operated in air to selectively oxidize region of a sample surface.
We experimented systematically with various parameters, mainly tip voltage bias and scanning speed.
SPM lithography allows not only oxide dot formation but also oxide lines and other patterns. Some of
silicon oxide patterns (dots and lines) on silicon surface were fabricated with this technique. It has
been found that tip voltage bias and scanning speed are the main parameters that influence the size
of silicon oxide patterns. The size of silicon oxide pattern (dots and lines) can be controlled by
adjusting the tip voltage bias and scanning speed.
The resulting of silicon oxide patterns size typically 30 – 100 nm in diameter and 3 – 8 nm height that
can be used a mask for selective etching. The advantage of the anodic oxidation technique is that it
provides a simple, reliable process for making a highly local chemical modification to surface. In
addition this process is fairly general and can be applied to most materials that can be anodized.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
71
RP27
The Role of Ige Antibodies in Protection against P.Falciparum
Reem Bairam1, Marita Troye Bloomberg2, Muntasir Eltayeb1, Ibrahim Elhassan1
1Institute
of Endemic Diseases, University of Khartoum
of Immunology, Stockholm University
2 Department
Malaria occurs in over 100 countries and territories. More than 40% of the people in the world are at
risk of getting malaria. There are approximately 200 million to 500 million new cases each year in the
world, and the disease is the direct cause of 1 million to 2.5 million deaths per year. Immunity to
malaria is complex partly due to the complicated life cycle of the parasite with different antigens
expressed at different times. In endemic malaria areas, infection with malaria is associated with
elevation of strong specific and non- specific antibody responses with the humoral immune responses
involving production of predominately IgM and IgG comparing both total IgE and ant malarial
antibodies has been reported in a several studies carried out in a number of different malarial
endemic areas review by (Perlman P. et al 1999). Further, studies have suggested that IgE may play
a role in the pathogenicity of malaria. On the other hand, it is well known that IgE mediates activation
of various effectors cells such as monocytes/ macrophages), also many studies suggested that. This
data may suggest that IgE may also play a role in protection against malaria. The main objective of
my research project is to determine the role of IgE in protection against acute P. falciparum malaria in
an area characterized by highly seasonal but stable malaria transmission in Sudan. To archive this
goal number of cytokines will be determined in the samples collected from my study subjects.
RP28
Physicochemical Studies of CdS Nanoparticles -Titanosilicate Hybrid
Mustaffa Shamsuddin, Ng Yew Choo
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Cadmium sulphide (CdS) nanoparticles have been known as few examples of visible-driven
photocatalyst. The band gap of 2.3 eV corresponded well with the spectrum of sunlight. Therefore, it
is expected that it could be fully utilize under solar energy conversion. Moreover, the conduction edge
of CdS nanoparticles is more negative than the H+/H2 redox potential, which allows the evolution of
hydrogen gas from water under sunlight or visible irradiation. In this study, CdS nanoparticles in the
cubic phase have been successfully synthesized by both reverse micelle method and direct in-situ
sulphur reduction. For reverse micelle method, CdS nanoparticles were prepared under an oil phase
by using Triton-X100 as surfactant, whereas, for in-situ reduction method, an aqueous solution of
DMF was used. The reflectance measurement of CdS nanoparticles prepared by both methods is
apparently blue-shifted compared to bulk CdS. This phenomenon of blue shift of adsorption edge has
been ascribed to an increase of band gap energy with the decrease in particle size. The XRD, FESEM,
and EDAX data indicated that the physicochemical of CdS nanoparticles prepared by both methods
were identical. Engelhard titanosilicate (ETS-10) that obtained from the hydrothermal synthesis,
consists of molar ratio TiO2 : 3.75SiO2 : 1.5NaOH : 0.54KF : 21.25H2O. The fundamental vibration of
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
72
octahedral TiO6 and tetrahedral SiO4 occurred at mid-infrared region of 450-1300 cm-1. The well
dispersion of CdS nanoparticles on ETS-10 is expected to create a good morphology for
photocatalytic reaction.
RP29
Catalytic Properties of Metallosalen supported on MCM-41 in Oxidation of Benzene
Salasiah Endud, Chin Tian Kae, Shajarahtunnur bt. Jamil and Wong Ka Lun
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
A series of metallosalen such as Fe(salen), Co(salen) and Cu(salen) supported on mesoporous
molecular sieve MCM-41 have been synthesized by post synthesis modification method. These
supported metallosalen were characterized by using Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR),
powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), diffuse reflectance ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-VIS DRS) and
atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). The catalytic activity of the supported metallosalen was
evaluated towards oxidation of benzene by using aqueous hydrogen peroxide 30% as the oxidant in
acetonitrile at 70 oC. The reaction was monitored by gas chromatography (GC) and gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The results show that metallosalen supported on
MCM-41 are active and selective in the formation of phenol. The catalytic activity of the metallosalen
increases in the order: Fe(salen) > Co(salen) > Cu(salen).
RP30
μ-Oxo Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complex Incorporated in MCM-48 as
Efficient Catalyst for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohol
Salasiah Endud, Lau Su Chien, Wong Ka Lun
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
A series of μ-oxo bridged dinuclear iron 1,10-phenanthroline complex (Fe-phen) supported MCM-48
mesoporous molecular sieves with 0.1 mmol, 0.3 mmol, 0.5 mmol and 0.7 mmol loadings of the
complex have been synthesized by post-synthesis modification method. The samples were
characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), nitrogen
adsorption measurement, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), diffuse reflectance ultraviolet-visible
spectroscopy (UV-VIS DRS), electron spin resonance (ESR), and atomic absorption spectrometry
(AAS). The XRD results showed that the long range order of MCM-48 structure is maintained even
after the incorporation of Fe-phen. The increase of unit cell parameter showed that encapsulation of
Fe-phen in MCM-48 channel has caused the expansion of the unit cell. The UV-VIS-DRS spectra for
Fe-phen-MCM-48 showed three peaks at 230 nm, 265 nm and 370 nm which correspond to the π →
π* transitions of phenanthroline ligand, charge transfer from µ-oxo to Fe orbital and d-d transitions of
Fe, respectively. The catalytic activity of Fe-phen-MCM-48 was tested in the oxidation of 1-naphthol
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
73
with aqueous hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatographymass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses showed that the only reaction product was 1,4-naphthoquinone
after 20 hours of reaction at 80 oC. The conversion of 1-naphthol for the first use of catalyst was in the
range of 65 – 75 %. Fe-phen-MCM-48 showed its reusability with 40 – 51 % conversion of 1-naphthol.
This may be due to the leaching of Fe-phen into the solution during reaction.
RP31
MCNP for Neutron Radiography Simulation
Sumilah Marto*, Wan Muhamad Saridan Wan Hassan**
and Azali Muhamad***
* Department of Physics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor.
** Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor.
*** Malaysian Nuclear Agency, Bangi, 43000 Kajang,Selangor.
The objective of the work is to use the MCNP simulation to investigate the contrast between a
massive object and air in a simple canister in neutron radiography. The canisters used for spent fuel
consist of copper and are filled with iron. The spent fuel bundles, which mostly consist of U-238, are
placed inside the canisters. Four objects with the same shape but different elements of Fe, U-238, Pb
and liquid hydrogen were investigated. The idea was to see whether it is possible to distinguish
between different elements with 100 MeV neutrons. The result showed a clear contrast between the
iron object and the air. The transmission through iron was about 2 × 10 -5. The projection of the object
on the detector implies that the shadow of the object should end at r = 4.13 cm. The resolution of the
neutron radiography system was estimated as 1 mm or better.
RP32
Measurement of Diamagnetic Susceptibility of Crude Oils
Mr. Abd. Aziz Abd. Kadir1, Hasrul Afendi Ahmad Khonif1, Rashdi Shah Ahmad2
1Petroleum Engineering Department
Faculty of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering
2Department of Physics, Faculty of Science
University Technologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Diamagnetism is a fundamental property of all matter. However because it is so weak it can only
be observed in materials that do not exhibit other forms of magnetism. Diamagnetic materials give
a value of magnetic susceptibility, K range about 10 -6. The objective of this study is to determine
the value of diamagnetic susceptibility of crude oils by utilizing Quincke method. It is believed that
paraffin deposition can be solved by using magnetic technique. So by doing this study we can
have initial knowledge about the magnetic characteristic in the crude oil. This study had been
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
74
conducted on four crude oils samples from Malaysian oilfields under the influenced of the
magnetic field, names Talisman, Corelab, GNPOC and sample A. These samples are different in
their properties such as density, viscosity and others. The apparatus was verified by using known
values materials as n-Hexane, n-Pentane and water. The percentage of error from the
measurement of known values materials was calculated and gave the error between 3-7%. The
value of diamagnetic susceptibility showed that Corelab have the highest value which is 0.644 x
10-6, followed by GNPOC (0.584 x 10-6), Talisman (0.567 x 10-6) sample A (0.482 x 10-6).
RP33
Growth and Characterization of Gallium Oxide Thin Films Deposited By DC Magnetron
Sputtering
Putut Marwoto, Sugianto and Wiyanto
Material Laboratory, Physics Department, Faculty of Science
Universitas Negeri Semarang
Indonesia 50229
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3) films were successfully fabricated by DC magnetron sputtering. The films were
grown on silicon (100) substrate at temperature of 600oC with plasma power between 40 – 50 watt.
Crystal structure, morphology and optic properties have been investigated. It is found that the
properties of the films are affected by growth conditions.
RP34
Mechanical Properties of Talc and Calcium Carbonate Filled PVC
Bee Soo Tueen, Azman Hassan and Aznziam Abu Bakar
Department of Polymer Engineering, Faculty of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
The main aim of this work was to compare the mechanical properties of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
and talc filled PVC. Talc and CaCO3 are common fillers in plastics such as PVC to reduce cost and
modify mechanical properties. The PVC resin and additives were blended by using high speed
laboratory mixer to produce a homogenized PVC formulation. Then, the dry blended samples were
melted and sheeted on the two roll mill machine. The sheeted PVC compounds were compression
moulded into impact and flexural test specimens. Flexural and impact tests were then performed to
determine and compare the mechanical properties of both PVC composites. Talc filled PVC
composite gave the highest flexural modulus but the lowest impact strength compared to all grades of
CaCO3 filled PVC composites. The SM90 CaCO3 gave the most optimum properties in terms of
impact strength and flexural modulus compared to all grades of CaCO 3.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
75
RP35
Effect of Na Loading On the Properties of Catalysts And N-Heptane Isomerization Over Pt/SO42-Zro2 Catalyst
Sugeng Triwahyono1 and Aishah Abdul Jalil2
1Ibnu
Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies,
of Chemical & Natural Resources Engineering
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
2Faculty
The acidic properties of Pt/SO42--ZrO2 (PSZ) have been characterized by a combined study using
temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) of ammonia and infrared (IR) spectroscopy. PSZ samples
were prepared by impregnation of Zr(OH) 4 with 1.0N of sulfate ion and calcined at 873 K, followed by
addition of 0.5wt% Pt. Then 0.1 and 0.5wt% of Na were loaded in order to change the acidity of PSZ.
The ammonia TPD spectra confirmed the existence of peaks at 443 and 623 K corresponding to the
weak and medium acid sites, respectively. The TPD plot did not change much by addition of 0.1wt%
Na, but changed considerably by addition of 0.5wt% Na which the intensity of peak at 623 K
decreased and the intensity of peak at 443 K increased. It is indicated the conversion of strong into
weak acid sites by addition of Na. IR spectra of pyridine adsorbed on samples showed the presence
of Na decreased the intensities of bands at 1450, 1490 and 1540 cm -1 which corresponding to
pyridine adsorbed on Lewis, Lewis-Bronsted and Bronsted acid sites. The addition of Na caused a
more extensive decrease in the number of strong Bronsted acid sites than in the number of strong
Lewis acid sites. The activity of PSZ samples were examined by isotherm hydrogen adsorption and nheptane isomerization. The presence of Na decreased the hydrogen uptake due to the reducing of the
number and strong acid sites. The hydrogen uptakes in 8 h for the samples unmodified and modified
with 0.1 wt% Na and 0.5 wt% Na were 6.19 x1017, 3.62x1017 and 2.66x1017 atom/m2-cat, respectively.
These numbers correspond to H/Pt ratios of 4.79, 2.75 and 2.01, respectively. The presence of Na
decreased the conversion of n-heptane and increased the isomerization selectivity of n-heptane due
to the weakening the acidity of catalyst.
RP36
A Supported Titanium and Copper Based Catalyst for Desulphurization Reaction
Junaidi Mohamad Nasir, Wan Azelee Wan Abu Bakar* and Mohd Yusuf Othman*
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Tenologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Natural gas is used as one alternative way to generate the largest scale of energy especially for
electricity in the world. Hence, many oil and gas companies try to explore a new crude natural gas
well for maximizing production of LNG. Malaysian crude natural gas contains various gases
components including methane (40-50 %), ethane (5-10 %) and propane (1-5 %). However, this crude
natural gas also contains toxic and acidic gases components such as H 2S (1–5 %) and CO2 (20-30 %)
which has the ability to corrode carbon steel used in the natural gas pipeline system and material in
the processing plant. Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Al2O3 and Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Ti4+/Al2O3 with the ratio 0.05:0.2:1 and
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
76
0.1:0.1:0.8:1 respectively, were found to be the best catalysts for reaction of H 2S desulphurization.
These catalysts were prepared via modified sol-gel and impregnation methods and calcined at 400oC
for 5 hours. The results of catalytic activity testing for the Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Al2O3 and
Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Ti4+/Al2O3 showed 100% H2S desulphurization reaction occurred at 100 oC of reaction
temperature. Both supported catalysts of Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Al2O3 and Fe3+/Zn2+/Cu2+/Ti4+/Al2O3 also had
the lowest H2S adsorption with 3.7 % and 1.9 % respectively, ranging from room temperature to 40 oC.
Furthermore, both catalysts could oxidize the highly concentration of H 2S with 90.6 % and 94.3 %
respectively, even at the light-off temperature of 40oC. Importantly, the both catalysts could be
regenerated via heating at 200oC for 3 hours under compressed air flow at the rate of 100mLmin -1.
The XRD analysis only showed the present of three peaks due to cubic phase of γ-Al2O3. The Ti, Cu,
Zn and Fe elements that were present in both catalysts matrix system were presumably dispersed on
the surface of alumina support and were detected through EDX analysis. The SEM micrograph
showed that the supported catalysts had agglomerated in undefined shape with various size particles.
RP37
PHOTONIC DEVICES PIGTAILING AND PACKAGING USING
LASER WELDING TECHNIQUE
Fadhali M. A.*, Zainal J., Munajat Y., Jalil A. and Rahman R
Institute of advanced Photonic Sciences,
Faculty of Science
University Technologi Malaysia
81310 Skudai, Johor,Malaysia
Abstract
In this paper we present some investigations and analysis of various parameters that contribute for
increasing the coupling efficiency of laser diode to single mode fiber coupling using Ball lens coupling
and butt coupling schemes. The fiber attachment process and the fixing of various coupling
components have been performed in what is so called active alignment process, where the system
continues measuring the coupled power during the process of coupling and welding of (lens holder,
fiber ferrule, and welding clips). Nd: YAG laser welding system (LW4000S from Newport) has been
used for the alignment and welding of the coupling components. Results of optimizing laser beam
parameters to get good welds with small heat affected zones (HAZ) such as (variation of weld
dimensions with changing of laser beam parameters are also presented. We also studied the
weldability of different materials to determine the suitability of using those materials as the base
material and welding tools for different types of photonic devices packaging.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
77
IO1
A 2-D Analysis of the Stability and Convergence of a Nonlinear Optimal Control Algorithm
Rohanin Ahmad & Mohd Ismail bin Abdul Aziz
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
A multipass process is one that possesses two distinct properties; repetitive operation and interaction
between the state and/or output functions generated during successive cycles of operation. A
repetitive process has strong structural links to two-dimensional systems, which propagate information
in two separate directions that are considered as two distinct dimensions. An algorithm is a repetitive
process that falls naturally into the area of 2-D systems where one dimensions is the time horizon of
the system under investigation and the other is the progress of the iterations. In this paper we used
the 2-D system theory techniques based on the theory of unit memory repetitive processes to analyze
the stability and convergence behavior of an algotihm developed for solving nonlinear optimal control
problems.
IO2
Using Genetic Algorithm (GA) for Solving Integer Linear Programming Problem (ILpp)
Shamsollah Ghanbari
Asstian Azad University, Ashtian, Iran.
Linear programming (Lp) is a branch of applied mathematics. Generally, linear programming problem
(Lpp) solving is done by simplex method. A kind of linear programming, named Integer Linear
Programming (ILpp) is being necessited to integer solution. There exist different methods for solving
integer linear programming problem (ILpp) for example: Gomory’s-all – integer Algorithm, Dantzig –
cut method, Branch and bound method, etc. These methods have time, space and computational
complexities. It is intended to try to solve ILpp with GA in this paper. This method has loss time, space
and computational complexities.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
78
IO3
Look Ahead Heuristics for Modeling Solid Waste Collection Problems
Zuhaimy Ismail, Irhamah & L.S.Lee
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The collection of solid waste in major cities is intrinsically complex, because it involves various relative
factors, which are often in conflict. It normally involved the multi-criteria urban management issues
that require multi-criteria analysis. This is categorized as an NP-hard problem where most of these
problems are solved using heuristic method. This paper presents the Look Ahead Heuristic (LAH)
algorithm developed for solving the scheduling problems of solid waste collection problems with the
inclusion of environmental issues such as the smell. Initially the problem is modeled as the
capacitated arc routing problem where the minimum deadheading cycles through all the required
edges are determined. The inconveniences due to smell was included which enables large quantity
of garbage to be removed as soon as possible. Results achieved from this multi-objective routing
problem put emphasis on both the cost and the smell. Based on the LAH strategy, we developed
solutions to optimize the routing problem for local waste management authority.
IO4
The PSB-SD’s Method for the Unconstrained Optimization Problem
1Mustafa
bin Mamat, 2Yosza bin Dasril, 3Ismail bin Mohd
1,3Department
of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science and Technology
Universiti Malaysia Terengganu
21030 Kuala Terengganu
2Department
of Electronic Engineering,
Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka.
A Quasi-Newton especially PSB method is a popular iterative method and had been used in many
real problems such as in engineering (Papadrakakis, 1993). The convergence of this method is also
quite faster because the computational problems in Hessian matrix can be avoided. The convergence
rate of the steepest descent (SD) is more slowly but it has a global convergence. In this paper, we try
to explain an algorithm that combined the PSB and SD search direction in determine the solution of
unconstrained optimization problem. Then, at the end we also explain about the convergence for this
algorithm.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
79
IO5
Optimization of Crude Palm Oil Transportation for Northern Peninsular Malaysia
1Shamsudin
Ibrahim, 2F.M. Abbas Al-Karkhi & 3Omar A. Kadir
1,2Fakulti
3School
Sains Kuantitatif,, Universiti Utara Malaysia,
06010 Sintok,
Kedah Darul Aman.
of Industrial Technology, Universiti Sains Malaysia,
11800 Pulau Pinang.
Transportation problem is a special class of linear programming problem that deals with shipping a
commodity from sources to destinations. This paper presents a method for finding the optimum
solution of a crude palm oil transportation problem with the objective of distance minimization. This
commodity originates at the mills and sent to the refineries using a single capacity tanker trucks. A
number of mills in the Northern part of Peninsular Malaysia are selected as the sources and a number
of refineries as the destinations. This is also an unbalanced transportation problem where demand
exceeded supply. An integer programming model was developed and run using the Ilog software.
The results indicate that this method performs well in terms of the solution exhibited the best mill-torefinery assignment. The study was further extended to see the effect on total distance when the
refineries were relocated at different towns in this part of the country. At one of these locations we
found that the total distance was reduced to almost half compared to the original optimal solution.
IO6
A Review on Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Solving Facility Layout Problems
formulated as Quadratic Assignment Problems
Phen Chiak See & Kuan Yew Wong
Department of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Since the first formulation of Facility Layout Problems (FLPs) as Quadratic Assignment Problems
(QAPs) by Koopmans and Beckman (1957), many initiatives have been taken to solve them through
various mathematical ways. However, due to the NP-Hardness of QAPs, solutions for large problem
instances ( n 30 ) could be computationally intractable. To date, researchers seek for various
approximate methods including various local search and metaheuristics approaches to find optimal
solution for the problems in a reasonable computational time. One of the metaheuristics that is
gaining momentum for solving QAPs is Ant Colony Optimization (ACO). This paper aims to review
the underlying concepts of ACO as well as its associated algorithm or variants. Based on the review,
it is found that existing ACO variants still possess certain limitations or drawbacks which could be
further improved. Hence, this call for a need to derive a more robust ACO variant for solving QAPs.
The paper culminates with conclusions and some future research directions.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
80
IO7
A Genetic Algorithm for Solving Vehicle Routing Problem with Stochastic Demands
Zuhaimy Ismail & Irhamah
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Vehicle Routine Problem (VRP) consists in finding the optimal route through a number of customers
from one or several depots to a set of geographically scattered points, such every point is visited once
by exactly one vehicle, all routes start and end at the depot, and the total demands of all points on
one particular route must not exceed the vehicle capacity. The objective to be minimized is usually a
function of the number of vehicles in the solution, the distance driven and the service provided to the
customers. One of important variation of VRP is in the demand structure where the demand of each
location is unknown when the route is designed, but it follows certain probability distribution. This is
known as the VRP with Stochastic Demand (VRPSD). The Algorithms for stochastic VRP such as
this are rather complex than deterministic and the computational intricacy is very demanding. Various
formulations and algorithms have been proposed and investigated but the work on the application of
Genetic Algorithm (GA) in VRPSD is lacking in the literature. GA is an effective search and
optimization method that simulates the process of natural selection or survival of the fittest. It has
seen widespread use amongst modern metaheuristics, and several applications to NP-hard problems.
This approach provides satisfactory results for optimization problems that are hard to solve using
exhaustive techniques. This paper presents the GA heuristic approach on VRPSD for single vehicle
and single depot. The chromosome representation of the problem is based on order/permutation
representation with the inclusion of the initial solution using constructive and insertion heuristic. The
GA is used to find the order in which the customers are initially visited, and a local search is applied
subsequently to detect possible improvement. The approach is tested on a set of randomly generated
problems following some discrete probability distributions and compared with existing heuristic
procedure. The problem data are inspired by real case of VRPSD in waste collection. The results
show that GA, although requiring slightly longer computational times, is better than previous algorithm
in terms of solution quality.
IO8
Mixed Integer Programming Model for the Portfolio Selection with Minimum Transaction Lots
Lucy K. Basar, Fajriana, Maryana, Putra B.J. Bangun, Rustam Sinaga, Zainal Azis & Herman
Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics
University of Sumatera Utara
The mathematical model of portfolio optimization has been largely written in terms of minimizing the
risk, given the return. The difficulty in dealing with the quadratic programming model due to
Markowitz has been overcome by the recent progress in algorithmic research, the introduction of
linear risk function has given rise to the interest in solving portfolio selection problems with real
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
81
constraints. This paper deals with the portfolio selection problem with minimum transaction lots. A
heuristic of neighborhood search algorithm is proposed to solve the mixed integer programming
model. The algorithm starts from the solution of the relaxed problem to find a solution which is close
to the continuous solution.
IO9
Statistical Modeling of the Incidence of Breast Cancer in NWFP, Pakistan
1Salahuddin
Khan & 2Arifullah
1Department
of Statistics,
University of Peshawar,
NWFP, Pakistan.
2Lecturer in Statistics,
Higher Education Department,
Peshawar, NWFP, Pakistan.
Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer that affects women. It is life threatening disease
and commonest malignancy in women through out the world. In this study an effort has been made to
determine the most likely risk factors of breast cancer and to select a parsimonious model of the
incidence of breast cancer in women patients of the age 50 years and above in the population of
NWFP, Pakistan. The data were collected from a total of 3000 women patients, arriving at Institute of
Radiotherapy and Nuclear Medicine Peshawar, NWFP, Pakistan. Logistic regression model was
estimated, for breast cancer patients, through backward elimination procedure. Brown tests were
applied to provide an initial model for backward elimination procedure. The logistic regression model,
selected through backward elimination procedure contain the factors Menopausal status (M),
Reproductive status (R), and the joint effect of Diet and family history (D*H). We conclude that
menopausal status, reproductive status and the joint effect of diet and family history were the
important risk factors for the breast cancer. Separate models were then fitted for married and
unmarried breast cancer patients. The best selected model for married females is of factors Feeding
(F), R, M, (D*H), whereas the best selected model for unmarried females has only one main factor
Menopausal status. We conclude that breast feeding, reproductive status, menopausal status and the
joint effect of diet and family history were the important risk factors of breast cancer in married women
and the menopausal status was the important risk factor of breast cancer in unmarried women.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
82
IO10
An Overview of Evaluation Criteria in Logistic Regression Models
1Hussain
Jassim N., 2Low Heng Chin, & 3F.M. Abbas Alkarkhi
1,2School
of Mathematical Sciences,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Pulau Penang
3School of Industrial Technology,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Pulau Penang
Survival regression models are used in many disciplines such as Social, Medical, Biological, and
Engineering Sciences. Choosing a model that represents adequately the data depends on a number
of criteria suggested by statisticians, but so far there is no agreement on any criterion as the best one
for evaluating the survival regression models. The present paper is an overview of more than
fourteen criteria used in evaluating logistic regression models, which is one of the survival regression
models. The criteria are divided into four groups. The first group consists of six criteria and related to
goodness of fit, the second group for evaluating the model coefficients using three criteria, the third
group is the criterion of testing association between the response probability variable and the linear
combination of explanatory variables in the model (link function), while the last group is for
comparison of logistic models and has three criteria. Two types of logistic models are considered
nested and not nested. The advantages, disadvantages, and the use of these criteria in evaluating
the logistic models are studied in this paper. The main conclusion is that although there are numerous
criteria, some of them are preferred and used more than others.
IO11
Projection Pursuit Regression A Method of Statistical Downscaling
A.H. Wigena and Aunuddin
Department of Statistics,
Bogor Agricultural University,
Jakarta 10640.
In climatology statistical downscaling techniques have been used for predicting local rainfall from
GCM (Global Circulation Model) output. Since the characteristics of GCM output are nonlinear and do
not follow any standard statistical distribution, the use of parametric technique will not be appropriate.
Projection pursuit regression (PPR) is one of nonparametric methods which can be used to model the
data that have such characteristics. The result of analysis shows that PPR performs better than the
common parametric method, i.e. principal component regression (PCR). In respective of the length of
data, the correlations of the predicted values of the PPR model with the observed data are much
higher (between 0.71 and 0.84) than those of PCR model (between 0.60 and 0.66).
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
83
IO12
The Determinants of Breast Feeding: Quantiles Regression Approach
Mahdiyah Mokhtar1, Wan Norsiah Mohamed2 & Kamarulzaman Ibrahim 3
1Department
of Home Economics, Faculty of Technology,Universitas Negeri Jakarta,13220
Rawamangun, Jakarta Timur.
2,3School of Mathematical sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology,Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor.
Breast milk is known to be very essential for the baby. Many researches have been carried out to
determine factors which influence the period of breastfeeding. Among the statistical tools treat are
often used for analyzing data regarding breastfeeding include logistic regression and multiple linear
regression. In this paper, quantiles regression approached and analyzed the data of Malaysian
Family Life Survey (MFLS), to identify the determinants of breastfeeding among mothers in Malaysia.
It is known that the classical linear regression methods based on minimizing sums of squared
residuals, but quantiles regression use a mechanism based on estimating models for the conditional
median function and the full range of other conditional quantile functions. An implementation of this
method is available with R software in the quantreg package. It is found that the period of
breastfeeding is significantly related to place of living, religion and totals number of children in the
family.
Keywords: Breastfeeding; Quantiles Regression; R-Program.
IO13
The Use of Logistic Regression Model to Indentify the Risk Factor of H5N1 Avian Influenza
Virus at Native Chicken in Sumatera and Kalimantan Island, Indonesia
1Etih
Sudarnika, 2Asep Saefuddin , 3Abdul Zahid and 4Chaerul Basri
1,3,4Laboratory
of Epidemiology,
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, IPB, 16680, Darmaga, Bogor, Indonesia.
2Department of Statistics,
Faculty of Mathematics and Science, IPB, Bogor, Indonesia.
The cross sectional study had been carried out in December 2005 at Kalimantan and Sumatera
Island, Indonesia. The objective of this study was to apply the logistic regression model to identify the
risk factor of H5N1 avian influenza virus at native chicken. 12,713 serum samples of chicken from
498 farmers were collected. The H5N1 virus was tested by Haemagglutination Inhibition (HI) test
from serum samples and the information of risk factor was obtained from questionnaire. The
questionnaire involved farmer's characteristic and farm management. Logistic regression Model
showed that an association with disease risk at a 5% significance level was found for cage hygiene
(OR: 1.64, 95%CI 1.21-2.23), feed equipment hygiene (OR: 1.53, 95%CI 1.12-2.09), drink equipment
hygiene (OR: 1.57, 95%CI 1.16-2.12), cage environment hygiene (OR: 1.60, 95%CI 1.13-2.21), the
quarantine actions (OR: 2.69, 95%CI 1.61-4.50) and movement control of poultry, vehicles and
humans (OR: 1.75, 95%CI1.03-2.99).
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
84
IO14
Sensitivity Analysis for Survival Regression Models
1Hussain
Jassim N., 2Low Heng Chin, and 3F.M. Abbas Alkarkhi
1,2School
of Mathematical Sciences,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Pulau Penang
3School of Industrial Technology,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Pulau Penang
Sensitivity analysis (SA) plays a central role in a variety of statistical methodologies, including
classification and discrimination, calibration, comparison and model selection. SA gives a simple
model by identifying the importance of covariates, so a few important covariates will be included in the
model based on their contribution in explaining the variation in the data. SA is the study of how the
uncertainty in the output of a model (numerical or otherwise) can be apportioned to different sources
of uncertainty in the model inputs. SA is hence considered by some as a prerequisite for a model
building in any setting, and in any field where models are used. It allows the impact of different
factors on response variable to be analyzed. It helps to explain the impact of different model
structures. Furthermore, SA can be used to find out which subset of input factors accounts for most
of the output variance. SA has been used extensively in linear regression models, but not in survival
regression models. Also SA is an easy and useful method to screening variables in survival
regression models. This study presents SA in survival regression models; an application in the
medical field is used to illustrate it.
IO15
Applying Robust M-Regression in Modeling Oil Palm Yield
Zuhaimy Ismail1 & Azme Khamis2
1Department
2Center
of Mathematic, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia.
of Science Studies, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn, Malaysia.
This paper will discuss the used of multiple linear regression in oil palm oil yield modeling. The foliar
nutrient compositions were used as independent variable and fresh fruit bunch as dependent variable.
Outliers in a set of data will influence the modeling accuracy as well as the estimated parameters
especially in statistical analysis. A statistical procedure is regarded as robust if it performs reasonably
well even when the assumptions of the statistical model are not true. If we assume our data follow
standard linear regression model, then least squares estimates and test perform quite well, but they
are not robust when the present of the outlier in the data set. In this case we are interested on Mregression to model the yield data. Since the quantile-quantile plot shows the existing of outlier, we
proposed to use robust M-regression to overcome the negative impact of outlier. The data used for
this study are prived by The Malaysian Oil Palm Board (MPOB) taken from two of the estates in
Peninsular Malaysia. The factors included in the data set were foliar composition and fresh fruit
bunches (FFB) yield.
The variables in foliar composition included percentage of nitrogen
concentration (N), percentage of phosphorus concentration (P), percentage of potassium
concentration (K), percentage of calcium concentration (Ca) and percentage of magnesium
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
85
concentration (Mg). The N, P, K, Ca and Mg concentrations were considered as independent
variables and the FBB yield as dependent variable. From this analysis, it shows that robust
regression gives better results than conventional regression in modeling oil palm yield.
Keywords: Multiple Linear Regression; Robust M-Regression; Oil Palm Yield.
IO16
Using Logistic Regression to Determine the Sex of Spiderhunters (Family: Nectariniidae)
Charlie J.M. Laman, Siti Nurlydia binti Sazali and Mustafa Abdul Rahman
Department of Zoology,
Faculty of Resource Science and Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Sarawak,
94300 Kota Samarahan,
Sarawak, Malaysia.
Spiderhunters (Family: Nectariniidae) are monomorphic birds. Sexing or sexual dimorphism of
spiderhunters was investigated, based on measurements of the specimens’ seven external
morphological characters (kept in the Sarawak Museum), and analyzed using logistic regression
analyses. The dependent variable of logistic regression is binary or dichotomous, and can be
represented by a binary indicator variable, taking the values of 0 and 1. Logistic regression is either
the simple model (1 independent variable) or multivariate logistic model (two or more independent
variables). A total of 8 species of spiderhunters, with 181 individuals (98 males, 83 females) were
examined. Four prediction models were found with their respective parameter: bill length (BL) for little
spiderhunter (Arachnothera longirostra), and wing length (A. modesta), respectively. However, the
other species including thick-billed spiderhunter (A. crassirostris), spectacled spiderhunter (A.
flavigaster), streaky-breasted spiderhunter (A. affinis) and whitehead’s spiderhunter (A. juliae) showed
no significant differences of gender, in their external morphological characteristics. Deviances method
was used to examine the goodness-of-fit of the 4 models; all models showed the favourable p-value,
depicting that there is no evidence of a lack-of-fit and therefore the models obtained were appropriate.
Overall, the percentages of correct predictions (correctly predicted specimens over total specimens)
were 81.36%, 91.89%, 85.71% and 80.0%, respectively, for the four prediction models. Generally,
spiderhunters showed that males are relatively larger than females in their selected external
morphological characters, which may have resulted from natural selection and/or sexual selection.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
86
IO17
Reliability Assessment of Corroding Pipeline – A Statistical and Probabilistic Approach
Norhazilan Md Noor
Fakulti Kejuruteraan Awam,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
Nowadays, the intelligent pig has become an important tool for in-line pipeline internal inspection.
Nonetheless, lack of knowledge in the interpretation of metal loss pigging data due to corrosion may
contribute to the inaccurate structural evaluation. The authors have used corrosion data gathered
through repeated in-line inspections on offshore pipeline at different time to examine the relationships
between the corrosion defect size and corrosion rate. The aim of statistical and probabilistic analysis
on pigging data is to determine the most likely actual behavior of the metal loss pattern in terms of the
type of distribution and the error severity. In order to provide an accurate statistical data for pipeline
assessment process, appropriate analysis on this pigging data is necessary. The analysis starts with
feature-to-feature data matching procedure based on repeated inspections over several years,
followed by the statistical analysis of the matched data to examine the statistical distribution of
corrosion dimension and corrosion growth rates. To reduce the embedded error within the data, a
correction method has been introduced in the process. The approach of predicting of the future size
of corrosion dimensions from previous pigging data is also highlighted. The results from data analysis
procedure are the applied to evaluate the current and future integrity condition of corroded pipeline
using Monte Carlo simulation method. The paper has demonstrated the application of statistic and
probability method in data analysis such as Weibull plot, Chi-square test, Box and Muller method and
Inverse transformation method so engineers can fully appreciate the importance of statistic and
probability method in engineering fields.
IO18
Estimating the Intensity of Point Processes Models for Earthquake Occurrences
1,3Nurtiti
Sunusi, 1Sutawanir Darwis, 2Wahyu Triyoso
1Statistics
Research Group, Faculty of Mathematics & natural Sciences, Institut Teknologi Bandung,
Indonesia.
2Geophysics Research Division, Faculty of Earth Sciences & Mineral Technology, Institut Teknologi
Bandung, Indonesia.
3Mathematics Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences, Universitas Haluoleo,
Kendari, South East Sulawesi, Indonesia.
The main task in earthquake prediction is to develop statistical model for analyzing the observation,
so that we can evaluate the probability of earthquake occurring in a certain space-time-magnitude
window. Earthquake is a physics phenomenon that appears at irregularly space and time. One of the
stochastic models most suitable for describing physical phenomena like that is called point process.
These processes are uniquely characterized by their conditional intensity, that is, the probability that
an event will occur in the infinitesimal interval t , t t , given the history of the process up to t .
Once the conditional intensity function is given, the joint density distribution for the realization of
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
87
occurrence data in (0,T) can be recorded, which is used to obtain the maximum likelihood estimates.
Consequently, it is important to obtain good parametric models of conditional intensity function. The
aim of this paper is estimating the conditional intensity of point processes models. In this paper, we
consider the type of earthquake sequences description as a renewal process with sojourn time
exponentially distributed. Our results show a promising direction of research of developing a
heterogeneous point process.
Keywords: Point Processes; Renewal Process; Conditional Intensity.
IO19
Statistical Profiling of Low Employability Graduates in Malaysia: Feasible?
Lim Hock-Eam
Lecturer, Faculty of Economics
Universiti Utara Malaysia
06010 Sintok,
Kedah, Malaysia
Using a panel data of 179 graduates of Universiti Utara Malaysia (UUM) and Universiti Tunku Abdul
Rahman (UTAR), this paper estimates the statistical profiling models of low employability graduates
with piecewise exponential and Weibull proportional hazard model. The estimated model suggest that
the significant determinants of the Malaysia’s graduate unemployment duration are income support
while unemployed, age, use of English as main communication language among friends, ethnicity,
types of degree, father’s employment status and education level and time dependency. These
determinants can be used to identify the group risk of being low employability graduates- those
receive no income support while unemployed, young, do not use English as main communication
language among friends, Malays, studied for degree other than UTAR Accounting, and those father’s
employment other than self-employed and with low education level; whereas, the predicted hazard or
survival function can be used to identify individual risk of being low employability. The estimated
piecewise exponential and Weibull models are found to be correctly predicted 75% and 62.5%
respectively, of the validation samples graduates. Thus, the piecewise exponential model with
flexibility in baseline hazard specification, outperforms Weibull model. It is concluded that the
implementation statistical profiling of low employability graduates in Malaysia, is feasible given the
widely available of information technology.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
88
IO20
The Effect of Imputing Missing SDs
Nik Ruzni Nik Idris
Kulliyah of Science
International Islamic University Malaysia
P.O. Box 10, 50728 Kuala Lumpur
Background and Objective
This paper examines the implication of (1) excluding studies with missing standard deviations (SDs)
and (2) imputing the missing SDs, on the standard error (SE) of the overall Meta analysis estimate.
Methods
The SE of the estimates from the above scenarios were compared with those based on all studies.
The SDs were assumed to be missing according to the following missing mechanism: (1) missing
completely at random (MCAR) (2) The SDs are more likely to be missing in studies with small sample
size small-size (3) The SDs are more likely o be missing in studies with large SDs (large-SD)
Results
If the SDs are missing under MCAR and under small-size missing mechanism, imputation is a good
approach. However, if the SDs were missing under large-SD missing mechanism, imputation leads to
bias in the SE of the estimate. The estimates of the between-study variances from the imputed data
were biased, resulting in overestimation of the SE of the estimate based on random effect model.
Conclusion
If the SDs are missing with MCAR or according to small-size missing mechanism, Multiple imputation
is recommended as it takes into account the uncertainty due to imputation. If the non-reporting is due
to larger size of SDs, the mean imputation is recommended as it produces the least bias SE of the
estimates.
IO21
The Modified Spatial Interpolation Methods for Missing Rainfall Data in Malaysia
Shariffah Suhaila Syed Jamaludin1, M.D. Sayang2 & Abdul Aziz Jemain3
1Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
2Center of Statistical Studies, Faculty of Information Technology and Quantitative Science,
Universiti Teknologi MARA, 40450, Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia.
3School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
A complete daily rainfall dataset with no missing values is highly demand in a variety of
meteorological and hydrological purpose. In most situations, spatial interpolation techniques such as
inverse distance and normal ratio methods were used for estimating missing rainfall values at a
particular target station which based on the available rainfall values recorded at the neighbor stations.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
89
However, these two methods are found to be very useful in the case where the neighbor stations are
very close and highly correlated with the target stations. In this study, several modification and
improvement have been proposed to these methods in order to estimate the missing rainfall values at
the target station using the information at the nearby stations. Four rain gauge stations at different
locations are selected as the target stations to test the improvised methods. The result indicated that
the modified methods improved the estimation of missing rainfall values at those target stations based
on the Similarity Index, root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE).
IO22
Cross – Sectional and Longitudinal Approaches in a Survival Mixture Model
Zarina Mohd Khalid
Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Johor, Malaysia.
Survival data modeling is one of main branches of medical statistics that specifically deals with timeto-event data. In particular, if the target population consists of long-term survivors, a survival mixture
modeling approach should be more suitable in modeling the time to a certain event by including the
fact that a group of patients will never experience the event of interest. A standard procedure in
estimating the unknown parameters in such model is by using cross-sectional information recorded at
any particular time point, usually during the first hospital visit. This study extends the standard
procedure by considering information obtained longitudinal approach has resulted in estimators
gaining better efficiencies and precisions.
IO23
Pipe Failure Probabilities of Water Distribution Systems
Syarifah Hidayah Syed Harun and Ismail bin Mohd
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu
Mangabang Telipot, 21030, Kuala Terengganu, Terengganu.
In this paper, we will describe two methods as we called Poisson method and Generic Expectation
Function (GEF) method for using to find pipe failure probabilities of water distribution systems which is
implicitly design by engineers. In reliability, one is concerned with system failure. In order to develop
GEF method using means and coefficients of variation of input random variables through employing
several probability distributions, normal and lognormal distributions are adopted. In this paper, 10
water distribution systems which are located in Terengganu, Malaysia have been used for illustrating
the mentioned above methods from which the comparison can be discussed. Besides that, hydraulic
simulation software, EPANET has been applied to get the input variables for each project. Failure
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
90
probability of each pipe is focus on failure probability of pipe to fulfill the demand P
replacement probability P
A
also pipe
B .
IO24
Correction and Preparation of Continuously Measured Rain Gauge Data in Malaysia
Marlinda Abd. Malek1, Ismail Mohamad2 & Sobri Harun3
1Department
of Civil Engineering, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Km 7, Jalan Kajang- Puchong,
43009 Kajang, Selangor. Malaysia.
2Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai.Johor. Malaysia.
3Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai. Johor. Malaysia.
This paper is another effort in developing a statistical model to patch missing rainfall data. The model
was developed and validated based on the past fifty years of observed hydrological data. Assuming
that the missingness mechanism is Missing Completely At Random (MCAR), the model utilizes the
basic theme of Expectation Maximization (EM) Algorithm, to repeatedly use complete-data methods to
solve incomplete data problems. The technique of Nearest Neighbour (NNeigh) Imputation is a
combined technique to overcome problems that are difficult or impossible for EM Algorithm.
Supported with robust statistical evidences, the study have managed to secure the overall size of the
data and proposed these methods to be the basis for preparing a clean and complete data set for
public domain.
Keywords: Missing Rainfall Data; Missingness Mechanism; Missing Completely At Random;
Expectation Maximization Algorithm; Nearest Neighbour Imputation.
IO25
Numerical Modelling of the 2004 Indonesian Tsunami along Peninsular Malaysia and North
Sumatra due to a Time Dependent Source
Ahmad Izani Md Ismail
Universiti Sains Malaysia,
Pulau Pinang,
Malaysia.
In a previous study (Roy et al. 2007), a nonlinear polar coordinate shallow water model was
developed to compute different aspects of the 2004 Indonesian tsunami along North Sumatra in
Indonesia and Penang Island in Peninsular Malaysia. In that study the initial tsunami wave was
generated instantaneously in the source zone along the fault line and that was used as the initial
condition of the model. But in reality, starting from the epicenter the rupture along the fault line
occurred gradually northward with a rupture front speed 2-3km/s and whole process was completed in
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
91
500-600 s (Ni et al. 2005). Thus the initial disturbance of the sea surface along the source zone is
also time dependent. In this study the model of Roy et al. (2007) has been used to simulate different
aspects of the tsunami associated with Indonesian tsunami 2004 using a time dependent source. The
computed results due to the time dependent source agree well with those of observations. A
comparison between the responses due to time dependent source and its corresponding
instantaneous version has also been carried out in order to test the efficiency of the instant source.
The comparison shows that the responses due to the time dependent source have significant
differences with those due to instantaneous version.
IO26
Half-Sweep Geometric Mean Method for Solution of Linear Fredholm Equation
M.S. Muthuvalu and Jumat Sulaiman
School of Science and Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Sabah,
Locked Bag 2073, 88999 Kota Kinabalu,
Sabah, Malaysia.
The objective of this paper is to examine the application of the Half-Sweep Geometric Mean (HSGM)
method by using the half-sweep approximation equation based on quadrature formulas to solve linear
integral equations of Fredholm type. The formulation and implementation of the Full-Sweep Geometric
Mean (FSGM) and Half-Sweep Geometric Mean (HSGM) methods are also presented. Some
numerical tests were carried out to show that the HSGM method is superior to the FSGM method.
IO27
Numerical Solution to Simulation of Time-Multiplexing Cellular Neural Network
R. Ponalagusamy and S. Senthilkumar,
Department of Mathematics,
National Institute of Technolofy,
Tiruchirappalli,
620 015, Tamil Nadu,
India.
This paper deals with a versatile algorithm for simulating CNN arrays and time multiplexing is
implemented using numerical integration algorithm. The approach, time-multiplexing simulation, plays
a pivotal role in the area of simulating hardware models and testing hardware implementation of CNN.
Owing to hardware limitations in practical sense, it is not possible to have a one-one mapping
between the CNN hardware processors and all the pixels of the image. This simulator provides a
solution by processing the input image block by block, with the number of pixels in a block being the
same as the number of CNN processors in the hardware. This article proposes an efficient pseudo
code foe exploiting the latency properties of Cellular Neural Network along with well known RK-Fourth
Order Embedded numerical integration algorithms. Simulation results and comparison have also
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
92
been presented to show the efficiency of the Numerical Integration Algorithms. It is found that RKEmbedded Centroidal Mean outperforms well in comparison with the RK-Embedded Harmonic Mean
and Embedded Contra-Harmonic Mean.
IO28
Edge Detection of Long Bone X-Ray Images using Cubic B-Spline Wavelet
1Nor
Ashikin Mohamad Kamal and 2Arsmah Ibrahim
1Pusat
Pengajian Sains Komputer
Pengajian Matematik
Fakulti Teknologi Maklumat dan Sains Kuantitatif
UiTM Shah Alam
2Pusat
Edge detection is a fundamental step in image analysis. This is because edges characterize object
boundaries useful for identification of object in a scene. The importance of edge detection increases
as more people seek for automation in image processing systems. Determining bone edges is
important because it can provide surgeons with important information for diagnosis, which in turn
enables them to give better treatment decision to their patients. Many edge detectors have been
developed and presently wavelet transform is one of the popular approaches. This is because
wavelet transform has the advantage of detecting edges using different scales. Edges can be
represented and detected efficiently through its local maximum. This paper discusses the
implementation of Cubic B-Spline wavelet on long bone x-ray images in detecting the edges using the
local maxima modulus. Preliminary results show that this method can identify edges very well which
can make it applicable to detect bone abnormalities.
IO29
Finite Elements Model of Shape Memory Alloy Anti-Symmetric Angle-Ply Composite Beams for
Active Shape Control
Nik Mohamad, N.A1, Mohd Ihsan, A.K.A.2 and A. Rasid, Z.3
1,2Department
of Mechanical & Material Engineering
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi
3Department
of Mechanical Engineering,
Kolej Sains dan Teknologi, UTMKL, KL
Shape memory alloy (SMA) wires are embedded within laminated composite beams to take
advantage of the shape memory effect property of the SMA. Active shape controls of these structures
are studied using the finite element method. A non-linear finite element model and its source codes
were developed for this purpose. Both Euler-Bernoulli’s and Timoshenko’s beam theories are used.
The former theory requires 4 degree of freedom elements while in the later the 6 degree of freedom
elements are used. The geometric non-linear model is based on the von Karman non-linear strain.
The effect of SMA is captured by adding the geometric stiffness matrix to the typical stiffness matrix of
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
93
composite plates. The Newton-Raphson method is then used to obtain the transverse deflections of
the beams. Two methods of shape controls are considered here: The active property tuning (APT)
and the active strain energy tuning (ASET). The values of recovery stresses for the ASET
improvement of the SMA are determined from the Brinson’s model. Studies are conducted on the
anti-symmetric angle ply SMA laminated composite beams. The effect of several parameters such as
the geometric, mechanical and SMA transformation effects on the deflections of the SMA composite
beams are studied. It was found that the effect of moment recovery on the beam deflection is
significant and with appropriate configurations of SMA composite beams, the deflection of the beams
due to external loading can be suppressed.
IO30
Convergence Monte Carlo Simulation to the Black-Scholes Formula in Pricing Warrants
Benny Yong
Department of Mathematics,
Parahyangan Catholic University,
Jalan Ciumbuleuit 94, Bandung,
40141 West Java,
Indonesia
Warrants are call options issued by firms, which gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset
from the firm by a certain date for a certain price. Many methods for pricing warrants. In this paper,
the value of the warrant will be determined by using Black-Scholes formula and Monte Carlo
simulation. Monte Carlo methods will be used here are standard Monte Carlo and antithetic variable.
Warrant value from Black-Scholes formula and Monte Carlo simulation will be compared each other.
Convergence warrant value from Monte Carlo simulation to the Black-Scholes formula will be
presented here.
IO31
Finite Elements Model of Shape Memory Alloy Anti-Symmetric Angle-Ply Composite Plates for
Active Modal Modifications
Z.A. Rasid, S. Sarip & M.Z. Hassan
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Kuala Lumpur
Shape memory alloy (SMA) wires are embedded within laminated composite plates to take advantage
of the shape memory effect property of the SMA. Active modal modifications of laminated composite
plates with SMA wires are studied using finite element method. A linear finite element model and its
source codes were developed for this purpose. The plate-bending model used in this study was
developed based on the first order shear deformation theory (FSDT) and the finite element model
used is the serendipity quadrilateral element with 40 degree of freedoms per element. The effect of
SMA is captured by adding the geometric stiffness matrix to the typical stiffness matrix of composite
plates. With the mass matrix, the typical eigen-value problem is solved where the eigen values
represent the natural frequencies of the plates. Two methods of frequency improvement are
considered here: The active property tuning (APT) and the active strain energy tuning (ASET). The
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
94
values of recovery stresses for the ASET improvement of the SMA are determined from the Brinson’s
model. Studies are conducted on the anti-symmetric angle ply SMA laminated composite plates. The
effect of several parameters such as geometric, mechanical and transformation effects on the natural
frequencies and the mode shapes of the SMA composite plates are studied. It was found that the
effect of SMA is similar for couples of frequency modes where frequencies of mode I and IV seems to
have the greatest effect in the case of simply supported and clamped-clamped boundary conditions.
IO32
A Preconditioning Technique for Elliptic Problems in Two Dimensions.
Sarah Flora Samson Juan
Universiti Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS)
The finite element method is a powerful tool to numerically solve differential equations derived from
diverse physical and engineering problems. When the problem is linear, this method leads to a
system of linear equations of relatively large size. The Conjugate Gradient method is used to solve
the resulting system of linear equations. This paper investigates the performance of the numerical
method when the number of iterations is reduced. To achieve this, a two-level addictive Schwarz
preconditioner is introduced, based on the domain decomposition method, in the CG method. The
quality of this preconditioner is important as this supports the reliability of the method to converge
faster. We validate the effectiveness of the preconditioner CG method for some two dimensional
elliptic problems and numerical results show that the number of iterations is reduced and the condition
number of the preconditioner matrix from the system is much smaller than the non-preconditioned
matrix.
IO33
Magnetic Contour Plane As A Historical Framework For Brainstorm
Tahir Ahmad *, Rashdi Shah Ahmad** and Liau Li Yun *
*Department Of Mathematics
** Department Of Physics
Faculty of Science
University of Technology Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
Embodied biological agents have histories which usually irreversible and reflected in their structure.
Without the historical context, we cannot understand their structure, appearance and behaviour. An
epilepsy disorder patient is an agent. This paper describes on how FTTM (Fuzzy Topographic
Topological Mapping), which has been developed initially as a mathematical model for solving the
inverse neuromagnetic problem, can be viewed as a framework for model of irreversible time for the
patient.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
95
IO34
Two-Generator Two-groups of Class Two of Order 32 and Their Application in Crystallography
1Norashiqin
Mohd Idrus, 2Nor Haniza Sarmin and 3Shahrizal Shamsuddin
1,3Fakulti
Sains dan Teknologi
Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris
35900 Tanjong Malim
Perak Darul Ridzuan.
2Department
of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai,
Johor Darul Ta’zim.
Group Theory is a beautiful area of mathematics that systematizes and formalizes mathematical study
of symmetry. Symmetry concepts have many applications in various scientific disciplines such as in
biology and chemistry. In physics, it should be emphasized that group theory is primarily valuable for
analyzing the effects of known geometrical symmetry on some systems. In this research, we focus on
2-generator p-groups of nilpotency class two of order 32, where p=2 and 3. Specific groups that are
isomorphic to each of the group in this classification will first be determined. By choosing those that
are symmetry, their application in crystallography, particularly in infrared and Raman spectra
activities, will be explored.
IO35
The Graph of Relative Diagram Groups from Relative Diagram Groups
Zn | t1, t2 | xt1 t1x, xt2 t2 x, x Zn
1Sri
Gemawati and 2Abd. Ghafur Bin Ahmad
1Department
of Mathematics,
Faculty Mathematics and Natural Siences,
Universitas Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia.
3School of Mathematical Sciences,
Faculty of Science and Technology,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
In this paper, we will discuss the construction of relative diagram groups from group that presented by
Zn | t1, t2 | xt1 t1x, xt2 t2 x, x Zn and
The graphs obtained are related to the word in W Zn *t1 , t2 .
relative monoid presentation
their graphs will be
presented.
Therefore, the number
of generator of the diagram group can be determined.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
96
IO36
Exterior Squares of Infinite Non-Abelian 2-Generator Groups of Nilpotency Class 2
1Nor
Haniza Sarmin, 2Nor Muhainiah Mohd Ali, 3Luise-Charlotte Kappe
1,2Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
Department of Mathematical Sciences,Binghamton University,
Binghamton, New York, 13902-6000 USA.
Let R be the class of infinite non-abelian 2-generator groups of nilpotency class 2. Using their
classification and non-abelian tensor squares given by N.H. Sarmin in 2002, we determine the exterior
squares of all groups in R.
IO37
On Counting the Conjugacy Classes of 2-Generator p-Group of Class 2
1Azhana
Ahmad, 2Robert F. Morse, 3Nor Haniza Sarmin, 4Satapah Ahmad
1,3Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
2Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Evansville,
Evansville, IN 47722, USA.
4Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
In this paper, we present results concerning the number of conjugacy classes and the structure of 2generator p-groups of class 2. Our results rely on the classification of 2-generator p-groups of class
two, p and odd prime number given by M. Bacon and L. –C. Kappe in 1993 and p=2 given by L. –C.
Kappe, N. H. Sarmin and M. Visscher in 1999. These groups have four types. For type 1, 2, and 3
groups we obtain a count of the conjugacy classes for a base case from which all other groups within
each type are central extensions. We derive a recursive formula to count the number of conjugacy
classes of the central extensions using our results for the base cases.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
97
IO38
Capability of Infinite 2-Generator Groups of Nilpotency Class Two
1Nor
Haniza Sarmin, 2Nor Muhainiah Mohd Ali and 3Luise-Charlotte Kappe
1,2Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
3Department of Mathematical Sciences, Binghamton University
Binghamton, New York, 13902-6000, USA
A group is called capable if it is a central factor group. R.Baer characterized finitely generated abelian
groups which are capable as those groups which have two or more factors of maximal order in their
direct decomposition. Using the explicit knowledge of the nonabelian tensor squares of infinite 2generator groups of nilpotency class two given by N.H. Sarmin in 2002, we characterized the capable
ones among those groups.
IO39
On the Rosenberger Monster II
Robert Fitzgerald Morse
University of Evansville, Evansville, IN 47722 USA
20345
The largest finite generalized triangle group has order 2
and is called the Rosenberger Monster
which we denote by R. The structure of R has been investigated by Rosenberger, Howie, Morse and
others both analytically and with computer calculations. In this talk we will report on computing various
homological functors for the Rosenberger Monster. This includes computing the Schur Multiplier and
the nonabelian tensor square and nonabelian exterior square for R.
IO40
Group Theoretical Approach in Determining the Molecular Vibration of the Square Pyramid
Molecule
1Rohaidah
Hj. Masri, 2Nor’aini Aris, 3Nor Haniza Sarmin & 4Satapah Ahmad
1Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
4Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
2,3Department
Group theory provides a systematic approach to describe the symmetry concept in molecular
vibrations. An exploitation of this symmetry in polyatomic structure is possible by using group
representation theory and the projection operator theory. The underlying group theory, such as the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
98
irreducible representations of symmetry group isomorphic to its point group is applied in the specific
example of the square pyramid model of AB5 molecule. The work presented in this paper is a
preliminary investigation of finding an efficient method of computing and describing molecular
vibrations of molecules which exhibit a large number of vibration modes. Here, all the main steps are
illustrated with the example of the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, D 4. The visualization of
vibration modes of AB5 are given in the last part of this paper.
IO41
Some Numerical Algorithms for Parallel Multigrid Method on Distributed Parallel Computer
Systems
Norma Alias, Tan Sui Chin, Shalela Mohd Mahali
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
UTM, Johor.
A highly parallel multigrid-like method for the solution of Partial Differential Equation. This paper, we
focuses on three major parallel techniques: domain decomposition, Full Multigrid and preconditioner
Multigrid method using F, V, W cycle. Based on some parallel techniques, these methods are straight
minimizing the execution time, computational complexity, communication cost, waiting and idle time.
The PVM library is implemented in order to exchange the data among processors on a distributer
parallel computer systems. The solver algorithms are developed for three-dimensional PDE problem
and validated with the available experimental data. Some sequential and parallel performance
measurements under consideration are speedup, efficiency, effectiveness, temporal performance,
accuracy, convergence and communication cost.
IO42
On The
Lp Boundedness Of Certain Rough Singular Integral Operators
Hussain M. AI-Qassem
Department of Mathematics and Physics, Qatar University
We establish the
Lp boundedness for a class of singular integral operators T ,h and a class of
related maximal operators M ,h when their singular kernels are given by functions in
Bq 0, 1 S n 1 and h satisfies a certain integrability condition. Our results shows that the class of
operators T ,h behaves completely different from the classical class of Calderón-Zygmund operators
T . Moreover, our results represent an improvement and extension over previously known results.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
99
IO43
A Note on the Partial Differential Equations and Convolutions
Adem Kiliçman & Hassan Eltayeb
Department of Mathematics, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor
A partial differential equation of second order,
A x, y uxx 2B x, y uxy C x, y u yy D x, y u y E x, y ux F x, y 0
and define the matrix
A x, y B x , y
B x, y C x , y
then the PDE is called
Parabolic if the
det 0
Hyperbolic if the
det 0
Elliptic if the
det 0
In this study we consider the
A x, y uxx 2B x, y uxy C x, y u yy D x, y u y E x, y ux F x, y u 0
and it was examined that, whether the convolution equation
F1 x, y * A x, y u xx 2 F1 x, y * B x, y u xy
F1 x, y * C x, y u yy F1 x, y * D x, y u y
F1 x, y * E x, y u x F1 x, y * F x, y u 0
is invariant under the type PDE where
F1 x, y and F2 x, y are solutions of non homogenous than
F1 x * F2 x and F1 x, y * * F2 x, y are also solutions for non homogeneous wave equation
where * single convolution and ** double convolution that is defined by
x
F1 x, y *x *y F2 x, y
y
0
where
y
F x , y F , d d
x
0
1
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
F1 x, y and F2 x, y are integrable functions, see [5].
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
100
IO44
A Study of Two Space Dimensions Generalized Order Partial Differential Equations of the
Parabolic Type
1Ithnin
Abdul Jalil and 2Rio Hirowati Shariffudin
1Department
2Institute
of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, Universiti of Malaya
of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science, University of Malaya
50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
In this paper we shall study on the methods pertaining to the numerical solution of the generalized
order parabolic equation
y u x, y , t
u x, y , t
u x, y , t
A
x
,
y
B
x
,
y
Q x, y , t
t y
x
y
on a finite rectangular domain xL x xH , yL y yH , t 0 with 1 2 , 1 2 and
0 y 1 . We still adopt the shifted Grünwald at all time levels, that is
u xi , y, t
1
x
x
i 1
g u x j 1 x, y, t with
j 0
j
i
g j as Grünwald weights. The numerical
scheme attempted is the Crank-Nicolson method which is implicit in nature. Unlike the classical
parabolic equation, the resulting matrix is the lower triangular matrix with non-zero elements on the
super diagonal. Normally the tri-diagonal matrix is reduced to bi-diagonal for direct solutions of the tridiagonal matrix equation. Yet iterative methods are extensively used to solve tri-diagonal matrix. In
this paper we report the iterative simulations of the above-mentioned problem. The simulations of
even numbers of unknowns are considered.
IO45
A Solution of Boundary Value Problem By Using the Double Laplace Transform Technique
Adem Kiliçman
Department of Mathematics, Kolej Universiti Sains dan Teknologi Malaysia(KUSTEM), 21030
Mengabang Telipot, Kuala Terengganu, Terengganu
In this study the linear second order partial differential equations are solved by using the double
Laplace Transform technique. In special cases, we solved three fundamental equations by replacing
the non-homogenous terms of three fundamental equations by addition of double convolution
functions.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
101
IO46
Application of Similarity Solution to Film Cooling for Flat Plate
Kahar Osman, Lee Tuck Kuen, Jamaluddin Md. Sheriff
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai Johor, Malaysia.
The purpose of this study is to solve film cooling problem for flat plate using mathematical model.
Two dimensional, steady, incompressible flow algorithm was developed to simulate the flow passing a
flat plate in the direction of surface. The continuity, momentum and energy equations along with the
boundary layer phenomenon in partial differential form were converted to similarity equations and
solved. Analysis was performed to study the effect of boundary layer on flat plate cooling. The plate
was modeled as porous medium to accommodate the injection holes. The injection-to-main stream
temperature ratio (IM), Prandtl number and surface mass flux were varied to compute the centerline
film cooling effectiveness. This study also shows better film protection is observed at high Prandtl
number for centerline cooling. It is also shown that the increase of surface mass flux of cool air tend
to increase centerline film cooling effectiveness. Similarity solution also shows that there is an
optimum number of injection holes for effective film cooling.
IO47
A Study of the Supercritical Solution of the Stationary Forced KdV Equation (sfkdv)
Abdelaziz Hamad Elawad, Mukheta Isa
Dept. of Mathematics, Gadarif University Sudan
Dept. of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, UTM Skudai Johor
In this paper we consider stationary Forced KdV equation with positive Forcing term. The
supercritical solitary wave solutions of the stationary Forced KdV equation are obtained. In order to
obtain the solutions the domain of the problem has been divided in three parts. The left, the middle
and the right parts. The solution on the left and the right parts are obtained by analytical method. The
solution on the middle part is expressed in the terms of weierstarss elliptic function. We have
designed computer programs using Mathematica to produce the solutions. The complete solution
was found by matching the solutions of all parts. We have found out that there are four solutions
according to the values of the phase shift L. Only one solution is positive. Further research can be
carried out for negative forcing terms.
Keywords: Stationary Forced KdV Equation; Supercritical Solution.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
102
IO48
Nonlinear Waves & Soliton Applications
Ong Chee Tiong1; Mohd Nor Mohamad2,Tay Kim Gaik3,
Tiong Wei King4, Chew Yee Ming5 & Anny Hii6
Department of Mathematics,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai,
81310 Johor Bahru, Malaysia.
Nonlinear waves phenomena can be observed when we solved nonlinear evolution equations liked
Korteweg-de Vries (KdV), Kadomtsev- Petviashvili (KP), Sine Gordon (SG), Burgers and Schr¨odinger
(NLS) equations. This talk contains both mathematical theory, numerical simulations and various field
of application using solitons. A numerical simulations on generation and propagation of solitons was
implemented by a user-friendly software package FORSO which is a VB computer programming that
gives the numerical simulation on solitons. Various interactions of resonant solitons have been
observed by using FORSO. Various application of nonlinear waves and solitons will also be discussed
in the field of medical and telecommunications.
Keywords Soliton, Korteweg-de Vries and Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equations.
IO49
Application of Taguchi Method to Investigate Several Network Parameters Affecting the
Performance of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol in a Self-Organizing Network
Mazalan Sarahintu, Muhammad Hisyam Lee, Hazura Mohamed
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai,
Johor Darul Ta’zim
A Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is a wireless multi-hop network formed by a set of mobile nodes
in a self-organizing way without relying on a predefined infrastructure such as base station, which
results in all networking functions must be performed by the nodes themselves. In this paper, the
application of the Taguchi method on understanding the functional relationship between the
performance of dynamic source routing (DSR) protocol and the influence of process parameters in
MANET is presented. The effect of various network parameters including terrain, network size, pause
time, node velocity, transmission range, traffic load, and packet rate was investigated on the following
performance metrics: number of routing packets (NRP) and number of packets dropped (NPD).
Results showed that packet rate had the strongest influence on the NPD, and network size had the
biggest effect on the NRP. Within the seven parameters investigated, the effect of network size,
pause time, node velocity, and traffic load was considered significant on the NRP and the effect of
pocket rate, transmission range, and terrain was considered significant on the NPD. The results of
this study would be helpful for routing designers in designing the future reactive protocols or improving
the DSR algorithms since by knowing the order of predominance established, when conducting
simulation, the designers can know what parameter should be given high priority compared to others,
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
103
which can act directly to improve and enhance the protocol performance. The experimental results
obtained also confirm the adequacy and effectiveness of the used approach.
IO50
Simulation of the Growth of Complex Geometric Patterns in Polymer Membrane
1S.
Amir, 2N.S. Mohamed and 3S. A. Hashim Ali
1,2Center
for Foundation Studies in Science,
Universiti Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur.
3Institute
of Mathematical Sciences,
Universiti Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur.
Normally polymer electrolyte membranes are prepared and studied for application in electrochemical
systems. In the present work, polymer electrolyte membranes have been used as the media to
culture fractals. Fern-like fractals have been successfully cultured in PEO-lithium slat films. The
structures that have been simulated are based on the Brownian motion theory (random walk). The
simulation program was written in a computer language and using the string production method of LSystem. The axiom used is F and three production rules have been chosen to best simulate the DLA
structures: F [ FF ]F { FF ] , F [ FF ]F and F [ FF ]F . More over, the DLA structures from the
model are statistically self-similar and its fractal dimensions,
f d were calculated using the box-
counting method. The fractal dimensions of the simulated model are comparable with the values
obtained from the original fractals observed in the polymer electrolyte membrane. This indicates that
the model developed in the present work is within acceptable conformity with the original fractal.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
104
IO51
Identifying Factors Affecting on Data Delivery Performance in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing
Protocol using a Systematic Approach
1Hazura
Mohamed, 2Muhammad Hisyam Lee and 3Mazalan Sarahintu
1Department
of Industrial Computing,
Faculty of Information Science and Technology,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
43600 Bangi, Selangor.
2,3Department
of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
A mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a collection of mobile nodes dynamically forming temporary
network without the use of any existing network infrastructure or centralized administration. Due to
the mobility of the nodes, as well as the continual arrival and departure of nodes, the topology of the
network changes constantly. To manage the transmission, routing protocols are needed. Therefore
analyzing performance of the protocols becomes crucial to finding efficient routing protocols. In this
work, we show a systematic procedure of using Taguchi parameter design in analyzing Destination
Sequence Distance Vector (DSDV) routing protocol performance. Using orthogonal arrays and
signal-to-noise (S/N) ratios we determine the most factor influence and the best combination of factor
levels. This paper evaluates the impact of terrain size, node speed, network size and pause time on
the data delivery. The study indicated that a maximum ratio of data delivery could be obtained with
terrain size of 150m x 150m, node speed of 1 m/s, network size of 200 nodes and pause time of 10
seconds.
IO52
Modeling of an Agent Based Schedule: Preliminary Study
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Centre of Advance and Software Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia City Campus,
Jalan Semarak 45410 Kuala Lumpur.
Agent is computer program that can do work for the user. They are responsible for doing task on the
behalf of the user and also train the user and monitor event. Therefore we propose an agent based
approach in scheduling reservation system which each person has an agent that negotiates with other
agents to schedule the meeting. The agent should support their associated human user in complex
process of meeting to be better and faster. In this paper, we also focus on benefit of agent during
handling the problems occur in meeting process. Agent based scheduler system is the system uses a
multi agent paradigm, where independent agent are responsible for deciding how the task is to be
achieved and actually performing the necessary set of action, including handling interaction with other
agent. We offer solutions using agent paradigm in this new application area, with aims to improve the
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
105
optimization of scheduling to achieve greater efficiency and throughout. To this end, we described
which agent is more suitable to improve the overall solution.
IO53
A Heuristic Algorithm for Solving Airline Crew Scheduling with Side Constraints
Ani Minarni, Faridawaty, Marlina Setia Sinaga, Pasukat Sembiring, Robinson Sitepu, Herman
Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics
University of Sumatera Utara
The airline crew scheduling problems at the planning level are typically solved in two steps: firstly,
obtaining crew itineraries/feasible pairings that partition all flights and the objective is to minimize
pairing costs; and secondly, assigning these optimal pairings to individual crew that minimizes crew
costs (called crew rostering). Side constraints that capture safety regulations, i.e. ‘duty time rules,
time connections and crew bases limitation (a limit on total; pairings per base)’; are embedded to the
standard problem constraints structure in the first stage, whereas additional rule at the rostering stage
that capture task coverage is added to the standard problem constraints structure in the second
stage. A heuristic algorithm is proposed to solve the airline crew scheduling with those side
constraints.
IO54
A Simulation-based Simulated Annealing for Stochastic Job Shop Scheduling Problem
Rashidah Ahmad & Sutinah Salim
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Solving a job shop scheduling problem optimally is difficult, but when the data are uncertain, the
problem is much more complicated because of the inaccurate objective estimation, large search
space, and multiple local minima. In this paper, simulated annealing incorporated with Mote-Carlo
simulation is applied to stochastic job shop scheduling problem when the processing times are
random variables with known means and variances, to minimize the expected make-span. To fine a
lower bound on the performance measure, a surrogate simulated annealing is proposed, in which an
extra penalty term is added to each of the expected value of the random processing times to
approximately account to some variations in the problem data. The effects of some parameters on
both algorithms are also discussed.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
106
IO55
Preliminary Analysis for Data Collection on Vehicle Inspection
Nuzulha Khilwani Ibrahim, Rozana Diana Ahmad Rusli, Nurulhuda Firdaus Mohd Azmi
Centre of Advance and Software Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia City Campus,
Jalan Semarak 45410 Kuala Lumpur.
This paper presents a preliminary analysis of data collection on vehicle inspection centre. From the
original data collected, data was improved by a little adjustment. The average value for every step of
inspection is calculate to get a brief idea on how much time taken by every inspection for each vehicle
before the value approximate into a range of additional maximum five seconds. There is a clash
between two vehicles at some points in this analysis, which it define by two vehicles conflicting in two
same time period at some point in first and second inspecting vehicle process. Knowing that there is
a clash between the two series of same colored points, we tried to resolve the situation by adding a
period of time called ‘waiting time’ to make sure that the conflicting points would be separated into
different time units. In this research, we offer solutions using constraint programming techniques, with
aims to improve the inspection process with greater efficiency and techniques.
IO56
An Effective Modelling and Solution Approach for the Hamiltonian p-Median Problem
M. Zohrehbandian
Department of Mathematics,
Islamic Azad University-Karaj Branch,
P.O.Box 31485-313, Karaj, Iran
Location-Routing problems involve locating a number of facilities among candidate sites and
establishing delivery routes to a set of users in such a way that the total system cost is minimized. A
special case of these problems is Hamiltonian p-Median Problem (HpMP). In attempting to solve this
problem, numerous mathematical formulations have been proposed. Most of them have in common
that their descriptions as integer optimization problems are not polyhedral ones (ILP formulation).
This paper introduces an ILP formulation for HpMP and proposes an approach for solving it. The
model based on the formulation of vehicle routing problem (VRP) that has been studied in depth in the
literature. Hence, for solving the HpMP, we can use plenty of methods in solution of VRP, which has
been proposed in the literature.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
107
IO57
A Simulated Annealing Approach for Uncapacitated Continuous Location-Allocation Problem
with Zone Dependent Fixed Cost
Tolhah Abdullah, Zaitul Marlizawati Zainuddin & Sutinah Salim
Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
Location analysis is concerned with locating one or more service facilities while fulfilling some
constraints such as the demand of the customers and minimizing the total cost. Despite the cost of
transporting goods or services, there is a fixed cost associated with opening a given facility such as
the cost of the land, taxes or trunking (or hauling) cost to supply product, services and labour. This
cost may vary from one area to another. This paper provides Simulated Annealing (SA) procedure for
solving uncapacitated continuous location-allocation problem in the presence of zone-dependent fixed
cost.
Several implementations are considered to test the effect of the parameter values.
Computational results are presented using data set from the literature.
IO58
Uncertainty Model for Solving Water Supply Problem in Agriculture Irrigation
Gayus Simarmata, and Herman Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics
University of Sumatera Utara
Irrigation demands depend on farmers’ decision on when and which crops to produce, how much
water to apply, and which irrigation technologies to use. Decisions involve short-and-long-term
commitment of resources. Therefore farmers need to make decision about water and land use for
economic purposes based on water availability. This paper proposes a two-stage economic
production model under uncertainty to examine the effects of hydrologic uncertainty and water prices
on agriculture [production, cropping patters and water and irrigation technology use. The model
maximizes net expected farm profit from permanent and annual crop production with uncertainty
water availability and a variety of irrigation technologies. There are some discussions and variations
on the model obtained.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
108
IO59
Stochastic Programming Model for Portfolio Optimization Problems
Nerli Khairani and Herman Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics
University of Sumatera Utara
Financial optimization is one of the most attracting areas in decision-making under uncertainty.
Prominent examples include: 1) asset allocation for pension plans; 2) security selection for stock and
bond portfolio managers; 3) currency hedging for multi-national corporations; 4) hedge fund strategies
to capitalize on market conditions. Stochastic programming models have been proposed as an
important tool in solving financial decision making problem, in which there are uncertainties in the
problem data. In this paper we study about building a stochastic programming model for solving
portfolio optimization problem. A scenario based approach is used to solve the result model.
IO60
Discrete-Time Linear Optimal Control with a Random Input Study
Kek Sie Long
Department of Mathematics,
Centre of Science Studies,
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia,
86400 Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia.
The purpose of this paper is to study the random input in a discrete-time linear optimal control system.
Since the random input includes the measurement noise and disturbance input, it is often referred as
white noise when evaluating a quadratic performance functional. With the random input presented in
a system, the state variable is impossible determined precisely at the later time. Due to the existence
of noise, the state variable is considered as a random sequence which satisfies the Markov property
and could be described by the probability transition matrix. Additional, the mean-value and the
covariance matrix of the state give the meaningful information for investigation of the stochastic linear
optimal control system. A simple simulation of scalar system is discussed and the graphical optimal
solution is represented.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
109
IO61
Assessment of Point Process Models Following the Neyman-Scott Process
Fadhilah Y1, Zalina MD2, Nguyen V-T-V3, Maizah Hura A1, Zulkifli Y4
1Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, UTM. Johor.
Pengajian Sains, ATMA, KL.
3McGill University, Quebec, Canada
4Instititute of Environmental and Water Resources Management, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Skudai 81310 Johor
2Pusat
In stochastic modeling of rainfall following the Neyman-Scott process, the parameter estimates are
strictly dependent upon the choice of moments used in the fitting procedures. In previous studies,
sample moments such as means and variances at different timescales were commonly used. In
addition, lag1 autocorrelations at various timescales were also used. However it was found that
autocorrelations tend to have large sampling errors due to large number of zero depths. Hence, two
strategies of fitting procedures were discussed in this paper. First was to replace the autocorrelations
with transition probabilities at hourly and daily timescales. The second was to replace the
autocorrelations with the non-central moments. The Shuffle-Complex-Evolution (SCE) was used in
estimating the parameters. The performances of the models were evaluated in terms of their ability to
preserve the statistical properties as well as the physical properties of the observed series. The rootmean-square error (RMSE) values were evaluated to determine the errors. Results of the
assessment indicated that the used of the transition probabilities in the fitting procedure produced the
smallest RMSE in most of the properties tested.
Keywords: Neyman-Scott Rectangular Pulses (NSRP) Model, Shuffle-Complex-Evolution (SCE),
Hourly rainfall, Transition Probability, Non-Central Moment.
IO62
Statistical Approach on Grading the Students Achievement via Mixture Modeling
1Zairul
Nor Deana Md Desa, 2Ismail Mohamad, 3Zarina Mohd Khalid, and 4Mohd. Hanafiah Md Zain
1Department
of Foundation Education, Faculty of Education,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
2-4Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The purpose of this study is to compare result obtained from three methods of assigning letter grades
to students’ achievement. The conventional and the most popular to assign grades is the Straight
Scale method (SS). Statistical approaches which used the Standard Deviation (GC) and conditional
Bayesian method are considered to assign the grades. In the conditional Bayesian model, we
assume the data to follow the Normal Mixture distribution. The problem lies in estimating the posterior
density of the parameters which is analytically intractable. A solution to this problem is using the
Markov Chain Monte Carlo approach namely Gibbs sampler algorithm. The Straight Scale, Standard
Deviation and Conditional Bayesian methods are applied to the examination raw scores of two sets of
students. The results showed that Conditional Bayesian out performed the Conventional Methods of
assigning grades.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
110
IO63
Estimation of Skewness and Kurtosis for Muscat Stock Market Data
Muhammad Idrees Ahmad
Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
Sultan Qaboos University,
Muscat, Oman.
It is well documented in the finance literature that the empirical distribution of daily stock market
returns has very specific shape which is far from normal. It may have very long left tail and
specifically high peak. The fund managers require information about the shape of distribution for their
portfolio diversification. Skewness is a measure of length of tail while the kurtosis measures are
highly correlated, they together are usually used to measure the shape of distribution. Conventionally
the skewness and kurtosis are estimated by first four central moments. But these estimates are
usually biased and have large variances which increases further if the underlying distribution is not
normal. In the present study several alternative and robust methods of measuring skewness and
kurtosis for the empirical distribution of Muscat Stock Market daily returns are investigated. These
consist of the methods based on Central Moments, Standardized moments, Linear Combination of
Order Statistics and percentiles. Estimates of skewness and kurtosis by each of these methods are
compared in terms of their non parametric bootstrap standard errors and length of percentile
confidence intervals.
IO64
On The Asymptotic Variance of Sample Vector Variance
Erna T. Herdiani and Maman A. Djauhari
Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
The most popular and widely used measure of multivariate dispersion is the generalized variance.
However, its computation is quite cumbersome when the number of variables p is large and it does
not work anymore when the covariance matrix is singular. The singularity of sample covariance
matrix occurs, for example, when p is greater than the sample size n. This paper discusses an
alternative measure called vector variance which can eliminate these obstacles and has been
successfully used as the stopping rule in Fast MCD algorithm. It is known that the sample vector
variance converges in distribution to a p2-variate normal distribution. The mean is quite sample, i.e.
equal to the trace of the square of population covariance matrix. However, the asymptotic variance
has a complicated formulation and is tedious to compute because it involves a matrix multiplication of
size (p2 x p2). Using the properties of vec operator, we show that the asymptotic variance can be
represented in a simple form.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
111
IO65
Generalized Addictive Mixed Models for Small Area Estimation
Anang Kunia & Khairi l A. Notodiputro
Department of Statistics
Bogor Agriculture University,
Jl. Meranti, Wing 22 Level 4
Kampus IPB Darmaga,
16680 Bogor,
Indonesia.
Small Area Estimation (SAE) is a statistical technique to estimate parameters of sub-population
containing small size of samples with adequate precision. This technique is very important to be
developed due to the increasing needs of statistic for small domains, such as districts or villages.
Some SAE techniques have been developed in Canada, USA, and UE based on real data. We
adapted this technique to produce small area statistic in Indonesia based on national data collected
by the Central Bureau of Statistic. We found that the linear model applied to auxiliary data produced
estimates with low precision. In this paper we propose a class of generalized additive mixed model to
improve the model of auxiliary data in small area estimation.
IO66
The Impacts of Age-Related Hearing Loss
Azmin Azliza Aziz
Department of Finance and Banking,
Faculty of Business and Accountancy,
Universiti Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur.
Hearing impairment has become a very common chronic health problem among the older generation
Presbycusis or age-related hearing loss is defined as the loss of auditory sensitivity that is the result
of aging. It may affect the quality of an individual’s life particularly in the social activities. In this
paper, the impacts of hearing loss are determined by investigating the association between the level
of hearing loss and their effects on the quality of life. This study considered two possible approaches
in analyzing the data, i.e. a single model and a correlated model. In both approaches, the concept of
logistic regression analysis was applied with the assumption that the responses have a binomial
distribution. Analyses using individual logistic regression and correlated data provide almost
consistent results for the greatest and least impacts of hearing loss. Finally, the comparisons
between the results for individual logistic regression models and correlated model are discussed.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
112
IO67
Practical Forecasting Approach for Malaysia Electricity Load Forecasting
Zuhaimy Ismail and Mohd Fuad Jamaludin
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,UTM
Interest in the appliedresearch on short and medium-term electricity load forecasting has been
remarkable during the past few years. Forecasting electricity loads with linear methods has always
been a challenging task, since the load series exhibit several superimposed levels of seasonality,
together with the nonlinear effects of many important exogenous variables, such as temperature,
holiday and special events. Furthermore, forecasting load profiles (the series of 24 hourly loads in the
target day) as a vector forecasting problem is an order of magnitude more difficult. Yet, it is precisely
the forecasting of these profiles that has been the typical operational, and the market requirement for
electric utilities. This paper examines the issues of forecasting using conventional regression-based
methods and other methods such as neural networks and expert system. Some discussion on the
practicality of using expert system and neural network for forecasting the 24 hours of daily electricity
load and very much conducive to this approach. We employ the data on the daily electricity load
demand from Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB). The forecast accuracy is measured based on the error
statistics of forecast between the models for half an hour ahead for the short term forecast and a
month ahead for the medium term are presented and behavior of data is also observed.
IO68
Analysis Effect of Terrorism toward Tourism by Intervention Model
Riswan Effendi1 & Suhartono2
1Mathematics
2Statistics
Department, UIN Suska Riau-Indonesia.
Department, ITS Surabaya-Indonesia.
Intervention model is a time series model that can be used for describing and explaining the effect of
an intervention caused by external or internal factor, which happens on a time series data. In general,
this model can also apply for modeling time series with change in regime. The aim of this paper is to
discuss the results of theoretical and empirical studies about intervention model, particularly pulse
function intervention. Theoretical study is focused on the derivation of statistics terms that be used as
basic for determining the order of intervention model. Then, the results of this theoretical study are
applied to construct a model building procedure of intervention model. Finally, the effect of the first
Bali bomb to the occupancy level of five star hotels in Bali is used as a case study. The data are
observed starting from January 1997 to September 2005. In this case, the first Bali bomb that
happens on October 12th, 2002 is an intervention of external factor whose effect will be evaluated.
The result of this empirical study shows that interventional model can describe and explained exactly
the quantity and the length of the first Bali bomb effect toward the decreasing of the occupancy level
of five star hotels in Bali.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
113
IO69
Generalization of a Stochastic Model for Analysis of Multivariate Longitudinal Measurements
Khalid Ali Salah
Institute for Mathematical Research (INSPEM), Universiti Putra Malaysia,
43400 Serdang, Selangor
For a given random process
random variable Y
1
Tv
F
over a time interval
0,T , and a function V x , we define a
V t dt , and wish to generalize its probability distribution in longT
0
. We consider the case of the Ornstein-Uhlenbck (OU) process, in which v
x2
depending upon whether V x exp
dx is non-vanished or vanished for the parameters
2
and . The process will be extended over the infinite time interval. Our emphasis will be on
time limit T
generalization of the stochastic process with particular regard to the concept of Integrated OrnsteinUhlenbck (IUO) process. To incorporate this process in multivariate longitudinal measurements, we
specify a structure for the within subject covariance based on a stochastic process. In general, for the
analysis of longitudinal repeated measurements data we consider the model
X i X i* i
X i* Gi H ibi Wi
where X i is the observed measurements of subject i , Gi , H i bi are fixed and random effects
respectively, Wi is the IOU stochastic process and i is the measurement error.
IO70
Stochastic Logistic Model for Fermentation Process
Arifah Bahar & Madihah Salleh
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
In our study we consider stochastic logistic model for modeling the microbial growth in fermentation
process. The model concerns on environmental stochasticity that affects the growth. Thus, we
introduce stochastic perturbation
growth
coefficient
max .
e
dw
dt
We
to logistic model dx t x t max 1
show
that
the
resulting
Itô’s
x t
dt via its
xmax
stochastic
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
differential,
114
x t
dx t x t max 1
dt e x t dw t has a positive and global solution which
xmax
does not contradict its deterministic counterpart. We also show that the solution is stochastically
bounded.
IO71
ARPS Hyperbolic Decline Model
1,4Sri
1Statistics
Wahyuningsih, 1Sutawanir Darwis, 2Agus Yodi Gunawan, 3Asep Kurnia Permadi
Research Group, Faculty of Mathematics & natural Sciences, Institut Teknologi Bandung,
Indonesia.
2Financial
& Industrial Mathematics Research Group, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia.
3Reservoir
Engineering Group, Faculty of Earth Sciences & Mineral Technology, Institut Teknologi
Bandung, Indonesia.
4Statistics
Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences, Universitas Mulawarman,
Samarinda, East Kalimantan Indonesia.
Estimating reserves and predicting production in geothermal reservoirs has been challenge for a long
time. Many methods have been developed in the last several decades. One frequently-used
technique is decline curve analysis approach. Most of the existing decline curve analysis techniques
are based on the empirical Arps equation. The equation was proposed more that sixty years ago.
However a great number of studies on production decline analysis are still based on this empirical
method. The equation represents the relationship between production and time for oil wells during
pseudo steady-state period. The three types of decline are exponential, hyperbolic and harmonic. It
is difficult to foresee which equation the geothermal reservoir will follow because geothermal product
is steam, no fluid and no gas. A wide variety of approaches to the problem of decline curve fitting
have been presented in the petroleum literature. The hyperbolic type of decline, which occurs most
frequently in applications, can be recognized by the fact that the lost ratios are constant or nearly
constant. Stochastic approaches have increasingly been used to study the uncertainty in remaining
reserves estimates. In this talk, we shall derive the hyperbolic decline model as AR(1) process, the
Autoregressive model with order 1, by means of the discretization of the flow rate equation. We found
that the hyperbolic decline model leads to an AR(1) process with time varying parameter. This is a
new approach in petroleum literature. This study will extend Kalman filter vector in reservoir multiwall
system. We then apply the present model to simulate the geothermal performance data. The results
can be used to forecast remaining reserves and optimum maintainance.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
115
IO72
Primary Hip Stem Stability: The Effect of Bone Pathology on Micromotion
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq & K. Nazri
Biomechanics and Tissue Engineering Research Group (Bio-TEG),
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The effect of bone quality on the success of hip arthroplasty remains a topic of debate. Skeletal
disease such as osteoporosis cause a significant loss of cancellous bone stock and structural
deterioration of bone tissue. The reduced bone quality affects the decision made by surgeons in
terms of selection of suitable hip stem as osteoporosis increases the likelihood of fracture and
instability. It has been suggested that patients with poor bone stock would be better served having
cemented hip stems to ensure strong primary fixation. However, there are reports that also
cementless stems are reliable for patients suffering osteoporosis. A finite element model in
conjunction with a novel methodology for predicting hip stem stability was experimentally validated in
a previous study. In this study the methodology was applied to two CT datasets from osteoarthritic
patients about to undergo hip replacement. Based on DEXA scans of the two patients, the Young
Adult T-score showed in one case marked osteoporosis in all regions of the femur. 3D models were
constructed from these two CT datasets and the material properties were assigned based on the
grey-scale values on an element-by-element basis. A third femur model was created as ‘nonpathological’ control using the Visible Human Project (VHP) CT dataset. During the analyses, all
interfacial contacts on surfaces with micromotion larger than a threshold limit for bone ingrowth of
were removed, and the iteration continues until either a stable-state condition is achieved or
instability occurred. The results showed that the stems fixed in the control and osteoarthritic bones
were stable. For the osteoporotic bone, the stem was found to be unstable due to a progressive
reduction in surface area feasible for bone ingrowth. The results showed that bone quality affects the
stability and therefore the potential success of hip stems.
IO73
Matrix Transfer and Coupled Mode Equation for Nonlinear Photonic Bandgap as Optical Signal
Processing
Ayi Bahtiar & Irwan Ary Dharmawan
Department of Physics, Universitas Padjadjaran,
Jl. Raya Bandung-Sumedang KM.21,
45363 Sumedang, Indonesia.
An all-optical switching device is a crucial component for developing high speed data transmission
and signal processing in telecommunication network. The device is based on nonlinear optical
material, whose refractive index depends on light intensity. Various concepts for all-optical switching
devices have been studied; however as the best of our knowledge, until now there is no purely optical
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
116
switching devices have been realized. Recently, photonic crystals have been considerable interest
both theoretically and experimentally for switching devices. Due to the practical reason, we studied
one-dimensional nonlinear photonic crystal for all-optical switching devices. We use transfer matrix
method and nonlinear coupled mode equation to determine photonic bandgap and optical switching
process. We applied both methods to three different structures: nonlinear Distributed Bragg Reflector
(DBR), photonic crystal with defect layer and nonlinear photonic crystal which has similar linear
refractive index but has different sign of nonlinear refractive index. By using an appropriate
combination of refractive indices, it was found that the first two structures can be used as all-optical
switching in telecommunication wavelength (1.55µm). The third structure can be used both for
switching and optical limiter at the wavelength of 1.0 µm.
IO74
Influence of Occlusal Loads on Stress Distribution of Dental Implants
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq & M. I. Mohd Norshahid
Biomechanics and Tissue Engineering Research Group (Bio-TEG),
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The primary stability of abutment-implant and implant-bone system in prosthetic dentistry is crucial to
its short-term and long-term success. The commercially available abutment designs can be
categorized into one of three different types – interference fit, screw and a combination of both screw
and interference fit. The interference fit design provide primary fixation through interface frictional
resistance and a large contact pressure whilst design where a combination of both fixation exists may
prove inefficient as the screw threads may not contribute to the fixation when the connection is
primarily made by the interference fit. The implant-bone system is also crucial because instability at
the interface would prevent surrounding bone from intimately attached to the implant. Though
attachment through biological means is more favorable, reports have suggested that mechanical
parameters could also achieve similar affects to biological active coating. Adequate stability and
surface roughness have been found to provide conducive environment for bone attachment and
growth. In this study, a new abutment mechanical interlocking design is proposed through an 8 o
double tape which locked mechanically once inserted into the dental implant body. In vitro finite
element non-linear contact analyses were carried out on the proposed design, as well as the design
based on screw and interference fit for comparison. The bone model simulating the mandible was
separated into cortical and cancellous region with load simulating the occlusal forces was applied on
the abutment. Results showed that stability for the two types of screw designs were 25% better than
the interference fit design. However, larger stresses were exerted on the neck of the abutment for the
screw design. Results also showed that implant with tapered design produced better load transfer
than a pure cylindrical design. Micromotion was larger for the tapered design, but did not exceed the
threshold limit for oseointegration. The double-tapered dental implant system has been found to
achieve maximum load transfer at an acceptable interface micromotion for bone integration.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
117
IO75
Doppler Frequency Model for Sea Surface Current Simulation from RADARSAT-1 SAR Images
Maged Marghany, Mohamed Miyas & Mazlan Hashim
Department of Remote Sensing,
Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
This paper presents results of Doppler frequency model has been applied over the RADARSAT-1
SAR data. Two dimensional Fourier transform was applied with kernel window size of 512 512
pixels to convert the RADARSAT-1 SAR data into frequency domain. The centeroid Doppler shift
frequency process applied on the subset images with kernel window sizes of 512 512 . Non-linear
transform spectra of Doppler frequency was applied in order to relate the Doppler frequency with real
sea surface current. The mathematical derivation of this relation is explained in details in this paper.
IO76
Performance of Glenoid Prostheses in a Conventional Glenohumeral Joint Arthroplasty
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq & I. Alhamzee
Biomechanics and Tissue Engineering Research Group (Bio-TEG),
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
One of the primary concerns in glenohumeral joint arthroplasty is loosening of the glenoid component.
Although there are many factors affecting glenoid component loosening, the design is arguably the
most important factor as has been reported of the high loosening rates of fully-constrained
prostheses. The off-center loading, normally termed the “rocking-horse” phenomenon is thought to be
the main reason behind loosening of the prostheses. Two types of fixation design are normally used
in glenoid component – the keeled and the pegged – with the pegged design varies in terms of its
numbers and the degree of alignment. The pegged design has the advantage of minimizing bone
resection but tend to be more difficult than the keeled due to problems getting adequate exposure of
the glenoid. Four glenoid components representing each of the fixation design were modeled in three
dimensions. The model of the scapula was created from CT datasets and truncated to a region
around the glenoid to make the analyses more manageable. The glenoid was then virtually reamed to
simulate the preparation of the bone bed for implant insertion. Each implant design therefore has its
own reamed glenoid. The implants were then inserted into their respective prepared glenoid and offcenter loading was then applied to simulate the “rocking-horse” phenomenon. The material properties
of the bone were assigned based on the Hounsfield units from the CT datasets. Results showed that
the maximum edge displacement of the pegged glenoids due to the off-center loading was clearly less
than that of the keeled glenoids, with the slanted peg perform slightly better than the aligned one. The
pegged design was superior than the keeled because the pegs are placed in the stronger peripheral
bone.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
118
IO77
Tricritical domination
Doost Ali Modjeh and Parisa Firoozi
Department of Mathematics
University of Mazandaran
Babolsar, IRAN, P.O. Box 47416-1467
A graph G is domination tricritical if the removal of any three of vertices decreases the domination
number. Properties of tricritical graphs are studied. We show that a connected tricritical graph has
minimum degree at least 4. Ways of constructing a tricritical graph from smaller tricritical graphs are
presented.
IO78
The Total Edge-Irregular Strengths of Gears
Nurdin
Mathematics Department
Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
Universitas Hasanudin (UNHAS)
Jl. Perintis Kemerdekaan.
KM 10 Tamalanrea,
Makassar, Indonesia.
For a simple graph
labeling
two
G V G , E G with the vertex set V G and the edge set E G , a
: V G E G 1, 2,..., k
different
edges
e e1e2 and
t e e1 e e2 .
is called an edge-irregular total k-labeling of G if for any
f f1 f 2 in E G we have t e t f where
The total edge-irregular strength, denoted by
smallest positive integer k for which G has an edge-irregular total k-labeling.
determine the total edge-irregular strength of gears.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
tes G , is the
In this paper, we
119
IO79
Graphs with Exponent 3
Didi Febrian & Saib Suwilo
Department of Mathematics,
University of Sumatera Utara,
Medan 20155, Indonesia.
A connected graph G is primitive provided there is a positive integer k such that for each pair of
vertices u and v there is a walk of length k connecting u and v. The smallest of such integer k is the
exponent of G, denoted by exp(G). This paper discusses a necessary and/or sufficient condition for a
primitive graph to have exponent 3 and determines the smallest number of edges for such graphs.
IO80
On The Basis Number and the Minimum Cycle Bases of the Wreath Product of Some Graphs
1M.M.M.
1Department
Jaradat & 2M.K. Al-Qeyyam
of Mathematics and Physices, Qatar Universtiy,
Doha-Qatar
2Department
of Mathematics, Yarmouk University
Irbid-Jordan
G is called a d fold if each edge of G occurs in at most d of the
cycles in B . The basis number, b G , of G is the least non-negative integer d such that C G
A cycle basis B of a graph
has a
d fold basis.
The length
l B of a cycle basis B is the sum of the lengths of its elements:
l B CB C . A minimum cycle basis is a cycle basis with minimum length. A construction of a
minimum cycle bases for the wreath product of some classes of graphs is presented. Moreover, the
basis numbers for the wreath product of the same classes are determined.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
120
IO81
2-Exponents of Two-Colored Lollipops
Saib Suwilo
Department of Mathematics,
University of Sumatera Utara,
Medan 20155, Indonesia.
A two-colored digraphs is a digraph in which each of its arcs is colored by either red or blue. A two
colored diagraph D is primitive provided there are nonnegative integers h and k such that for each pair
of vertices u and v one can find a walk from u to v consisting of h red arcs and k blue arcs. The
smallest positive integer h+k among all such nonnegative integers h and k is the 2-exponent of D and
is denoted by exp2(D). An (n,s)-lollipop is a symmetric connected digraphs on n vertices consisting of
a cycle of length s and a path of length (n-s). In this paper we give an upper bound for 2-exponent of
two-colored (n,s)-lollipops in terms of s and n, and determine two-colored (n,s)-lollipop whose 2exponent attains the upper bound.
IO82
Computers-Assisted Student Learning in Engineering Mathematics
Maya Pundoor & Ramadas Narayanan
1Lecturer in Mathematics, Curtin University of Technology, Sarawak Campus, Malaysia
2Lecturer in Mechanical Engineering, Curtin University of Technology, Sarawak Campus, Malaysia.
Engineering Mathematics is compulsory subject in foundation year of all engineering programs. This
will be one of the staring subjects they will be taking in this university. Their paces of learning have
very wide range. In addition, the current educational environment does not allow them to remedy their
deficiencies in mathematics at their own pace. Another problem is that some students who do decide
to stay with engineering programs achieve only minimal proficiency in mathematics. This is later a
serious handicap to their educational and is the cause of endless problems for them and for their
instructors. Computer-assisted student learning in Engineering Mathematics have will have immense
scope in the area.
In this paper, an aspect of Engineering Mathematics that is challenging for the students and mastered
poorly by some students is identified. This aspect is analyzed to determine the reasons for getting a
less than optimal outcomes. An instructional approach that draws on some of the principles of adult
learning developed and the factors that it will lead to improve student outcomes are identified. The
key elements of your approach are implemented with a group of students and the effectiveness of the
strategies is concluded.
Keywords: Computer Based Assessment; Engineering Mathematics.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
121
IO83
Lattice Boltzmann Simulation for the Permeability of Reconstructed Porous Media
Irwan Ary Dharmawan
Department of Physics, Universitas Padjadjaran,
Jl. Raya Bandung-Sumedang KM.21, 45363 Sumedang, Indonesia.
Relating the transport properties of rocks to their pore structure has been a long-term goal of great
interest to petroleum engineers, hydrologists, and other earth scientists. This problem can be
addressed at various levels of detail, with the resulting models requiring varying amounts of
microstructural data. The empirical permeability models such as Kozeny-Carman predict values of
the permeability using knowledge only of porosity and a characteristic length such as the mean pore
diameter, mean grain size, or specific surface. At the other approach of complexity lie those models
that attempt to reconstruct the pore space of a rock, and then numerically solve the Navier-Stokes
equations in the pore space. We present results for predicting permeability of the full threedimensional porous media. The method consists of two key components, reconstruction of threedimensional porous rock from two-dimensional thin sections and three-dimensional flow simulation
using the Lattice-Boltzmann technique. We construct three-dimensional porous rock using serial
sectioning method and Monte Carlo method. The last method is used with conditional data and input
two-point correlation functions from thin sections. Permeability is then estimated through flow
simulation on the reconstructed porous media by solving the Navier-Stokes Equations. The result
shows that the reconstructed porous media have anisotropy permeability properties and agreed very
well with empirical statement from Cozeny Karman law.
IO84
The unsteady Power Law blood flow through a multi-irregular stenosed artery
1Norzieha
1,2 Department
Mustapha, 2Norsarahaida Amin
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
The non-Newtonian pulsatile model of blood flow through a multiple stenoses with irregular
surface is considered. The generalized Power Law model of blood viscosity is chose to study the
characteristics of blood flow in a multi-irregular stenosed artery. The flow is assumed to be unsteady,
laminar, two-dimensional and axisymmetric. The calculation of the governing equations of motion in
terms of the viscous shear stress in the cylindrical coordinate system is employed using a finite
difference scheme based on the non-uniform grids. The numerical results obtained for a multiirregular stenoses on flow velocity, wall shear stress, resistance to flow and flow rate are represented
through some graphs. The results obtained show that the axial velocity, flow rate and wall shear
stress produced lower values, while the resistance to flow presented higher values than a Newtonian
model.
Keywords: Generalised Power-law model; Multi-irregular stenosed artery; Blood flow.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
122
IO85
Mathematical Modeling of Boundary Layer Flow over a Moving Thin Needle with Prescribed
Wall Temperature
1Syakila
Ahmad, 1Norihan Md Arifin, 2Roslinda Mohd Nazar, 3Abdul Aziz Jaafar, 4Ioan Pop
1Institute
for Mathematical Research & Department of Mathematics,
Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
2School
of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Kebangssan Malaysia,
43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
3Department
of Aerospace Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
4Faculty
of Mathematics, University of Cluj,
R-3400 Cluj, CP 253, Romania.
The steady laminar forced convection boundary layer flow of an incompressible viscous fluid over a
moving thin needle with variable wall temperature is considered. The governing boundary layer
equations are first transformed into no-dimensional forms. These equations are then transformed into
similarity equations using the similarity variables, which are solved numerically using an implicit finitedifference scheme known as the Keller-box method. The numerical solutions are obtained for a bluntnosed needle (m=0). Numerical computations are carried out for various values of the dimensionless
parameter of the problem, namely the parameter a representing the needle size, with Prandtl number,
Pr = 0.7 (air) and 6.8 (water at room temperature). It has been found that the heat transfer
characteristics are significantly influenced by these parameters. However, the Prandtl number has no
effect on the flow characteristics due to the decoupled boundary layer equations.
IO86
Effect of Body Acceleration on a Micropolar Blood Flow through a Mild Stenosed Artery
Ilyani Abdullah, Norsarahaida Amin
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
The pulsatile flow of blood under the influence of externally imposed body acceleration is considered.
The situation like riding in vehicles, flying in airplanes and fast body movements during sport activities
can lead to serious health problems in the cardiovascular system. A mathematical model is developed
by treating blood as a micropolar fluid which takes into account blood rheology, as blood consists of
microelements suspended in plasma. The governing equation involving unsteady nonlinear twodimensional partial differential equations are solved employing finite difference scheme.
Computational results on the velocity profiles and the flow characteristic are presented.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
123
IO87
Wireless Sensor Network Deployment in Water Retention Problem
Shaharuddin Salleh, Ruzana Ishak, and Shazirawati Muhd Puzi
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
A sensor network is a deployment of massive numbers of small, inexpensive, self-powered devices
that can sense, compute, and communicate with other devices for the purpose of gathering local
information to make global decisions about a physical environment. This self-organized network has a
powerful node as its sink which has computational capability, and transmitter and receiver for
communicating with all other nodes in the network. One useful application of the wireless sensor
network is in its deployment for collecting and disseminating information from a body of water. This
paper discusses the computational model of a single-sink network for computing water retention in a
medium such as a lake or water reservoir. We discuss a possible deployment of sensor nodes for
various problems in water retention. They include computing the volume of water in an arbitrary size
lake, estimating its surface area, generating an approximated lake floor and detecting the presence of
certain harmful chemicals. In most cases, the most relevant mathematical technique for modeling is
the finite element method. The domain in the problem consists of a mesh of triangles formed from the
sensor nodes through Delauney triangulation. The model has a lot of potential especially in tackling
environmental issues in the water retention problem.
IO88
Verification of Mathematical Model of A Splicing System
1Nor
Haniza Sarmin , 2Noor Aini Abdul Rashid, 3Fong Wan Heng, 4Mohd Firdaus Abdul Wahab
1,3Department
of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
2,4Department
of Biology,
Faculty of Science,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
A splicing system describes the action of sets of restriction enzymes and a ligase that acts on DNA
molecules in order to produce further molecules. The language generated by a splicing system is
called a splicing language, which can then be analyzed using concepts in formal language theory. It
consists of the strings in the initial set and all strings in the closure of initial set under the operation of
splicing. Adult language and limit language are subsets of the slicing language. This research
initiates the connection between formal language theory and the study of informational
macromolecules. A laboratory verification of the mathematical model of the actual wet-lab procedure
is discussed, where the adult language and limit language are distinct in this case.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
124
IO89
2-Dimensional Fuzzy Number in Multi-Stage Dynamical System: An Improved Algorithm.
Normah Maan & Tahir Ahmad
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science
UTM
The concept of one-dimensional fuzzy number is successfully used in many industrial applications
such as in modelling of microstrip lines and furnace systems. But most applications in real world
problems involved multivariable systems. Therefore, in this paper, 2-dimensional fuzzy number
concept, specifically pyramidal fuzzy number is discussed. The verification of its properties and the
definition of alpha-level set are also given. This concept is then employed in modelling the mass
transfer process of multi-stage dynamical system.
IO90
An Introduction to Mathematical Models of Linguistic Theories
Tengku Muhammad Andri
Beg Berkunci 101, 86400 Parit Raja
Batu Pahat, Johor Darul Takzim
Grammatical rules of natural languages can be built in non mathematical ways as well as
mathematical. Linguistic theories, Chomskyian or non Chomskyan, tried to explain the language
phenomenon to understand the works of mind, therefore it is very interesting to see how mathematics
can contribute to those linguistic theories. This paper will try to describe how mathematics can
contribute and what obstacles and limitations it has.
IO91
Stable Self Similar and Locally Self Similar Processes
S. Rezakhah
Faculty of Mathematica and Computer Sciences,
Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran – Iran
This paper considers wavelet based estimates for the Self Similar parameters of the Linear Fractional
Stable Motions. The Consistency of the estimators is also studied. We obtain some statistical results
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
125
for the Hurst parameter estimation of Fractionally Integrated Auto Regressive Moving Average,
FARIMA, time Series with Stable innovations. We also consider a class of Locally Self Similar
processes called linear linear Multifractional Stable Motions, which extends Multifractional Brownian
Motion and provide where the distributions can have Heavy tail and be non-symmetric. New results
for Multifractional Brownian Motion are obtained.
IO92
Metaheuristics for Solving Facility Layout Problems: Concepts and Trends
Nadia Nurul Nordin, Zaitul Marlizawati Zainuddin 2 & Kuan Yew Wong3
1,2Faculty
of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor,
3Faculty
Facility Layout Problems (FLPs) are combinational optimization problems, which are relevant to both
manufacturing and service sectors. FLPs are known to be NP-hard. They usually involve the
arrangement of departments to minimize the distance traveled by units of flow, people, material,
information, and other supporting services in the safest and most effective manner. Due to the
practical importance of FLPs, many approximate algorithms i.e. metaheuristics have been developed
to tackle them. This paper provide a review on the fundamental of some metaheuristics commonly
used to solve FLPs, as well as the previous and current research trends in this area. Discussion and
comparison of the metaheuristics will be made in terms of their formulations, the solutions obtained
and the types of layout involved. It is hoped that this paper will provide a new perspective for
research in FLPs.
IO93
Optimization Investment Models With a Single Stochastic Factor
Sugiyarto Surono1 & Ismail Mohd2
1Universitas
2Department
Alunad Dahlan Yogyakarta, Indonesia
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu,
Mengabang Telipot, 21030 Kuala Terengganu, Terengganu, Malaysia.
This paper will discuss about a class of stochastic optimization models of expected utility in markets
with stochastically changing investment opportunities. The prices of the primitive assets are modeled
as diffusion processes whose coefficients evolve according to correlated diffusion factors. Under
certain assumptions on the individual preferences, we are able to produce reduced form solutions.
Employing a power transformation, we express the value function in terms of the solution of a linear
parabolic equation, with the power exponent depending only on the coefficient of correlation and risk
aversion. The new result demonstrate an interesting connection with valuation techniques using
stochastic differential utilities and also, with distorted measures in a dynamic setting.
Keywords: Stochastic Differential Equation; Investment Model; HJB Equation
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
126
IO94
A Solution of Optimal Control Problem of Continuous Interconnected Nonlinear System Using
DISOPE Approach
Nor Hazadura Hamzah, Hazadura Hamzah & Mohd Ismail Mohd Aziz
Institute of Mathematical Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UNIMAP),Perlis.
The main concerns of this study is to investigate and advance the knowledge of a hierarchical
algorithm for solving continuous – time optimal control of interconnected nonlinear dynamical system,
known as Hierarchical Dynamics Integrated System Optimization and Parameter Estimation
(HDISOPE) algorithm. HDISOPE algorithm is developed by extending Dynamics Integrated System
Optimization and Parameter Estimation (DISOPE) approach to a hierarchical structure of optimal
control problem of interconnected system, to take into account model-reality difference that may have
been deliberately introduced to facilitate the solution of the complex nonlinear problem or due to the
uncertainty in the model used for computation. In this study, HDISOPE algorithm based on a linear
quadratic model is implemented in MATLAB software. Two simulation examples with different levels
of nonlinearities are carried out to investigate the effectiveness and the convergence properties of the
algorithm.
IO95
Thermal Performance of a Microchannel with Entropy Generation Minimization
Ummikalsom Abidin & Normah Mohd. Ghazali
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Studies have established that a good microchannel design is based on its lower thermal resistance.
However, the latest theory, entropy generation minimization (EGM), stated that lower entropy
generation rate must also be considered for an optimized microchannel design as is discussed in
basic thermodynamics theory. The present study applies entropy minimization on a parallel flow
rectangular microchannel with geometry previously identified as optimized but without EGM. The
thermal resistance agreed with that of past studies with channel aspect ratio of 6 and a channel
number of 120, but the entropy generation rate obtained for the design was not minimized. For the
same entropy generation rate value with the same design, an optimum channel number is found to be
60. Lower thermal resistance is obtained with higher overall pumping power at the expense of
increasing entropy generation rate. Future optimization microchannel heat sink design procedure
should take into account EGM to reduce thermal resistance as well as entropy generation.
Keywords: Thermal Performance; Microchannel; Optimization; Entropy Minimization
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
127
IO96
Agent’s Coordination and Cooperation in the Water Resources Reallocation Project under
Uncertainties
Sharmila Karim & Mohd Ismail Abdul Aziz
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
Conflict of interest arises among agents (players) in the decision making process, when a reallocation
water resource is planned due to climate, social, and economic change. Then the agent’s
coordination and cooperation under incomplete information cost/benefit allocation of water resources
reallocation project is a suggested solution, if one has appropriate technical and economic modeling.
Cooperative game theory with a hierarchical structure is introduced as alternative tools in the decision
making processes.
IO97
Modelling and Controlling of a Human-Like Arm with Muscle Flexibility
Musa Mailah, Suhail Kazy, Hossein Jahan Abadi, Mohd Zarhamdy Mohd Zain
Department of Applied Mechanics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor.
The paper deals with the modeling and control of a two-link planar robotic manipulator that partially
resembles a human arm. The simplicity and ease of computation of the control algorithm are
particularly highlighted in the study. The arm is subjected to a tremor excitation at a specific location
on the arm while performing a predefined task in space, taking into account the flexibility of the
‘muscle’ that are mathematically modeled. A feedback control system is applied using an active force
control strategy (AFC) in order to suppress the introduced disturbance so that the arm remains
invariant or robust to the applied force. A number of loading and operating conditions were also
simulated and tested to establish the system behaviors. Results clearly suggest the effectiveness of
the proposed method in countering various forms of conditions as the control mechanism renders the
arm accurate and robust I performing the desired task.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
128
IO98
Hybrid Model for Subdistribution of Competing Risks
Abdul Kudus1, Noor Akma Ibrahim2, Isa Daud3 & Mohd Rizam Abu Bakar4
1Department
of Statistic, Bandung Islamic University, Jl. Tamansari No. 1,
Bandung, 40116 Indonesia.
2,3,4Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang,
Selangor, Malaysia.
2,3,4Institute for Mathematical Research, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor,
Malaysia.
Studies with multiple endpoints are common in medical and engineering research. In such
cases, the endpoint consists of several distinct events of interest and the eventual failure being
attributed to one exclusively to the others, which defines a “competing risks situation”. One observes,
for each subject, simply a failure time and a cause of failure.
In the competing risks setting, the subdistribution function is the primary measure summarizing the
likelihood of a specific event. Given a certain time point t, the subdistribution gives the probability to
fail from particular cause up to this time point.
The subdistribution hazard regression proposed by Fine and Gray (1999) models the
relationship between subdistribution and the explanatory variables. Selection amongst regression
models with subset of explanatory variables can be done by Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC); the
model with the smallest AIC is chosen. This paper discussed on the method to boost smallest AIC
model by augmenting it with tree-structured regression called as hybrid model. This effort stems from
the interesting observation that subdistribution hazards regression and tree-based models tent to
complement each other in many aspects. The main idea is to first fit the ‘best’ subdistribution hazard
regression model and then use a tree structure as an augmentative tool to explain the remainder that
has been left out by the first fit.
The application of the proposed method to contraceptive discontinuation data finds that the
smallest AIC subdistribution hazard model for abandonment and switching risk can be boosted by this
method resulted in hybrid models with lower AIC. However, hybrid model for failure risk does not
constitute a substantial improvement over associated smallest AIC model.
Keywords: AIC; Competing Risk; Subdistribution Hazard Regression; Tree-Structured Regression
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
129
IO99
Statistical Analysis Of The Wireless Internet Usage Among Students In Universiti Malaysia
Sabah
Darmesah Gabda, Suriani Hassan, Sathissan a/l Ragavan
School of Science and Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Sabah,
Locked Bag 2073, 88999 Kola Kinabalu,
Sabah, Malaysia.
The aim of this paper is to investigate the wireless internet usage among students in Universiti
Malaysia Sabah. 126 Universiti Malaysia Sabah students had responded to a set of questionnaires.
Factor analysis was used to identify the academic and non-academic purposes of wireless internet
usage and the impact of wireless internet usage among Universiti Malaysia Sabah students.
MANOVA analysis was conducted to identify whether there is any gender difference and year of study
of the students between factors contribute to wireless internet usage. Two factors were attributed to
academic purpose of wireless internet usage; which include usage for communication and to gain
additional information. Three factors were obtained from the non-academic purposes which include
usage for social activities, entertainment and communication. Two positive and two negative impact
of wireless internet usage were identified. The positive impacts consisted of increase general
knowledge and ability in computer usage and also boost confidence of the students. The negative
impacts consisted of waste of time with non-beneficial activities and addictive of internet usage for a
longer period of time. The result of MANOVA analysis indicated that the factors that contributed to
wireless internet usage were the same according to gender and the year of study.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
130
IO100
Bootstrapping Nonlinear Regression
Sutawanir Darwis1, Agus Yodi Gunawan2, M. Ali Ashat3, Sri Wahyuningsih1,4, Nurtiti Sanusi1,5, Rian
Febtrian Umbara1, Elis Nurzannah1.
1Statistics
Research Group, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia.
2Financial & Industrial Mathematics Research Group, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia.
3Geothermal Laboratory, Faculty of Earth Sciences & Mineral Technology,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia.
4Statistics Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences,
Universitas Mulawarman, Samarinda, East Kalimantan Indonesia.
5Mathematics Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics & Natural Sciences,
Universitas Haluoleo, Kendari, South East Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Geothermal energy is the heat that can be extracted from the interior of the earth and
considered as renewable energy. Energy resources like coal and petroleum are located at specific
places. Renewable resources, like geothermal, are moving and are approximately site specific.
Regression analysis is one of statistical tools that frequently used in geothermal data analysis.
However, nonlinear regression is rarely used in analyzing geothermal data. The combination of
nonlinear regression and bootstrap is used in extracting information from geothermal database. A
random resampling of stochastic components in stochastic model is used to generate a large number
of geothermal data to be used in evaluation of production performance. This resampling scheme,
called bootstrap analysis, does not rely on the assumption of normality; i.e. nonparametric. The
approach can be used to forecast the probability of specific outcomes such as the traveling time
between injector and producer. Bootstrap was developed based on one-sample model where a single
unknown distribution F produces the data by random sampling. Applications of bootstrap in decline
curve analysis involve complicated data such as time series of steam flow rates. Bootstrap algorithm
was developed for AR(1) process similar to bootstrapping regression residual. Moving blocks
bootstrap, close to one-sample bootstrap, was developed to retain the correlation structure present in
the observations. Markov bootstrap is based on nonparametric estimate of transition density. Since
the generating process of dependent data is not specified, bootstrap algorithm for dependent data
differ from iid sample. The resampling plan should be design such that the dependence structure
should be preserved. Reinjections are an important part of geothermal steam production, and have
been used extensively, but a comprehensive interpretation is limited. Tracer test aims to determine
the degree of connectivity between injections well and production well. Parameters of tracer profiles
related to the parameter of the system and can be estimated using non-linear regression approach.
The parameter confidence interval is based on assumption of normal distribution. This paper aims to
explore the applicability of bootstrap nonlinear regression to estimate confidence interval of decline
rate parameters and mean transit time of the tracer. Bootstrap mean, bootstrap regression and
bootstrap nonlinear regression are reviewed and some examples will be given.
Keywords: Bootstrap Nonlinear Regression; Tracer Test.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
131
IO101
Small Area Estimation: A Review and Comparison on Various Methods
Dian Handayani1 & Noor Akma Ibrahim 2
1Department
2Institute
of Mathematics, State University of Jakarta, Indonesia.
for Mathematical Research (INSPEM), Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia.
The attention to small area estimation has increase along with the increased of government and
private sector demand to provide accurate information quickly, not only for national level but also for
small domain such as district or village. However, problem which often emerges is that data in small
areas are sparse which result in a difficulty to produce reliable estimates because the sample size
from these areas is not large enough to support the specified accuracy. For these reason, to provide
more reliable estimate in a small area, it is very convenient to use information (borrowing strength)
from other related areas. The procedure to borrow information from other small domain (areas)
depends on the estimator and it usually involves using a class of regression methods. This paper will
discuss and review several small area estimation methods and comparisons will be made with respect
to a case-study in Indonesia. We will introduce some methods like synthetic estimator, empirical
Bayes, and (empirical) best linear unbiased prediction.
Keywords: Small Area Estimation; Small Domain; Small Sample Size; Reliable Estimate.
IO102
Permutational Tests of Interaction Effects in Multi-Factorial Experiments
Bidin Yatim
Department of Statistics
Faculty of Quantitative Sciences
Universiti Utara Malaysia
06010 Sintok, Kedah.
Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is an extremely powerful analytical tool to analyze
multivariate data from multi-factorial experiments where observations are partitioned into a priori
groups, defined by multiple categorical independent variables. However, use of MANOVA requires
the data to be continuous and normally distributed, the covariance matrices for all treatment groups to
be homogeneous, the observations to be independent, and the number of variables not to exceed the
number of observations.
This paper is concerned with situations that do not meet these assumptions, specifically when the
data are non-normal. Possible methods of handling such data are: (i) analysis of distance (AoD) or (ii)
permutational MANOVA. Steps in AoD include: (i) calculation of appropriate distances between
observations, (ii) partition of the total sum of squared distances into appropriate components, (iii)
permutation tests of hypotheses.
Here, we describe the AoD and the permutational MANOVA, and report the results of our
investigation on the appropriateness of each technique for analyzing the significance of the interaction
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
132
effects in multi-factorial experiments. We investigate the performance of each method and compare it
with MANOVA whenever appropriate. We focus on testing interaction effects for various data types
and the comparisons are conducted via Monte Carlo studies, using size and power of tests. To avoid
complexity and extensive computer time, we focus on experiments having two cross-classified factors
which can easily be extended to more complex designs. Here, we generate correlated response
variables from multivariate Gamma and multivariate Logit distributions to represent non-normal data.
Analyses in AoD are based on both Euclidean and Mahalanobis distances.
Our results indicate that, while Euclidean-based AoD tends to overestimate power, Mahalanobisbased AoD recorded better results. Interestingly, in situations with small samples from non-normal
data, both permutational MANOVA and Mahalanobis-based AoD tend to perform slightly better than
MANOVA. With no restriction on the number of variables or the nature of their individual distributions,
both methods therefore provide good alternative to MANOVA.
IO103
A Heuristic Method of Scenario Generation in Multi-Stage Decision Problem under Uncertainty
Suherman, Herman Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics
University of Sumatera Utara
In most applications, the probability distribution of random variables is unknown or if it is given, it
would be too expensive to consider the discrete distribution with a huge possible realization or to
handle the continuous distribution with numerical integration. It is common to choose a set of
representative realizations with relatively small in number called scenario to present random events.
Scenario can be a quartile of a known distribution or historical data, prediction of several trees or
constructed using simulation. Each scenario is assigned to a probability value to reflect the likelihood
of the occurrence of a random event. For multi-stage model the information of scenario can be
organized in a tree structure. In this paper we purpose an algorithm for generating efficiently tree
decision of multi-stage stochastic programming problem. A heuristic method is used to generate
discrete probability distribution specified by four first marginal moment and correlation.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
133
IO104
Error Estimation in the Charge Simulation Method for Two and Three Dimensional Potential
Problems
Dai Okano, Li Tao, Kaname, Amano,
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Computer Science,Graduate School of
Science and Engineering, Ehime University,3 Bunkyo-cho, Matsuyama, Ehime, 790-8577 Japan.
The charge simulation method is a fast and simple solver for potential problems. The basic idea of the
method is to provide an approximation by a linear combination of fundamental solutions and
determine the weights by interpolation of boundary conditions. For Laplace equations, simulation
charges are placed outside the problem domain, and used as the basis fundamental solutions.
Logarithmic potentials are used for two-dimensional problems. For example, when we have a
Dirichlet boundary problem of Laplace equation on simply connected domain D in complex plane,
2u 0
z D , u z b z z D where b z is a given boundary value function.
An
N
approximation by the charge simulation method,
u z U N z Q j log z x j , is provided by
j 1
the charge points,
determined
x1 , x2 ,..., xN , placed outside D. The weights of the basis, Q1 , Q2 ,..., QN are
to
satisfy
the
collocational
boundary
conditions
N
U N yk Q j log yk x j k 1, 2,..., N at the collocation points y1 , y2 ,..., yN . If the exact
j 1
solution u
method
z is extensible beyond the boundary, and the simulation charges are placed properly, the
offers
highly
sup u z U N z c
accurate
N
zD
approximations
0 c,1 1 .
with
exponential
Where, the constants,
c
and
decay
of
error,
depends on u
z,
D, and the arrangement of the charge and collocation points. Above conditions guarantee the
existence of such proper arrangement of the points, but there is no practical method to place the
points properly in general. We here propose a method to place charge and collocation points for two
dimensional potential problems on multiply connected domains with smooth boundary curves.
Exponential decay of error is available, if the boundaries and the boundary conditions are smooth.
Our method uses conformal maps of simply connected domains as the premap functions of the
problem. The preamp functions are available by our method of numerical conformal mappings using
the charge simulation method [2].
In addition, we propose a charge and collocation point arrangement for the charge simulation method
for three-dimensional potential problems on sphere, by which the approximation error decays
exponentially, similar to the results of the charge simulation method for the two-dimensional problems,
sup u z U N z c
zD
N
0 c,1 .
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
134
IO105
A Weighted Ostrowski Type Inequality for Twice Differentiable Mappings and Applications.
Ather Qayyum
H.No.94 Khan Village Bosan Road Multan, Pakistan 60000.
A weighted Ostrowski type inequality for twice differentiable mappings in terms of the lower and upper
bounds of the second derivative is established. The inequality is applied to Numerical Integration and
some special Means also.
IO106
Asymptotic of Finite Difference Time Domain Method
Otong Nurhilal, Irwan Ary Dharmawan & Ayi Bahtiar
Department of Physics, Universitas Padjadjaran, Jl. Raya Bandung-Sumedang KM.21, 45363
Sumedang, Indonesia.
The finite difference time method is frequently used as a numerical solver for the Maxwell equation
and its application. We present a method to analyze a Finite Difference Time Domain method. The
method is based on asymptotic analysis approach in connection with standard truncation error. This
approaches leads to a consistency analysis, which provides order-by-order information about the
numerical solution of the FDTD method. In order to present the basic ideas of the analysis, we will
consider a simple one-dimensional FDTD method. The results show that the analysis gave accurate
prediction of the solution and can be applied to other analysis such as initial and boundary conditions.
Keywords: Finite Difference Time Domain Method; Asymptotic Analysis.
IO107
The application of homotopy analysis method for Lotka-Volterra equations
A. Sami Bataineh & M.S.M. Noorani
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
In this paper, we solve the 3-D version of Lotka-Volterra equations by using the homotopy analysis
method initially proposed by Liao. We compare our results with the classical Runge-Kutta method
(RK4). We conclude that the homotopy analysis is a reliable and powerful method for solving nonlinear system of first order ODEs.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
135
IO108
The Computation of the Comrade Matrix and the Greatest Common Divisor of Polynomials
Nor’aini Aris
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
The comrade matrix is an analogue of the companion matrix when a polynomial is expressed
in terms of a basis set of orthogonal polynomials. Let
a x and b x be polynomials expressed as
a linear combination of orthogonal polynomials such that deg
matrix associated with
a x deg b x .
The comrade
a x can be used to find the greatest common divisor of a x and b x .
We present the algorithms for computing the comrade matrix and the coefficient matrix for the
corresponding linear system. An analysis of the theoretical computing time is also given. The
ultimate aim is to incorporate these two algorithms into the algorithm for computing the greatest
common divisor of the generalized polynomials, and then use the computing time results to study the
performance of the algorithm.
IO109
Variability issues in manufacturing process: A perspective from industrial practitioners
Jafri Mohd Rohani1, Sha’ ri Mohd Yusof1 & Ismail Mohammad2
1Department
of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor.
2Department of Mathematic, Faculty of Sciences, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor.
All manufacturing and business processes have some form variability that exist in their respective
operations. It has become a real problem and enemy for any company to deal with this variability
issues. The key for any company to survive in a competitive world market for quality product or
process improvement is through reducing variability systematically. There are two types of variability
that exists in processes, namely common cause and special cause. Control chart is the most powerful
statistical tool and techniques that can monitor the variability and be able to distinguish between
common cause and special cause. This paper presents a case study in which a local plastic injection
moulding company applied some types of control charts application to monitor product variability.
However, to make them successful as problem solving tools, other factors such as strong
management commitment, training, teamwork and others are required.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
136
IO110
Convexity – Preserving Scattered Data Interpolation
Abd. Rahni Mat Piah, Azizan Saaban & Ahmad Abd. Majid
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 USM Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
This paper deals with the construction of convexity-preserving bivariate C1 interpolants to scattered
data if the original data are convex. This study is motivated by our earlier works on positivity and
monotonicity preserving scattered data interpolation, respectively. Sufficient conditions on lower
bounds of Bezier points will be derived in order to ensure that surfaces comprising of cubic Bezier
triangular patches are convex and satisfy C1 continuity conditions. Initial gradients at the data sites
will be estimated and then modified if necessary to ensure that both convexity and C 1 continuity
conditions of the surface patches are satisfied. The construction is local and easy to be implemented.
Graphical examples will be presented using several test functions.
Keywords: Scattered Data; Interpolation; Convexity; Continuity.
IO111
Automatic Reading of Node Values in a Numerical Model
Rudi Heriansyah & S. A. R. Abu Bakar
Computer Vision, Video & Image Processing Lab. (CVVIP), Department of Microelectronics &
Computer Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
In numerical modeling using numerical finite elements and finite difference based software,
sometimes it is important to know the value for each node. These software commonly have no facility
to read automatically the value and to compose them into a two dimensional form. For a model with
less number of nodes, the reading can be done manually usually by clicking directly on the node of
interest, but as the nod numbers become larger, this manual way is certainly not an efficient and
effective way. Other alternative is by saving the node values, but usually the data is saved in one
dimensional form. This paper proposes an algorithm for automatic reading of node values in a
numerical model, composing them into a two dimensional form, and displaying them as a graphic
object. Since the software usually has a facility to save the data in a spreadsheet format, the
proposed algorithm is implemented in this environment by using spreadsheet script programming.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
137
IO112
Improving Parallel Pipeline Algorithm using Message Passing Interface for Time Dependent
Problem
Ng Kok Fu & Norhashidah Mohd Ali
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800, Penang, Malaysia.
Numerical solution of time dependent partial differential equations often require a large number of
time steps to arrive at the desired solution. Time-marching algorithm with spatial parallelization is
commonly used where computation is done in each time step using all processors available before
advancing to the next time step, sequentially. This can result in fine granularity and decreased
scalability especially in cases where few spatial components are involved and still there are relatively
many processors available. Naturally one option is to parallelize the temporal domain. Several
algorithms have been suggested for the past two decades such as pipeline (Womble, 1990) and
parareal algorithm (Lions, Maday and Turinici, 2001). This paper presents a modified parallel time
stepping algorithm based on delayed pipeline concept to improve execution time. We discuss the
parallel implementation and propose a parallelization framework using Message Passing Interface
(MPI) in distributed memory environment. Numerical result shows that the modified algorithm is faster
compared to the original pipeline algorithm or the serial-time parallel-space method of solving time
dependent problems with fine granularity. With the advent of massively parallel processors and large
scale grid computing, this algorithm demonstrated that temporal parallelization would be a practical
mean of utilising the enormous raw computational power promised by these computing environments.
Keywords: Message Passing Interface, Parallel Time Stepping, Pipeline Algorithm, Temporal
Parallelization, Time Dependent Problem.
IO113
Approximate Analytical Solution of the El Nino – Southern Oscillation Model
Noor Fadiya Mohd Noor & Ishak Hashim
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
In this paper, a coupled system of nonlinear equations representing the El Nino – Southern Oscillation
(ENSO) phenomenon is considered. Approximate analytical solution to the ENS oscillator model is
derived by the Adomian decomposition method (ADM). The stability of the solution of the system of
equation is determined based on the approximate solution.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
138
IO114
Fuzzy Edge Connectivity Relates the Variables in Clinical Waste Incineration Process
Sabariah Baharun , Tahir Ahmad & M Rashid M Yusof
Structured networks of interacting components are hallmarks of several complex systems and clinical
waste incineration process is an example of such a system. Fuzzy graph theory provides important
tools to capture various aspects of complexity, imprecision and fuzziness of the network structure of
the incineration system as compared to the discrete description of relation of its crisp graph. This
paper discusses the use of fuzzy edge connectivity in describing the relation between the variables in
the incineration process. It begins with the definition of fuzzy graph that involves five different types of
graph fuzziness in which fuzzy edge connectivity constitute its third type. The fuzzy edge connectivity
and the membership values of the fuzzy edge connectivity based on the chemical reactions of the
variables of the system are defined and illustrated respectively. Fuzzy graph showing the relation
between the variables are also depicted in a diagram to give a better picture of the relation between
these variables.
Keywords: Fuzzy Edge Connectivity; Incineration Process
IO115
An Integral Equation Method For Conformal Mapping Of Doubly Connected Regions Involving
The Kerzman-Stein Kernel
Ali H. M. Murid, Laey-Nee Hu & Mohd Nor Mohamad,
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
We present an integral equation method for conformal mapping of doubly connected regions onto a
unit disc with a circular slit of radius 1 . Our theoretical development is based on the boundary
integral equation for conformal mapping of doubly connected region derived by Murid and Razali
(1999). In this talk, using the boundary relationship satisfied by the mapping function, a related system
of Fredholm integral equations is constructed, provided is assume known. For numerical
experiment, the integral equation is discretized which leads to a system of linear equations. Numerical
implementation on a circular annulus is also presented. If is unknown, a different numerical
procedure will be outlined.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
139
IO116
An Optimization Problem in Ergodic Theory
Mohd Salmi Md Noorani
School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
0 1
Let A be a
irreducible
nn
matrix and let
1,..., n
be given the discrete topology.
The
subshift of finite type with transition matrix A is defined as the compact set
X A x xi 1,..., n : A xi , xi 1 1 for all i Z
i
Acting on X A is the shift-map : X A X A which is defined by x i xi 1 . Let M denote the
set of all
-invariant Borel probability measures , i.e. 1 A A
of X A . Given M , let
Now let
m
for all Borel subsets A
h be the metric entropy of X A with respect to .
be a fixed positive integer and let
fi : X A
be Holder continuous functions for
each i 1,..., m . In this talk we shall be interested in the following type of optimization problem: For a
given constant c , what is the value of
sup h : fi d c, i 1, 2,..., m ?
M
Another question which is of related interest is: What is the structure of the
realizing the above supremum?
-invariant
measures
IO117
Subclass of Function Close-to-Convex with respect to Symmetric Points
Aini Janteng1, Suzeini Abdul Halim 2 & Maslina Darus3
1School
of Science and Technology, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Locked Bag No.2073, 88999 Kota
Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia.
2Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
3School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor Malaysia
In this paper, we consider functions of the form
close-to-convex with respect to symmetric points.
f z z n2 an z n belonging to the class of
In specific,
convex with respect to symmetric points. The class
K s denotes the class of close-to-
K s was first introduced by Das and Singh in
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
140
1977. The aim of paper is to introduce new subclass of
K s . Sharp upper bounds for a 2 , a 3 , a 4
and the Fekete-SzegÖ functional are considered for this class.
Keywords: starlike with respect to symmetric points, close-to-convex with respect to symmetric points,
Fekete-SzegÖ functional
IO118
On Sufficient Condition and Angular Estimation for
-like Function
Saibah Siregar & Maslina Darus
School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia, Bangi, 43600 Selangor Darul Ehsan
In this paper we introduced the class, that is
zf " z z f z '
1
f
'
z
f
z
b
zf ' z
f z
which analytic in unit disk U and also we obtained sufficient condition, angular estimation for that class.
IO119
Improved Boundary Integral Equation for Dirichlet Problem on Region with Corners
Munira Ismail, Ali Hassan Mohamed Murid & Bahrom Sanugi
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor,
Malaysia.
Swarztraubers’s integral equation for the Dirichlet problem on region with corners, a class of boundary
value problems for analytic functions on a region with a finite number of corners provides results that
need to be adjusted by a constant for its solution. In this paper, we would like to provide a new
integral equation for the problem that produces results directly without such adjustment. Dirichlet
problem is in fact a special case of the Riemann problem that is non-uniquely solvable. Previously we
have obtained some integral equations for the Riemann problem to obtain a special case of the
integral equation for the Dirichlet problem. What we have is an integral equation which is a
modification of Swarztrauber’s integral equation. The proof that this integral equation is uniquely
solvable is included and its advantage over Swarztrauber’s integral equation for the Dirichlet problem
is given.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
141
IO120
An Application of a Fractional Calculus Operator to a Subclass of p-Valently Analytic
Functions with Negative Coefficients of Complex Order
Ajab Akbarally & Maslina Darus
School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science ad Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
A new subclass
, p
M p A, B, b, is derived by applying a fractional calculus operator f z to
a subclass p-valently analytic functions with negative coefficient of complex order.
If
f z '
1 z
1 Az
where
f M p A, B, b, then it satisfies the condition 1
p
, p
1 Bz
b
f z
denotes subordination, b 0 is a complex number with Re b 0 , A and B are arbitrary fixed
, p
f z is a fractional calculus operator defined by
number, 1 B A 1 .
where
, p
f z
Dz f z is given by
Dz f z
, p
p 1 p
z Dz f z
p 1
z
f
1
d
d , 0 1
1 dz 0 z
Coefficient estimates for functions in this subclass are found. Growth and Distortion Theorems are
also proven for function in the subclass
M p A, B, b,
IO121
Recent Results on Ruscheweyh Operators
Maslina Darus
School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science ad Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
Recently, many problems related to operator associated to harmonic functions have been
investigated. One of the important operators is the Ruschewyeh derivatives. Ruscheweyh (1975)
introduces a very powerful operator which has been used as an essential tools in extending various
problems in the theory of univalent functions. The operators stated as the following:
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
142
k 1
k n 1
Dn f z z C n, k ak z k , 0 where C n, k
k 2
n
j n
j 1
k 1!
In this paper, we will show recent theorems regarding the Ruscheweyh derivatives operator in a
generalized form. In fact, many findings have been obtained for various problems related to this
generalized operators, see for eg. Darus and Shaqsi (2006) and Shaqsi and Darus (2007).
IO122
The Boundary Layer Flow past a Moving Wall with Mass Transfer
Anuar Ishak1, Roslinda Nazar2 & Ion Pop3
1,2School
of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science & Technology,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia.
3Faculty of Mathematics, University of Cluj, R-3400 Cluj, Cp 253, Romania.
The behavior of an incompressible steady thermal boundary layer flow past a permeable semi-infinite
flat plate moving in a free stream is discussed in this paper. In addition to the mass transfer from the
plate (suction or injection), the viscous dissipation term is also included into the energy equation. The
solutions of the transformed ordinary differential equations are obtained numerically using an implicit
finite-difference method. The numerical results are given for the velocity and temperature fields as
well as for the skin friction coefficient and the heat transfer (local Nusselt number) from the plate for
various values of the suction/injection parameter, f0, ratio of the wall velocity to the free stream fluid
velocity parameter, λ, Prandtl number, Pr and Eckert number, Ec. It is found that for all values of Ec
considered, suction increase the heat transfer by decreasing the thermal boundary layer thickness
and the reverse happens for injection. As expected, increasing of Pr is to increase the local Nusselt
number. It is also found that the boundary layer equations have non-unique (dual) solutions in some
cases.
IO123
3D Numerical Simulation of Tsunami Runup from QUICKBIRD Satellite Data
Maged Marghany & Mazlan Hashim
Department of Remote Sensing, Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
This paper presents results of Doppler frequency model has been applied over the RADARSAT-1
SAR data. Two dimensional Fourier transforms was applied with kernel window size of 512 512
pixels to convert the RADARSAT-1 SAR data into frequency domain. The centeroid Doppler shift
frequency process applied on the subset images with kernel window sizes of 512 512 . Non-linear
transform spectra of Doppler frequency were applied in order to relate the Doppler frequency with real
sea surface current. The mathematical derivation of this relation is explained in details in this paper.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
143
IO124
Effect of Magnetic Field and Conduction on Natural Convection Flow along a Vertical Flat Plate
in the Presence of Heat Generation
A. A. Mamun1, Z.R.Chowdhury2 & M.A.Azim3
1Institute
2Department
of Natural Sciences, United International University, Dhaka-1205, Bangladesh
of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, United International University, Dhaka-1205,
Bangladesh
3School of Business Studies, Southeast University, Bangladesh
The natural convection flow of an incompressible, viscous and electrically conducting fluid has been
studied by several research groups due to its potential application in nuclear reactors’ cooling system
design. The effect of conduction on magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) natural convection flow along a
vertical flat plate [1] in the presence of heat generation is investigated. The momentum and the
energy equations for this investigation are made dimensionless using a suitable transformation. The
converted non-linear partial differential equations of the dimensionless equations are then solved
using the implicit finite difference method with the Keller-box scheme. A discussion is given for the
effects of the magnetic parameter, Prandtl number, heat generation coefficient and conjugate
conduction parameter. Numerical results of the velocity, temperature, skin friction coefficient and rate
of heat transfer are presented graphically while the numerical values of the surface temperature are
displayed in a tabular form.
IO125
Numerical Modeling of Inviscid Acoustic Waves in a Closed Chamber
Mah T.C & Normah Mohd Ghazali
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Thermoacoustic theory is relatively new with studies being done to better understand the concept and
explain the factors that may or may not affect the solid-fluid interactions in a thermoacoustic resonator.
Currently, experimental reports are very much ahead of the theories with disagreements still existing.
In this study, a two-dimensional numerical simulation of acoustic waves in a closed chamber is
completed. Computations are performed by solving the two-dimensional, unsteady, inviscid NavierStokes system of equations. Finite-difference methodology was used accurate to second-order. A
vibrating membrane or a piston is used to generate the acoustic waves and progression of the waves
with time is observed. Results on the flow and temperature profiles showed similarities between that
from the inviscid model and previous study on viscous acoustic waves. Vortices, cross-flows and
beatings are complex behavior were observed which were similarly reported in past studies. This
indicates that the simpler inviscid simulation may be adequate to model thermoacoustic behavior.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
144
IO126
Development of 2D and 3D Double Population Thermal Lattice Boltzmann Models
Nor Azwadi Che Sidik1 & T. Tanahashi2
1Department
of Thermo-Fluids, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
of Mechanical Engineering, School for Open and Environmental Systems, Keio
University, Hiyoshi, Yokohama, 3-1-14 Japan.
2Department
In this paper, an incompressible two-dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D)
thermohydrodynamics for the lattice Boltzmann scheme are developed. The basic idea is to solve the
velocity field and the temperature field using two different distribution functions. A derivation of the
lattice Boltzmann scheme from the continuous Boltzmann equation for 2D is discussed in detail. By
using the same procedure as in the derivation of the discretised density distribution function, we found
that new lattice of four-velocity (2D) and eight-velocity (3D) models for internal energy density
distribution function can be developed where the viscous and compressive heating effects are
negligible. These models are validated by the numerical simulation of the porous plate 2D Couette
flow problem where the analytical solution exists and the natural convection flows in a cubic cavity.
IO127
Unsteady Boundary Layer Flow of a Micropolar Fluid near the Stagnation Points of a Plane
Semi-Infinite Wall
1Anati
1,2Department
Ali, 2Norsarahaida Amin and 3Ioan Pop.
of Mathematics,Faculty of Sciences,Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia.
3Faculty
of Mathematics, University of Cluj,
R-3400 Cluj, CP 253,Romania.
The problem of an unsteady two-dimensional boundary layer flow of a viscous and incompressible
micropolar fluid at the stagnation point of a semi-infinite wall is considered. Both the forward and rear
stagnation points will be considered. The unsteadiness in the flow field is introduced by the freestream velocity, which varies with time. The governing boundary layer equations in a rectangular
Cartesian coordinate are solved using an implicit finite-difference method known as Keller-box
method. The numerical solutions for the skin friction coefficient, velocity profiles and microrotation
profiles are presented in some graphs and are discussed in detail. The numerical results show that
as the material parameter of the micropolar fluid increases, the skin friction decreases. The velocity
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
145
increases while the microrotation decreases as the value of time increases so that the steady-state
flow is attained.
IO128
Quasistationary Approximation for One Phase Stefan Problem
Halijah Osman, Choong Ai Mei & Khairil Anuar Arshad
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor,
Malaysia.
Nonlinearity is the source of difficulties in moving boundary problems. As a result, analytical solutions
for phase change problems are only known for a couple of physical situations that have a simple
geometry and simple boundary conditions. The most well known analytical solution for a onedimensional moving boundary problem, called the Stefan problem, was discovered by Neumann.
Some analytical approximations for one-dimensional moving boundary problems with different
boundary conditions have been produced. These include the quasistationary approximation,
perturbation methods, the Megerlin method, and the heat balance integral method [1]. In all these
methods, it is assumed that the melting or solidification temperature is constant. The quasistationary
approximation technique can be applied to one phase Stefan problems to obtain closed form solutions
for a semi-infinite domain with imposed temperature at one end, imposed flux and also for a
convective boundary condition at one end of the slab. However, this approximation is valid only for
the case of low Stefan Number.
Keywords: Quasistationary Approximation; Moving Boundary; Stefan Problem.
IO129
Comparative Analysis for Jukes-Cantor and Kimura Evolutionary Model
Ivonne Martin
Parahyangan University, Bandung, Indonesia.
Evolution as a process that every organism try to adjust itself to its surroundings in order to stay alive.
This process is begun from small change even replacement of nucleotide in the DNA which is called
substituting process. Evolution process becomes very important in bioinformatics field since it can be
used for analyzing the relationship of the two organisms. It can be derived from its DNA whether
those organisms are come from the same ancestor. In this paper, the Jukes-Cantor and Kimura
evolutionary model are compared to estimate the number of substitution that can be happen in such
evolution.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
146
IO130
Modeling of the PDE’s in a Silver Substrate using Finite Difference Method
Noraini Abdullah
School of Science & Technology, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Locked bag No. 2073, 88999 Kota
Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia.
This paper presents a mathematical model on the spread of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD),
scientifically known as Enteroviral Vesicular Stomatitis with Exanthem which had occurred in
Sarawak. Using stochastic differential equations, the spread of the disease can be represented by
the SIR model. Comparisons of the plotted graphs of the simulated and true data obtained, showed
that they are almost identical within the acceptable range of numerical approximations, hence
providing a new insight in modeling the spread of infectious disease such
as HFMD.
IO131
Using Delay Time Analysis To Study Palm Oil Mills Maintenance Problem
Abd Samad Hasan Basari
Department of Industrial Computing, Faculty of Information & Communication Technology,
Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka
This paper discussed on the methodology to support an efficient and effective policy to maintain the
most critical machines, which is press machines, within palm oil mill, the United Bell palm Oil Mill in
Malaysia. The preliminary findings are included in this paper. This study is commenced at investigate
the possibility of improving the effectiveness of the maintenance policy for the press machines
currently being operated by palm oil mill by using the delay time model. The expected results
hopefully will be the issues of minimizing the maintenance cost of the screw press. It is predicted
based on the model generated, regarding the effects on consequences measure in terms of cost and
downtime. This study also proposed the introduction of changes of the company’s current
maintenance practice.
IO132
On the Performance of Group Krylov Iterative Methods on Systems Arising from a TwoDimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
147
Sam Teek Ling & Norhashidah Hj. Mohd Ali
School of Mathematics Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia,11800 Minden,
Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
Research on the general iterative solution of linear systems based on Krylov subspace methods have
been increasing in recent years since it has been shown that these methods combined with
preconditioning techniques may accelerate the convergence process. In this paper, we apply and
compare four preconditioned Krylov subspace methods, such as preconditioned Conjugate Gradient
(CG), preconditioned Bi-Conjugate Gradient Stabilized (Bi-CGSTAB), preconditioned Generalized
Minimal Residual (GMRES) and preconditioned Transpose-Free Quasi-Minimal Residual (TFQMR), to
solve a large sparse linear system that arise in the iterative solution of the two-dimensional elliptic
partial differential equations (PDEs). The preconditioner used is the modified blockwise incomplete
LU factorization and the systems under study are the ones originated from the application of group
iterative schemes based on the standard and rotated five-point finite difference discretisations. We
will investigate whether this preconditioner is capable of improving the convergence rates of the
original methods. Finally, numerical experiments are performed which will show that it is possible to
considerably reduce the total iteration number of original methods when the preconditioner is used.
IO133
Modeling of the Spread of HFMD (Exteroviral Vesicular Stomatitis with Exanthem) using
Stochastic Differential Equations
Noraini Abdullah
School of Science & Technology, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Locked bag No. 2073,
88999 Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia.
This paper presents a mathematical model on the spread of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD),
scientifically known as Enteroviral Vesicular Stomatitis with Exanthem which had occurred in
Sarawak. Using stochastic differential equations, the spread of the disease can be represented by
the SIR model. Comparisons of the plotted graphs of the simulated and true data obtained, showed
that they are almost identical within the acceptable range of numerical approximations, hence
providing a new insight in modeling the spread of infectious disease such as HFMD.
IO134
Branch and Bound Approach for Solving Two-Stage Mixed-Integer Stochastic Programming
Problems
Jafaruddin Harahap & Herman Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics, University of Sumatera Utara, Medan 20155, Indonesia.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
148
In this paper we address a general class of two-stage mixed integer stochastic programming model
with simple recourse and discrete probability distributions. We exploit the structure of the second
stage mixed integer problem to develop a novel global optimization algorithm. The proposed scheme
departs from those in the current literature in that it avoids explicit enumeration of the search space
while guaranteeing finite termination.
IO135
Revisiting Missingness Mechanism
Ismail Mohamad
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Missing data is a problem faced by many practicing statisticians. It is believed that a certain
mechanism is responsible in creating missing data. In the statistical literature three types of
missingness mechanism are identified namely Missing Completely at Random (MCAR), Missing at
Random (MAR) and Not Missing at Random (NMAR). It is important to identify the mechanism so as
to choose the right method to deal with the data. Most studies about missing data consider the type
of missingness mechanism and the proportion of missing data. This study look at the effect of the
missingness mechanism on the resulting observed sample. Not only the type of missingness
mechanism and the proportion of missing data are considered but the strength of the missingness
mechanism is also considered. In this study data which follow the simple linear regression model
Y 0 1 X is generated. Some of the X values are hypothetically made missing which follows
the logistic regression model
P X is missing | data
exp 0 1Y 2Y
1 exp 0 1Y 2Y
to see the effect on the resulting observed data. The value of
data and the values of
1
and
2
0
determine the proportion of missing
determine the missingness mechanism and its strength. The
resulting observed samples are shown using scatter plots. Most missing data methods approach is to
reestablish the missing values. The study explain why some methods are successful when other
methods fail in dealing with missing data with differing missingness mechanism.
IO36
Characteristics of Deterministic Equivalent Model for Multi-Stage Mixed Integer Stochastic
Programs
Irvan & Herman Mawengkang
Department of Mathematics, University of Sumatera Utara, Medan 20155, Indonesia.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
149
Stochastic programming is an important tool in medium to long term planning where there are
uncertainties in the data. In this paper, we consider multi-stage mixed integer stochastic
programming model. The model is not well defined, since there are random vectors imposed in the
model to present the uncertainties of the model parameter. Therefore a revision of the modeling is
necessary, leading to so-called deterministic equivalent model and the characteristics of the result
model.
IO137
Comparing the Accuracy of Density Forecast from Competing Models: An Application to KLCI
Returns
Abu Hassan Shaari Mohd Nor1, A. Shamiri2 & Fauziah Maarof3
1Faculty
of Economic and Business, National University Malaysia
of Science and Technology, National University Malaysia
3Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia
2Faculty
In this paper we introduce the Kullback-Leibler information criteria (KLIC) as a statistical tool to
evaluate and compare the predictive abilities of possibly misspecified density forecast models. The
main advantage of this statistical tool is that we use the censored likelihood functions to compute the
tail minimum of the KLIC, to compare the performance of a density forecast models in the tail areas.
We include an illustrative simulation and an empirical application to compare a set of distribution,
including symmetric and asymmetric distribution, and a family of GARCH volatility models. We
highlight the use of our approach to Kuala Lumpur Composite Index (KLCI). The results show that the
choice of the conditional distribution appear to be a more dominant factor in determining the adequacy
of density forecasts than the choice of volatility model. Furthermore, the results support the Skewed-t
distribution for modeling the KLCI return.
IO138
Development of Small Area Estimation Research in Indonesia
Khairil A. Notodiputro & Anang Kurnia
Department of Statistics, Bogor Agriculture University, Jl. Meranti, Wing 22 Level 4,
Kampus IPB Darmaga, Bogor 16680 Indonesia.
There has been a rapidly growing demand for small area statistic in Indonesia as the country political
system has shifted from centralized to more decentralized system. The demand for the reliable
statistic is smaller regions such as sub-district area is inevitable as a basis for a good planning and
effective decision-making processes. The Central Bureau of Statistic (BPS) in Indonesia has put
many efforts to meet this demand using direct estimation but there are some instances in which direct
estimation fails to produce estimates with the required precisions due to the limited number of
effective sample size. The increasing demand for small area estimates has motivated the need to
develop more reliable methods for producing small area estimates with higher precision compared to
the direct estimates.
This paper discusses the development of research activities in small area statistic in Indonesia. The
discussion includes the importance of small area statistic in Indonesia and research activities
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
150
regarding models of small area statistic based on BPS data. A brief description of enhancement on
model-based indirect estimation on area level small area models is also discussed.
Keywords: Small Area Estimation; Area Level Model; EB-EBLUP.
IO139
The Performance of MM-Estimators on Simple Mediation Analysis
1,3Anwar
Fitrianto & 1,2Habsah Midi
1Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, University Putra Malaysia,
43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
2Institute for Mathematical Research, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor,
3Department of Statistics, Faculty of Science, Bogor Agriculture University, Darmaga 16680, West
Java, Indonesia.
Mediation is said to occur when a causal effect of some variables X on an outcome Y is explained by
some intervening variables M. Simple mediation model involves a series of regression equations.
The Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) is the most popular technique to estimate the parameters of the
model. However, this technique is easily affected by an outlying observation. In order to rectify this
problem, we may turn to robust methods which are not sensitive to any deviations from some ideal
assumptions. In this paper, we compare the OLS and MM parameter estimation methods on simple
mediation analysis. We do screening steps from the data to make sure that the data clean enough.
Then we contaminate the clean data with different outlier scenarios and then examine their impact on
the mediation estimates. The results from the numerical examples indicate that the performance of
the MM-estimator is more efficient than the OLS estimator in x, m and y-direction. A numerical
example is created using simulated data set with the Proc Robustreg of SAS version 9.13.
Keywords: Simulation; Mediation Analysis; Unusual Observation; Outliers; Indirect Effect; MMEstimator.
IO140
An Efficient Parallel Numerical Integration Algorithm for Multilayer Layer Raster CNN for
Simulation
R. Ponalagusamy & S. Senthilkumar
Department of Mathematics, National Institute of Technology,
Tiruchirappalli, 620 015, Tamil Nadu, India.
The aim of this paper is focused on developing an efficient simulator using parallel numerical
integration algorithms for Cellular Neural Networks (CNNs). The role of the simulator is that it is
capable of performing Raster Simulation for any kind as well as any size of input image. It is a
powerful tool for researchers to investigate the potential applications of CNN. This article proposes an
efficient program fragment exploiting the latency properties of Cellular Neural Networks along with
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
151
well known numerical integration algorithms. Simulation results and comparison have also been
presented to show the efficiency of the Numerical integration Algorithms. It is observed that the
Parallel Arithmetic Mean (PAM) RK-Algorithm outperforms well in comparison with the Parallel
Geometric Mean (PGM) RK-Algorithm of Type-2 and Type-1 respectively.
IO141
Sliding Mode Tracking Controller For Hydraulic Robot Manipulators With Numerical Analysis
Syarifah Zyurina Nordin1, Haszuraidah Ishak2, J.H.S Osman2
1Department
2Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science
of Mechatronics & Robotics, Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
This abstract is concerned with the problems controlling the electrohydraulic robot manipulators. The
control of electrohydraulic robot manipulator is challenging due to the dependence of system
parameters on variables such as displacement and velocity, on the geometry and inertia of the links,
uncertainties associated with gravity, coriolis and centrifugal forces, variations in payload handled by
the manipulator, and environmental influences. To overcome these problems, the variable structure
control (VSC) strategy will be utilized to overcome the inherent high nonlinearity in their dynamics
under centralized frameworks. In the approach, a variant of the VSC known as the Sliding Mode
Control (SMC) was adopted to ensure the stability of the system dynamics during the sliding phase
and to render that the system insensitive to the parametric variations and disturbances. The
performance and robustness of the proposed controller is evaluated through computer simulation by
using Matlab and Simulink. The parameter governing the hydraulic robot manipulators have been
studied through forth-order Runge-Kutta (RK4) and extrapolation method. The desired state trajectory
of the system representing the three joints of a robot have been compared with the corresponding
state vector at different time intervals using the above mentioned RK4 and extrapolation method. The
system’s error dynamics during sliding mode also have been determined between the desired and
corresponding state trajectory. Well composed comparison has been carried out with the aid of the
obtained results and graphs. The results prove that the controller has successfully provided the
necessary tracking control for the 3 DOF electrohydraulically driven robot manipulator system
IO142
Dynamic Geometry: Theory and Practice
Robert L. Pour
Department of Mathematics, Emory & Henry College, Emory, Virginia 24327, U.S.A
This paper gives an overview of the pedagogical foundations supporting the use of software to teach
geometry. The “The Van Hiele Model of Geometric Thought” is the principle model. Activities are
discussed which demonstrate this model and reinforce the “constructivist” approach to teaching and
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
152
leaning. Examples are provided using the Software Cinderella. The theoretical basis Cinderella
construction is briefly discussed.
IO143
Biomechanical Analyses of Two Lumbar Vertebrae Implanted with an Artificial Disc (IVD)
A. K. Mohammed Rafiq & W.H. Wan Mohd Musyris
Biomechanics and Tissue Engineering Research Group (Bio-TEG), Faculty of Mechanical
Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Lower back pain is normally related to the degeneration of the spinal intervertebral discs (IVD) due to
the natural process of aging. Even though conservative treatments are normally sought after, in some
severe cases surgery would be the only solution to alleviate pain and prevent mechanical instability.
Lumbar pack pain can be surgically treated either through arthrodesis or arthroplasty. Arthrodesis
consists of surgical immobilization or fusion of the joint, whilst arthroplasty consists of implantation of
an artificial disc between the vertebrae. The objective of this study was to analyses, using finite
element method, the biomechanics of two lumbar vertebrae treated with an artificial intervertebral disc.
A three dimensional model of lumbar vertebrae was created from CT datasets of L3. The model was
then used to create a two level lumbar segment with a normal healthy IVD. Another model was
created where the IVD is replaced with an artificial IVD to simulate total disc replacement (TDR). The
artificial IVD consists of two endplates made of metal which is separated by a polyethylene liner with
dome structure on both sides to allow rotation of the endplates. The material properties of the bone
were obtained from the CT datasets Hounsfield unit, and pressure was applied on the top vertebra.
The results showed that the artificial IVD exerted more stress to the vertebrae, reducing the
cushioning effect of an intact healthy IVD. The differences observed between the biomechanics of
surgically treated and intact IVD were associated with the geometrical and surgical features of the
devices.
IO144
Biological Classifiers for Problem Solving
Siti Maryam Shamsuddin
Soft Computing Research Group, Research Management Center,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
The structure of HUMAN BODY (cells, emotion, perception, etc) and living organism have inspired the
creation of human intelligence, and sparks a lot of research in solving complex problems. These
nature creations have introduced the concept of Biological Inspired Computing (BIC) by the Scientist.
BIC is an area of investigation that draws upon methaphors or theoretical models of biological
systems in order to design computing machines that could allow the creation of new machines with
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
153
promising characteristics, such fault-tolerance, self replication, reproduction, evolution, adaptation and
learning, and growth. BIC plays a significant role in the area of pattern recognition in a variety of
engineering, and scientific disciplines such a biology, psychology, medicine, marketing, computer
vision, artificial intelligence, and remote sensing. In this paper, we present few examples of in-house
BIC techniques that have been implemented in the areas of Computer Science. These include the
enhancement of identifying the individuality of document authors, abnormality of stock market
behavior with Artificial Immune System (AIS), and hyper sausage neuron that uses the principle of
homology-continuity to take optimal cover of distribution of one kind of samples in feature space in
Biomimetic Pattern Recognition.
Keywords: Biologically Inspired Computing; Artificial Immune System; Brain-Inspired System;
Biomimetic Pattern Recognition.
IO145
Newton-Kaczmarz Methods for Reconstruction of Electrical Impedance Tomography with
Multiple Measurement Data: A Numerical Result
Agah D. Garnadi
Department of Mathematics, Institut Pertanian Bogor, Indonesia
We report numerical results on reconstruction of Electrical Impedance Tomography from multiple
measurement data. The basic algorithm for reconstruction we use Newton-Kaczmarz, as a
combination of Iteratively Regularized Gauss Newton algorithms which is have a good theoretical
behavior for non-linear inverse problem; and projection method, i.e. Kaczmarz methods, to reduce
memory requirement during reconstruction. We utilize two-level refinement from coarse to finer
triangulation to reduce segmentation effect in the case of coarse triangulation. The triangulation
refinement fully adapted using a-posteriori error estimation.
IO146
Students’ Approach on Delivering A Simple and Alternative Euclidean Division Algorithm
Mohd Sulhi1, Azniah2, Noraishiyah2, Tuan Salwani2 & Siti Mistima2
1Student, Industrial Automation and Networking Section;
Unit, General Studies Section; Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute
Section 14, Jalan Teras Jernang 43650 Bandar Baru Bangi, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
2Mathematics
Consider the two polynomials defined by
by
D x , i.e.
D x and F x ; where D x 0 . If we divide F x
F x
, then, there exist a quotient and remainder; denoted by Q and R respectively.
D x
This can later be written as
F x Q x .D x R x . This relationship is found by using long
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
154
division algorithm or factor theorem. However, there exists an alternative algorithm called Euclidean
Division Algorithm (EDA). This is not to be confused with Euclidean Algorithm where it is used to find
the greatest common factor of two natural numbers or two polynomials. The EDA is a special set of
algorithm used in determining the result of two polynomials dividing each other. In other words, EDA
is an alternative method to that of a long division. This method later develops the remainder and the
factor theorem. The algorithm presented in this paper is quite different to that to the algorithm of long
division; however, it produces the same result if the long division method was used. There have been
numerous proofs on verifying that the EDA works properly. However, this paper will discuss the
alternative proof on EDA in a simple and not-so-complicated language. Examples on implementing
the EDA method as prescribed in this paper are also included.
Keywords: Euclidean Division; EDA; Factor Theorem and Long Division
IO147
Cardinality of the Sets of Solution to Congruence Equation Associated with a Seventh Degree
Form
Siti Hasana Sapar & K.A Mohd Atan
Laboratory of Theoretical Mathematics, Institute for Mathematical Research,
Universiti Putra Malaysia
The exponential sum associated with f is defined as
S f; q exp 2 if x / q
where the sum is taken over a complete set residues modulo q and let
vector in the space
coefficients in Z.
The value of
x x1 , x2 ,..., xn be a
n with Z ring of integers and q be a positive integer, f a polynomial in x with
S f ; q has been shown to depend on the estimate of the cardinality V , the number
of elements contained in the set
V x mod q f x 0 mod q where f x is the partial derivative of
f with respect to x x1 , x2 ,..., xn .
This paper will give an explicit estimate of
V for polynomial f x, y in Z p x, y of degree seven
based on the p-adic Newton polyhedron technique associated with the polynomial. The seventh
degree polynomial is of the form
f x, y ax7 bx6 y cx5 y 2 dx4 y3 ex3 y 4 mx2 y5 nxy 6 ry 7 sx ty k
estimate obtained is in terms of the p-adic sizes of the coefficients of the dominant terms in f .
IO148
On Higher Order Analogues of the RSA Cryptosystem
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
The
155
Mohamad Rushdan Md. Said
Institute for Mathematical Research, University of Putra Malaysia,
43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
In this paper, we investigate and review public-key cryptosystems which are derived from higher order
linear recurrence relation which are based on the Lucas function. The RSA scheme is based on hard
mathematical problem, the intractability of factoring large integers. This application of a hard
mathematical problem to cryptography revitalized efforts to find more efficient methods to factor. The
first motivation to develop a new cryptosystem analogous to RSA is the possibility that the higher
order analogues are more secure than the RSA. The explicit formulation involves a generalization of
the Euler Totient function, which underlie the algebra of the RSA cryptosystem.
Keywords: Public-key Cryptosystem; Quartic Polynomial; Resolvent Cubic Polynomial; Lucas
Sequence; Euler Totient Function.
IO149
Effect of Control on the Onset of Marangoni-Bénard Convection with Uniform Internal Heat
Generation
Norfifah Bachok, Norihan Md Ariffin & Fadzillah Md. Ali
Department of Mathematics, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
The effect of control on the onset of Marangoni-Bénard convection in a horizontal layer of fluid with
internal heat generation heated from below and cooled from above is investigated. The resulting
eigenvalue problem is solved exactly. The effects of control are studied by examining the critical
Marangoni numbers and wave numbers. It is found that the onset of Marangoni-Bénard convection
with internal heat generation can be delayed through the use of control.
IO150
Modeling of Concentration and Capacity Profile of Solid Diffusion in Lithium-Ion Cell
Siti Aishah Hashim Ali
Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
In the effort to produce high performance batteries, mathematical model has become a vital tool in
helping batteries developers to understand the behavior of the battery systems during charge,
discharge and relaxation. In this work, a mathematical model of a lithium-ion (Li+) cell under the solid
phase diffusion limitation is presented. The model equation is used to derive the Li + concentration
and the capacity profiles under galvanostatic discharge. Two cases are being considered. In first
case, the active material is considered to be thin film of thickness 2 (where >> the height of the
film) with both sides exposed to the electrolyte, while in the second case, the active material is
considered to be spherical of radius R.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
156
IO151
Maximum Density Effects on G-Jitter Induced Free Convection between Vertical Plates Heated
and Asymmetrically
Sharidan Shafie1, Norsarahaida Amin1 & Ioan Pop2
1Department
of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
2Faculty of Mathematics, University of Cluj, R-3400 Cluj, CP 253, Romania.
The effect of g-jitter induced free convection in the fluids at the temperature of the maximum density
T
m
3.98o C in microgravity is considered.
The problem is studied under a simple system
consisting of two heated vertical parallel infinite flat plates held at constant but different temperatures.
The governing equations are solved analytically for the induced velocity and temperature distributions.
Graphical results for the velocity profile of the oscillating flow in the channel are presented and
discussed for various parametric physical conditions such as the wall temperature parameter, rT and
oscillating frequency, . It has been found that these parameters affect considerably the velocity of
the flow.
IO152
Analysis of a Dengue Disease Transmission Model without Immunity
Yusuf Yaacob
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 Skudai, Johor Malaysia
A transmission model for dengue fever is discussed in this paper. Restricting the dynamics for the
constant host and vector populations, and also with no immunity to the disease, the model is reduced
to a two-dimensional planar system. In this model the endemic state is stable if the basic
reproduction number of the disease is greater than one. For a relatively small series of outbreaks of
the disease in population sufficiently large for the number of susceptible to remain effectively constant,
the model is reduced to a population model for the group of infectives.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
157
IO153
Time-Dependent Generation Of Fluid Motion Along A Channel By A Traveling Magnetic Field
Mohd Noor Saad
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, University Putra Malaysia,
Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
A two dimensional multi Fourier-component magnetic field is moved at a uniform velocity along a
closed channel filled with an incompressible conducting fluid. Induced currents in the fluid interact with
the field to give a Lorentz force which drives fluid motion. Under the assumption of small magnetic
Reynolds number and a small magnetic interaction parameter the time-dependent fluid flow is
investigated. In the case of a two Fourier-component source an analytical expression for the source
term is derived and it is shown that for effective stirring the width of the channel has to be at most
equal to the wavelength of the applied magnetic field. For the case of multi-Fourier component source
numerical methods were used and it is shown that four vortices could be obtained
IO154
Numerical Solutions Of The One-Dimensional Shallow Water Equations
Salemah Ismail1, Zainal Abd. Aziz2, Mohd Nor Mohamad3 & Nazeeruddin Yaacob4
1Center
for Mathematical Studies, Faculty of Information Technology & Quantitative Sciences,
Universiti Technologi MARA, 40450 Shah Alam, Selangor , Malaysia
2,3,4Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, University Technology Malaysia, 81310 Skudai,
Johor, Malaysia
A numerical model of the one-dimensional shallow water equations is developed to simulate the
propagation of water waves above slopes of constant inclination. The discretization of the internal
grid points is based on the Lax-Richtmyer finite difference scheme. The values of the surface
elevation and the fluid velocity at the left and right boundaries are estimated using the left-running and
right-running Riemann invariants. The results showed an increase in wave amplitude as waves run
into shallower water. The model is then extended to the case of a stepwise change in the water depth.
Keywords: Shallow water equations; Finite difference
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
158
IO155
Computer Based Assessment in Engineering Mathematics: A Case Study
Maya Pundoor & Ramadas Narayanan
1Lecturer in Mathematics, Curtin University of Technology, Sarawak Campus, Malaysia
2Lecturer in Mechanical Engineering, Curtin University of Technology, Sarawak Campus, Malaysia.
There are different kinds of assessments, which are suitable for Engineering Mathematics. The
developments in Computer Based Education have been driven by advances in Instructional
Technology and the increased capability of the technology to respond to the needs of students.
Ensuring that the assessment methods adopted reflect both the aims and objectives of the course and
any technical developments which have taken place is becoming increasingly important, especially as
quality assurance procedures require departments to justify the assessment procedures adopted.
Here in this paper, the current form of assessment for the subject Engineering Mathematics is
described and critically evaluated its effectiveness as a formative and then as a summative form of
assessment. An alternative form of assessment to accompany your new instructional approach is
devised. The new form of assessment is compared with the old form, in terms of its effect on the
students, and its validity as a measure of mastery of the curriculum topic. The new form of
assessment is implemented, evaluated as assessment instrument, identified strengths and
recommended improvements in the light of new experience.
Keywords: Computer Based Assessment; Engineering Mathematics.
IP1
Oblique Stagnation Slips Flow of a Micropolar Fluid
Lok Yian Yian1, Norsarahaida Amin2, Ioan Pop3
1, 2Department
of Mathematics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
3Faculty of Mathematics, University of Cluj, R-3400 Cluj, CP 253, Romania
This paper considers the problem of steady two-dimensional boundary layer flow of a micropolar fluid
near an oblique stagnation point on a fixed surface with slip condition. It is shown that the governing
partial differential equations admit exact similarity solutions. The resulting nonlinear ordinary
differential equations are solved numerically using the Keller’s box method for some values of the
governing parameters. It is found that the flow characteristics depend heavily on the micropolar and
slip parameters.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
159
IP2
The Important of Statistical Orientation for Quality Improvement in Automotive Parts
Manufacturing and Supply in Malaysia
Muzalwana Abdul Mutalib
Department of Applied Statistics, Faculty of Economy and Administration, Universiti Malaya
With intense competition at the regional and global marketplaces, issue on quality and cost is no
longer a compromise to automotive suppliers. Quality and reliability is the surviving factor for long
term participants in the supply chain of major vehicle manufacturers. This paper aims to review the
general quality practices of Malaysian automotive suppliers and the deployment of statistical
knowledge, training and understanding are the root cause to low statistical application as quality tools
and techniques. Well drawn trainings are needed in these areas. While previous studies mainly
probe into the Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation as quality framework, this paper
highlights the paramount importance of statistical thinking as a roadmap in the pursuit of quality
excellence of these Malaysian automotive suppliers. With the need to build up the image of stringent
quality automotive parts so as to increase competitiveness, it is apt for the Malaysian automotive
suppliers to integrate the statistical tools and techniques such as Statistical Process Control and
Designed Experiments into their quality management practice.
IP3
Comparison of Two Algorithms for Production Layout Improvement – The Application
Syed Ahmad Helmi bin Syed Hassan
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Plant layout can be defined as a plan of optimum arrangement of industrial facilities, including
personnel, operating equipment, storage space, material handling and all other supportive services.
Every factory encounters layout problems from time to time and the operating efficiency of a
manufacturing company is significantly influenced by its plant layout. This paper basically shows the
needs of layout improvement at a glass manufacturing factory located in Penang, Malaysia. The
objective of the project is to study the current layout and propose a better alternative, which can
improve the material flow and the total traveled distances in the production plant. Systematic Layout
Planning (SLP) has been used as the layout procedures in the study. Whereas Graph-based method
and Pairwise Exchange method has been proposed as the algorithms for layout alternatives
generation. These two algorithms are different from the type of algorithms and objective. Quantitative
evaluation using from-to chart and qualitative evaluation using weighted factors comparison is then
proposed to evaluate the alternatives generated. As a result, the best selection is done based on the
evaluation.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
160
IP4
Identifying Statistically Significant Protein Spots in 2-DE Protein Expression Data
Norhaiza Ahmad1 & J. Zhang2
1Department
of Mathematics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
81310 UTM Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
2Institute of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Kent, Canterbury, Kent, UK
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) is one of the major techniques to simultaneously
separate and quantitate thousands of cellular proteins. Due to the nature of 2-DE proteomic
investigations there will always be’process variability’ factors in any data set collected in this way.
Some of this variation will arise during sample preparation, gel running and staining, while further
variation will arise from the gel analysis procedure. Therefore, in order to identify all significant
changes in protein expression between biological samples when analysed by 2-DE, the system
precision or ’error’, and how this correlates to protein abundance, must be known. Only then can the
system be considered robust and investigators accurately and confidently report all observable
statistically significant changes in protein expression. In this study we have undertaken 2-DE
proteomic profiling on a series of cell lines with different recombinant antibody production rates. We
introduce an expression variability test to identify protein spots whose expression correlates with
increased antibody production. The results have highlighted a small number of candidate proteins for
further investigation.
Keywords: 2D-PAGE; proteomic profiling; NSO cells; variability; rank correlation
IP5
Regression Model for Forecasting Malaysian Electricity Load Demand
Zuhaimy Ismail & Faridatul Azan Jamaluddin
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
This paper presents a study on the use of time series regression model for forecasting Malaysian
electricity demand with various non-deterministic factors influencing demand. The data of electricity
demand in this study is provided by Tenaga Nasional Berhad, the main electricity supplier for
Malaysia. Factors influencing the load demand include temperatures, holidays, daily and monthly
seasonality. The data comprises of daily peak electricity load L t (megawatts/hour, MWh-1) in
Peninsular Malaysia from January 1997 until December 2000. Due to the nature of the data, time
series regression model with autoregressive errors where the errors are serially correlated among
observations is proposed. This enables the modeling of serially correlated error using Box-Jenkins
autoregressive model. Forecast for one month ahead reveal that a time series regression model with
load reduction weights yield better accuracy. Model validation is performed by comparing model
predictions with the standard Box-Jenkins model. The results obtained bear out the suitability of the
adopted methodology for the forecasting short-term electricity load demand.
Keywords: Regression; Forecasting; Electricity Load Demand; Box-Jenkins and Short-Term
Forecasting.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
161
IP6
Least Cost and Highest Demand Procedure as Feasible Solution for Dedicated Vehicle Routing
Problem
Zuhaimy Ismail & Mohammad Fadzli Ramli
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The most fundamental and well-studied routing problem is without doubt the Traveling Salesman
Problem (TSP) while the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is a generalization of the TSP. The VRP is
to determine m vehicle routes, where a route is a tour that begins at the depots, visits a set of
customers in a given order and returns to the depots. All customers must be visited exactly once and
the total customer demand of a route must not exceed the vehicle capacity with the objective of
minimizing the overall distribution costs. This paper presents various issues concerning VRP,
focusing on a dedicated vehicle routine problem (DVRP), which is one variation in the problem. The
VRP and its dedicated counterparts, the DVRP are introduced with the objective of finding the
minimum routing traveled for one vehicle within a predetermined network using deterministic cost and
quantity. In solving the VRP, its initial feasible solution does have a role in determining the final
optimal solution. Here, two procedure algorithms namely the least cost and the demand priority are
proposed as the initial feasible solution for the DVRP.
IP7
Selected Heuristic Algorithms for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
Zuhaimy Ismail & Wan Rohaizad Wan Ibrahim
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The traveling salesman problem (TSP) asks for the shortest route to visit a collection of cities and
return to the starting point. Despite an intensive study by mathematicians, computer scientists,
operation researcher, and others, over the past 50 years, it remains an open question whether or not
an efficient general solution method exists. Given a collection of cities and the cost of travel between
each pair of them, the traveling salesman problem, or TSP for short, is to find the cheapest way of
visiting all of the cities and returning to your starting point. In the standard version we study, the travel
costs are symmetric in the sense that traveling from the city X to city Y costs just as much as traveling
from Y to X. The complexity of the problem increase in the size of the cities visited and testing every
possibility for N city tour would be N! possible tours. A 30 city would have to measure the total
distance of be 2.65X1032 different tours. Adding one more city would cause the time to increase by a
factor of 31. Obviously, this is an impossible solution. This paper presents the product of an
investigation research on the selected heuristic based on the most recent optimization techniques and
at the same time produce a prototype program that can be used to generate a possible route for TSP.
The heuristic methods used are based on the selected method such as the Greedy Search method,
Simulated Annealing and Tabu Search. A user friendly optimization program developed using
Microsoft C++ to solve the TSP and provides solutions to future TSP which may be classified into
daily or advanced management and engineering problems.
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
162
IP8
An Electricity Load Demand Analysis Based on Day-Type using Exponential Smoothing
Zuhaimy Ismail & Rosnalini Mansor
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia.
The intrinsic uncertainties associated with demand forecasting become more acute when it is required
to provide an invaluable dimension to the decision-making process in a period characterized by fast
and dynamic changes. This dynamic nature of the demand for electricity call for more research in
areas such as the estimation methodology of peak demand, factors affecting load demand, the
system used, the organizational structure involved in forecasting and the types of forecasting methods.
One of the main factors that influence electric demand is types of day such as weekday, weekend and
holiday. The behavior patterns of the end-user are based on a few actual observations, which are
divided into daily and annual weekly load profile. The annual daily and weekly load profile is used to
explain the general lifestyle throughout the year. The daily load profiles for a typical week and during
festive season, is used to explain behavioral pattern during a typical week and an hourly load profile is
used to explain the lifestyle on a normal working day. This paper presents the influence of types of
day in forecasting electricity load demand in Malaysia. We use separate forecasting model to forecast
day and named the weekday and weekend model. In this study we include the analysis of load
demand using exponential smoothing model of electricity load forecasting. We use several
exponential techniques to forecast short-term electricity demand and compare performance among
them. The data used was the 1826 daily maximum demand time series from 1 January 2001 to 31
December 2005. A case study was conducted at Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB), a public listed
electric company who builds, operates and maintains electricity transmission and distribution network
in Peninsular Malaysia. TNB has the largest generation capacity of over 10450 MW that accounts for
about 60% of the total power installed (17300MW). The other 40% is provided by the Independent
Power Producers (IPPs). The result shows that Log seasonal Exponential Smoothing is a reasonable
good model for forecasting daily load demand.
IP9
Mixed Convection Boundary Layer of a Viscoelastic Fluid near a Stagnation Point
Nur Ilyana Anwar Apandi, Norsarahaida Amin & Sharidan Shafie
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
A mathematical model for the two dimensional boundary layer flow of a viscoelastic fluid near the
stagnation point of a circular cylinder is discussed. Viscoelastic fluid is an incompressible nonNewtonian second-grade fluid that exhibits a combination of both fluid and solid characteristics.
Problems involving viscoelastic fluids are encountered in several industrial processes particularly in
the polymer industry. The governing equations which consist of third order non-linear partial
differential equations are transformed to a fourth order ordinary differential equation, which is then
solved numerically using the Keller-box method, by augmenting an extra boundary condition at infinity.
Numerical results obtained in the form of velocity distributions and temperature profiles are presented
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
163
for a range of values of the dimensionless viscoelastic fluids parameter, K. Increasing the viscoleastic
parameter has the effect of raising both the velocity and heat transfer performance.
IP10
The Parallel AGE Method for Solving Incomplete Blow-Up Problem Using Heterogeneous
Multiprocessor Systems
Norma Alias, Nurul Ain Zhafarina Muhamad
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
University Technology Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
High performance computing (HPC) is build from supercomputers and computer clusters. Computing
systems comprised of multiple (usually mass-produced) processors linked together in a single system
with commercially available interconnects. The HPC archtecturer under consideration is called
heterogeneous multiprocessor systems. This paper concentrates on solving incomplete blow-up using
the Alternating Group Explicit Scheme (AGE) algorithms by using the heterogeneous multiprocessor
systems. The standard numerical procedure is based on Gauss Seidel method. Incomplete blow-up is
a condition under the quasilinear heat equation. The Porous Medium Equation (PME) with power
source admitting incomplete blow-up. It also used as one of the process in the industry such as in
filtration. This filtration process has been used globally in the medical and laboratory applications. The
performance measurements such as convergent rate, number of iteration, execution time, speedup,
efficiency, effectiveness, computational complexity and stability are also investigated.
Keywords:
High performance computing, heterogeneous multiprocessor systems, Alternating Group Explicit
Scheme, incomplete blow-up
RAFSS 2007 and ICoMS 2007
May 28-29, 2007, Ibnu Sina Institute for Fundamental Science Studies
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia