Stage_6_PACKET
advertisement

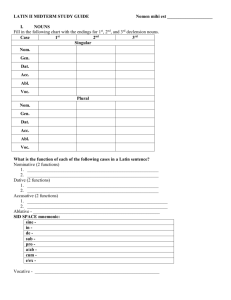
UNIT 1 DERIVATIVES STAGE 6 WORD WC DEFINITION LATIN MEANING celerity ________________________________________________________________________________ company ________________________________________________________________________________ fidelity ________________________________________________________________________________ fortify ________________________________________________________________________________ furtive ________________________________________________________________________________ peninsula ________________________________________________________________________________ pugnacious ________________________________________________________________________________ serpentine ________________________________________________________________________________ sorority ________________________________________________________________________________ taciturn STAGE 6 VOCABULARY NOUNS ADVERBS M farmer celeriter swiftly f fight facile easily i m freedman igitur therefore furis c thief ita thus; in this way infantis c baby, small child laete happily panis m bread numquam never pistor m baker nunc now sororis f sister olim once, formerly serpentis c serpent, snake paene almost ADJECTIVES statim immediately, at once fidelis,-is, -e faithful, loyal tacite silently fortis, -is,-e brave, strong tum then maximus,a,um largest, greatest CONJUNCTIONS parvus,a,um small postquam after, afterwards tuus,a,um your ubi where, when VERBS do,dare, dedi, datum – to give neco –are, -avi, atum to kill excito, -are, -avi, -atum to awaken paro -are, -avi, -atum to prepare festino, -are, -avi, -atum to hurry porto -are, -avi, -atum to carry habito, -are, -avi, -atum to live in pugno, -are,avi, atum to fight lacrimo, -are, -avi, -atum to weep pulso, -are, -avi, -atum to knock, strike libero, -are, -avi, -atum to free rogo, -are, -avi, -atum to ask narro, -are, -avi, -atum to tell servo, -are, -avi, -atum to save sto, stare, steti, statum to stand supero, -are, -avi, atum agricola pugna libertus fur infans panis pistor soror serpens ae ae IInd IIIrd habeo, -ere, habui, habitum to have emo, -ere, emi, emptum iaceo, -ere, iacui, ----- to rest, lie down vendo, -ere, vendidi, venditum to sell to buy timeo, -ere, timui,---- to fear III “io” capio, -ere, cepi, captum to take, seize IVth custodio, -ire, -ivi, -itum to guard IRREGULAR sum, esse, fui, futurum - to be IDIOMATIC EXPRESSION gratias tibi ago - Thank you! DECLENSION REVIEW declension of noun____ declension of adj. ____ nauta parvus _______________________ _________________________ declension of noun____ declension of adj. ____ negotium tuum ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ ________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ ________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ declension of noun____ declension of adj. ____ declension of noun____ declension of adj. ____ fur maximus _______________________ _________________________ soror optima ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ ____________________ _______________________ _____________________ _________________________ STAGE 6 IMPERFECT TENSE Tense: the time an action takes place Present tense: used for things happening NOW: “I see you (now.)” “You are walking (now.)” Past tenses: used for things that happened in the past. **There are several different types of past tenses! We start with the easiest one, the imperfect Example ad forum ambulābāmus. We were walking to the forum (when all of a sudden….) We used to walk to the forum (every day, rarely, etc) The Imperfect tense is used to talk about actions that were repeated or habitual, or that were happening for a continuous period of time. In English, we use the helping verbs “was” or “were” plus the verb ending in “-ing” OR “used to” In Latin, you just put the tense marker habitā + bā + -m -s -t -mus -tis = -nt -bā- or -ēbā- between the verb stem and ending habitābam I was living habitābās you were living habitābat he was living habitābāmus we were living habitābātis y’all were living habitābant they were living -bā- is used with 1st and 2nd conjugation verbs (stem that ends in ā or ē) -ēbā- is used with 3rd and 4th conjugation verbs (stem that ends in consonant, -i, or -ī) Try to translate the following: vendēbātis_________________________ iacēbant__________________________ custodiēbāmus_____________________ timēbam__________________________ rogabās__________________________ capiēbat__________________________ stābam__________________________ dabātis__________________________ laudābam__________________________ vidēbamus________________________ scribēbāmus________________________ faciēbant________________________ she was coming_____________________ you (pl) were hearing_______________ we used to laugh____________________ he had__________________________ Imperfect Tense: Verb of Being What is the tense marker for the imperfect? __________________ Is the verb of being a regular or irregular verb? ________________ This his how you conjugate the verb of being in the imperfect eram I was erāmus we were erās you were erātis you all were erat he was erant they were These forms are super common! They give background information about an event. Translate: Caecilius argentarius erat. In Italiā erāmus. tū in cubiculō erās. Roma magna erat. barbarī fortēs erant. Translate sunt erās erāmus sumus erant they were erat you guys used to be es he is I used to be I am We were erātis you are sunt he is er PUGNA Answer the Latin questions in ENGLISH! 1. Quid servi et ancillae in foro faciebant? 2. Quid Graecus mercator faciebat? 3. Quid agricola fecit? Cur? 4. Quid Pompeiani faciebant? 5. Quis superavit quem? 6. List four prepositional phrases with different prepositions. 7. Find one IMPERFECT tense verb of being. ___________________________ 8. Find 1 noun/adjective agreement in Nominative Case (there are 2) __________________________ and 1 Accusative Case_______________________ Decline this noun/adjective serpens parvus NOM___________________________ ___________________________ GEN___________________________ ___________________________ DAT___________________________ ___________________________ ACC___________________________ ___________________________ ABL___________________________ ___________________________ On the page opposite of this paper, conjugate: DUCO in present, imperfect, and perfect tenses and then translate!!! STAGE 6 FELIX Answer the Latin questions in ENGLISH! 1. Ubi intravit Clemens in foro?_______________________________________________ 2. Quem videt Clemens in taberna?____________________________________________ 3. Quis erat Felix?_________________________________________________________ 4. “Felix erat valde commotus” - Quando? (When?)_____________________________ 5. Ubi est Grumio? Quid facit?_______________________________________________ VERB OF BEING PRESENT SUM SUMUS ES ESTIS EST SUNT IMPERFECT ERAM ERAS ERAT ERAMUS ERATIS ERANT Study the conjugation of the VOB and write out both tenses 2X. QQ next class. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------FELIX ET FUR 1. Cur erat Felix solus in villa?_______________________________________________________ 2. Quis erat in villa cum Felice?______________________________________________________ 3. Quis venit ad villam? Cur? _______________________________________________________ 4. Quid infans fecit?______________________________________________________ 5. Quid Felix fecit?________________________________________________________________ 6. Quis erat infans?________________________________________________________________ 7. Qui erant dominus et domina?_____________________________________________________ 8. Write out lines 9-18 in English: STAGE 6 SLAVERY/MANUMISSION p. 97-100 You may use the back of this paper to complete explanations. 1. List 6 limitations placed on slaves: ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 2. How did the law regard slaves?___________________________________________________ 3. Describe their living arrangements.________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 4. How did a human being become a slave?____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 5. A Senator puts forth a plan in the time of Augustus to have the slaves dress in a distinctive manner. Explain why you think this is a good plan or a poor plan.__________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 6. What happened to the 400 slaves of Pedanius Secundus?_______________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 7. List 5 ways slaves could be used in the country. ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 8. Explain why you would prefer to be a slave in the city. _______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Give some reasons why a slave could be set free. ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________________ 10. What is manumissio?________________________________________________________ 11. Explain three methods of manumissio___________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 12. Name 2 privileges of citizenship that a freedman never received. ______________________________ _______________________________ 13. List some occupations of known freedmen: STAGE 6 QUO VADIS IMPERATIVE MOOD/COMMANDS VERBS Some commands are gentle, i.e., “Mother, read me a story.” Other commands are strong, “Go to bed!” Think of 3 gentle and 3 strong commands. Write them on the back of this paper. Imperatives (commands) in English remain the same for the singular and plural because the subject is implied “you.” Check the examples you wrote. Do you have to change them to show singular/plural? Other languages, however, DO differentiate between singular and plural just as they differentiate in the 2nd sing. and 2nd plural verb forms, E.G., es estis. Both mean “you are” in English. In Latin IMPERATIVES are easy to form in both singular and plural. Use the 2nd principal part, the infinitive, as the base. Examine these examples: conjugation infinitive singular imperative plural imperative I portare porta portate _______________ II tenere tene tenete _______________ III emere eme emite _______________ III “IO” capere IV cape audire capite audi translation _______________ audite ________________ Explain how all singular imperatives are formed. ________________________________________________________________________________ Explain how the plural imperatives of the Ist, IInd, and IVth conjugations are formed. ________________________________________________________________________________ Form the singular and plural of these verbs: translate: singular plural translate festinare ___________________________________________________________________ timere ____________________________________________________________________ vendere ____________________________________________________________________ capere ____________________________________________________________________ custodire __________________________________________________________________ lacrimare __________________________________________________________________ dormire ___________________________________________________________________ iacere __________________________________________________________________ contendere __________________________________________________________________ quaerere ____________________________________________________________________ videre ____________________________________________________________________ STAGE 6 MORE IMPERATIVES singular venire plural translation ___________________________________________________________________ cantare ___________________________________________________________________ scribere ___________________________________________________________________ respondere ____________________________________________________________________ surgere ____________________________________________________________________ narrare ___________________________________________________________________ liberare ____________________________________________________________________ tradere ___________________________________________________________________ audire ____________________________________________________________________ 4 IRREGULAR IMPERATIVES infinitive singular imperative plural imperative dicere dic! dicite! ducere duc! ducite! translation Say! Speak! Tell! Lead! facere fac! facite! ferre fer! ferte! Do! Make! Bring! Bear! Carry! Write these irregular imperatives out 3x and memorize them. QUIZ: 26 verbs to form imperatives! Change these singular imperatives to the plural form and translate the new sentence. 1. tene canem meam! _________ ________________________________________________ 2. sta in viam! _______________ _______________________________________________ 3. gusta cibum meam! ___________ ________________________________________________ 4. duc me ad forum! ____________ ________________________________________________ 5. fer aquam ad villam! __________ ________________________________________________ 6. narra fabulas! ___________ _______________________________________________ 7. fac cenam! ___________ _________________________________________________ 8. eme panem bonum! ____________________________________________________________ 9. libera servos! ___________ ________________________________________________ 10. neca pestes! ___________ _______________________________________________ 11. excita pistores! ____________ _______________________________________________ 12. serva sorores! ____________ _________________________________________________ 13. pulsa serpentes! ____________ _________________________________________________ STAGE 6 VOCATIVES/NOUNS QUO VADIS NOUNS We are now going to learn that 6th case that is located on our USES OF THE CASES QUO VADIS SHEET. It is called the VOCATIVE CASE. The vocative case is the case of direct address—we speak directly to someone. We frequently use the person’s name to address them, e.g., Mary, come here. The vocative case is easy because the vocative case looks just like the nominative case in both singular and plural----except for 2 places, 2nd masculine -us ending nouns and –2nd masculine ius ending nouns, singular only. The plurals are identical to the nominative plurals. EXAMPLES: nominative vocative nominative vocative Rufus amicus Rufe amice Herminius filius Hermini fili CONVERT THESE NOMINATIVES TO VOCATIVES: servus ______________________________ argentarius _____________________________ Vincentius____________________________ coquus _____________________________ puer _________________________________ venalicius _____________________________ Otto _________________________________ mater _________________________________ Anna ________________________________ dominus ______________________________ pastor ________________________________ nuntius_______________________________ List the nouns that have vocatives different from their nominative singulars. ________________________________________________________________________________ Now, let’s translate some sentences. The only thing you have to remember is that Latin does NOT usually begin the sentence with a vocative word. Mother, tell a story narra, mater, fabulam! BUT Slave, bring water! fer, serve, aquam! 1. Friend, hurry! __________________________________________________________ 2. Sister, save the baby! ______________________________________________________ 3. Slave dealer, lead the handmaidens! __________________________________________ 4. Master, sell the country house! ______________________________________________ 5. Father seize the thief! ___________________________________________________ 6. Farmer, buy the doves! ____________________________________________________ 7. Bakers, bring the bread to the forum! ________________________________________ QQ REVIEW FOR TEST on STAGE 6 1. 2. 3. 4. Sententiae Antiquae Derivatives Vocabulary Imperatives : form the singular and plural commands as required parare (s)______________________________ tenere (pl) ____________________________ scribere (pl)_______________________________ facere (s) ______________________________ venire (s) _______________________________ ducere (pl) _____________________________ 5. Insert the correct IMPERATIVE (s. or pl.) based on the VOCATIVE given: a. (narrare) Mater, ___________________fabulam. _________________________________ b. (tenere) Infans, panem_______________________________! c. (emere) _______________________cibum nunc, agricolae! __________________________ d. (facere) panem__________________, pistor! _______________________________ 6. The PRESENT tense tells us what’s going on__________________________. The IMPERFECT tense shows______________________time. The PERFECT tense shows ______________________time. Explain the difference between IMPERFECT and PERFECT tenses: _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. On the opposite side of the page, conjugate and translate facio in the present tense venio in the imperfect tense iaceo in the perfect tense 8. Translate these forms into English: pugno_______________________________ habebat_______________________________ necaverunt_______________________________ emite _______________________________ custodiebam_______________________________ vendidistis_____________________________ fecit_______________________________ dedisti_______________________________ you (s) used to fear________________________ hurried__________________________ she has bring! (pl) _______________________________ he was resting__________________________ 9. Noun/Adjective Agreement: infans parva GEN S. ___________________________ GEN PL. ________________________ pistor maximus DAT S. ________________________ DAT PL. ________________________ forum magnum ACC S. __________________________ ACC PL. ________________________ serpens iratus ABL S. ____________________________ ABL PL. ________________________ 10. Prepositional Phrases: translate: in viam________________ per theatrum____________________ cum patre__________________