High Speed Networks
advertisement
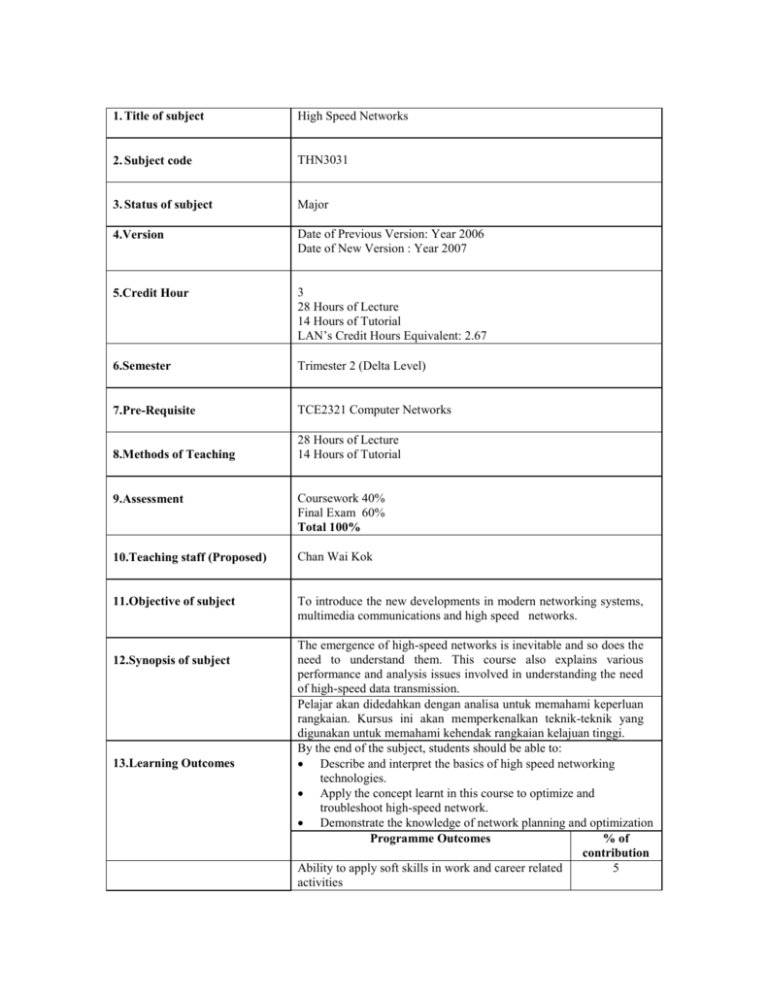
1. Title of subject High Speed Networks 2. Subject code THN3031 3. Status of subject Major 4.Version Date of Previous Version: Year 2006 Date of New Version : Year 2007 5.Credit Hour 3 28 Hours of Lecture 14 Hours of Tutorial LAN’s Credit Hours Equivalent: 2.67 6.Semester Trimester 2 (Delta Level) 7.Pre-Requisite TCE2321 Computer Networks 8.Methods of Teaching 28 Hours of Lecture 14 Hours of Tutorial 9.Assessment Coursework 40% Final Exam 60% Total 100% 10.Teaching staff (Proposed) Chan Wai Kok 11.Objective of subject To introduce the new developments in modern networking systems, multimedia communications and high speed networks. 12.Synopsis of subject 13.Learning Outcomes The emergence of high-speed networks is inevitable and so does the need to understand them. This course also explains various performance and analysis issues involved in understanding the need of high-speed data transmission. Pelajar akan didedahkan dengan analisa untuk memahami keperluan rangkaian. Kursus ini akan memperkenalkan teknik-teknik yang digunakan untuk memahami kehendak rangkaian kelajuan tinggi. By the end of the subject, students should be able to: Describe and interpret the basics of high speed networking technologies. Apply the concept learnt in this course to optimize and troubleshoot high-speed network. Demonstrate the knowledge of network planning and optimization Programme Outcomes % of contribution Ability to apply soft skills in work and career related 5 activities 14.Details of subject 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Good understanding of fundamental concepts Acquisition and mastery of knowledge in specialized area 35 30 Acquisition of analytical capabilities and problem solving skills 15 Adaptability and passion for learning 5 Cultivation of innovative mind and development of entrepreneurial skills 5 Understanding of the responsibility with moral and professional ethics 5 Topics Covered Hours 1. Introduction The need for speed and Quality of service. Emeregnce of High-speed LANs. Corporate WANs. IP based Internet. ATM networks. Congestion in Data networks. Effect of Congestion. Ideal Performance. Practical Performance. Congestion Control. Traffic Management. 2. ATM Technologies Protocol Architecture. Logical Connections. Cells. Service Castegories. ATM Adaption Layer. 3. High Speed LANs Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. ATM LANs. 4. Network performance measurement and modelling Queuing analysis: queue behaviour, single-server queues, multi-server queues, queues with priorities, network queues, other queuing models. Internet traffic: self-similarity, Ethernet traffic, World-WideWeb traffic. 5. Congestion control and traffic management Effects of congestion, congestion and control, traffic management, congestion control in packet-switching networks, TCP traffic control: TCP flow and congestion control. 6. Internet routing Graph theory concepts, least cost paths, interior routing protocols: internet routing principles, distance-vector protocol - RIP, link-state protocol – OSPF, exterior routing protocols: path-vector protocols – BGP and IDRP, multicasting. 7. Quality of service (QoS) in IP networks Integrated service architecture (ISA), queuing discipline, differentiated services, resource reservation protocol (RSVP), Multi-protocol label switching (MPLS), Real-time transport protocol (RTP). 2 2 2 4 6 6 6 Tutorial TCP/IP and Legacy LAN ATM, FR and X.25 High Speed LAN QoS and Network Performance Congestion Control & traffic Management Internet Routing QoS in IP networks Total Contact Hours 15.Text Text Book Reference Books 28 High-Speed Networks and Internets: Performance and Quality of Service, William Stallings, Prentice Hall. 2nd Ed. 2002. T. S. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks, 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall. E. Ramos, A. Schoroeder and A. Beheler, Computer Networking Concepts, Macmillan. Gallo & Hancock, Computer Comm. And networking Technologies, Thomson Learning. Douglas E. Comer, Network Systems Design Using Network Processors, Prentice Hall.