Urban Growth and Decline in Sydney
advertisement

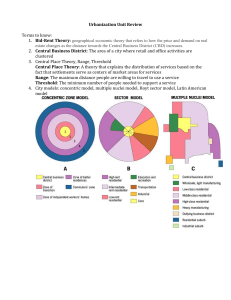
Population decrease in areas of the city. Suburbs become neglected: slums. Push factors away from Sydney include: Land prices, air pollution, Traffic congestion, Overpopulation. Areas become derelict (rundown) forcing people to move away from urban locations. Economic restructuring: movement of business e.g Pyrmont wharves to Port Botany Urban decline Pyrmont pre 1980s. Suburbs move outwards causing urban sprawl - ¼ acre blocks. Human environment (houses, roads) dominate physical environment (trees, bushland) Increase in waste disposal, water consumption, traffic congestion The population of Sydney is predicted to reach 4.9 million by 2026 Increased spending of infrastructure. Example: Western Suburbs Sydney Issue Waste: Increased population – more waste. Resources: Extra Demand for water, food Infrastructure: traffic congestion, demand for hospitals and schools. Energy: power grid failure, fossil fuel energies. Management More recycling schemes, incentives to reduce packaging Water restrictions, food regulations Public transport initiatives, decentralisation of economy, government funding. Green energy technologies, reduction in over use of energy. Urban government policy initiative (renewal, consolidation) Halting the process of urban sprawl by building mediumhigh density residential areas. Rejuvenating old buildings, proving green space, improving public transport. Urban renewal = Gentrification Balance between human and physical environments: Ecological Sustainability