basic computer glossary
advertisement

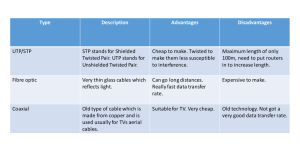
What is computer? What are some of the operating programs? Read the follow chart. Hardware (peripheral devices) Hardware is machinery and electrical parts of the computer - the parts you can see and touch, for example, the monitor, the keyboard , CPU, motherboard, power supply, graphic card, sound card and circuits inside it. Software capacity of disks -Hard disk up to 500 GB (giga byte) or TB -CD: 700 MB -DVD: 4.2 GB -Flash drive/USB Up to 64 GB/128 GB driver modem Modem connects computer to the internet. It converts computer signals into a telephone or cable signal and vice versa. It stands for formatting Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 Software is all the facts the lists of instructions that a computer receives to carry out its tasks. All the different lists of instructions are called programs, which are called software, such as Microsoft office, internet explorer, PowerPoint, Excel, etc. It is the software needed to operate each device connected to the computer. Formatting is preparing disk to receive data, erasing all previous information. MODULATOR DEMODULATOR unit of memory Unit of memory is Byte. It is equal to 8 bits of binary code. booting unit of speed Unit of speed is Hertz. It is measured as cycles processed per second. wifi ROM ROM (Read Only modem Memory) refers to pre-recorded memory. It cannot be changed. It is read only. RAM RAM (Random Access Memory) is temporary working memory of the computer. Everything in RAM is lost when the electricity is turned off. input and storage configurations Input is whatever goes into the computer such as commands that is entered by user, data from another computer or device, pictures from cameras, sounds etc.. Input device include keyboard, mouse, web cam, microphone, Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 Booting is the loading of operating system such as Window into RAM of the computer. Virus is a software program that interferes with the operation of a computer and may causes damage to the computer. scanner, fingerprint scanner, etc. output Output is anything that comes out of the computer such as binary numbers, characters, pictures, images, sounds and printed pages. Output devices include display screens, loudspeakers, and printers. the operating system Operating system tells other programs how to work, and other programs talk through an operating system. It is an interface between a user, application software, and CPU. It manages all files and data. Some operating systems used today are Windows, Linux, and Mac OS. the mouse The mouse moves a pointer on the screen. Clicking - pressing and releasing Double clicking pressing twice on a mouse button Clicking and dragging means holding down a button as you move the mouse Scrolling wheel is used to scroll down/up the page Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 An ergonomic mouse is curved to fit your hand. Most mouses are linked to the computer by a cable/tail. Mouses without tails are called cordless or tail-less mouses. the keyboard monitors the printer It is used to enter date into a computer. With word processing software, keyboards can be used to type documents and to send instructions to the CPU. A monitor displays computer data on a screen. It works in the same way as televisions. Like monitors, printers decode binary code and print it onto a form that you can understand on paper or film. Hard disk drive (HDD) 1.What is the Internet? The Internet is the connection of millions of computers around the world into a network. The computers are thus linked together or inter-connected. The Internet's main purpose is to inter-connect net works. The Internet is made up of thousands of small networks that are independent of each other. No one individual, company or government owns the Internet. 2. What does WWW stand for? The Internet is a collection of linked computers. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a collection of information or web pages. Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 Each page may contain links to other pages of information, known as hyperlinks. Each page can contain text, graphics, buttons, animations, sounds and video. 3. What is a home page? A home page is the starting page for a collection of web pages. This will usually have links to all the other web pages in this web site. 4. What is a browser? A browser allows you to view and interact with web pages. There are a variety of companies that make browsers, and many are free, e.g. Internet Explorer. The browser needs to be set up to communicate with the Internet. This is usually done by an install program, given to you when you sign up with an Internet service provider (ISP). Once you have a Web browser installed and working, you will only need to learn a few navigational commands and you are off and running exploring the Internet. 5. What is an Internet address? An Internet address that is called a URL (uniform resource locator). This address will help you find the information you require. For example: http://www.kogarhnews.wikispaces.l5communication.com The URL is made up of the following parts: http:// indicates the protocol used www.kogarahnews indicates the domain name .wikispaces indicates the directory name l5communication.com indicates the type of file 6. What is a link /hyperlink? There are links on a web page to take you to other web pages. These are hyperlinks. When you move your cursor over the top of a hyperlink, the cursor changes to a picture of a hand. You'll see the location of the link displayed on the status bar in a different colour. bluetooth: A type of wireless network standard used for short distances with devices such as cell phones and laptops. broadband: Any high-speed Internet connection, whether provided through cable, DSL, or satellite. upgrade: A complete revision of a computer program that you use to replace the current program. Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 uninterruptible power supply (UPS): A power strip combined with a battery to keep your computer running when the power goes out. USB: Universal Serial Bus; a computer connection that you can use to attach many different kinds of devices and peripherals to a computer Windows: The most common operating system on PCs. WiFi: Wireless fidelity; the original 802.11b standard wireless base station. wired network: A network connected by cables. wireless: Making a connection between computers or a computer and devices without physically connecting them with wires or cables; usually involves using radio signals to send and receive information. Wireless Access Point (WAP): An intermediary device that exchanges information between various configured wireless devices. wireless network: A network that features specific equipment, such as network interface cards and routers, in place of wires (copper or optical fiber) for connectivity. word processor: A computer program in which you generate, edit, store, transmit, or duplicate electronic text documents. SPAM Bluetooth: A type of wireless network standard used for short distances with devices such as cell phones and laptops. broadband: Any high-speed Internet connection, whether provided through cable, DSL, or satellite. brower CD: Compact disc; a removable storage medium that can hold data, text, and graphics. CD/DVD recorder: A type of drive that you can attach to your computer in order to copy data from your PC to a recordable CD or DVD. chip: An integrated computer circuit containing many elements connected on a single unit. Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 chipset: A group of chips that work together to perform a specific task or function. For example, a motherboard on a computer contains chips for the BIOS, CPU, memory, expansion slots, and other components; this collection of chips is the motherboard’s chipset. circuit: An electrical device that provides a path for electrical current to flow. CPU: Central processing unit; A computer component, often called a processor and microprocessor, whose speed determines how fast your PC operates. cursor: The blinking icon on the computer screen that shows you where the characters you type appear; also called an insertion pointer. desktop: A normal computer setup; A type of computer made up of a PC console, monitor, mouse, keyboard, and any additional attachments. A desktop PC isn’t easily portable. dialup: A kind of computer Internet connection that uses existing phone lines. digital: A means of storing, transmitting, manipulating, or reproducing data, images and sounds by using groups of electronic bits represented by 1 and 0. ergonomics: Adapting work or working conditions to suit the worker. file: A binary (not physical) container that holds a chunk of information stored in a computer. firewall: A software or hardware device designed to block unauthorized intruders from gaining entry to an individual computer or a network. flash drive: A keychain-size storage unit that saves files on memory cards; you can plug it into your computer and access it like any other external hard drive. hard drive: A disk drive on your PC that can store the greatest amount of information and access it in the quickest manner; therefore, it’s the main source of permanent storage. hardware: The physical part of a computer — anything you can touch and see, such as the computer console, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. headphones/speakers jack: The I/O jack where you plug in your headphones or external speakers. headset: Headphones that include a built-in microphone for online communications and game playing. Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 hibernate: A computer function by which it saves all the computer’s memory (everything the system is doing), then turns the computer off. hub: A common connection point for devices in a network. hyper-threading: A feature of certain Pentium processors that makes one physical CPU appear as two logical CPUs, overlapping two instruction streams in order to achieve a gain in performance. IP address: An identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network. keyboard: The device you type on; it’s the primary way you communicate with the computer, with input. LCD: Liquid crystal diode; A type of computer monitor, also called a flat-panel monitor, that’s thin and uses relatively little electricity log in: To identify yourself on a computer by entering a user name and password. log off: To tell Windows that you’re done using the computer without actually turning off the computer; you must log in to use it again. log on: To identify yourself on a computer by entering a user name and password. log out: To tell Windows that you’re done using the computer without actually turning off the computer; you must log in to use it again. upgrade: A complete revision of a computer program that you use to replace the current program. uninterruptible power supply (UPS): A power strip combined with a battery to keep your computer running when the power goes out. DVD: Digital video disc; a removable computer storage medium that has a larger capacity than a CD. URL: Windows: The most common operating system on PCs. WiFi: Wireless fidelity; the original 802.11b standard wireless base station. wired network: A network connected by cables. wireless: Making a connection between computers or a computer and devices without physically connecting them with wires or cables; usually involves using radio signals to send and receive information. Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013 Wireless Access Point (WAP): An intermediary device that exchanges information between various configured wireless devices. wireless network: A network that features specific equipment, such as network interface cards and routers, in place of wires (copper or optical fiber) for connectivity. word processor: A computer program in which you generate, edit, store, transmit, or duplicate electronic text documents. Please type the answers to these qs: You can email to Adapted from ICAU1133ABooklet and EAP ss work/S1 2013