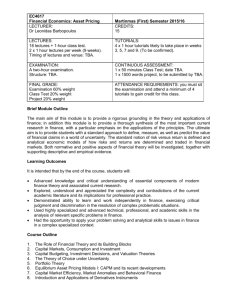
Annual Course Reports
advertisement

Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Course specifications Human anatomy University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course specifications: Program on which the course is given: bachelor of medicine and surgery (M.B., B.Ch.). Elements (major or minor) of the program (undergraduate): The first year: a- Human biology (introduction to human anatomy, growth, and genetics), b- Upper limb, c- Thorax, d- Abdomen (including pelvis and perineum), e- General embryology. Department offering the program: Dept of anatomy. Department offering the course: Dept of anatomy. Academic year/level: First year medical students. Date of specification approval: 2010. A- Basic information: Θ Title: human anatomy. Θ Code: anat. ) 111 )ت ش Θ Credit hours: to be determined. Θ Lecture: 120 Θ Practical: 120 Θ Total: 240 B- Professional information: 1- Overall aim of the course: To provide the student of the 1st year of Medicine with the normal structure of the upper limb, thorax, and abdomen, pelvis and perineum. To provide the student of the 1st year of Medicine with the clinically related anatomical data that will be helpful in medical profession To provide the student of the 1st year of Medicine with general ideas about the structures of various body tissues. Know the surface anatomy of the various structures of the body. Know the radiological anatomy of the various structures of the body. Know the embryological development, prenatal growth, and congenital defects of the various systems and organs of the body. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 1 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2- intended learning outcomes of the course (ILOs): a- Knowledge and understanding: Θ Identification of the site of various organs and their positional relations to each other. Θ Visualization of the surface anatomy of various organs on the skin of the patients during clinical examination. b- Intellectual skills: The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during clinical examination of patient (history taking, examination, and choosing and interpretation of investigations) to reach for the anatomical diagnosis (i.e. where, in which system or organ, the disease process is occurring in the patient) c- Professional and practical skills: The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during joint examination to determine the their integrity, and the degree and type of the defect if any. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during muscle examination to determine the their function. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during nervous system examination to determine the their integrity, the site and type of lesion if any. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during surgical procedures or operations to perform a perfect surgical interference and avoid unnecessary injury to healthy surrounding organs. d- General and transferable skills: Communicate with colleagues about anatomical basis in diseases. Manage anatomical problems such as variations and defects related to clinical problems. Manipulate anatomical specimens. Work in/with different groups. 3- contents: Topic No. of hoursLecture Practical FIRST YEAR 240 120 120 a- human biology (introduction to human 14 14 00 anatomy, growth, and genetics), b- upper limb, 64 24 40 c- thorax, 42 18 24 d- abdomen (including pelvis and perineum), 106 50 56 e- General embryology. 14 14 00 -------------------------4- Teaching methods 4.1- Lecture (using boards, overhead and slide projectors, data show). Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 2 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4.2- Practical dissection in anatomy laboratory. 4.3- Demonstrations through: previously dissected specimens and models. 4.4- Audio-visual learning through video films & CDs. 5- Student assessment methods: 5.1- written essay questions exam to assess the students recall, comprehension, organization, understanding of anatomical topics whether in long essay or in short essay questions. 5.2- written MCQs questions exam to assess the students overall comprehension and association. 5.3- written fill in the spaces questions exam to assess overall comprehension and association of students. 5.4- practical examination to assess student’s ability to identify various anatomical structures and their relations in the anatomical specimens and cadavers. 5.5- oral examination to assess overall comprehension and association of students and the way they present their knowledge. Assessment schedule Assessment 1: mid-year exam (written). Assessment 2- periodic exam. (written, and practical). Assessment 3- final year exam (written, practical and oral). Weighting of assessments Method of assessment Percentage of total Written examination 70% Oral examination 12% Practical/laboratory work 8% Other assignments/class work 10% Total 100 % 6- list of references 6.1- Course notes Course notes done by teaching staff. 6.2- Essential books (textbooks) Cunningham’s manual of practical anatomy. Gray’s anatomy. Snell anatomy series. Moore embryology series. 6.3- Recommended books there is a long list of anatomy books present in the faculty library for the student to choose from. 6.4- periodicals, web sites etc.. Periodicals such as anatomy journal, anatomical records are available in the faculty’s library Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 3 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Web sites are to be determined and updated during course work. 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning. 7.1- dissecting room (with cadavers, and dissecting instruments). 7.2- anatomical plastic models, pictures, etc. 7.3- Plastinated anatomical specimens 7.4- computers (with CDs for teaching anatomy films). 7.5- TV and VCR (for anatomy video films). 7.6- X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans Course Coordinator Dr. Mostafa Abdel-Hamid, MD Head of Department Ass. Professor Dr. Mostafa Abdel-Hamid, MD Date: / /2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 4 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Human anatomy Course specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Department: Anatomy. Human anatomy for SECOND year medical students Program on which the course is given: Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery (M.B., B.Ch.). Elements of the program (undergraduate): The SECOND year: a- Head and neck, b- Neuroanatomy, c- Lower limb, d- Special embryology Department offering the program: dept of anatomy. Department offering the course: dept of anatomy. Academic year/level: Second year medical students. Date of specification approval: 2010. A- Basic information: Θ Title: human anatomy. Θ Code: anat (211) ت ش Θ Credit hours: Θ Lecture: 120. Θ Practical: 120. Θ Total: 240. B- Professional information: 1- Overall aim of the course: To provide the student of the 2nd year of Medicine with the normal structure of the head and neck, lower limbs, and nervous system. To provide the student of the 2nd year of Medicine with the clinically related anatomical data that will be helpful in medical profession. To provide the student of the 2nd year of Medicine with the normal development of the various organs of the body. To provide the student of the 2nd year of Medicine with the congenital anomalies of the various organs of the body. 2- intended learning outcomes of the course (ILOs): By the end of the course, the student should be able to: a- Knowledge and understanding: Description of the site, shape, size, and positional relations of studied organs. Definition of the external appearance and the internal structure of the organs. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 5 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications List of the arterial supply, venous drainage, lymphatic drainage of studied organs. Description of the normal development and congenital anomalies of systems and organs. Highlighting the clinical application of anatomical data. Identification and description of various anatomical specimens. b- Intellectual skills: The course will assist the students to: Develop the skills of relating anatomical data to surface of the body (surface anatomy). Develop the skills of relating anatomical data to X-rays (radiological anatomy) and others such as Sonar, CT and MRI. Develop the skills of relating anatomical data to clinical problems. c- Professional and practical skills: The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during joint examination to determine the their integrity, and the degree and type of the defect if any. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during muscle examination to determine the their function. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during nervous system examination to determine the their integrity, the site and type of lesion if any. The course will assist the students to develop the skills to apply anatomical data during surgical procedures or operations to perform a perfect surgical interference and avoid unnecessary injury to healthy surrounding organs. d- General and transferable skills: Communicate with colleagues about anatomical basis in diseases. Manage anatomical problems such as variations and defects related to clinical problems. Manipulate anatomical specimens. Work in/with different groups. 3- contents: Topic SECOND YEAR a- head and neck b- neuroanatomy c- lower limb d- special embryology No. of hours 240 104 62 50 24 Lecture 120 46 30 20 24 Practical 120 58 32 30 -- 4- Teaching methods 4.1- Lecture (using boards, overhead and slide projectors & data show). 4.2- Practical dissection in anatomy laboratory. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 6 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4.3- Demonstrations through: previously dissected specimens and models. 4.4- Audio-visual learning through video films & CDs. 5- Student assessment methods: 5.1- written essay questions exam to assess the students recall, comprehension, organization, understanding of anatomical topics whether in long essay or in short essay questions. 5.2- written MCQs questions exam to assess the students overall comprehension and association. 5.3- written fill in the spaces questions exam to assess overall comprehension and association of students. 5.4- practical examination to assess student’s ability to identify various anatomical structures and their relations in the anatomical specimens and cadavers. 5.6- oral examination to assess overall comprehension and association of students and the way they present their knowledge. Assessment schedule Assessment 1: mid-year exam (written). Assessment 2- periodic exam. (Written, and practical). Assessment 3- final year exam (written, practical and oral). Weighting of assessments Method of assessment Percentage of total Written examination 70% Oral examination 12% Practical/laboratory work 8% Other assignments/class work 10% Total 100 % 6- list of references 6.1- Course notes Course notes done by teaching staff. 6.2- Essential books (textbooks) Cunningham’s manual of practical anatomy. Gray’s anatomy. Snell series Moore series. 6.3- Recommended books there is a long list of anatomy books present in the faculty library for the student to choose from. 6.4- periodicals, web sites etc.. Periodicals such as anatomy journal, anatomical records are available in the faculty’s library Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 7 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Web sites are to be determined and updated during course work. 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning. 7.1- dissecting room (with cadavers, and dissecting instruments). 7.2- computers (with CDs for teaching anatomy films). 7.3- TV and VCR (for anatomy video films). 7.4- X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans Course Coordinator Dr. Mostafa Abdel-Hamid, MD Head of Department Ass. Professor Dr. Dr. Mostafa Abdel-Hamid, MD Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 8 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Physiology Course Specifications For 1st Year Medical Students 2010/2011 University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Programme(s), on which the course in given: First year of MBBCh programme. Major or minor element of programme(s): Physiology for First year medical students. Faculty offering the program: Faculty of Medicine. Department offering the course: Physiology Department. Academic year/level: First year of M.B.B.Ch. programme. Date of specification approval: A. Basic Information Title: Physiology Code: 113 ف س credit Hours: Not applicable Lectures: Total of 150 hours; 5 hours/week, for 30 weeks Practical: Total of 60 hrs; 2 hours/week, for 30 weeks Tutorial: Not applicable Total: 210 hours B. Professional information 1. OVERALL AIMS OF COURSE The aims of the course are to enable students to: 1- Explain the functional background of cells, tissues, organs and systems. 2- Assess physiological data and mechanisms with ongoing basic sciences. 3- Utilize the rapidly changing and inflating details about molecular biology and genetics. 4- Apply the basic scientific research skills as well as effective communication and team work attitudes. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 9 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2. INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES OF COURSE (ILOS) a. Knowledge and understanding: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. To create an idea about the functional relationship between various organ systems of the body. 2. Understand the concept of the internal environment and its regulations by homeostatic mechanisms. 3. Define feedback mechanisms and identify the various components of the control systems. 4. Analyze the general organization and function of ANS. 5. Demonstrate the physical, chemical and electrical properties of cell membranes. 6. Assess the different properties of cardiac muscle so as to predict myocardial diseases such as heart failure. 7. Discuss the general organization and function of the respiratory system, digestive system. b. Intellectual skills: The course will assist the students to: B1. Develop the skills for demonstrating different functions of different systems to diagnose deviation from normality as detected disease state. B2. Prepare the student to develop ability to assess the problems associated with different factors, which affect the normal function of different body systems. c. Professional and practical skills: After completing the course the students should be able to apply practical experiment to demonstrate different functions (e.g., how to utilize sphygmonometer, stethoscope, electrocardiogram, etc.. d. General and transferable skills: By the end of the course, the student should be able to: D.1. Prepare a scientific topic. D.2. Explain clearly and effectively a scientific topic in tutorial, a staff meeting or the yearly scientific day.. D.3. Create a graphical representation of physiological data. D.4. Design protocol for examination of all body systems. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 10 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 3. CONTENTS Topic Introduction to Physiology Autonomic nervous system Excitable tissues The blood Cardiovascular system Respiratory system Biophysics Digestive system Total Hours 10 22 30 30 46 38 10 24 Lectures/4hrs/w Practical/4hrs/w 6 18 20 20 30 30 6 20 4 4 10 10 16 8 4 4 4) TEACHING AND LEARNING METHODS 4.1. Lectures: the students are divided into two groups (about 250 students each). 4.2. Practical training : small group training(about 15 students each). 4.3. Self learning activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4.4. Tutorial classes : (Not applicable). 4.5.A yearly scientific day for students, in the form of small group presentations. The title of the subjects are determined during several meetings with staff. 5) STUDENTS ASSESSMENTS METHODS 5.1. Written exam to assess the student’s comprehension, understanding and problem solving, in the form of short essay questions and /or MCQ. 5.2. Practical exam to assess the student’s professional skills to demonstrate functions of body systems. 5.3. Oral exam to assess student’s knowledge, understanding and intellectual skills as well as assessing the verbal communication abilities. Assessment Schedule: Assessment 1: Written exam/MCQ Assessment 2: Mid-term written exam Assessment 3: Practical exam Assessment 4: End of year exam (written & oral) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System week 5 week 15 week 20 week 30 11 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Weighting of assessment: Mid- term written Exam Final- term written exam Practical Periodic Oral exam Total Any formative only assessment (Not applicable) 20% 50% 8% 10% 12% 100% (250 marks) 6) LIST OF REFERENCES 6.1. Department books and notes. 6.2. Essential books (Text Books): Ganong review of medical physiology. Gyton textbook of medical physiology. Illustrated medical physiology.. 6.3. Periodicals, Web sites: American Journal of physiology The Journal of physiology www.pubmed.com 7) FACILITIES REQUIRED FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING Physiology laboratories equipped with different instruments needed to assess physiological functions on experimental animals. Classrooms with data show, slide projector and overhead projector for lectures and/or practical classes. Head of Department: Prof Dr. Ibrahim Y. Ibrahim Course Coordinators: Dr. Salah El-Din Aziz MD Dr. Magdy K.A. Hassan MD Signature Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 12 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Physiology Course Specifications For 2nd Year Medical Students 2010/2011 University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Programme(s), on which the course in given: second year of MBBCh programme. Major or minor element of programme(s): Physiology for second year medical students. Faculty offering the program: Faculty of Medicine. Department offering the course: Physiology department. Academic year/level: second year of M.B.B.Ch. programme. Date of specification approval: A. Basic Information Title:Physiology Code:213 ف س credit Hours:Not applicable Lectures:Total of 150 hours; 5 hours/week, for 30 weeks Practical:Total of 60 hrs; 2 hours/week, for 30 weeks Tutorial:Not applicable Total:210 hours B. Professional information 1. OVERALL AIMS OF COURSE The aims of the course are to enable students to: 1- Explain the functional background of cells, tissues, organs and systems. 2- Assess physiological data and mechanisms with ongoing basic sciences. 3- Utilize the rapidly changing and inflating details about molecular biology and genetics. 4- Apply the basic scientific research skills as well as effective communication and team work attitudes. 2. INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES OF COURSE (ILOS) a) Knowledge and understanding: Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 13 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. To create an idea about the functional relationship between various organ systems of the body. 2. Understand the concept of the internal environment and its regulations by homeostatic mechanisms. 3. Define feedback mechanisms and identify the various components of the control systems. 4. Discuss metabolism and regulation of body temperature 5. Discuss the anatomical consideration and function of the eye and ear. 6. Central nervous system, endocrine system, reproductive system, and urinary system. b) Intellectual skills: The course will assist the students to: B1. Develop the skills for demonstrating different functions of different systems to diagnose deviation from normality as detected disease state. B2. Prepere the student to develop ability to asses the problems associated with different factors which affect the normal function of different body systems. c) Professional and practical skills: After completing the course the students should be able to apply practical experiment to demonstrate different functions (e.g., how to utilize sphygmonometer, stethoscope, electrocardiogram, etc.. d) General and transferable skills: By the end of the course, the student should be able to: D1. Prepare a scientific topic. D2. Explain clearly and effectively a scientific topic in tutorial, a staff meeting or the yearly scientific day.. D3. Create a graphical representation of physiological data. D4. Design protocol for examination of all body systems. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 14 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 3. CONTENTS Topic 1. General metabolism 2. Renal physiology 3. Endocrine glands 4. Reproduction 5. Central Nervous System 6. Special senses Total Hours 18 28 35 23 66 30 Lectures/4hrs/w Practical/4hrs/w 10 20 25 15 60 20 8 8 10 8 16 10 4. TEACHING AND LEARNING METHODS 4.1. Lectures: the students are divided into two groups (about 250 students each). 4.2. Practical training : small group training(about 15 students each). 4.3. Self learning activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4.4. Tutorial classes : (Not applicable). 4.5.A yearly scientific day for students, in the form of small group presentations. The title of the subjects are determined during several meetings with staff. 5. STUDENTS ASSESSMENTS METHODS 5.1.Written exam to assess the student’s comprehension, understanding and problem solving, in the form of short essay questions and /or MCQ. 5.2.Practical exam to assess the student’s professional skills to demonstratee functions of body systems. 5.3.Oral exam to assess student’s knowledge, understanding and intellectual skills as well as assessing the verbal communication abilities. Assessment Schedule: Assessment 1: Written exam/MCQ Assessment 2: Mid-term written exam Assessment 3: Practical exam Assessment 4: End of year exam (written & oral) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System week 5 week 15 week 20 week 30 15 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Weighting of assessment: Mid- term written Exam Final- term written exam Practical Periodic Oral exam 20% 50% 8% 10% 12% Total 100% (250 marks) Any formative only assessment (Not applicable) 6. LIST OF REFERENCES 6.1. Department booka and notes. 6.2. Essential books (Text Books): Ganong review of medical physiology. Gyton textbook of medical physiology. Illustrated medical physiology.. 6.3. Periodicals, Web sites: American Journal of physiology The Journal of physiology www.pubmed.com 7. FACILITIES REQUIRED FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING Physiology laboratories equipped with different instruments needed to assess physiological functions on experimental animals. Classrooms with data show, slide projector and overhead projector for lectures and/or practical classes. Head of Department: Prof Dr. Ibrahim Y. Ibrahim Course Coordinators: Dr. Salah El-Din Aziz MD Dr. Magdy K.A. Hassan MD Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 16 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Histology First year Course specification 2010/2011 - Program(s),on which the course is given: first year medical students. - Major or minor elements of program : histology for medical students. This Course includes general and systemic histology. - Faculty offering the program: faculty of medicine. - Department offering the course: histology department. - Academic year: first year of M.B & B.Ch.degree. - Date of specification approval: A. Basic information : Title: histology Code:112 هـ س Credit hours: include the following; Lectures: 28 lectures(56 hours; 2hours/week ,for 28 weeks). Practical: total of 60 hours (2hours/week for 30 weeks). Tutorial: not applicable Total: 116 hours. B . Professional information : (1)Overall aims of course: By the end of the course the student should be able to : 1-Recognize different methods used to prepare a tissue or an organ specimen in a manner suitable for viewing with the microscope. 2-Spread a blood film and tissue smears. 3-Stain tissue sections and blood films . 4-Know how to adjust and use the microscopes to view the prepared tissue sections . 5-Recognize what is the normal structure of the different tissues and organs of the body . To be able to define the abnormal changes studied in pathology in the third year of medical study. (2)Intended learning outcomes of course: a- Knowledge and understanding : By the end of the course , the student should be able to : 1-Recognize the morphology of the cells and tissues of the body . 2-Identify the ultrastructure of cells and tissues of the body 3-Understand the basis of cytogenetics. 4-Become aquainted with the histochemistry of the cells and tissues of the body . Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 17 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications b- Intellectual skills : 1- The course will assist the student to develop the skills for analyzing the morphological and the staining characteristics of the different cells and tissues of the body. 2- To be able to define the part of the body from which the tissue section is taken and prepared for microscopic examination. 3-Grasp the specific characteristics of cell components in relation to function of each one. 4-The course will assist the student to develop the ability to understand how the chemistry of the cells and tissues be translated into microscopic observations c- Professional and practical skills : After completing the course , the student should be able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquired during the course into professional application such as managing a research work concerning cytogenetics and molecular biology. The latter is the key for understanding much about the secrets of the human body during health and sickness. d-General and transferable skills : After completing the course the student should be able to : 1- Appreciate the importance of long life- learning and show a strong commitment to it . 2- Use the sources of biomedical information to remain current with advances in knowledge and practice . 3- Give his or her opinion regarding update scientific problems (e.g.transcription). 3- Course contents : Topic 1- Introduction, Microtecniqes & Cytology 2- Cytogenetics 3- Blood 4- Epithelium 5- Connective tissue 6- Cartilage 7- Bone 8- Muscle 9- Nervous tissue 10- Receptors 11- Vascular system 12- Lymphatic system 13- Revision Total (116 hours) Lectures 12 6 4 4 4 2 4 2 4 4 4 4 2 56 Practical 12 4 6 6 6 2 4 2 4 2 2 4 6 60 (4) Teaching and learning methods: Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 18 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 1- Two hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year for first year medical students(for 28 weeks). 2- Two hours of practical training and demonstration weekly throughout the academic year .The students are divided into 12 sections each section is comprised of 4o students,Each two students share one microscope. 3- Self training activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4- Tutorial classes (not applicable). (5) Student assessment methods: 1-Written exam.(in the form of short essay and/or MCQ), to assess: 1- The student,s comprehension and good understanding of subjects regularly studied during the course . 2- The capability of the student for assimilitoin and application of the knowledge included in the course throughout the semester. 2- Practical exam. to assess the professional skills of the student regarding the ability of applying information studied in the course in diagnosis and drawing of different microscopic and projector slides. 3- Oral exam. -To assess the student intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics. -To help the teaching staff to evaluate the % of achievement of the intended learning outcome of the course . (6) Assessment schedule: *Assessment 1: regular MCQ exam. held twice a year in November and March. This is determined after approval by the department council and according to internal regulations within the faulty. *Assessment 2: mid-term written exam. Week 15. *Assessment 3: End-year exam. (written, practical and oral) week30. Weighing of assessment: Mid-term written exam. Final- term written exam. Oral final exam. Practical final exam. Semester work 30 degrees 75 degrees 15 degrees 15 degrees 15 degrees (8 degrees MCQ Exams+7 degrees practical note book) Total 150 degrees Any formative assessment Not applicable Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 20% 50% 10% 10% 10% 100% 19 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 7- List of references : A- Course notes and handouts . 1- Department book by prof Dr. Saadia Ragab and Prof. Dr. Entesar Ali . 2- Histology part I and part II for medical students by Prof. Dr. Zakaria Abd Al-Hamid. 3- Introduction to functional and clinical histology part I and part II Prf. Dr. Ayman Ghalab . 4- Manual of practical histology by Prof. Dr. Saadia Ragab. B- Recommended textbooks : 1- Basic histology, Junqueira et al., 1998. 2- Bloom and fawcett: Cnscise Histology. Fawcett, 1999 . 3- Cell biology and histology. Gartner et al., 1998 . 4- Clinical and functional histology for medical students. Snell, 1984. 5- Functional histology: A text and color Atlas, wheather et al., 1997. 6- Cormack D.: A textbook, Ham's Histology 1997. 7- Human Histology, Stevens and Lowe 1997. 8- A text and Atlas of Histology by Leeson and Leeson 1995. C- Periodicals, web sites, …Etc . To be determined and update during the course work . 8- Facilities required for teaching and learning: 1-Laboratories equipped with histological tools such as electric microscopes, slide projectors and requirements for microtechniques. 2-Class rooms for theoretical lectures provided with overhead projector. Course coordinators: Prof Dr. Saadia Ragab Sayed . Prof Dr. Entesar Ali Saber . Head of department Prof Dr. Saadia Ragab Sayed . Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 20 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Histology Second year Course specifications Course specification: -Programme(s) on which the course is given: Second year medical students. -Major or minor elements of program: histology for medical student including different systems and C.N.S. Faculty offering the program: Faculty of Medicine. Department offering the course: Histology department. Academic year: Second year of M.B& B.Ch.degree. A. Basic information: Title: Histology Code: 212 هـ س Credit hours: including the following: Lectures: 28 lectures (56 hours; 2hours/week, for 28 weeks) Practical: total of 60 hours (2hours/week for 30 weeks). B. Professional information (1)Overall aims of course a- To help the student to understand normal structure of different organs and various systems of the human body. b- To shed down alight on the functional significance of different histological parts within the system and organ. c- To make it easy for the student to differentiate between normal and abnormal histological findings preparing him for the study of histopathology in the 3 rd year. (2)Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs) a- Knowledge and understanding: By the end of the course, the student should be able to:1- Describe the normal histological structure of various systems and organs. 2- Describe various levels of sections in the spinal cord and brain stem. 3- Describe both cerebrum and cerebellum with its connections. b- Intellectual skills By the end of the course the student should be able to:1- Correlate between histological structure and function of different organs and systems 2- Define the part of the body from which the section is taken. 3- Diagnose slides different from those seen during the course but of the same organs and systems previously studied. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 21 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications c- Professional and practical skills: After completing the course, the student should be able to:1- Enumerate various types of special stains of different organs. 2- Describe ultra-structure of different cells studied in various organs. 3- Differentiate between different organs seen in the same slide. 4- Label diagrams of different levels of in the spinal cord and brain stem. d- General and transferable skills: After completing the course the student should be able to:1. Reach microscopic diagnosis of normal structure and notice any abnormal changes. 2. Work in / with different groups. 3. Give his or her opinion regarding update scientific problems (e.g. transcription). 3-course contents: topic Skin and its appendages Respiratory system Digestive tract Digestive glands Endocrine glands Urinary system Male genital system Female genital system Eye Ear C.N.S Total Lectures 4 4 8 6 6 4 6 4 4 2 8 56 Practical 2 6 10 8 6 4 6 6 4 4 8 64 (4) Teaching and learning methods: 4-1- Lectures: Two hours of lectures per week through the academic year for second year medical students (for 30 weeks). 4-2- Practical sections: Two hours of practical training and demonstration weekly throughout the academic year. The students are divided into 10 groups each is comprised of 40 students; each four students share one microscope. (5) Student assessment methods 1- Written exams.( in the form of short essay and/M.C.Q) to assess 1- Students comprehension and understanding of subjects regularly studied during the course. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 22 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2- Capability of the student for application of the knowledge included in the course. 2- Practical exam. To assess ability of the student for applying information studied in the course in diagnosis and drawing of different microscopic and projector slides. 3- Oral exam. -To assess the student intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge. -To help the teaching staff to evaluate the% of achievement of the intended learning outcome. (6) Assessment schedule: *Assessment 1: regular MCQ exam. Held twice a year in November and March. *Assessment 2: mid-term exam. Week 15. *Assessment 3: End-year exam. (Written, practical and oral) week 27. Weighing of assessment Mid-term exam Final term exam Oral exam Practical exam Semester work Total 30 degrees 75 degrees 15 degrees 15 degrees (5 degrees MCQ Exam +5 degrees practical notebook +5degrees research activities 15 degrees 150 degrees 20% 50% 10% 10% 10% 100% (7) List of references: A- Course notes and handouts . 2- Department book by prof Dr. Saadia Ragab and Prof. Dr. Entesar Ali . 3- Histology part I and part II for medical students by Prof. Dr. Zakaria Abd Al-Hamid. 4- Introduction to functional and clinical histology part I and part II Prf. Dr. Ayman Ghalab . 5- Manual of practical histology by Prof. Dr. Saadia Ragab. B- Recommended textbooks: 1- Basic histology, Junqueira et al, 1998. 2- Bloom and fawcett: Concise Histology. Fawcett, 1999 . 3- Cell biology and histology. Gartner et al, 1998. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 23 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4- Clinical and functional histology for medical students. Snell, 1984. 5- Functional histology: A text and color Atlas, wheather et al., 1997. 6- Cormack D.: A textbook, Ham's Histology 1997. 7- Human Histology, Stevens and Lowe 1997. 8- A text and Atlas of Histology by Leeson and Leeson 1995. C- Periodicals, web sites, Etc. TBD and update during the course work. (7) Facilities required for teaching and learning 1- Laboratories equipped with histological tools. 2- Class rooms for theoretical lectures and tutorials. Course coordinators Prof Dr. Saadia Ragab Sayed. Prof Dr. Entesar Ali Saber. Head of department Prof Dr. Saadia Ragab. Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 24 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications First Year Medical Biochemistry Course Specifications 2010/2011 University: Minia Course Specifications: Date of Approval:18/6/2007 Faculty: Medicine Program(s) on which the course is given: Medical, Dental and Nursery Schools (MBBCh) Major or Minor element of programs: Medical Biochemistry for medical, dental and Nursery students. This course includes Chemistry of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Vitamins, Enzymes, Nucleic acids, Molecular biology and biochemical techniques are also included. Institute offering the program: Faculty of Medicine Department offering the course: Department of Medical Biochemistry Academic Year/Level: First year, First year dental and First year Nursery students. A. Basic Information Title: Medical Biochemistry Code:114 ك ح Credit Hours: TBD Lecture: 76 Tutorial: TBD Practical: 48 Total: 124 B. Professional Information 1. Overall Aims of the Course By the end of the course, the student should be able to: 1-Understand the chemistry of different food continents to prepare the student to understand the metabolic processes taking place in healthy human. 2- Understand the role of vitamins and enzymes in human body and their different clinical applications. 3- Recognize the different molecular techniques and their biochemical applications. 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 25 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications a. Knowledge and Understanding By the end of the course, the student should be able to know the following: 1- Chemistry of carbohydrate, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids 2- Structure and function of different vitamins. Also the student should able to understand the role of enzymes in driving the chemical reactions in the body. 3- How the information in living cells is transferred from DNA to RNA and finally translated to functional proteins. b. Intellectual Skills 1. The course will assist the students to develop the skills for analysis of molecular diseases to reach a final diagnosis. 2. The course will assist the students to develop the ability to solve problems associated with molecular diseases that will be treated in the future by gene therapy. 3- Interpret the information as the results of some used techniques as electrophoresis, TLC and PCR. c: Professional and Practical Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquired during the course into professional applications such as managing a biochemical laboratory, diagnosis of different metabolic and molecular diseases. Also the student should be able to use simple biochemical tests in laboratory diagnosis, apply some techniques as electrophoresis, DNA isolation. d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to 1. Communicate with colleagues and patients regarding a case caused by molecular defects 2. Work in/with different groups. 3. Solve biochemical and molecular problems. 3- Contents a. First year medical students Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 26 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Topic No. of hours Lectures Physical chemistry 2 1 Carbohydrate chemistry 10 5 Lipid chemistry 10 5 Chemistry of amino acids 12 6 Nucleic acids chemistry 6 3 Vitamins 6 3 Enzymes 6 3 Biological membranes 2 1 Molecular biology 22 11 Total 76 38 Note: The course is modified to fit the requirements and first year nursery students. Tutorial/Practical 4 10 8 8 2 2 4 0 10 48 of first year dental 4- Teaching and Learning Methods 1. Three hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year 2. Two hours weekly of practical training and demonstration throughout the academic year. 3. Self learning activities 5- Student Assessment Methods 1. Practical exam to assess the student's ability to identify different methods of identification, detection, determination of different diseases by using biochemical methods. 2. Multiple choice questions (MCQ) to assess the student progress during the academic year (week 8 & 20). 3. Oral examination by the end of year to assess student's intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics,. 4. Written exam (mid term and by end of year) to assess the student's comprehension and understanding of the class work. Weighing of Assessments Mid-Term Examination 20% Final-Term Examination 50% Oral Examination 10% Practical Examination 10% Semester Work/MCQ 10% Other types of assessment 0% Total 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work 6- List of References Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 27 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 1- Department Books and notes: -Course notes, and handouts -Medical biochemistry from other universities such as the books written by Prof. Saeid Oraby, Emad zaki, El-Azhar and Cairo universities 2- Essential Books (Text Books) - Harper's Biochemistry, Robert K.Murray, Daryl K.Granner, PeterA.Mayes, and VictorW. Rodwell (27th edition, 2005) 3- Recommended Books Lubert Stryer, Biochemistry Lehninger, Biochemistry Lippincott, Biochemistry 4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning Biochemistry laboratory equipped with molecular biology tools Class rooms for theoretical lectures Internet rooms Course Coordinator: Dr Salama Rabei Head of Department: Professor Professor Mahmoud Elrehany Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 28 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Second Year Medical Biochemistry Course Specifications 2010/2011 University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Date of Approval:18/6/2007 Program(s) on which the course is given: Second year Medical, First year Dental and First year Nursery Schools (MBBCh) Major or Minor element of programs: Medical Biochemistry for medical, dental and Nursery students. This course includes Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, Heme, purine and pyrimidine and integration of metabolism. The course will include bioenergetics, xenobiotics metabolism, hormones, and minerals. Faculty offering the program: Faculty of Medicine Department offering the course: Department of Medical Biochemistry Academic Year/Level: Second year medical, First year dental and First year Nursery students. Authorization date of course specification: September 2004 A. Basic Information Title: Medical Biochemistry Code:214 ك ح Credit Hours: 5 hours per week Lecture: 3 hours per week Tutorial: 1 hour per week Practical: 1 hour per week Total: 124 B. Professional Information 1. Overall Aims of the Course By the end of the course, the student should be able to: 1-Understand the basic metabolic processes taking place in healthy human and recognize biochemical techniques in order to apply them in analyzing the practical problems in clinical biochemistry. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 29 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2-To understand the biochemical changes that may be acquired in certain diseases and recognize and apply different methods for laboratory diagnosis of different diseases. 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding By the end of the course, the student should be acquitted with the following: 1- Various metabolic processes of carbohydrate, lipid and protein. 2- Role of minerals and hormones in metabolism. 3- The composition of different body fluids; milk, blood CSF, sweat, semen, and urine in health and disease. b. Intellectual Skills 1. The course will assist the students to develop the skills for analysis of different diseases to reach a final diagnosis. 2. The course will assist the students to develop the ability to solve problems associated with metabolic diseases. c: Professional and Practical Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquire during the course into diagnosis of different metabolic and molecular diseases. Also the student should be able to use simple biochemical tests in laboratory diagnosis. d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to 1. Manipulate body fluid samples and reach a biochemical diagnosis of many diseases. 2. Write protocols for identification of a given metabolic disease. 3. Communicate with colleagues and patients regarding a case caused by a metabolic defect 4, Work in/with different groups. 5. Solve biochemical and molecular problems. 3- Contents Topic Bioenergetics Carbohydrate Metabolism Lipid metabolism Metabolism of proteins Purines and pyrimidine metabolism Integration of metabolism No. of hours 4 12 12 16 6 2 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Lectures 2 6 6 8 3 1 Tutorial/Practical 0 8 10 8 4 0 30 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Minerals Hormones Tissue chemistry Xenobiotics Body fluids Total Note: The course is modified to fit the first year nursery students. Cours Specifications 6 6 2 2 8 76 requirements 3 2 3 2 1 0 1 0 4 14 38 48 of first year dental and 4- Teaching and Learning Methods 1. Three hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year 2. Two hours weekly of practical training and demonstration throughout the academic year. 3. Self learning activities 5- Student Assessment Methods 1. Practical exam by the end of year to assess the student's ability to identify different methods of identification, detection, determination of different diseases by using biochemical methods for body fluids analysis. 2. Multiple choice questions (MCQ) to assess the student progress during the academic year (week 8 & 20). 3. Oral examination by the end of year to assess student's intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics,. 4. Written exam (mid term and by end of year) to assess the student's comprehension and understanding of the class work. Weighing of Assessments Mid-Term Examination 20% Final-Term Examination 50% Oral Examination 10% Practical Examination 10% Semester Work/MCQ 10% Other types of assessment 0% Total 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work 6- List of References 1- Department Books and notes: -Course notes, and handouts -Medical biochemistry from other universities such as the books written by Prof. Saeid Oraby, Emad zaki, El-Azhar and Cairo universities Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 31 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2- Essential Books (Text Books) - Harper's Biochemistry, Robert K.Murray, Daryl K.Granner, PeterA.Mayes, and VictorW. Rodwell (27th edition, 2005) 3- Recommended Books Lubert Stryer, Biochemistry Lehninger, Biochemistry Lippincott, Biochemistry 4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning Biochemistry laboratory equipped with molecular biology tools Class rooms for theoretical lectures Internet rooms Course Coordinator: Dr Salama Rabei Head of Department: Professor Mahmoud Elrehany Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 32 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Templates for Course Specifications English language programme Minia University Faculty of Medicine Course specifications Programme(s) on which the course is given: English language programme Major or minor element(s) of programme 1-A thorough study of medical terminology (The components, definitions and pronunciation of technical terms). 2-Medical passages to study with questions involved. 3-Review of English traditional grammar focusing on the different structures of English sentences. 4- A study of English vocabulary: (Synonyms, antonyms, derivations, abbreviations etc…..) 5-Studying a good number of English Idioms and expressions that may enrich the students styles. 6- Essay- writing and passages for translation. 7-Dialogues and conversations. Department offering the programme English department , Faculty of Arts Department offering the course English department, Faculty of Arts Academic year/ Level 2006/ 2007 Date of specification approval A- Basic Information Title: Code: 115 ل ج Credit Hours: Lecture: One hour per week Tutorial: Practical: Total: one lecture per week B- Professional Information 1. Overall aims of course 1-Familiarity with English language, its structures, vocabulary and contexts. 2-Studying English language in a medical context. 3-The students should become acquainted with every day- English (dialogues and conversations). 4-Developing reading, writing, listening and talking skills. 2. Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs) a- Knowledge and understanding: a1- The students are trained to acquire knowledge and information from various sources ( Books, web sites, etc……) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 33 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications a2- Promoting the students abilities to think, collect, understand and summarize data in a way that conforms to the structural rules of English. a3- The students are trained to write essays and pieces of research in an appropriate scientific style. b- Intellectual skills b1-Teaching the students how to discriminate between the different contexts in which words are used. b2- Enhancing the students spontaneity in writing correct English through mastering eh basic structures of the language. b3- Medical students should know well a good number of technical terms in addition to English Idioms and expressions. c- Professional and practical skills c1-Increasing the students abilities to dialogue and hold a conversation in an attempt to improve their spoken English. c2-The students should be aware of the relationship between familiarity with English and success in practical life. c3-The students should gain mastery of the technical terms related to their career. d- General and transferable skills d1- Developing the students abilities to analyse, criticize and give judgments of their own. d2-Students should learn to be accurate in doing research. 3- Contents Topic No. of Hours Lecture Tutorial/Practical 1- Medical terminology: -medical prefixes -medical suffixes 2 or 3 of the -technical and popular terms items -abbreviations mentioned are 2- Grammar and vocabulary: tackled 3- Essay writing weekly 4- Conversations and dialogues 5- Medical passages: -Acupuncture, Alzahaimer’s, tension headaches, doctor patient relationship, insomnia, antibiotics, complying with doctor’s orders …..etc. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 34 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4- Teaching and learning methods 1- Oral discussions through passages to read, translate and comment on; or through essays, already prepared by the students, for discussion. 2-Paragraphs written in class to check the students spontaneity in writing. 3-Language skills and exercises for homework . 4-Written exams. 5- Student assessment methods 1-Questions answered orally by the students to assess their spoken English. 2-Paragraph writing to assess the students written English . 3- Passages for translation to assess the student's ability to translate through context and not literally. 4-Written exams to assess the general standard of the students in mastering the language. Assessment schedule Assessment 1 Week Questions answered orally by the students to assess their spoken English. Assessment 2 week Paragraph writing to assess the students written English. Assessment 3 Week Passages for translation to assess the student's ability to translate through context and not literally. Assessment 4 Week Written exams to assess the general standard of the students in mastering the language Weighting of assessments Mid-term examination % Final-term examination 100 % Oral examination. % Practical examination % Semester work % Other types of assessment % Total 100% Any formative only assessments √ 6- List of references 1. Course notes 2. Essential books (text books) 3. Recommended books 4. Periodicals, Web sites, ... etc √ √ Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 35 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning 1- The students should pay more attention to language course since the majority of them are in different and less enthusiastic in following or attending the lectures . 2- Mid-Term Exam in English language should be reconsidered. It is one of the ways leading the students to take language course more seriously. 3- Two hours per week instead of one hour would be better so that the students may have more time for practicing English and deriving more benefit. 4-English department in the faculty of Arts should continue introducing new courses that go along with the technical developments in the field of medicine. 5- The increasing number of students may stand in the way of achieving aims of language course. Dividing the students into groups is proposed if the faculty of Medicine finds it possible. Course coordinator: Dr. Saadia Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 36 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Pharmacology Course Specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Program(s) on which the course is given: Medical Schools Major or Minor element of programs: Pharmacology for medical and dental students. This course includes the following topics: General Pharmacology, Autonomic Pharmacology, Autacoids, Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Kidney, Respiratory Pharmacology, Blood Pharmacology, CNS Pharmacology, Endocrine Pharmacology, Chemotherapy, Drugs and the Immune System, Chelators and Heavy Metals, Vitamins, Drugs acting on the GIT and Locally Acting Drugs. Department offering the program: Pharmacology Department offering the course: Pharmacology Academic year/Level: Third year medical students. Date of specification approval: To be determined (TBD) A. Basic Information Title: Pharmacology Code: 312 ف ل Credit Hours: TBD Lecture: 120 Tutorial: TBD Practical: 60 Total: 180 B. 1. Professional Information Overall Aims of Course The main activities of the pharmacology course delivered to medical students are: a. To help the medical student to understand the principles of drug actions, establishing enough adequate scientific background when using drugs and to be critical in coping with new drugs in his future practice. b. To impact an essential knowledge base of information about each prototype drug for a better understanding of current practices in medicine and therapeutics. c. To establish a critical attitude and intellectual skill towards the proper choice of drug(s) to treat each particular patient putting into consideration the appropriate route of administration, drug pharmacokinetics, age, sex, associated disease(s), habits, Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 37 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications compliance, socio-economic status, environmental conditions and ethical values. d. To detect the earliest manifestations of side-effects of drugs and to be able to expect, avoid, recognize and treat the possible drug interactions. e. To be aware of the problem of non-medical use of drugs and chemicals (drug abuse) and know how to avoid and manage the abusers. f. To provide the students with proper background to continue his/her own self-education though critical reading and evaluation of drug information in the future, f f. concerning new coming as well as old drugs and to be critical in detecting the suitable drugs for managing the patients. 2. a. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) Knowledge and Understanding: When the student finishes the course, he will be able to achieve the following objectives: 1General pharmacokinetics as well specific properties of different groups of drugs putting into consideration age, sex and genetic related variations that affect the response to drugs (pharmacogenetics), etc. 2General pharmacodynamics as well specific properties of different groups of drugs that include the drug's mechanism of action and pharmacological effects. 3Pharmacotherapeutics which reflects the role of drugs in prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases as well as prevention of conception. It includes also pathophysiology of diseases and drugs, indications, contraindications, adverse reactions and drug interactions especially in high risk groups (extremes of age, pregnancy and lactation, liver kidney and cardiac diseases). Pharmaco-economics is include in this category. b. Intellectual Skills: 1. The course will assist the students to develop the skills in selecting and using drugs safely and efficiently knowing their limits and the potential risks 2. The course will assist the students to develop the ability to solve medical problems arising from use of drugs and the development of resistance or tolerance encouraging them to search for alternative approaches after revising the diagnosis. c. Professional and Practical Skills: After completing the course, the student should be: Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 38 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 1. Able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquired during the course to allow the students to allow this knowledge and to gain attitude in order to manage the individual patients among his community. 2. Able to be a critical learner and prescriber during his/her clinical studies and career. d. General and Transferable Skills: After completing the course, the student should be able to: 1. Acquire the skill of choosing drugs as therapeutic agents. 2. Develop the concept of consideration of the social, economic, environmental and emotional status of the patient and the impact upon the family. 3. Communicate with colleagues and patients regarding drug- or patientrelated problems and try to solve such problems. 4. Work in/with different medical groups. 3. Contents Topic Lectures Laboratory Clinical (in hours) demonstrations (in hours) (in hours) 14 8 1. General Pharmacology 16 8 2 2. Autonomic Pharmacology 4 3. Autacoids 16 20 4. Cardiovascular System 2 5. Kidney 3 4 6. Respiratory System 4 2 7. Blood 16 2 4 8. Central Nervous System 14 4 9. Endocrines 18 10. Chemotherapy 11. Drugs and the Immune System 2 12. Chelators and Heavy Metals 2 2 13.Vitamins 4 4 1. Drugs acting on the GIT 3 2 2. Locally Acting Drugs Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Tutorial Classes (TBD) 39 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4. Teaching and Learning Methods 1. Five hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year. 2. Two hours of practical laboratory demonstrations and pharmacology classes; weekly throughout the academic year. 3. Self-learning activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4. Tutorial classes (TBD) clinical 5. Student Assessment Methods 1. Practical exam to assess the student’s ability to identify and interpret major drug actions in isolated animals or living animals. Also, major clinical applications of such actions as well as side effects are of concern. 2. Mid-term exam to assess the student’s progress during the course. 3. End of year written exam to assess the student’s comprehension and understanding of the class work. 4. Oral exam to assess student’s intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics. Assessment Schedule Assessment 1 MCQ Assessment 2 Mid-term exam Assessment 3 MCQ Assessment 4 End of year exam (Written, practical/clinical and oral exam) Week 10 Week 15 Week 20 Week 27 Weighing of Assessments: May Examination Mid-Term Examination: 60 Marks 20% Final-Term Examination: 150 Marks 50% Oral Examination 30 Marks 10% Practical Examination 30 Marks 10% Semester Work/MCQ 30 Marks 10% Other types of assessment 0% Total 300 Marks 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work. September Examination Written Examination: Oral Examination Practical Examination Total 170 Marks 56.7% 60 Marks 20.0% 70 Marks 23.3% 300 Marks 100% Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 40 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6. List of References 1. Department Books and Notes: a. Course notes and handouts by staff members of the department. b. Practical and Clinical Pharmacology Notes by staff members of the department. c. Spotlights on Pharmacology edited by F. Osman, A.-E. Elkoussi, A. A. Gomaa and H.I. El-Bitar. d. Hawary Khayyal Zarif "Handbook of Pharmacology" edited by M.T. Khayyal and Z. Isaak. e. Principles of Pharmacology and Therapeutics. edited by A. Bastawy and A. El-Melegy. f. Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews "Pharmacology", series editors R.A. Harvey and P.C. Champe, edited by M.J. Mycek, R.A. Harvey and P.C. Champe, 2nd ed. (1997), Lippincott-Raven (Publ.) 2. Essential Books (Text Books) a. Pharmacology edited by H.P. Rang, M.M. Dale and J.M. Ritter, 4th ed. (2000), Churchill Livingstone (Publ.), International edition. b. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology edited by B.G. Katzung, 8 th ed. (2001), Appleton & Lange (Publ.), Middle East Edition. c. Clinical Pharmacology edited by P.N. Bennett and M.J. Brown, 9 th ed. (2003), Churchill Livingstone. 3. Recommended Books a. Goodman & Gillman's "The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics", edited by J.G. Hardman, L.E. Limbird and A.G. Gilman, 10 th ed. (2001), McGraw-Hill (Publ.), International Edition. b. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach edited by J.T. Dipiro, 5th ed. (2002), McGraw Hill (Medical Publishing Division). c. Therapeutic Drugs edited by C. Dollery, 2 nd ed., (1999). Churchill Livingstone. 4. Periodicals, Web Sites, etc. TBD and updated during the course work Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 41 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 7. Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning Pharmacology laboratories equipped with pharmacological tools. Class rooms for theoretical lectures and tutorials. Course Coordinator: Dr. Mohamed Aly Morsy Head of Department: Prof.Dr. Aly Mohamed Omar Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 42 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Pathology Course Specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Programme(s), on which the course in given: 3rd year medical students. Major or minor element of programme(s): Pathology for medical students. This course includes general and systemic pathology. Faculty offering the program: Faculty of Medicine. Department offering the course: Pathology department. Academic year/level: Third year of M.B.B.Ch. degree. Date of specification approval: A. Basic Information Title: Pathology Code: 311 ب ث Credit Hours: Lectures: 65 lectures (116 hours; 4 hours/ week, for 29 weeks) Practical: Total of 86 hrs (4 hours/ week, for 21.5 weeks) Tutorial: Not applicable Total: 202 hours B. Professional information 4. OVERALL AIMS OF COURSE By the end of the course the student should be able to: Recognize the basic facts, concepts, theories and terms in the field of pathology as well as understanding the underlying pathologic bases of structural and functional changes of the body during various diseases and their underlying mechanisms within specific organs so as to develop the capacity to recognize, define, analyze and solve problems later on in medical practice. 5. INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES OF COURSE (ILOS) a. Knowledge and understanding: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. Define, recognize and discuss the pathologic basis of diseases principally: etiology (especially those related to the environment), pathogenesis, pathological changes and natural history with Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 43 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications emphasis on the incidence and identification of risk factors for proper preventive measures. 2. Recognize, identify and describe the morphological changes (gross and microscopic) that occur in different diseases as a result of such diseases processes in various organs. 3. Recognize and indicate the clinical manifestations, fate and complications of common and important diseases for later on developing a plan for general management procedures. b. Intellectual skills: The course will assist the students to: B.1. Differentiate between pathological features (gross and microscopic) of different diseases and develop the skills for analysis of different cases. B.2. Interpret the gross and microscopic findings with those of clinical manifestations for a proper diagnosis. B.3. Define, analyze and solve problems related to different diseases. c. Professional and practical skills: After completing the course the students should be able to: C.1. Examine slides using electric microscopes, and take precautions during handling of slides and samples C.2. Recognize, observe and describe gross and microscopic pathological pictures of different diseases and interpretation of this information to reach accurate diagnosis as well as interpreting pathology reports. C.3. Develop the skills to choose the most appropriate diagnostic techniques. d. General and transferable skills: Students are given opportunities to develop skills to: D.1. Recognize new recent techniques for early detection of different diseases and malignancies. D.2. Search the literature and internet and collect, analyze, critically appraise and present the obtained information either in oral presentation, written form or in posters. D.3. Communicate with colleagues and staff members and work within groups. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 44 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4. CONTENTS Topic Total Lecture Hours I. GENERAL PATHOLOGY 3. Introduction & Inflammation 7 3 4. Repair 3 2 5. Cell injury and cell death 5 3 6. Circulatory disturbances 5 3 7. Immunopathology 2 1 8. Acute bacterial infection 3 2 9. Granulomas 5 3 10. Viral infection 2 3 11. Mycotic diseases 1 3 12. Parasitic infestation 5 3 13. Disturbances of cell growth and adaptation 2 14. Neoplasia 10 15. Environmental and nutritional diseases & 2 ionizing radiation Total 52 hrs II. SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY 1. Cardiovascular & blood vessels 8 2. Respiratory system 8 3. GIT 8 4. Disease of liver and Biliary tract 4 5. Diseases of exocrine pancrease and 1 peritoneum 6. Diseases of the kidney 5 7. Diseases of urinary bladder and ureter 2 8. Diseases of female genital system 5 9. Diseases of male genital system 2 10.Diseases of female breast 2 11.Endocrine diseases 4 12.Diseases of musculoskeletal system 6 13.Blood diseases 3 14.Diseases of lymph nodes and spleen 3 15.Diseases of nervous system 5 Total 64 hrs Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Practical 4 2 4 4 4 4 1 5 1 2 12 - 29 36 hrs 4 4 4 2 1 4 4 4 4 - 3 1 3 1 1 2 3 2 2 3 36 4 2 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 50 hrs 45 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4. TEACHING AND LEARNING METHODS 4.1. Lectures 4 hours weekly. 4.2. Practical training and demonstration for small groups, 4 hours weekly. 4.3. Self learning activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4.4. Tutorial classes (Not applicable) 5. STUDENTS ASSESSMENTS METHODS 5.1. Written exam to assess the student’s comprehension, understanding and problem solving, in the form of short essay questions and /or MCQ. 5.2. Practical exam to assess the student’s professional skills regarding ability of applying information in the course of pathology for diagnosis of microscopic slides and jars. 5.3. Oral exam to assess student’s knowledge, understanding and intellectual skills as well as assessing the verbal communication abilities. Assessment Schedule: Assessment 1: Written exam/MCQ week (TBD)* Assessment 2: Mid-term written exam week 15 Assessment 3: Written /MCQ/Practical exam week (TBD)* Assessment 4: End of year exam (written, practical & oral exams) week 30 *TBD: To be determined before the beginning of the course after approval by the department council and according to the internal regulations within the faculty. Weighting of assessment: Mid- term written Exam 20% (60 marks) Final- term written exam 26.7% (80 marks) Practical exam 33.3% (100 marks) Oral exam 20% (60 marks) Periodic exams 20 marks (deduced from the practical exam) ………………………………………………………………………… Total 100% (300 marks) Any formative only assessment (Not applicable) 6. LIST OF REFERENCES 6.1. General and systemic pathology course notes 6.2. Essential books (Text Books): Robbins Basic Pathology,7th edition, 2002. 6.3. Recommended books: Atlas of histopathology Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 46 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6.4. Periodicals, Web sites: American Journal of pathology The Journal of pathology Histopathology www.pubmed.com www.pathmax.com 7. FACILITIES REQUIRED FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING Pathology laboratories equipped with electric microscopes and sets of teaching slides' boxes and another laboratory contains all requirements for preparing and staining such slides. Museum equipped with cupboards containing the preserved specimens in formalin inside glass jars. Classrooms with data show, slide projector and overhead projector for lectures and/or practical classes. Course Coordinator: Dr. Dalia Abd-Elrehim Head of department: Prof Dr. Reda Fekry Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 47 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Medical Microbiology Course Specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Program(s) on which the course in given: Medical and Dental Schools Major or Minor element of programs: Medical Microbiology and Immunology for medical and dental students. This course includes General and systematic Bacteriology, Immunology, Virology, Mycology Applied Microbiology and Nosocomial Infection. Department offering the program: Microbiology and Immunology Department offering the course: Microbiology and Immunology Academic year/Level: Third year medical and second year dental students. Date of specification approval: / / A. Basic Information Title: Medical Microbiology Code: 313 م ك Credit Hours: TBD Lecture: 78 Tutorial: TBD Practical: 42 Total: 120 B. Professional Information. 1. Overall Aims of Course By the end of the course, the student should be able to: 1. Know the different types of pathogens, their structure and pathogenesis. 2. Know the different methods for laboratory diagnosis and control of different infectious agents. 3. Know the different molecular microbiological techniques and their applications. 4. Know the basics of the host-parasite relationships and the role of the immune system in defending the body against different pathogens and its role in health and disease. 5. Know the principles of biosafety measures and aseptic precautions. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 48 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding: By the end of the course, the student should be able to: A. General Microbiology: 1. Know microbial morphology, structure, metabolism and physiology of medically significant microorganisms. 2. Understand the basis of microbial genetics and biotechnology techniques and their applications. 3. Know different methods for in vivo and in vitro control of different microorganisms. B. Systematic Bacteriology, Virology and Mycology: 1. Recognize the taxonomy and classification of different microorganisms. 2. Identify the natural habitat, source of infection and mode of transmission of the different classes of pathogens. 3. Know the different laboratory methods for identification of different infectious agents and acquire the skills for their performance. 4. Know the different methods for treatment, prophylaxis and control measures of the common infectious agents. C. Immunology: 1. Identify the different levels of host-parasite relationship and recognize the microbial virulence factors. 2. Know the natural barriers for infection (innate immunity) 3. Understand the structure and functions of different components of the immune system. 4. Know the role of the immune system in the health and disease of the human being. 5. Know the different methods for assessment of the immune response. 6. Understand the different methods of immunemodulation and their applications. D. Applied Microbiology and Nosocomiology: 1. Know the basis of nosocomiology practice. 2. Know the different methods for infection control 3. Know the principles of biosafety measures and aseptic precautions in Clinics and Hospitals. b. Intellectual Skills b1. The course will assist the students to develop the skills for analysis of different cases of infection to reach a final diagnosis and microbiological identification of the causative organism b2. The course will assist the students to develop the ability to solve problems associated with different infections such as microbial resistance to antimicrobial agents, reach a final diagnosis of a certain pathological condition caused by an infectious organism. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 49 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications c. Professional and Practical Skills c1. After completing the course, the student should be able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquired during the course into professional applications such as managing a microbiology laboratory. d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to d1. Manipulate microbiological samples and reach a microbiological diagnosis of an infection. d2. Write protocols for identification of a given microorganism. d3. Communicate with colleagues and patients regarding a case caused by a microorganism. d4. Work in/with different groups. d5. Solve microbiological problems. d6. Manage a microbiological laboratory. 3- Contents Topic General Bacteriology Immunology Systematic Bacteriology Virology Mycology Nosocomial infection Applied Microbiology No. of hours 24 18 48 16 8 3 3 Lecture Tutorial/Practical 12 14 26 14 6 3 3 12 4 22 2 2 0 0 4- Teaching and Learning Methods 4.1.Three Hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year 4.2. Two hours of practical training and demonstration; weekly throughout the academic year. 4.3. Self-learning activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 5- Student Assessment Methods 5.1 Practical exam to assess the student’s ability to identify different infectious pathogen and manage a Microbiology laboratory. 5.2 Mid-term exam to assess the student’s progress during the course. 5.3 End of year written exam to assess the student’s comprehension and understanding of the class work. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 50 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 5.4 Oral exam to assess student’s intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics. Assessment Schedule Assessment 1 MCQ Week 10 Assessment 2 Mid-term exam Week 15 Assessment 3 MCQ Week 20 Assessment 4 End of year exam (written, practical and oral exam) Week 27 Weighing of Assessments: Mid-Term Examination: Final-Term Examination: Oral Examination Practical Examination Semester Work/MCQ Other types of assessment Total 15% 50% 15% 15% 5% 0% 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work. 6- List of References 6.1.Department Books, and notes: Course notes, and handouts. Department book(s) by Dr Abdel-Ghafar Farid et al. Medical Microbiology and Immunology by Samira Shoeb, Cairo University. Medical Microbiology and Immunology by Abla El-Mishad, Cairo University. Manual of practical Microbiolgy by Abala El-Mishad, Cairo University. 6.2- Essential Books (Text Books) Jawetz E. et al., Medical Microbiology, 22nd edition, Appleton and Lange, 2001. Immunobiology by Janeway C. and Travers, P. et al., 2003; Garland Publishing Inc. NY, London. 6.3- Recommended Books Madell, G. et al., Manual of clinical Microbiology, 7th ed. ASM, 1999. Essential Immunology By Roitt, I., 1997. Blackwell Scientific publishing; Oxford. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 51 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Topley and Wilson, Microbiolgy and microbial infections, 9th ed. Arnold, 1998. 6.4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc TBD and updated during the course work 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning Microbiology laboratory equipped with microbiological tools Class rooms for theoretical lectures Course Coordinator: Dr Sayed F. Abdelwahab Head of Department: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Adel-Hamid Ahmed Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 52 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Ophthalmology course specifications University: El-Minya Faculty: Medicine Department offering the course: Ophthalmology Department Academic year: fourth year of M.B.B.Ch Title: Ophthalmology Credit Hours: Tutorial: 39 Hours A-Basic Information Code: 411 ج ع Lectures: 64 Hours Practical: 78 Hour Total: 117 Hours B- professional Information 1- Overall aims of the course By the end of the course the student should has: 1) knowledge about common ophthalmic diseases 2) skills of dealing with ophthalmic emergencies 3) capability of referring to higher level of specifications 4) transferable skills of basic ophthalmic care and preventive measures to community 5) integration of progress in ophthalmic knowledge and ability of self education 2-Intended learning outcome of course (ILOS) a) Knowledge and understanding: a1) to identify manifestation of common ocular disorders a2) to recognize the ocular manifestations of the systemic disease a3) to define the main therapeutic lines of ophthalmic health care b) Intellectual skills: b1) to interpret the most important ophthalmic symptoms and signs b2) to interpret the basic investigations related to ophthalmic disease b3) to solve simple ophthalmic clinical problems c) Professional and practical skills: c1) to practice basic ophthalmic examination c2) to provide first aids in ophthalmic emergencies d) General and transferable skills d1) to perform general medical examination d2) transfer skills of ophthalmic care and preventive measures Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 53 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 3- Course contents: Topic Anatomy and physiology of the eye Eye lids Lacrimal system Conjunctiva & sclera Cornea Uvea Lens and cataract Glaucoma Orbit Errors of refraction Strabismus Retina and vitreous Optic nerve & neuro ophthalmology Eye injuries Tumors The eye and systemic diseases The eye and drugs Laser in ophthalmology Revision No. of Hours 3 12 6 15 12 12 12 12 9 12 15 18 6 6 6 6 3 3 13 Lectures 1 4 2 5 4 4 4 4 3 4 5 6 2 2 2 2 1 1 8 Tutorial/ practical 2 8 4 10 8 8 8 8 6 8 10 12 4 4 4 4 2 2 5 4- teaching and learning methods 4.1) data-show presentations 4.2) clinical rounds 4.3) video presentations 4.4) out patients clinics 5.5) small groups attending ophthalmic operative theatre 5- Student assessment methods 5.1) written exams to assess knowledge and understanding of subjects 5.2) MCQ exams to assess knowledge, interpretation and criticism 5.3) oral exams to assess communication abilities and judgement 5.4) clinical exams to assess clinical skills and ability to solve clinical problems Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 54 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Assessment schedule Clinical exams held 5 times / year once for each group Mid-term MCQ exam Final exams at the end of academic year Formative oral exams for each group at the end of clinical round and formative MCQ exam before the mid term exam Weighting of assessments Total score 250 marks Periodic clinical exams 10 marks Midterm MCQ exam 40 marks Final exam: written exam 100 marks Oral exam 50 marks Clinical exam 50 marks 6- List of references 6.1 El-Minya ophthalmology department notes 6.2 El-Refai ophthalmology book 6.3 American academy series 6.4 kanski clinical ophthalmology 6.5 periodics: British journal of ophthalmology Ophthalmology 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning Desktops, laptops data- show systems and model for clinical rounds and tutorials Course coordinator: Dr. Ahmed ElShafei Head of department: Prof Dr. Rabie Hasanin Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 55 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Ear, nose and throat "E.N.T" Course Specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Date of approval: 18/6/2007 Program(s) on which the course in given: Medical Schools Major or Minor element of programs: Ear, nose and throat disease for medical student. This course include anatomy, physiology and diseases of the ear, the nose and paranasal sinuses , the month and pharynx. Department offering the program: Ear, Nose, throat, phoniatrics and audiology department. Department offering the course: Ear, Nose, throat, phoniatrics and audiology department. Academic year/Level: Fourth year medical students. A. Basic Information Title: Oto-rhino-laryngology . Code: 412 ن ذ Credit Hours: TBD Lecture: 60 hours Clinical rounds: 60 hours Total: 120 hours B. Professional Information. 1. Overall Aims of Course The main objective for the E.N.T theoretical and clinical training course delivered to the fourth year medical student is that by the end of that cour vbse the student should be familial with : a. Emergencies in E.N.T and their first aid treatment which may be life saving in several conditions. These emergencies are: I. Airway obstruction. II. Inspired or ingested foreign bodies. III. Epistaxis. IV. Laryngial and tracheal trauma. V. Facial trauma. b. The main causes of sore throat, dysphagia, deafness, hoarseness of voice stridor, nasal obstruction, headache and other problems which encounter a Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 56 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications general practitioner in children and in adults and the recent methods of diagnosis and proper treatment of such common disease. c. Complete ear exam including pure tone audiometry and tympanometry. d. Although exposure to the operating room is not emphasized, it would be very useful for the students to observe common procedures. Fourth year medical student should understand: a. The basic anatomy and physiology of the ear, nose, pharynx, larynx, esophagus and trachea. b. The management of simple cases. c. The idea of management of major cases. d. The relationship between some general symptoms or illness and E.N.T disease, and the interaction between E.N.T an other specialities and vice verse. 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding: By the end of theoretical and clinical course, the fourth year medical student should know and understand: Anatomy of external, middle and internal ear; physiology of hearing and equilibrium, disease of the external ear, disease of the middle ear, disease of the inner ear, types of hearing loss in adults and children, management of deafness, symptoms and signs of ear diseases, principles of some operations. Nose and paranasal sinuses: anatomy, physiology, examination, and investigations, symptoms and signs of nasal disease, principles of some operations on the nose and paranasal sinuses. Anatomy, examination and investigations of mouth and pharynx, diseases of the nasopharynx, diseases of the oropharynx, diseases of the hypopharynx, tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Anatomy, physiology, examination, investigations, including of the larynx, diseases of the larynx, symptoms of laryngeal diseases, principles of some laryngeal operations, principles of Phoniatrics. Anatomy, physiology, investigations of he oesophagus, dysphagia, anatomy, physiology, examination, of the investigations Anatomy, physiology, investigations of Trochea and tracheostom. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 57 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications b. Intellectual Skills To ensure that all medical school graduates have a firm grasp of the basic principles related to the speciality. To provide sufficient exposure to the speicality to assist in informed career planning. Ability for application of information. Skills which can be applied practically. c. Professional and Practical Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to apply and adopt the basic knowledge acquired during the course and clinical rounds into professional applications such as diagnosis and first aid management of the most common ear, nose and throat problems. d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to 1. Take an adequate history of the illness from the patient. 2. Perform a basic head and neck examination with equipment available. 3. Know the useful investigations. 4. Diagnose simple cases. 5. Suspect complications. 3- Contents Topic Ear ( include audiology ) Nose and paranasal sinuses Larynx and trachea (include Phoniatrics) Pharynx and Oesophagus No. of hours 30 30 30 30 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Lecture 15 15 15 15 Clinical Rounds 15 15 15 15 58 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 4- Teaching and Learning Methods 4.1.Two Hours of lectures per week throughout the academic year medical students . 4.2. Students must attend at least 60 hours clinical training for 40 continuous days including clinical E.N.T round, outpatient, audiology room, phoniatric department and operative attendance. 4.3. Self training and activities such as use of internet and multimedia. 4.4. Tutorial classes . 4. 5. Group discussion. 5- Student assessment methods: 5.1- End-term the exam to assess the student's progress during the course. 5.2- End of year written exam to assess the student's comprehension and understanding of the class work. 5.3- Oral exam to assess students intellectual and communications abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding the course topics. 5.4- Practical exam including identification of instruments, slides and videotapes to assess the student's ability to identify different E.N.T problem. Assessment Schedule : Assessment 1 : End-term exam at the end of clinical round. Assessment 2 : End of year exam. "Written, practical and oral exams" at the end of the year. Weighing of Assessments: End-term exam: 20 % Oral exam: 20 % Practical exam: 10 % End year exam: 50 % Other types of assessment: 0% Total 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work. 6- List of References 6.1- Student Books and Notes : Course notes, and handouts. Department book(s) otolaryngology-the essentials by Allen M, Thomas A, Robin T 4. Synopsis of otolaryngology 5. El shenawy manual of otolaryngology Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 59 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Recommended Books (Text Books) Otolaryngolgy-Head and Neck Surgery by: Cumming W.C. et al. Diseases of the Nose, Throat and Ear by: Birrell J.F. 6.3- Periodicals, Web sites, ….. Etc TBD and updated during the course work . 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning Class rooms for theoretical lecture and tutorials . Outpatient (E.N.T clinic). Outpatient (Audiology clinic). Outpatient (Phoniatrics clinic). E.N.T operative room including microscopic surgery of Ear and Nose. Course Coordinator: Prof. Dr. Abd Elrahim Ahmed Abd El Karim(MD) Head of Department: Prof. Dr. Adel Abd Elbaki Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 60 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Appendix D1 Course Specifications Forensic Medicine & Clinical Toxicology University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course specifications: Date of approval: 18/6/2007 Programme on which the course is given: M.B.B.Ch. Major element of programmes: Forensic Medicine& Clinical Toxicology. Department offering the programme: Forensic Medicine & Toxicology Dept. Department offering the course: Forensic Medicine & Toxicology Department. Academic year/ Level: 4th year. Date of specification approval: 18/6/2007. A- Basic Information Title: Forensic medicine & Toxicology. Code: 413 ط ش Credit Hours: Lecture: 80 hr. Tutorial: 26hr. Practical: 38hr. Total: 144hr. B- Professional Information 1- Overall aims of course:at the end of the course the student will be able to 1- Provide basic knowledge of medical ethics and malpractice. 2- Provide basic background of different medicolegal aspects of living and dead individuals. 3- Provide ability to diagnose and treat intoxicated patients. 2-Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs): a-Knowledge and understanding: a1-Explain various medicolegal aspects of malpractice &ethics. a2-How to apply his/her medical knowledge in the service of law with emphasis on medicolegal aspects of medical practice. a3-Explain medicolegal aspects of blood grouping and DNA in forensic field. a4-Explain medicolegal aspects of different cases of sexual offences. a5-Explain maternal and infant morbidity and mortality from medicolegal aspects. a6-List different classes of common toxic substances and environmental pollution and how eliminate toxin from body. a7-Explain different groups of toxic substances and drugs and its differential diagnosis and how to do first aid measurements for each one. b-Intellectual skills: b1-Analyze different problems of malpractices. b2-Analyze different traumatic/ wound cases and how to write a report for each case and how to deal with it. b3-Analyze different intoxicated patients and formulate a treatment plan. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 61 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications b4-Recognize common ethical dilemma and suggest a proper solution. c- Professional and practical skills: c1-Identify living and dead individuals. c2-Diagnose death by different clinical and investigatory methods. c3-Estimate time pass since death through assessment of P.M.changes. c4-Identify different mechanisms and manners of death. c5-Examine different wounds and injuries and write a proper primary report. c6-Make a preliminary tests for blood grouping and toxicological screen. d- General and transferable skills: d1-Know when and how to ask for senior consultation. d2-Achieve informed consent from the patient or the patient's surrogate for the treatment plan. 3-Contents: I. Forensic medicine: TOPIC 1. Identification (of living and deceased. 2. Death (Manner of death aspects of brain death, death under anesthesia, estimation of postmortem interval) 3. ML. Aspects of sudden death. 4. ML aspects of wounds (Firearm injuries, head injuries, thermal injuries, injuries of other parts of the body, transpor-tation injuries) 5.Paternity investigations 6. ML aspects of child abuse and domestic violence (ML Conflict) 7. DNA Evidence 8. Sexual Offences 9. ML aspects of abortion 10.ML aspects of pregnancy and delivery 11.Violent Asphyxia 12.ML aspects of suspected death in childhood 13.Medical Ethics 14.Malpractice Total No. Of Hours Total Lectures Practical 9 11 4 6 5 (Museum & Morgue) 5 (Museum & Morgue) 2 16 1 8 1 (Morgue) 8 (Museum & Causality Department) 5 7 2 3 3 (Lab.) 4 (Museum & Morgue) 3 4 4 3 4 4 6 6 84 1 2 2 1 2 2 3 3 40 2 (Lab.) 2 (Museum) 2 (Museum) 2 (Museum) 2 (Museum) 2 (Museum & Morgue) 3 (case studies) 3 (case studies) 44 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 62 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications II. Toxicology: TOPIC 1.Classification of poisons 2.Toxicokinetics 3.Focused clinical examination of a poisoned patient 4. Management of an intoxicated patient 5.Household intoxications (Corrosives, insecticides, bleaching substances) 6.Medical Toxicology (CNS depressants and stimulantsanalgesics-antipyretics-opioidsanticholinergic and cardiovascular drugs) 7.Inhalants (Co, Co2, Cyanide) 8.Volatile poisons (Ethyl and methyl alcohol and kerosene) 9.Substances of abuse 10.Metals Total Total 4 2 8 No. Of Hours Lectures Practical 4 2 4 4(Models & Case studies) 8 4 4(Models & Case studies) 6 4 2( Lab.& case studies) 12 8 4 (Lab. & case studies) 6 6 4 4 2 (Lab.&case studies) 2(Lab.&case studies) 4 4 60 2 4 40 2(Lab.&case studies) 20 4-Teaching and learning methods: 4.1-Lectures 4.2-Small group discussions using role play, models, demonstration(slides and photographs, museum specimens and video films), case study 4.3-Clinical visit to Minia university hospital morgue. 4.4-Clinical visit to Causality department. 5-Student assessment methods: 5.1-Written exams (essay-short questions- MCQ-true and false questions & problem solving) to assess 2a, 2c, 2d. 5.2-Practical exams to assess 2b. 5.3-Oral exam to assess 2a, 2c. 5.4-Log book and researches for some subjects to assess 2b. Assessment schedule: Assessment 1 MCQ 10th Week. Assessment 2 True and false questions 15th Week. Assessment 3 Mid year written exam 25th Week. Assessment 4 Final exam (essay) 36th Week. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 63 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Weighting of assessments: Mid year examination Final- term examination Oral examination Semester work 20% 50% 10% 10% (the percent is taken from the exams of 10th, 15th weeks). Other types of assessment (scientific activities and attendances) 10% Total 100% Formative assessments (twice per year, one in each term). 6-List of references: 6.1-Course notes: Prof. Dr. Aly Hussein books. 6.2- Essential books (text books): -Keith Simpson Forensic medicine. -Haddad Clinical Management of poisoning & drug overdose. 6.3-Recommended books: -Forensic Medicine Encyclopedia. -Principles of Clinical Toxicology. 6.4-Periodicals, Web sites,...etc: -Journal of Forensic Science. 7-Facilities required for teaching and learning: -Dept. Laboratory. –Dept. Museum. -Clinical Tox. Unit in university hospital. -Hospital lectures hall. -Causality Dept. -Minia university hospital morgue. Course Coordinator: Dr.Ahmed Hefnawy Head of department: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Abd Elmohsen Date : 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 64 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Public Health and Community Medicine Course Specifications NOT UP TO DATE! University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: 1- Program(s) on which the course in given: Medical School 2- Major or Minor element of programs: The course of public health and community medicine introduces the student to the field of epidemiology, environmental health and the basic principles of nutrition. 3 - Department offering the program: Public Health 4- Department offering the course: Public Health 5- Academic year/Level: Third year medical students. 6- Date of specification approval: 18 / 6 / 2007 A. Basic Information Title: General Epidemiology & Environmental Sanitation and Nutrition. Code: PHCM3 (suggested) Credit Hours: ( Not applicable yet) Total teaching hours: 96 hours Lecture: 1 hr/week = 32 hours. Practical: 2 hr/week = 64 hours B. Professional Information. 1. Overall Aims of Course The graduate will be responsible for preventing and controlling diseases through community-based prevention strategies, including environmental sanitation, immunization programs and nutritional interventions. 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding: By the end of the course, Students will be able to: 1-List the basic principles of epidemiology of infectious diseases and infectious process and preventive and control measures of communicable diseases. 2-Determine the principles of basic nutrition; diet planning and nutritional problems. 3-Recall sources of environmental risks and methods of its assessment and measures used to prevent and control these risks. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 65 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications b. Intellectual Skills By the end of this course, the student will be able to: 1-Discuss determinants of diseases and the interacting ecological factorsaffecting the occurrence of disease 2-Design public health surveillance system and types of epidemiological studies and describe the study design, uses, and limitations. 3-Identify the nature, health effects, sources, methods for monitoring and controlling of environmental risks 4-Plan diets for normal individuals throughout the life cycle, especially the vulnerable groups 5-Analyze diet to its nutrients using food composition tables 6-Assess malnutrition problems. c. Professional and Practical Skills By the end of this course, the student will be able to: 1-Perform public health surveillance system. 2-Apply epidemiologic measures used for prevention and control of communicable diseases 3- Monitor the quality of drinking water 4-Calculate nutritional requirements and compare it with the real intake 5-Prescribe diet plans for selected disease conditions (therapeutic diets) d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to: 1-Identify prevalent health problems in a community, using various epidemiological strategies. 2-Anticipate and participate in investigation of an epidemic/outbreak as part of a health team. 3-Participate in vaccination campaigns and control activities/mass treatments as required 4-Participate in conducting public health surveillance. 5-Anticipate, assess and advice on management of environmental health hazards in various settings 6-Communicate with relevant authorities for environmental control. 7-Describe diets for normal individuals throughout the life cycle, especially the vulnerable groups 8-Anticipate malnutrition problems by the assessment of nutritional status. 9-Prescribe diet plans for selected disease conditions Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 66 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University 3- Contents TOPICS N0.Of Hours 30 General Epidemiology of Diseases 18 Environmental Health 48 Nutrition 96 TOTAL HOURS Cours Specifications Lecture 10 6 16 32 Tutorial/Practical 20 12 32 64 Detailed Contents of the course Contents of General Epidemiology & Environmental Sanitation Concepts of health and disease Dimensions of health Positive health Concept of well – being Man and disease The origin of health problem in the community General epidemiology of infectious diseases Carriers and subclinical transmission Mode of transmission Zoonosis Ecology of diseases Epidemiology of infectious diseases Epidemiological studies Control of contacts Diagnosis of infectious diseases Disinfection and sterilization Screening Environmental health Environmental sanitation Nature of environmental pollutants Chemical Air pollution Biological pollutants Noise Water sanitation Collection and disposal of wastes Hospital Waste Food sanitation Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 67 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Contents of Nutrition Course Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Fats Energy Fat soluble vitamins Water soluble vitamins Minerals Calcium Iodine Iron Fluorine Phoshorus Pattern of egyptian diet Assessment of nutrional status Feeding of vulnerable groups Malnutrition Protein energy malnutrion (pem) Osteoprosis Antioxidants Dietitics 4- Teaching and Learning Methods IV-A: Methods used: Lectures Practical sessions Self learning. Field visit IV-B: Teaching plan: 1. One hour lecture / week throughout the academic year (32 Weeks/y) 2. Two hours of practical training and demonstration / week including just one field visit to water purification station throughout the academic year. Classroom Teaching 1. Interactive presentations (lectures with discussion) 2. Brainstorming 3. Case studies 4. Demonstrations Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 68 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Practical and field visits Students work together in small groups, observe or participate in role plays, perform practical simulations and practice skills with anatomic models. Field practice sites include field visits to water purification station within the community. 5- Student Assessment Methods A: Attendance criteria The minimum acceptable attendance is 75% .Students who fail to attend the required stated percentage will not be allowed to take the exam B: Assessment Tools: Tool Mid-term exam Practical exam 1 Practical exam 2 End of year written exam Purpose to assess the student’s progress during the course to assess the student’s ability to apply different topics of the course to assess the student’s ability to apply different topics of the course to assess the student’s comprehension and understanding of the class work C-Assessment Schedule Practical exam 1 Assessment 1 Mid-term exam Practical exam 2 Assessment 2 End of year exam D-Weighing of Assessments: Mid-Term Examination: 40% Practical Examination 10% Total 50% ========================== Final-Term Examination: 40% Practical Examination 10% ============================= Total 50% Week 10 Week 16 Week 26 Week 32 20 5 25 (to be added to 4th year grade) 20 5 25 (to be added to 5th year grade) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 69 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6- List of References 6.1. Department Books, and notes: 1-Community Medicine for Medical Students “General Epidemiology & Environmental sanitation" and “Nutrition" books. Editor: Staff members of Community Medicine Dept. EI-Minia, Egypt. 2006. 2- Practical book "Log book" to record and assess skills learnt during practical cessions 6.2- Essential Books (Text Books) MAXCY - ROSENAU PUBLIC HEALTH AND PREVENTIVE MEDICINE TWELFITH EDITION, JOHN M. LAST, (EDITOR), APPLETON- CENTURYCROFTS/NORWALK, CONNECTICUT. USA. 6.3- Recommended Books BSC NSI SS BSNN COBOCIO MO OO O OC NOC - OCNON . COCOC OMO SN ,SOS OOC OMO OSC ONOBOC CIOB ROOI R O SBOO OSC SOS OOC R NOO , C F 1015 FO ROCC SC, MB 20005 6.4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc International journal of Epidemiology Journal of Egyptian Association of community Medicine Journal of Egyptian Association of Occupational Medicine http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/Pub-Occup-Health/?yguid=121150878 (web site of the department) www.who.org, www.cdc.gov , www.mohp.gov.eg , www.aafp.org 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning 1- Lecture halls. 2- Public Health and Community Medicine skill lab. 3- Class rooms for theoretical lectures and practical cessions. 4- Equipment: a) Computers b) Data show. c) Overhead Projectors d) Buses ( provided by University for field visits) Course Coordinator: Dr. Emad Gergis, PhD Head of Department: Professor Dr. Refaat Raouf Sadek, MD Date: / / 2007 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 70 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Public Health and Community Medicine Course Specification University: El-Minia Course Title: EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SELECTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Faculty: Medicine COMMUNICABLE ANDNON- 4th year of M.B. & B.Ch. Program 2006-2007 Allocated marks: 100 marks Course duration: about 30 weeks Total teaching hours: 51 hours: Lectures: 30 hrs Practical: 21 hrs Code:414 ط ج Course Director: Professor Dr. Refaat Raouf sadek Professor and Chairperson of Community Medicine & Public Health Department Teaching Staff: 3 Professors, 1 Assistant Professors, 4 Lecturer, 6 Assistant Lecturers and 3 Demonstrators. I- Course Aims: 1- Prepare a community- oriented physician capable of implementing preventive and control measures for common communicable diseases on the individual, family and community levels and within the primary health care (PHC) setting following MOHP policies and protocols. 2- Develop a graduate who is aware about the potential emerging/ threatening diseases and who can act as the first line of defense and management. 3- Promotion of outstanding programs of medical care to serve society and to promote environmental development II- Course Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO’s) 1- Knowledge and understanding 2- Professional & intellectual skills 3- General skills and attitude 1-Knowledge and Understanding: By the end of the program, the student should be able to: Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 71 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Identify the infectious cycle for each selected diseases Define methods of prevention and control for each of these diseases Identify routine, recommended, and potential vaccines Describe the MOHP programs for prevention and control of selected diseases Make a decision about the appropriate control measures related to specific situations Apply risk factors relevant to selected non-communicable diseases Explain the importance of periodic examinations Plan the screening tests pertinent to selected diseases and the at-risk approach in the application of screening tests Define the role of the PHC physician in the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases List the health education messages pertinent to a healthy life style, prevention, and control includes : 1. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SELECTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES 1- The selected diseases will include: Common diseases Emerging diseases International diseases Potentially threatening diseases 2- The infectious cycle (identification of the disease/clinical picture and occurrence of the disease; causative agent; reservoir: human and animal/zoonosis; mode of transmission; incubation period; period of communicability; susceptibility and resistance) for each of the selected diseases 3- Prevention and control, and special programs as available 4- Immunization: routine, recommended, and potential vaccines a7. NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES 5- General concepts, risk factors, healthy lifestyle, risk modification, primary and secondary prevention 6- Periodic examination and screening tests 7- Epidemiology of selected non-communicable diseases (ischemic heart disease, hypertension, rheumatic heart disease, diabetes, cancer, blood disorders, bronchial asthma) 8- Prevention and control of the selected diseases 9- Smoking and drug abuse Accident/injury Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 72 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 2- Professional and Intellectual skills: 1. Anticipate and participate in investigation of an epidemic /outbreak as part of a health team and design an epidemiologic study to address a question of interest 2. Apply epidemiologic skills in a public health setting, specifically in the formulation or application of public health programs or policies 3. Demonstrate trends in health and disease including epidemiological causes of high prevalence of certain infections, causes of eradication, emerging or reemerging previous infections worldwide and in Egypt 4. Use appropriate health promotion, disease prevention and control measures to identified priority communi-cable diseases and under specific situations 3- General skills and Attitude By the end of the program, the student will be able to: 1. Evaluate indicators of health and disease 2. Identify prevalent health problems in a community, using various epidemiological strategies 3. Collect and verify data from different sources 4. Organize and manage data, including graphic and tabular presentations 5. Analyze and interpret data 6. Anticipate and participate in investigation of an epidemic/outbreak as part of a health team 7. Apply appropriate health promotion, disease prevention, and control measures 8. Apply disease prevention and control measures to identified priority communicable and non-communicable diseases 9. Participate in conducting public health surveillance. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 73 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University III- Cours Specifications Course Content Topic % total hrs 70 Epidemiology of selected communicable diseases: Diseases transmitted by contact Diseases transmitted by droplet Diseases transmitted by ingestion Sexually Transmitted Diseases Diseases Transmitted by Arthropod Diseases Transmitted by Parasites Quarantinable diseases Emerging Diseases Immunization Non-communicable diseases: 30 General concepts, risk factors, and healthy lifestyle Epidemiology of ischemic heart disease Hypertension Rheumatic heart disease Diabetes Cancer Smoking and drug abuse Accidents/ injuries TOTAL 100 Teaching hours Total Lectures Practical Field visits 18 4 5 32 28 4 Practical includes pre visit orientation seminars IV- Teaching and Learning Methods 1. One hour of lecture/week throughout the academic year (30 weeks/y) 2. Three hours of practical training as field visits week on Monday in the course of internal medicine round ( one and half month) throughout the academic year. . Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 74 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications SYLLABUS Information usually found in a course syllabus includes: 1. Course title and description 2. Course and supporting objectives 3. Course prerequisites 4. Course logistics: location, length, and dates of the course 5. Description of teaching methods 6. Description of learning materials 7. Description of assignments 8. Description of student assessment methods 9. Attendance criteria 10.Course schedule A sample course syllabus is included following this section. CLASSROOM TEACHING Frequently used teaching methods include: 1. Interactive presentations (lectures with discussion) 2. Brainstorming 3. Discussions 4. Case studies 5. Clinical simulations 6. Demonstrations 7. Games 8. Guest speakers 9. Panel discussions 10.Role plays CLINICAL OR FIELD PRACTICE After learning a new topic or skill during classroom teaching, students need opportunities to apply their new knowledge or practice new skills in a simulated or safe environment whenever possible. Simulated environments are places where students can work together in small groups, observe or participate in role plays, perform clinical simulations, watch videos, practice skills with anatomic models, or, if available, work on computers. Once students have practiced new skills in a simulated environment, they can then practice their skills in a supervised clinical or field practice site. Clinical practice sites may include health centers, outpatient clinics, hospitals, and other health care sites. V: Teaching and Learning Facilities: Facilities utilized include: - lecture halls in the main building. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 75 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications -Selected field training sites with free transportation: * health centers, outpatient clinics, and hospitals. VI: Student assessment 1- Practical exam to assess the student’s ability to identify different topics of the course. 2- Mid-term exam to assess the student’s progress during the course. 3- End of year written exam to assess the student’s comprehension and understanding of the class work. 4- Oral exam to assess student’s intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics. Assessment Schedule Assessment 1 MCQ Week 8 Assessment 2 Mid-term exam Week 16 Assessment 3 MCQ Week 24 Assessment 4 End of year exam (Assay written, practical and oral exam) Week 32 Weighing of Assessments: Mid-Term Examination: Final-Term Examination: Oral Examination Practical Examination Semester Works/MCQ Other types of assessment Total 20% 40% 20% 10% 5% 5% 100% Any formative only assessment: TBD during the course work. STUDENT EVALUATION The main purpose of student evaluation or assessment is to improve student learning. This is more likely to happen if assessment is closely integrated with teaching as described in the departmental course syllabus. Evaluation of students’ knowledge and skills helps teachers decide if students should progress to the next stage of study, motivates students by providing feedback on their progress, determines if the course is meeting its objectives, ensures that important subjects are given priority within the course, and offers evidence to national authorities that standards are being met. Evaluation methods should be objective; this means that the personal opinion of the faculty member evaluating the student has no effect on the student’s score. The student should be evaluated during the course (formative Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 76 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications assessment) as well as at the end of the course (summative assessment). Common objective knowledge assessment methods include: 1. Drills, quizzes, and practice tests 2. Written exercises 3. Case studies, clinical scenarios, and patient management problems 4. Project reports 5. Objective written examinations 6. Structured practical examinations 7. Clinical rounds Common skill assessment methods include: 1. Direct observation with checklists 2. Structured feedback reports 3. Logbooks (casebooks), learning journals, and care plans 4. Structured practical examinations MONITORING TEACHING Monitoring is a continual, cyclical process of teaching, collecting information about teaching, and reviewing the information to identify needed changes. For monitoring to be effective, there should be an open organizational culture that encourages a commitment to students’ learning, self-awareness, constructive feedback, reflection, and professional development. In addition, monitoring requires a clear understanding of the course goals and objectives, and the responsibilities of different teachers and administrators. It also requires resources both to conduct monitoring activities and to implement necessary changes in teaching. The most common methods for collecting information about teaching are self-assessment, feedback from students, peer review, and review of examination results. These methods often use tools such as questionnaires, guidelines for interviews, and observation checklists. A number of different methods can be applied to help identify strengths and areas for improvement to guide planning for future courses. COURSE EVALUATION: This curriculum is a dynamic document and will be regularly revised and updated. Monitoring information submitted by departments (e.g., results of student evaluations, feedback from faculty members) coupled with developments in research and technology, changing needs of the country, and the evolving professional environment, will provide the information needed to update it periodically to meet the needs of the faculties, departments, and students. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 77 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 7- List of References 7.1.Department Books, and notes: - Book; Communicable and non-communicable diseases Editors: R. R. Sadek. Abou Helal Press, EI-Minia, Egypt. 2006 7.2- Essential Books (Text Books) BSC NSI SS BSNN COBOCIO MO OO O OC NOC OCNON . COCOC SC, OMO SN SOS OOC OMO OSC O SBOO OSC ONONOBOC CIOB ROOI R SOS OOC R NOO , C F 1015 FO ROCC SC, MB 20005 RONNO SC NOCBO IO SS OC ONCOI NOMOBOCO NSCON C. O ON MSNS, OMO SN ,NO OMO OSC10 ROII CSSK BSN OCH-NACNOF COF HSNK - MAXCY - ROSENAU PUBLIC HEALTH AND PREVENTIVE MEDICINE TWELFITH EDITION, JOHN M. LAST, (EDITOR) APPLETON- CENTURY-CROFTS/NORWALK, CONNECTICUT. USA 7.3- Recommended Books 7.4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc www.cdc.gov www.who.gov 8- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning 1. Public Health and Community Medicine skill laboratory equipped with skill tools. 2. Class rooms for theoretical lectures and tutorials. Course Coordinator: Dr. Fadia Abdel Hamid , MD Head of Department: Professor Dr. Refaat Raouf Sadek, MD Date: 27 / 3 / 2007 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 78 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Course Specifications Public Health and Community Medicine For 5th year medical students University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Course Specifications: Program(s) on which the course is given: MBBCH program for Medical School Major or Minor element of programs: This course introduces students to the principles of management and public health administration because they will be responsible after graduation for managing health units and applying Ministry of Health and Population (MOHP) policies, regulations, and standards. In addition, this course will introduce students to the area of occupational and environmental health. And other important topics, such as mental health, reproductive health, and health of the elderly and people with special needs, including people with disabilities. Department offering the program: Public Health Department Department offering the course: Public Health Department Academic year/Level: Fifth year medical students. Date of specification approval: 18 / 6 /2007 A. Basic Information Title: Public Health Administration and Community Health Programs Code: 414 ط ج Credit Hours: (Not applicable yet) Total teaching hours: 30 hours Lecture: 1 h/ week Field visits: 1d/wk ( Each Tuesday of internal medicine rotations) (about 8 visits each is 3 hours) Field training: 1 week of field training in summer before the start of academic year Total: B. Professional Information. 1. Overall Aims of Course 1- Develop a graduate who is aware of principles of health administration and management. 2- Prepare a community-oriented physician capable of implementing public health programs on the individual, family and community levels and within primary health care setting while following and implementing MOHP policies. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 79 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Specific goals of the course is To introduce the student to the basics and principles of Community Medicine; including: 1 Influence the students to adopt a healthy lifestyle and sound behaviors to become role models for the individuals, families, and the communities they will serve in the future. 2 Prepare a community-oriented physician capable of anticipating and responding to community health needs within the primary health care (PHC) setting according to the policies, regulations, and guidelines of the MOHP. 3 Develop a graduate who will apply the knowledge and skills learned, and is able to take leadership in motivating the community served. 4 Students will acquire the knowledge, attitudes, and skills needed in order to anticipate, assess, and advise on management of environmental and occupational hazards in various settings 2. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding: By the end of the course, Students will able to: A1. Define quality, quality assurance, quality control, total quality management, continuous quality improvement [CQI], performance improvement), dimensions of quality, the quality improvement cycle, tools for CQI, accreditation, and clinical audit. A2. Explain overview of different health systems. A3. Define mental health and the risk factors related to mental health. A4. Define PHC, its principles and elements. A5. List components of comprehensive RH A6. Identify health hazards among elderly, adolescents and work related hazards b. Intellectual Skills By the end of this course, the student will be able to: B1. Analyze the current situation and prioritization of health and health-related problems. B2. Assess quality of a MCH center services B3. Plan a program for solving common health problems amonh rural inhabitants. B4. Compute different vital indices and health indicators. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 80 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications c. Professional and Practical Skills By the end of the course, the student should be able to: C1. Design the organizational structure of the MOHP at the central, governorate, and district levels C2. Apply health behavior theories to different community health problems C3. Apply the different heath education methods and materials in preparation of health education message. C4. Participate in conducting public health surveillance. d. General and Transferable Skills After completing the course, the student should be able to: D1. Utilize the principles of management, and the management cycle of planning, implementation, and evaluation. D2. Communicate effectively with clients, the health care team, and the community. D3. Prepare counselling cession utilizing computer, data show and overhead projectors. 3- Contents TOPICS Communication and Health Behavior Health education Community participation Referral system Health Care Management and Administration Planning, Organizing and controlling Leadership Motivation Health Systems and Health Services in Egypt Primary Health Care Programs Primary Health Care, Basic Health Services, and Family Practice Mental Health Rural Health Reproductive Health, including Maternal and Child Health and Family Planning Adolescent and Faculty Health Health of the Elderly lecture 1 1 1 1 4 2 1 1 2 1 1 3 FIELD VISITS (3 HOURS) Health office - Eastern Medical center - Westrern Medical center - Suzan mobarak center MCH unit 1 1 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 81 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Health of People with Special Needs, including People with Disabilities School health program Family medicine 1 Quality assurance program Occupational Health TOTAL HOURS 1 5 30 1 1 - Family health unit - Eastern Medical center Selected factory in Minia city * One week of field training in Summer Grades: Total = 125 + 25 (from 2nd term 3rd year) =150 4- Teaching and Learning Methods 4.1. One hour of lectures / week throughout the academic year (32Weeks/y) 4.2. Three hours of field visits / Tuesday of internal medicine round. 4.3. Field training (One week/year in Summer) for every student/y. Frequently used teaching methods: 1 Interactive presentations (lectures with discussion) 2 Brainstorming 3 Discussions 4 Case studies 5 Clinical simulations 6 Demonstrations CLINICAL OR FIELD PRACTICE After learning a new topic or skill during classroom teaching, students need opportunities to apply their new knowledge or practice new skills in a simulated or safe environment whenever possible. Simulated environments are places where students can work together in small groups, observe or participate in role plays, perform clinical simulations, watch videos, practice skills with anatomic models, or, if available, work on computers. Once students have practiced new skills in a simulated environment, they can then practice their skills in a supervised clinical or field practice site. Clinical practice sites may include health centers, outpatient clinics, hospitals, and other health care sites. Field practice sites might include nurseries, child care centers, faculties, workplaces, homes, or other settings within the community. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 82 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 5- Student Assessment Methods 5.1 Round exam (short assay) to assess the student’s ability to identify different topics of the course. 5.2 Mid-term exam (MCQ + short assay) to assess the student’s progress during the course. 5.3 End year written exam to assess the student’s comprehension and understanding of the class work. 5.4 Oral exam to assess student’s intellectual and communication abilities regarding basic knowledge and understanding of the course topics. Assessment Schedule formative assessment first term Week 12 nd formative assessment 2 term Week 24 Summative assessment 3 End of year exam (Written and oral exam) Week 32 Weighing of Assessments: Mid-Term 1 Examination: 5 Mid-Term 2 Examination: 5 Logbook 1 field visits 1.5 Round exam 2.5 Semester Works( students researches) 5 Summer training camp attendance 5 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total yearly activities 25 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Final-written Examination: 60 Oral Examination 40 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total 125 6- List of References 6.1.Department books, and notes: - Book 1: Public Health Administration and Community Health Programs Editors Staff members of community medicine department Minia, Egypt. 2004 -Book 2: Practical book “Log book” to record and assess skills learnt during practical cessions. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 83 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6.2- Essential books (Text books) - MAXCY - ROSENAU PUBLIC HEALTH AND PREVENTIVE MEDICINE TWELFITH EDITION, JOHN M. LAST, (EDITOR) APPLETONCENTURY-CROFTS/NORWALK, CONNECTICUT. USA 6.3- Recommended books - Principles of Internal Medicine, Editor, Harrison, 10th edition, Mac Grow Hill Book company, New York 6.4- Periodicals, Web Sites, ....... etc -International Journal of Epidemiology - Journal of IOHTEAIA SA CEA LHICRL I MAEIREMA - Journal of Egyptian Association of Community Medicine -Journal of Egyptian Association of Occupational Medicine http://health.groups.Yahoo.com/group/Pub-OccupHealth/?yguid=121150878 (web site of the department) www.who.org www.cdc.gov www.mohp.gov.eg www.aafp.org 7- Facilities Required for Teaching and Learning 1 Public Health and Community Medicine skill laboratory equipped with skill tools. 2 Class rooms for theoretical lectures and tutorials. 1 Lecture halls 2 Computers 3 Data show 4 VCR 5 Overhead projectors 6 Internet access 7 Buses (provided by University for field visits) Course Coordinator: Dr. Eman Mohamed Mahfouz, Assisstant professor Head of Department: Professor Dr. Refaat Raouf Sadek, MD Date: / / 2007 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 84 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Obstetrics and Gynecology Course specifications 2010/2010 Course Title: Obstetrics and Gynecology, 6th year of MBBCh program Date of approval: 18/6/2007 Code: 612 ن ت -Allocated marks: 500 marks -Course director: Prof. Mostafa Kamel Eissa, Head of OBGYN department -Teaching Staff: 10 professors, 4 assistant professors, 8 lecturers and 8 assistant lecturers I. AIM OF THE COURSE: The aim of this course is to: Supply the undergraduate student with the knowledge, skills and attitude to deal with common OB/GYN problems competently at the level of primary health care facility. II. INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES II-A: KNOWLEDGE and UNDERSTANDING: By the end of the course, all students should be able to: 1. Describe the basic physiological background of fertilization, implantation and early development of the fetus, placenta, and cord. 2. Describe the anatomical features and development of the female genital tract and their clinical application. 3. Recognize the basic physiological changes produced by pregnancy occurring in each trimester and the basic principles of antenatal care. 4. Explain the physiology of menstruation, puberty (its abnormalities and their management), menopause (abnormalities and their management) 5. Discuss different medical disorders occurring during pregnancies and their management (eg: hypertension, pyelitis, hyperemesis, diabetes, anemia...) 6. Discuss etiology of bleeding in early pregnancy (i.e. Abortion, cctopic, vesicular mole) and their management, and causes of bleeding in late pregnancies (placenta praevia, accidental hemorrhage) and their management. 7. Recognize high-risk pregnancies, their magnitude, and different etiologies with emphasis on preventable and avoidable causes and their management. 8. Illustrate different methods of assessment of fetal well-being 9. Illustrate the basic anatomy and surgical anatomy of the female pelvis and fetal skull Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 85 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 10. Explain the physiology, mechanism, management of normal labor and different abnormal presentations and positions 11. List the causes of complications of third stage of labor and outline their management 12. Describe the physiological changes during puerpurium and the recommended program of postnatal visits with abnormalities occurring in puerpurium and their management 13. Outline the indices, causes and prevention of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality 14. Recite the types, causes and treatment of dysmenorrhea and premenstrual syndrome (PMS) 15. Discuss types, causes, proper investigation and management of life threatening severe bleeding conditions 16. Explain the normal human sexual response and common sexual problems and their management 17. Discuss the magnitude of the infertility problem and its different etiologies, basic diagnostic tools, and treatment of infertility 18. Describe causes, types, and methods of diagnosis and management of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) with emphasis on methods of prevention and serious complication of STDs. 19. Outline the pathology of cervical, uterine, ovarian, vaginal and vulval cancers, with emphasis on screening methods and early recognition and broad lines of management of these conditions 20. Recite different contraceptive methods: their uses, types, advantages, disadvantages, and complications II-B: CLINICAL and INTELLECTUAL SKILLS By the end of the course all students should be able to: 21. Assess the gestational age of a pregnant lady through history taking, focused clinical examination, beta-HCG level, and ultrasound assessment 22. Clinically differentiate between normal pregnancies and high risk pregnancies. 23. Distinguish between different causes of bleeding in early pregnancies with judgment of life threatening conditions e.g.: hypovolemic shock of inevitable abortion, disturbed ectopic pregnancy, through vital signs, general, abdominal and pelvic examinations. 24. Point out the warning signs of late pregnancy and early referral to specialized centers 25. Evaluate the risk of bleeding in late pregnancy and how to start management with emphasis on NOT doing vaginal examination 26. Appraise different methods of assessment of fetal well being with proper use of Pinard, Sonicaid, US to evaluate fetal well being, and distressed fetuses which need immediate intervention Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 86 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 27. Manage normal labor appropriately and identify cases requiring referral 28. Examine the female during labor and early recognition of obstructed labor through clinical symptoms and signs and call for help or refer to a special center 29. Assess complication of the third stage of labor and apply first aid management of each till a senior obstetrician is involved 30. Differentiate normal from abnormal neonate through Apgar score and participate in the initial management of those in need of resuscitation. 31. Counsel problems occurring in menopause with emphasis on postmenopausal bleeding, (any case of postmenopausal bleeding should be considered malignant until proved otherwise) 32. Counsel regarding methods of contraception suitable for each patient and how to use or apply it II-C: PROFESSIONAL and PRACTICAL SKILLS: By the end of the course all students should be able to: 33. Examine a pregnant woman regarding blood pressure measurement, abdominal examination; inspection, palpation (fundal level, fundal grip, umbilical grip, first and second pelvic grips) and auscultation of fetal heart sounds (patients and models) 34. P/V examination during labor for cervical dilatation and effacement, station and position of the presenting part and pelvic assessment (models) 35. Conduct of normal labor; monitoring during first stage (partogram and CTG), delivery of the baby (second stage) and delivery of the placenta (third stage) (models) 36. Postpartum assessment and care including inspection of cervix, vagina and perineum (models) 37. Handle a case of breech delivery and shoulder dystocia (models) 37. Manage a case of eclamptic fit (role play) 38. Control PPH; Aortic compression and bimanual compression of the uterus (models) 39. Manage a case of shock and perform blood transfusion (models) 40. Perform gynecological examination including digital, bimanual, and speculum examination and breast examination (models) 41. Perform VIA and take a cervicovaginal (Pap) smear 42. Interpret the results of a semen analysis and HSG 43. Insertion and removal of IUD and Implanon (models) 44. Identify and handle different OB/GYN instruments e.g. sound, volsellum, ring forceps….etc 45. Practice infection control procedures Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 87 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications II-D: GENERAL, ETHICAL and TRANSFERABLE SKILLS: By the end of the course all students should be able to: 46. Communicate with the patient as a person, not as a disease, and understand that the patient is a person with beliefs, values, goals, and concerns, which must be respected in addition to respecting the patient's dignity, privacy, information confidentiality and autonomy. 47. Counsel the patient before doing any intervention and in different situations with respect to her wish whenever this is possible 48. Maintain the atmosphere of cooperation, peer relationships, and mutual respect in the university society 49. Advance the knowledge base of medicine by developing and encouraging scientific researches III. COURSE CONTENTS: III-A: TOPICS: Topic OBSTERICS Basic Obstetrics and normal Pregnancy 1. Fertilization, implantation and early development 2. Placenta, cord and fetal membranes 3. Maternal changes during pregnancy 4. Diagnosis of pregnancy 5. Antenatal care and risk assessment 6. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital anomalies Abnormal Pregnancy Bleeding in early pregnancy 7. Abortion 8. Ec topic pregnancy 9. Hydatidiform mole Antepartum hemorrhage 10. Placenta previa 11. Placental abruption Maternal problems complicating pregnancy 12. Vomiting in pregnancy 13. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy 14. Diabetes Mellitus with pregnancy 15. Cardiac diseases with pregnancy 16. Rh isoimmunization No of hours Lectu Practical Clinical Total res 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 88 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University 17. Anaemia with pregnancy 18. Urinary tract infections 19. Venous thrombo-embolism Normal labor and delivery 20. Anatomy of the female pelvis and fetal skull 21. Introduction to labor 22. Normal labor 23. Analgesia and anesthesia during labor Abnormal labor and delivery 24. Occipito-posterior position 25. Face and brow presentations 26. Breech presentation 27. Shoulder, cord and complex presentations 28. Multifetal pregnancy 29. Abnormal uterine action 30. Abnormal labor Patterns 31. Contracred pelvis and cephalopclvic disproportion 32. Obstructed labor Obstetric injuries 33. Ruptured uterus 34. Lacerations of the cervix, vagina and perineum Complications of third stage of labor 35. Postpartum hemorrhage 36. Retained placenta 37. Acute inversion of the uterus 38. Shock in obstetrics 39. Hypofibrinoginemia Fetal and neonatal problems in obstetrics 40. Assessment of fetal well-being 4 1. Intrauterine growth restriction 42. Preterm labor and prematurity 43. Postterm pregnancy 44. Premature rupture of the membranes 45. Amniotic fluid and its disorders 46. Fetal and neonatal asphyxia 47. Fetal birth injuries The puerperium 48. Puerperium Cours Specifications 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 89 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 49. Puerperal pyrexia and sepsis Operative obstetrics 50. Induction of labor and abortion 5 1. Operative vaginal delivery 52. Episiotomy 53. Caesarean section 54. Ultrasound in obstetrics 55. Maternal and perinatal mortality GYNECOLOGY Basic Gynecology 56. Anatomy of the female genital tract 57. Embryology of the female genital tract 58. Physiology of menstruation 59. Dysmenorrhea and PMS Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility 60. Puberty 61. Menopause 62. Amenorrhea 63. Ovulation disorders 64. Hirsutism 65. Infertility General Gynecology – Injuries 66. Abnormal bleeding from the genital tract 67. Genital prolapse 68. Retroversion of the uterus 69. Old complete perineal tear 70. Urinary incontinence in females 71. Genito-urinary fistulas 72. Rectovaginal fistula Infections in Gynecology 73. Infections of the female genital tract 74. Acute and chronic PID 75. Chronic specific pelvic infections 76. Vaginal discharge 77. Sexually transmitted diseases Gynecologic Oncology 78. Diseases and swellings of the vulva - Classification and clinical presentation - Non neoplastic epithelial disorders - Vulvar swellings (non-neoplastic neoplastic) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 90 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications - Cancer of the vulva (VIN - invasive cancer) 79. Diseases and swellings of the vagina Tumors of the uterus including endometriosis 80. Uterine fibroid 81. Endometriosis and adenomyosis 82. Carcinoma of the cervix and CIN 83. Endometrial carcinoma 84. Choriocarcinoma 85. Benign and malignant swellings of the ovary - non neoplastic cysts of the ovary - Benign neoplastic cysts of the ovary - Benign solid ovarian tumors - Malignant ovarian tumors - Para-ovarian cysts 86. Contraception and family planning - General considerations - Non hormonal contraception - Hormonal contraception - Surgical sterilization techniques 87. Human sexuality and female sexual dysfunction Climical and operative Gynecology 88. Molecular biology in gynecology 89. Endoscopy in gynecology 90. Imaging in gynecology 91. Differential diagnosis in gynecology 92. Operative gynecology III-B: CLINICAL CASES and DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS: 1. Normal Pregnancy: • History taking from pregnant ladies in 1st, 2 nd and 3 rd trimesters • Abdominal examination of a female in the 3 rd trimester • Pinard and Sonicaid use to detect FHS in 3rd trimester 2. Abnormal Pregnancy: • History taking from pregnant females complaining of vomiting, hypertension, DM, cardiac disease, urinary tract infection, bleeding, threatened preterm labor or history of recurrent abortion. • Vital signs taking (sphygmomanometer, stetoscope...etc • Laboratory results interpretation. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 91 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications • Ultrasound interpretation. 3. Normal Labor: • Observe normal labor in Labor ward 4. Abnormal Labor: • Observe management of breech, shoulder presentation, cord prolapse and multiple pregnancies in Lador ward 5. Ultrasound in Obstetrics: • Observation and interpretation of different ultrasounds done in the outpatient clinic 6. Anatomy and Development of the Female Genital Tract: • Female bony pelvis and fetal skull inspection and identification of different diameters 7. Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility: • Interpretation of different HSG (Hysterosaipingographies) to determine uterine, cervical, and tubal lesions that may cause infertility • History taking and examination of cases of amenorrhea and infertility 8. Displacements, Traumatic Lesions, and Urogynecology: • History taking and examination of different cases of genital prolapse and cases with SUI (Stress Urinary incontinence) • History taking and examination of genital fistula. 9. Contraception and Family Planning: • Examination of different types of contraceptive devices, and observation of the methods of their application in the outpatient clinic. 10. Pelvi-abdominal mass cases: • History taking and examination of different cases. 11. Abnormal genital tract bleeding cases: • History taking and examination of different cases. NB: different jars and instruments are available in the Maternity Hospital to help eliciting different obstetrics and Gynecological conditions in addition to the use of different instruments in Obstetrics and Gynecology. List of available specimen jars: Obstetrics: 1- Hydatidiform mole. 2- Ruptured uterus Gynecology: 1- Fibroids. 2- Cysts of the ovary. 3- Benign ovarian neoplasms. 4- Malignant ovarian neoplasms. List of available instruments: Gynecology: 1- Uterine curettes (types). 2- Uterine sound. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 92 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 3- Cervical dilators (types). 4- Cervical biopsy punch forceps 5- Ayre's spatula. 6- Novak's endometrial biopsy curette. 7- Volsellum forceps (types) 8- Vaginal specula (types). 9- Trocar and cannula for laparoscopy. 10- Verres needle 11- Female metal catheter. 12- Trocar and cannula for Norplant insertion. Obstetrics: 1- Obstetric forceps (types). 2- Vacuum extractor. 3- Ovum forceps. 4- Ring forceps. 5- Suction curette. 6- Drew Smythe's induction catheter. 7- Meltal mucus catheter. 8- Pinard's fetal stethoscope. 9- Doyen's retractor. IV. TEACHING and LEARNING METHODS IV-A: METHODS USED: 1. Lectures 2. Clinical and small group sessions: (Clinical demonstrations, practice of skills, lectures and discussions): a. General obstetrics and gynecological inpaticnt ward teaching b. Outpatient clinic (obstetrics and gynecology) c. Emergency department demonstration d. OR theatres. IV-B: METHODS FOR DISABLED STUDENTS No special arrangements are available. IV-C: TEACHING PLAN: Lectures: Four lectures every week; two on Monday from 12:00-01:00pm then from 01:00-02:00pm, Wednesday from 12:00-01:00pm and Thursday from 12:0001:00pm Clinical rounds and small group activities: • Each term, students are divided into two equal groups; one group will have a ward round in the morning from 08:30-10:00am discussing cases from inpatients wards then they are subdivided to small groups to examine the patients. The other group will have practical lessons in the skill lab for the Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 93 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications same duration. Then both groups unite together and have will have a clinical round with case discussion presented by one student from 10:00-11:00am. Time Plan Item Inpatient rounds Skill lab Clinical rounds Lectures Time schedule Daily: 8:30-10:00am Daily: 8:30-10:00am Daily: 10:00-11:00am 4 times weekly Teaching hours 24 sessions x 1.5 hrs 24 sessions x 1.5 hrs 48 sessions x 1hr Sessions x 1hr Total hours 36 hrs 36 hrs 48 hrs Total V. TEACHING AND LEARNING FACILITIES Facilities used for teaching this course include: LECTURE HALL: In the lecture hall building for the forth, fifth and sixth years medical students located at Menya University Hospital SMALL GROUP CLASSES: • 3 rooms at the clinical wards of the OB/GYN Dept. at Suzan Mubarak University Hospital for OB/GYN and Pediatrics. Writing boards are available in all rooms, overhead and slide projectors are available for use when needed. • One Skill Lab room at the clinical wards of the OB/GYN Dept. at Suzan Mubarak University Hospital for OB/GYN and Pediatrics with models, flip chart and data show available when needed. CLINICAL FACILITIES: • Obstetric outpatient clinic serving about 40 patients a day • Gynecological outpatient clinic serving about 40 patients a day • OB/GYN inpatients wards in the hospital • Emergency room serving about 50 patients a day • Operating theater in the emergency room with 2 delivery rooms and 2 theaters • Operating theater in the 2nd floor with 2 operating beds • Laparoscopy unit in the 2nd floor • Colposcopy unit in the 2nd floor PATHIOLOGY MUSEUM: • Specimens demonstrating different obstetrics and gynecological diseases SKILL LAB • Models used in demonstration Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 94 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications • Different instruments used in obstetric and gynecological practice VI. STUDENT ASSESSMENT: VI-A: ATTENDANCE CRITERIA: The minimum acceptable attendance is 75%. Students who fail to attend that percentage of activities will not be allowed to take the end of term examination. They may be allowed to take it during a subsequent term if they satisfy the required attendance, otherwise the marks allocated for the end of term examination would be reduced as a proportion from the final examination score. Students need to attend at least 60% in order to sit for the final examination. A log book for clinical cases and attendance in emergency department and theatre must be fulfilled. VI-B: ASSESSMENT TOOLS: TOOL PURPOSE Written examination Assessment of knowledge and understanding Oral examination Assessment of knowledge and understanding Clinical examination Assessment of clinical skills and ethical and transferable skills Practical examination Assessment of professional and practical skills VI-C: ASSESSMENT SCHEDULE: • TERM EXAMINATION: held at the end of each 2 clinical rounds. It is a practical examination for each 2 rounds together. • EXAMINATION: held after the midyear holiday. It is an MCQ examination. • FINAL EXAMINATION: at the end of the academic 5lh year for all students of this year, and the one failing from the previous year VI-D: GRADING SYSTEM Examination Marks allocated Term Examination Midyear examination (MCQ) Final Examination Written 200 Oral OB 60 Oral GYN 60 Clinical 80 Skill lab Total 500 • The minimum passing score ismarks provided at least marks are obtained in the final written examination Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 95 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications • Passing grades: EXCELLENT >85%, VERY GOOD 75-85%, GOOD 6575%, and FAIR 60-65%. Examination Description Marks Term exam Practical, 5 stations Midyear 40 MCQs exam Final exam Written 10 short essay questions (5 OB & 5 GYN) 200 (3hrs) Oral Two oral exams: Obstetrics 60 Gynecology 60 Clinical One long case (history taking and 80 examination) followed by discussion of the case (whether obstetrical or gynecological case) Skill lab Five stations Total 500 VII. LIST OF REFERENCES: • The handouts from Overhead projections, slides, computer presentations used during teaching • Novak's gynecology 13th edition, 2002: available at bookshops • Speroff clinical gynecologic endocrinology and infertility, 6 th edition, 1999: available at bookshops • Fernando-Arias high-risk pregnancy, 2nd edition, 1993: available at bookshops • Williams Obstetrics, 21st edition, 2001: available at bookshops • Gyn&Obst., ( Ain ShamsUniversity ) available at book-shops. • Gyn&Obst., ( Farouk Hasseb ) available at book-shops. Course coordinator: Dr/ Mahmoud El-Morsi Head of department: Dr/ Moustafa Kamel Essa, 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 96 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Pediatrics Course Specifications University: Minia Faculty: Medicine Programme(s) on which the course is given: 5th year medical students Major element programmes Faculty offering the programme: Minia Faculty of Medicine Department offering the course: Department of Pediatrics Academic year/ level 5th academic year Date of specification approval Title: Pediatrics Daily schedule system Lecture: 100 Tutorial and clinical: 100 Total: 200 A- Basic Information Code:512ط ط B- Professional Information 1- Overall Aims of course To support acquisition of basic knowledge of normal and abnormal growth and development (physical, physiologic, psychosocial), and its clinical application from birth through adolescence. To provide students with an appropriate background covering the common and important Pediatric emergencies and diseases. To enable the development and application of appropriate professional attitudes, communication and problem solving skills. To enable students to provide basic health care for individuals in the Pediatric age group (neonates, infants, children and adolescents) 2- ntended learning outcomes of course (ILOs) a- Knowledge and understanding: By the end of the course, students should be able to: Describe normal growth and development during infancy, childhood and adolescence and recognize appropriate management for abnormalities affecting growth and development. Recognize an understanding of the impact of congenital and inherited diseases on children and their families. Determine the nutritional requirements and the most common nutritional disorders affecting infants and children, and describe appropriate management for disorders. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 97 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Describe the indications, contraindications, administration and precautions of the immunizations necessary for infants and children according to the national schedule and the condition of the child. Recognize the most important behavioral and social issues during childhood and adolescence. Describe the management priorities for different neonatal and Pediatric emergencies. List the causes and pathogenesis of the most important neonatal and pediatric problems and describe the clinical symptoms and signs of the most important neonatal and Pediatric problems. Identify the appropriate diagnostic tools (and describe how they would be interpreted) and therapeutic lines for the most important neonatal and Pediatric problems. b- Intellectual skills: By the end of the course, students should be able to: Interpret the most important symptoms and signs of disease in Pediatric patients. Demonstrate appropriate management plans for individual patients presenting with the most common Pediatric disorders. Schedule management regarding common clinical situations using appropriate problem solving skills. Interpret X ray and blood picture reports covering the most important Pediatric conditions. c- Professional and practical skills By the end of the course, students should be able to: Measure vital signs, and assess anthropometricmeasuerments in neonates, infants, children and adolescents. Assess physical and mental development in neonates, infants, children and adolescents according to standard milestones and recognize abnormalities. Assess the nutritional status of infants and children. Recognize different neonatal and pediatric emergencies and schedule appropriate management for them. Construct a proper history for a patient in the Pediatric age group. Perform an adequate clinical examination for a patient in the Pediatric age group and identify deviations from normal. Interpret patient’s data in an organized and informative manner. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 98 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Classify and describe appropriate treatment for sick children according to the principles of integrated management of childhood illness. d- General and transferable skills: By the end of the course, students should be able to: Communicate effectively with the children, adolescents and his family using appropriate communication skills and organize patient’s data in informative manner. Demonstrate appropriate professional attitudes and behaviors in different practice situations. Communicate with different websites for pediatrics. 3- Contents : TOPICS Total houres Lictures Practice 1. Growth and Development 10 5 5 2. Nutrition and Infant Feeding 20 10 10 3. Perinatology/Neonatology 20 10 10 4. Social and Preventive Pediatrics 12.5 5 7.5 5. Genetics and Dysmorphology 7.5 2.5 5 6. Nephrology 10 5 5 7. Cardiovascular System 15 7.5 7.5 8. Respiratory System 15 7.5 7.5 9. Hematology/Oncology 15 7.5 7.5 10. Infectious and Parasitic Diseases 15 7.5 7.5 11. Endocrinology and Metabolism 7.5 5 2.5 12. Neuromuscular Disorders 12.5 7.5 5 13. Gastroenterology and Hepatology 17.5 7.5 10 14. Pediatric Emergencies 17.5 10 7.5 15. Behavioral Pediatrics 5 2.5 2.5 100% 100% 100 hrs 100 hrs TOTAL 200 4 - Teaching and learning methods: Lectures Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 99 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University 1) 2) 3) Cours Specifications Clinical and small group sessions General pediatric inpatient ward teaching Outpatient clinic . Skill lab teaching Tutorial classes and problem solving sessions 5 - Student assessment methods: Clinical round exam to assess clinical achievement after clinical round for each group. It includes a) Multiple stations: 4 short cases. b) Multiple skill lab stations: X ray, laboratory reports and practical skills evaluation. Mid year written exam. to assess lecture achievement. It includes short account questions and MCQ questions. Final year exam: It includes a) Written short essay questions b) Two short cases clinical exam c) Oral exam d) X ray exam Assessment Schedule: Clinical round exam : for each group after 8 weeks clinical attendance.( four times per year ) Med year exam : in April each year Final year : in July each year Weighing of assessment: Clinical round exam: 6% Mid year written exam: 14% Final term exam : 80% a) Oral Exam: 40% b) Written Exam: 40% TOTAL 100 % 6 -List of references Course notes Essential books: Hand book of pediatrics prepared by staff member of the department. Recommended books : Essential Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics Periodical websites : www.pubmed.com 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning Lecture Hall: At Suzan Moubarak University Hospital. Writing board, overhead &slide projector, data show are needed. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 100 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Small group classes: 3 classes for clinical are available now. Classes now are in need for teaching facilities (Writing board, overhead &slide projector, data show are needed.) Skill lab room: we have 1 skill lab room with teaching models. Course Coordinators: Dr. Basma Abd Elmoez Head of Department Professor Doctor: Salah Mahmoud Saleh Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 101 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications General Surgery Course Specifications - Program on which the course is given : MBBCH. - Major or minor element of programs : induction, junior, senior & training courses in : * Gastro-intestinal tract (Upper GIT, Lower GIT & peritoneum). * Biliary system, pancreas, liver & spleen. * Abdominal emergencies (Acute abdomen & abdominal injuries). * Vascular surgery. * Pediatric surgery. * Plastic surgery. * Neurosurgery. * Cardiothoracic surgery. * Urology. * Orthopedics. * Anaesthesia. * Care of surgical patient. * Emergency & first aids. - Departments offering the program & course : * General Surgery department (including units of sub-specialities : vascular, pediatric, plastic, neurosurgery, cardiothoracic & emergency). * Urology department. * Orthopedics department. * Anaesthesia.department. - Academic year / level : 6th year - Date of specification approval : 31/ 8 / 2007 A- Basic information - Code:611 ج ح - Title: General surgery. - Credit hours: 678 - Lectures: 216 - Tutorial: 67 - Practical: 395 - Total: 678 B- Professional Information 1- Overall aims of course : provide student with: * Knowledge & skills to identify, analyze, manage / or refer clinical surgical problems to provide efficient, cost effective and human patient care. * Background covering the common and/or important surgical emergencies. * Background to detect cancer at an early stage. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 102 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications * Professional attitudes, ethical principles & communication skills. 2- Intended learning outcomes of course ( ILOs ) a- Knowledge & understanding: on completion of the course, student is able to : a1. Describe anatomy of surgically-important structures & surgical pathology of important and / or common surgical diseases a2. Discuss clinical manifestations, complications, diagnostic modalities, outcome and treatment plans for common and/or important surgical problems, stressing on emergencies and malignancies with early detection of cancer . a3. Discuss principles & practice of preoperative preparation & postoperative care. a4. Describe the basics of safe anesthesia. b- Intellectual skills: on completion of the course, student is able to : b1. Interpret results of history taking, examination, diagnostic tools. b2. Design the proper plan of management. b3. Analyze and make problem solving. c- Professional & practical skills: on completion of the course, student is able to : c1. Perform routine beside procedures. c2. Apply principles of sterile techniques & infection control guidelines c3. Perform an emergency directed examination for common surgical emergencies. d- General & transferable skills: on completion of the course, student is able to : d1. Conduct sincere patient interviews, properly explain the condition & plan of management, obtain consents and convey bad news in a professional way . d2. Write patient records with proper presentation. d3. Treat the patient as a person, respecting his confidentiality and deliver care in an honest, considerate and compassionate manner . d4. Communicate, consult and respect the role of other health-care providers and work effectively and cooperatively in a team d5. Formulate a focused clinical question based on real or hypothetical case, search effectively medical literature using electronic resources, retrieve appropriate information and appraise them using the principles of evidence based medicine . d6. Discuss professional errors in an honest way - Contents : Lectures (8 weeks = 24 hours) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 103 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Topic Hours Basics of trauma: (8) - Metabolic response to trauma & Hemorrhage. - Shock. - Blood transfusion. - Hemostatic disorders. - Homeostasis. - Electrolytes imbalance. - Acid base imbalance. Wounds: (4) - Wounds (in general). - Wound healing. - Specific wounds & wound infection.. - Burns. Infections: (4) - Surgical infections. - Antibiotics. - Systemic infections. - Infection control. Swellings (in general): (4) - Acute inflammatory swellings. - Hand infections. - Cysts & Benign tumours. - Malignant tumours. (4) - Rodent ulcer & Epithelioma. - Mixed tumors: Hemangioma, neurofibroma & melanoma Total Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Lecture Tutorial/Practical 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 24 24 104 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Clinical Rounds (6 weeks = 72 hours) Topic Hours Lecture - Ethical approach to surgical patient & 4 2 History taking. 6 - General examination & Vital signs. - Local examination: Swellings & Ulcers 12 (in general). 12 - Thyroid gland (& Neck swellings). 12 - Hernias. - Scrotal swellings (inguino-scrotal swellings) - Acute conditions : * Acute abscess, cellulitis, acute lymphadenitis 2 * Hand infections, ingrowning toe nail. 2 * Acute epididymo-orchitis, torsion of testis 2 - First aids & emergency : * 1st aids of wounds (control of bleeding), burns. 4 st * 1 aid : Haemostatic disorders. 2 st * 1 aids of shock (& comatosed) & Basic life 4 support. - Care of surgical patient : 4 * Temp. & BP. 4 * Use of IV fluids & Blood and its components. - Skills (Training) : * S.C., I.M. & IV injections. * Venous access. * CVP. Total 72 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Tutorial/Practical 2 1 3 6 6 6 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 36 105 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Lectures (8 weeks = 32 hours) Topic Hours Lecture Tutorial/Practical 1 1 - Lips & Oral Cavity. 1 1 - Tongue. 1 1 - Parotid & submandibular glands. 1 1 - Salivary tumours. 1 1 - Jaw Swellings & Block neck dissection. 1 1 - Scalp swellings & ulcers. -Thyroid gland (anatomy, anomalies & physiology) 1 1 - Simple goiter. 1 1 - Toxic goiter. 1 1 - Solitary nodule & retrosternal goitre. 1 1 - Malignant goiter. 1 1 - Inflam. & hypothyroid goiter - Lymphadenopathy (causes types & groups). 1 1 1 1 - TB lymphadenitis. 1 1 - Lymphomas. 1 1 - Neck Swellings. - Breast (anatomy, anomalies & infections). 1 1 - Fibroadenosis, benign tumors, bleeding per nipple. 1 1 - Carcinoma. 1 1 - Sarcoma. -Male breast. 1 1 - Axillary & chest swellings. 1 1 - Abdominal wall & Umbilicus: - Inguinal hernia (definitions, anatomy). 1 1 - Indirect inguinal hernia. 1 1 - Direct Inguinal Hernia, special types, D.D. 1 1 - Femoral Hernia. 1 1 - Umbilical Hernia 1 1 - Recurrent & Incisional hernias 1 1 - Burst abdomen. Rare types of hernias. 2 2 - Complicated hernia (obstructed & strangulated). - Testis (anatomy & anomalies). 1 1 - -Hydrocele, cysts of epididymis & Varicocele. 1 1 - Torsion of testis & acute epididymo-orchitis 1 1 Chronic Nodules. - Testicular tumours. 1 1 Total 32 32 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 106 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Clinical Round (8 weeks = 96 hours) Topic - All of that in the 4th year - Head & Face: * Skull, Scalp & Face. * Lips, Floor of mouth & Tongue. * Salivary glands. * Jaw swellings. - Breast swellings (& bleeding per nipple). - Abdominal Examination (& Abdominal masses) Hours Lecture Tutorial/Practical 24 12 6 12 6 4 12 6 3 6 3 2 6 3 4 2 4 2 - First aid & Emergency : * Advanced life support & CPR. 6 3 - Care of surgical patients : * Blood transfusion. * Antiseptics, dressings & drains. 4 4 2 2 4 2 - Acute Conditions : * Acute cheilitis, tongue ulcers, acute parotitis & submandibular sialadenitis (Ludvig's angina). * Acute breast abscess (Lactational mastitis). - Skills (Training) : Wound dressing & Stitches. Total Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 96 48 107 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Lectures (25 weeks = 100 hours) Topic No. of hours Lecture Tutorial/Prctical Work 5 Upper GIT: 1 (12) - Oesophagus (anatomy, anomalies). 1 - Hiatus Hernia & Reflux oesophagitis. 1 - Oesophageal motility disorders. 1 - Carcinoma. 1 - Dysphagia. 1 7 - Stomach: (anatomy & physiology). Acute peptic ulcer. 1 - Chronic peptic ulcer 1 - Bleeding peptic ulcer. 1 - Perforated peptic ulcer. 1 - Pyloric obstruction. 1 - Gastric carcinoma. 1 - Cong. hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Rare diseases. Lower GIT & peritoneum: 5 (22) - Small intestine & colon (anatomy, physiol & 1 anomalies) 1 - Inflammatory bowel diseases. 1 - Intestinal tumours & familial polyposis. 1 - Carcinoma of colon. 1 - Carcinoma of rectum. - Intestinal Obstruction: Pathology. 1 7 - Intestinal Obstruction: Clinical Picture. 1 - Intestinal Obstruction: Investigations & 1 Treatment 1 - Intessusception & Volvolus 1 - Adhesive intest. obst. Paralytic ileus. Mesentic. 1 vas. occ. 1 - Neonatal Intestinal obst: Hirschsprung's diseases - Anorectal anomalies - Appendix: anatomy, pathology, cinical picture, 1 2 treatment 1 - Appendicular mass, abscess Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 108 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University - Localized peritonitis. - Acute peritonitis. - TB peritonitis. - Retroperitoneum. Abdominal tumours of infancy. - Ano-Rectum: anatomy - Anorectal suppurations, pilonidal sinus - Anal fissure & Piles. - Rectal prolapse. Anal carcinoma. Anal incontinence. - Lower GIT bleeding. Biliary System, Pancreas, Liver & Spleen: (18) - Biliary system: Anatomy, physiology, anomalies. - Acute cholecystitis - Chronic cholecystitis - Jaundice: aetilogy, types - Calcular obstructive jaundice. - Malignant obstructive jaundice. - Pancreas: acute & chronic pancreatitis. Carcinoma. - Principles of endocrine Surgery - Liver: anatomy, physiology. Liver Cirrhosis. - Portal hypertension. - Attack of hematemesis due to oesophageal varices. - Upper GIT bleeding. - Amoebic Liver abscess & Hydatid cyst. - Liver tumours & Malignant liver. - Hepatomegaly & Splenomegaly. - Blood diseases corrected by splenectomy. - D.D. of abdominal Swellings. (4) - Acute abdomen (in general). - Abdominal injuries. Vascular, Plastic & Pediatric: (14) Arterial diseases: - Acute ischemia. - Arterial injuries. - Chronic ischemia. - Diabetic ischemia & foot. - Burger's disease, Vasospastic diseases. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Cours Specifications 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 5 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 1 1 2 4 6 1 2 1 1 1 109 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University - Gangrene. – Thoracic outlet syndrome. Venous Diseases: - Varicose Veins. - Venous Ulcer. - Superficial thrombophlebitis. - DVT. - Lymphodema. - D.D. of leg swellings - Principles of Plastic Surgery: Skin grafts & flaps. - Principles of pediatric surgery. Advanced trauma, Cardiothoracic & Neurosurgery: (22) 1 - Approach to multiply injured patients. - Maxillo-Facial injuries 1 - Neck injuries 1 - Hand injuries 1 2 - Peripheral nerve injuries. 4 - Chest injuries: Rib fractures, haemothorax, pneumothorax, heart injuries 2 - Chest diseases. - Mediastinum, Heart & Pericardium 1 - Head injuries: Scalp, Skull & Brain Injuries 2 - I.C. haematomas: extradural, subdural, subarachnoid. 1 - Management of head injuries 2 1 - Intracranial infections : Brain abscess. - Skull : Hydrocephalus 1 - Intracranial tumours. 1 1 - Spine. Care of surgical patients : (8) - Preparation of critical patients for surgery: cirrhotics, jaundiced, pediatrics, Geriatrics,…. - Preoperative care : evaluation, selection, fitness & Preparations for surgery... - Operative principles: sterilization, disinfection… Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Cours Specifications 1 1 2 4 2 2 2 2 6 4 3 5 4 1 1 1 110 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University - Postoperative care: immediate, intermediate & Convalescence… - Postoperative complications… - Surgical Nutrition : Oral (Diets), tubal (Preparations) & Parenteral (PPN, TPN) - Hospital Infection & infection control. - Tetanus & Gas Gangrene. Total 100 Cours Specifications 1 2 1 1 100 Clinical Round (8 weeks = 144 hours) Topic Hours Lecture th - All of that in 4 & 5 years: 6 (6) - Head & Face: skull, scalp, face, lips, mouth 12 floor, (27) Tongue, parotid and submandibular glands & 9 6 jaws. - Neck: Thyroid, lymphadenopathy & Neck swellings. 3 - Breast, axilla & chest wall. 3 - Abdomen: 3 (18) * GIT symptoms & surgical dyspepsia. 2 * Abdominal exam. 1 * D.D. of abdominal swellings. 3 * Retroperitoneal swellings. 3 * Exam. of back (Spine) * Splenomegaly & Hepatomegaly. * Malignant liver. * Jaundice. th Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Tutorial/Practical 6 12 9 6 3 3 3 2 1 3 3 111 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University -Hernias… (21) - Scrotal swellings, inguino-scrotal swellings, Maldescended testis & Penis. - Chronic ischemia of lower limbs - Varicose veins. - Chronic leg swellings - Neuro-surgery cases & Nerve Injuries. (16) - Cardio-thoracic surgery cases. - X-rays. (28) - Surgical pathology (Jars). - Operative (theoretical) - Operative (practical) - Acute conditions: (12) * Acute abdomen. * Acute anal conditions. * Upper & Lower GIT bleeding. * Acute ischemia. * DVT. - First Aids & Emergency: (10) * 1st aid of vascular injuries. * 1st aid chest injuries * 1st aid of head, neck, maxillo-facial injuries. * 1st aid of abdominal injuries. * 1st aid : Corrosive injury of oesophagus * 1st aid: newly-borne surgical lesion (& transport of newborn): exomphalos, gastrocheisis, congenital diaphragmatic hernia & neonatal intestinal obstruction. * Airway management (oro-pharyngeal tube & endotracheal intubation. * CPR. - Care of surgical patients & Skills (Training): (6) * Surgical Nutrition : Oral (Diets), tubal (Preparations), Parenteral (PPN, TPN). * Ryle's tubing. * CV line. * P.R. examination. * Uretheral catheterization. Total 144 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Cours Specifications 6 6 6 6 3 3 3 3 3 3 8 8 8 8 8 4 8 8 8 4 8 8 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 6 1 1 2 3 2 3 28 116 112 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Special Surgery : A- Urology: Lectures (4 weeks = 24 hours) & Clinical rounds (4 weeks = 72 hours) Topic Hours Lectures Tutorial/ Practical _________________________ _____________ _____________ ________________ - Surgical anatomy 1 1 - Symptomatology 3 1 1 - Urologic investigations 1 1 - Embryology& Congenital 9 3 3 anomalies 9 3 3 - Genitourinary infections 9 3 3 - Urolethiasis 18 3 3 - Obstructive urobathy 18 2 2 - Genitourinary oncology 1 1 - Neurogenic bladder 6 2 2 - Andrology 2 2 - Genitourinary trauma 1 1 - Urology emergencies 1 1 - Endourology procedures 54 - Urology clinical cases 18 - Urology x-rays Total 24 18 54 B- Orthopedics: Lectures (4 weeks = 24 hours) & Clinical rounds (4 weeks = 72 hours) Topic Hours Lectures Tutorial/ Practical - General lines of fractures 2 2 - Injuries of upper limb 9 4 4 - Injuries of trunk 3 2 2 - Injuries of lower limb 9 4 4 - Congenital diseases 15 2 2 - Bone and joint Infections 3 3 3 - Arthropathy and soft tissue 3 1 1 problems 18 3 3 - Musculoskeletal tumours 3 1 1 - Neurological conditions 9 1 1 - Common hip conditions - Orthopedic clinical cases 51 - Orthopedic x-rays 21 Total 24 21 51 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 113 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University C- Anesethiology: hours) Cours Specifications Lectures (12 hours) & clinical rounds with surgery (6 Topic - Anesthesia - ICU - Pain management Total Hours 8 2 2 12 Lectures 8 2 2 12 Tutorial/ Practical 6 6 4- Teaching and Learning methods : 4-1- Lectures & Tutorial sessions.. 4-2- Clinical rounds. 4-3- Bedside teaching. 4-4- Outpatient clinic 4-5- Operating room teaching (OR) . 4-6- Emergency room contact with surgical team (ER) . 4-7- Skill laboratory sessions. 4-8- Seminars & conferences… 4-9- Self-directed learning (& teaching). 5- Students Assessment Methods : 5-1- Written examination to assess knowledge and understanding . 5-2- Clinical examination to assess clinical, intellectual skills, general skills & attitude. 5-3- Oral examination to assess knowledge and understanding, including : * X rays. * Surgical natomy. * Surgical pathology (Jars). * Acute conditions, first aids and emergency & care of surgical patients. A- MID-TERM EXAMINATION: Methods of evaluation : - MCQ examination (multiple choice or single choice) : at end of each course… - Oral examination: during ward practice (OSCE) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 114 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications . At end of 1st course (2 months): exam. on history & exam. . “ “ “ 2nd course (2 months): “ . “ “ “ 3rd, 4th courses (4 months): “ “ “ “ + diagnosis. “ + diagnosis + management. Objective structured clinical examination (OSCE): assess clinical competence of students (objective rather than subjective): * Student rotates a number of “stations”: spending 5 minutes at each station, with ½ minute allowed to move to next station…! * Content of stations depends on experience of students: - At question stations: no examiner is present, but student is asked about his findings at the previous station and their interpretation. - At procedure stations: examiner is present to assess: student’s technique in taking history and in examination (general & local). B- FINAL EXAMINATIONS : 3 parts : 1- WRITTEN EXAM: 2 papers (Each of 3 hours duration) * 1st paper for general surgery: consists of: - Long or short answer questions (General surgery). - Commentary or patient management problem (Emergency cases). - Short question (Care of surgical patients). * 2nd paper for special surgery: consists of: - Short questions (Vascular, neuro-, cardio-, paediatric, plastic). - Commentary or a case problem in (surgical anatomy). - Short answer questions (Urology, orthopaedics, anaesthesia). * 50 MCQs: single response, multiple responses, matching responses.. 2- CLINICAL EXAM: 2 sections: * Long case section: Student is allowed 30 minutes for history taking, physical examination & preparation of a surgical case in details… to be discussed by 2 examiners over 30 minutes. * Short case section: Student is accompanied by 2 examiners to examine & discuss 2 or 3 cases... along 30 minutes… 3- ORAL EXAM: includes 6 sessions: * X-ray exam session (single response, multiple responses...). * Surgical anatomy session (single response, multiple responses..). Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 115 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications . In above 2 sessions, student rotates a number of “stations”spending 5 minutes at each station, with ½ minute allowed to move to next station…! No examiner is present, but student is asked about his findings at the previous station and their interpretation. * Operative surgery & instruments session. * Surgical pathology (Jars) session. * Emergency surgery (casuality) & First-aid session. * Care of surgical patients session. * Acute surgical conditions session C- Assessment & evaluation Grading system: Total marks: 900 - distributed as follows: * Mid-term evaluation exam (in 4 courses): 20% (including log book + cases presentations + attendance in rounds, lectures) * Final year written exam: 50% * Final year clinical-oral-practical exam: 30% Grading system Subtotal (marks) Total (marks) * Midterm examination (end of round): - General surgery 4th year round 40 th - General surgery 5 year round 30 - General surgery 6th year round 60 - Special surgery rounds 50 (Urology, Orthopedics, Anesthesia) * Final examination (General Surgery) - Written paper 1 180 - Written paper 2 (General + Special) 180 - Long case 60 - 2 short cases 60 - Jars 30 720 - Operative 30 - Surgical anatomy 30 - Acute conditions 10 - First aids & emergency 10 - Care of surgical patients 10 Special surgery clinical, oral & x-rays (Urology, Orthopedics, Anesthesia) 90 Total 900 Minimum passing score, provided at least 108 are obtain in the written examination . Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 116 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Passing grads are: - Excellent = 85% or more . - Very good = 75% to < 85% . - Good = 65% to < 75% . - Fair = 60% to < 65% . - Failed = less than 60% . D- Attendance criteria: - In general surgery: Minimum acceptable attendance in the surgical rounds is 75% students who fail to attend that percentage of activities will not be allowed to take the end of them examination and the marks allocated for this exam would be recorded as a proportion from the final written score. - In special surgery: student is not allowed entry to the exam if his absence exceeds 9 days. - Students need to attend at least 60% of the rounds to be able to site for the final examination . E- Practice training presented with Log-book: 1. Case presentation. 2. Bed-side rounds. 3. Skills & procedures. 4. Seminars, meetings & conferences. 5. Preoperative note, short operative note & operative problems. 6- list of refrences: 6-1- Course notes 6-2- Essential books (text books): Bailey and love's short practice of surgery 6.3- Recommended books: Fundamental surgery (Prof. Gamal S. Saleh). 6.4- Periodicals… 6-5- Web sites: www.miniasurgery.com 7- Facilities required for teaching and learning : 7-1- Clinical round rooms (3 rooms for 4th, 5th & 6th years). 7-2- Lecture halls (3 halls for 4th, 5th & 6th years). 7-3- Beds and clinical facilities of Minia University Hospital. 7-4- Audio-visual aids (data show, overhead projector, slide projector,...). 7-5- Black and white board. 7-6- Skill lab. 7-7- Library (faculty & electronic). Coarse coordinator : Dr.Ashraf Abd Elazeim Head of department : Prof. Hamdy Abo Beih Date : 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 117 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Department of Internal Medicine MINIA UniversityFaculty of Medicine Course title: Internal Medicine course specification Course specification: -Major and minor elements of programs: Clinical training and teaching courses in cardiology, chest, hepatology, gastrointestinal diseases, rheumatology, nephrology, hematology, neurology, psychiatry, endocrinology, dermatology, and clinical pathology. -Departments offering the program: Internal medicine departments and special medicine departments that includes; Cardiology, chest, rheumatology, neurology, psychiatry, tropical medicine, dermatology, and clinical pathology departments. -Academic year levels: 5th year. Date of approval: October 2007 A) Basic information: Course duration: Fourth year teaching hours Clinical rounds One month course each section group of students - Two hours daily: internal medicine department = 2 x 5 x 4 = 40 hours - Two hours daily: special medicine departments = 2 x 5 x 4 = 40 hours Total clinical hours: 40+40=80 hours Lectures teaching -Two hours weekly for both internal medicine and special medicine departments along 6 months course (2 x 4 x 6= 48 hours totally) Totally 128 hours at minimum (80+48) Fifth year teaching hours Clinical rounds Two months course each section group of students - Two hours daily: internal medicine department = 2 x 5 x 4 x 2= 80 hours - Two hours daily: special medicine departments = 2 x 5 x 4 x 2= 80 hours Total clinical hours: 80+80=160 hours Lectures teaching - One hour weekly: Internal medicine department= 1x4x6=24 hours in 6 months) - One hour weekly: special medicine departments= 24 hours in 6 months Total lectures hours: 24+24=48 hours Totally 208 hours at minimum (160+48) Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 118 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Sixth year teaching hours Clinical rounds Ten weeks course each section group of students - Two hours daily: internal medicine department = 2 x 6 x 4 x 2= 96 hours - Two hours daily: special medicine department = 2 x 6 x 4 x 2= 96 hours -Two hours daily clinical rounds for dermatological diseases for 2 continuous weeks (clinical case demonstration and practical training) *(2 X 6 X 2=24 hours for two groups sections X 2 for whole group of student = 48 hours totally per year). Total clinical hours: 96+96+48=240 hours Lectures teaching - One hour lecture weekly for clinical pathology 1 x 4 x 6 = 24 hours. - One hour lecture weekly for dermatological diseases = 1 x 4 x 6 = 24 hours. - Two hours weekly: Internal medicine department = 2X4 X 6 = 48 hours. - Two hours weekly: special medicine departments = 48 hours. Total lectures hours: 24+24+48+48=144 hours Totally 384 hours at minimum (240+144) Total teaching hours along the academic 3 levels (4th, 5th, and 6th): 128 +208 + 384 = 720 hours B) Professional information: I. Aim of the Course: By the end of the internal medicine course the student should be qualified as a general practitioner who is able to: a) Get information and understand of: Health in normal and how to promote it. Disease state and how to diagnose; prevent and treat. b) Development of intellectual skills regarding: - Identify basic knowledge of medical problems at health and disease. - Interpretation of the data available. - Recall of this knowledge to be able to diagnose and treat medical diseases. c) Get acquainted and experienced with the professional and practical skills: -At first the student should get information about the basic requirements to be fulfilled for a proper practical skill. - Assisted practical skills are offered by supervising staff. - Self practicing these skills is monitored by the in charge staff. d) General and transferable skills also tended to be conducted by professional staff to medical student through: -Ethical and professional dealing with a diseased person. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 119 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications -Special skills that can be learned out from observing a professional speciality in internal medicine. e) Attitude: -Creation of the concept of respect to both patients and medical staff. -Advocate the concept of patient’s rights regarding confidentiality and informed consent. -Establishment of appropriate attitude, medical ethics and legal responsibilities in the medical practice. These objectives shall be achieved through 3 levels of teaching: Junior level (4th year) clinical training (Two hours daily for 2 months). Senior level (5th year) clinical training (Two hours daily for 4 months). Final (sixth year) clinical training (Two hours daily for 4 months). II) Intended learning outcome of the course:(ILO) Fulfillment of the course is achieved through the following courses: Junior clinical training: 4th year By the end of this 8 weeks course (80 hours), the student should be aware of the spectrum of clinical symptomatology related to different body systems. Appreciate the clinical spectrum of common medical conditions with multi-system reflections. Able to: 1- Take a good medical history. 2- Adequately measure the vital signs. 3- Conduct a proper general examination and identify normal and major abnormal physical signs. 4- conduct proper regional examination of the chest and abdomen by inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation to identify: - Surface anatomy of internal organs. - Normal physical signs. - Major abnormal physical signs. Senior clinical training: 5th year& 6th year: By the end of this 16 weeks course (160 hours) in 5th year and 18 weeks (240 hours) in 6th year; the student should be able to: 1- Develop and present a comprehensive medical sheet including history and physical examination. 2- Develop the clinical skills of eliciting abnormal physical signs. 3- Interpret the significance and relevance of abnormal physical signs. 4- Identify the appropriate supportive investigations relevant to a particular patient and adequately interpret the results. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 120 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 5- Integrate the patient’s symptomatology, historic data, abnormal physical signs and investigations into comprehensive differential diagnosis. 6- Identify adequate logistics of further patient assessment and management. Clinical training in selected medical specialities: The student is expected to rotate among 6-8 specilities for a total of 176 hours (40 hours in 4th year, 40 hours in 5th year, and 96 hours in 6th year). By the end of each course, the student should be able to: *Become acquainted with the specialist approach to the diagnosis of common medical conditions related to the speciality. *Get exposed to less common medical disorders within the domain of the speciality. *Get update information about and demonstration on modern diagnostic tools with the speciality. *Get acquainted with special therapeutic and interventional technique related to the speciality. *Adequately interprets the results of common laboratory investigations as urine analysis, blood picture and kidney functions tests, etc. *Proper interpret ECG recordings of common conditions as ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial infarction, common arrhythmias etc. Associated activities: (from 9 am- 11.30 am) Activities MCQ Seminars Commentary cases Teaching Staff Ass. Prof. Prof. Ass. Prof. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Saturday Sunday Wednesday 121 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications III) Contents: Topic Cardiology Respiratory diseases Neurology Psychiatry Endocrinology Hematology Rheumatology GIT& hepatology Nephrology Tropical medicine Clinical pathology Dermatology Total hours Total hours 149 169 Lectures 4 5th year year 7 12 6 th th 6 year 45 46 Clinical teaching hours 4th 5th 6th year year year 10 17 58 34 42 41 124 64 76 63 126 222 4 8 6 3 15 4 16 6 9 17 22 26 32 27 32 49 8 4 7 36 12 6 4 21 41 74 38 14 16 54 64 48 54 5 12 5 16 20 26 4 - 4 - 10 - 24 - - 24 - - - 48 1167 60 91 24 373 103 147 24 393 IV) Student’s assessment methods: *At the end of each clinical round: 1-Clinical evaluation to all through attendance of the course in the form of: -Five short cases in all specialties of internal medicine -Written MCQs assessment. Final term examination( End of 6th year) includes: -Written MCQs assessment. -Sixteen questions + 4 commentary cases for short discussion in 2 separate papers (Each one includes 8 questions + 2 commentary cases). -Clinical stations assessment in various clinical cases (one long case and 5 short cases of different specialities of internal medicine). -All clinical assessment is aiming to evaluate the following parameters: -Knowledge: 35% - Skills: 50 %. - Attitude: 15 %. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 122 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications V) Teaching and learning facilities: Facilities used for teaching this course include: • Lecture halls A &B&C. -Rooms for small groups teaching. -Black and white boards. -Audio visual aids (data shows, overhead, slide projector. etc). -Electronic library -Faculty library -Beds and clinical facilities of Minia university hospital. VI) Teaching Methods: 1) Illustrated lectures: Large group plenary sessions in lecture theatres are time-tabled, 2 hours weekly. They set the scene for a particular topic, highlight important issues and, hopefully, arouse curiosity in relevant areas. 2) Seminars: Students are expected to search and prepare certain topic in a team work manner. This work will be orally presented using information technology, role play and group discussion under supervision of a senior tutor for 2 hours. Seminars are held once weekly during 6th year study. 3) Clinical Rounds: Tutors demonstrate the core practical clinical skills that are essential prelude to undertaking a confident and competent clinical history and examination of patients and the students practice these skills on patients under supervision for 3 hours daily, 5-6 days weekly. 4) Problem-based learning (PBL): Students work in small groups to study written descriptions of clinical situations. By using a specific set of study skills, they use those scenarios to guide them towards relevant theoretical and practical learning. PBL tutorials are shared learning in small groups with other students aiming at developing skills in communication, team work and leadership. 5) Tutorials: For giving introduction, indications, and interpretation of clinical laboratory tests, radiography, and electrocardiography. Groups will work on ECGs, laboratory reports and X- rays reports to identify abnormalities, interpret findings, and put diagnosis. Recommended Readings and BOOKS for Students: •DAVIDSON'S Principles and Practice of Medicine. •Clinical Medicine KUMMAR and CLARK. •HUTCHISON'S Clinical Methods. Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 123 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications •Methods of Clinical Examination, by Salah Ibrahim (AL Azhar University) •A Guide to Physical Examination, by Barbara Bates. •National books approved by the Internal Medicine committee. •CDs and Floppy disks in the electronic library of AL quasr EL-aini. Cardiology teaching 4th year teaching NO. 1- 2345- 6789- Subject The physician and his patient: Ethics in medicine Making the diagnosis History taking Date processing and recording Resources in medical knowledge: Books, periodicals, net. Case taking: -Symptomatology: -Chest pain -Dyspnea -Palpitation Acute rheumatic fever Rheumatic heart disease Infective endocarditis Congestive heart failure Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 1 2 1 1 7 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 Cardiology department Lectures Clinical 1 hour / 1 hour / week week - Total hours Cardiology department Lectures Clinical hours / hours / week week - Total hours 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 17 5th year teaching NO. 123- 456789Total Subject History taking: Case taking: -Symptomatology: -Chest pain -Dyspnea -Palpitation Acute rheumatic fever Rheumatic heart disease Infective endocarditis Congestive heart failure Hypertension Ischemic heart disease: Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical hours hours per week per week 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 12 17 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 2 2 2 1 1 1 4 4 4 4 2 2 29 124 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6th year teaching NO. 1- 234567- 89101112131415- Subject Case taking -Symptomatology -Chest pain -Dyspnea -Palpitation Local cardiac examination Acute rheumatic fever Rheumatic heart disease Infective endocarditis Congestive heart failure Ischemic heart disease: *Stable angina pectoris *Unstable angina pectoris *Acute myocardial infarction Cardiomyopathy Congenital heart diseases Arrhythmias Myocarditis Pericarditis Cor pulmonale Diseases of aorta ECG Clinical cases Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical hours/week hours 8 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 4 1 8 17 37 Cardiology department Lectures hours 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 4 28 Total hours Clinical hours/week 2 2 4 2 2 1 8 21 Total teaching hours: 149 hours Respiratory diseases teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 12- History taking Symptomatology: Dyspnea Chest pain Oedema Cough and expectoration Hemoptysis 3- General examination: Vital signs Cyanosis Pallor lymphadenopathy Examination of the neck Examination of limbs, clubbing, oedema Local examination of chest: Clinical cases: 45Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 0 21 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Chest diseases department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per week per week 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 0 13 Total hours 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 6 34 125 10 2 8 8 8 7 8 2 2 2 2 5 2 2 2 3 8 2 4 16 103 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 5th year teaching NO. Subject 12- History taking Symptomatology: Dyspnea Chest pain Oedema Cough and expectoration Hemoptysis 3- General examination: Vital signs Cyanosis Pallor lymphadenopathy Examination of the neck Examination of limbs, clubbing, oedema Local examination of chest: Clinical cases: Upper respiratory tract infections Pneumonias Tuberculosis 45678Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical hours /wk hours/ wk 2 1 1 1 1 1 -1 1 2 2 6 Chest diseases department Lectures Clinical hours/ wk hours/ wk 2 1 1 1 1 1 -- 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 1 2 23 2 4 4 2 19 Total hours 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 8 8 1 3 6 48 6th year teaching NO. Subject Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 4 4 1 4 Chest diseases department Lectures 2 hours per week 3 4 - Total hours Clinical 2 hours per week 2 3 - 1234- Bronchial asthma COPD Upper respiratory tr. infections Pneumonias 5- Suppurative lung diseases: -Lung abscess -Bronchiectasis - Empyema -Cystic fibrosis 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 - 1 1 1 - 3 3 3 2 678910- Tuberculosis Interstitial lung diseases Respiratory failure Bronchial carcinoma Lungs in systemic diseases 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 4 3 3 - 4 2 3 - 12 9 2 6 4 11- Pleural diseases: - Effusion - Pneumothorax - Malignancy 1 1 2 26 2 2 2 21 1 1 1 20 1 1 1 20 5 5 6 87 Total 7 15 1 4 Total teaching hours: 169 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 126 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Gastroenterology and hepatology teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 12- History taking: Symptomatology: Abdominal pain Dysphagia / heart burn Vomiting Dyspepsia GIT hemorrhage Diarrhea Constipation Jaundice General examination: Local examination of abdomen: Clinical cases: Gastroenteritis: Helicobacter infections: Diarrhea disorders: 345678Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 2 2 2 9 18 Tropical diseases department Lectures Clinical 1 hours 2 hours per week per week 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 2 2 -2 6 18 Total hours Tropical diseases department Lectures Clinical 1 hours 2 hours per week per week 1 2 2 2 2 4 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 Total hours 51 5th year teaching NO. Subject 12- Abdominal case taking: Symptomatology: Abdominal pain Dysphagia / heart burn Vomiting GIT hemorrhage Diarrhea / Constipation Jaundice General examination: Local examination: Clinical cases: Bilharzial liver disease Chronic hepatitis Hepatic cirrhosis Portal hypertension Ascites and peritoneal diseases Hepato-cellular failure 34567891011Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 9 22 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 1 8 2 19 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 5 4 4 8 1 2 5 5 5 4 5 58 127 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6th year teaching NO. Subject Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 12- 34- Abdominal case taking: Symptomatology: Abdominal pain Abdominal distension Dysphagia / heart burn Vomiting Dyspepsia Gastrointestinal hemorrhage Diarrhea -Constipation Jaundice General examination: Local examination: 567891011- Esophageal disorders Gastro-esophageal junction dis. Peptic ulcer Non- ulcer gastric diseases Disorders of gastric motility Upper GIT bleeding Gastrointestinal malignancy 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 - 121314151617181920- Jaundice Acute hepatitis Chronic hepatitis Hepatic cirrhosis Portal hypertension Ascites and peritoneal diseases Hepato-cellular failure Hepatic focal lesions Gall bladder diseases 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 2122232425Total Diarrhea and dysentery Functional colonic disorders Inflammatory bowel diseases Mal-absorption syndromes Pancreatic diseases 2 2 2 2 2 35 2 4 2 2 4 2 32 Tropical diseases department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per per week week 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2 4 2 2 2 2 14 32 Total hours 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 1 1 2 2 1 6 1 6 4 4 12 8 5 10 5 1 4 2 4 4 2 113 Total teaching hours: 222 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 128 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Rheumatology teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 1- 1-Regional pain syndrome *Upper limb * Cervical spine 2- Regional pain syndrome *Lower limb *Thoracic spine *Lumbar spine 3- Evaluation of patient with rheumatic diseases: 4Total Clinical cases: Internal medicine department Lectures 1 hour per week - Clinical 10 hours per week 2 0 2 4 Rheumatology and rehabilitation department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 1 1 1 3 3 3 Total hours Rheumatology and rehabilitation department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 1 3 Total hours 1 1 6 2 10 5th year teaching NO. 1- Subject Classification of rheumatic diseases -Soft tissue rheumatism 23- Mono & polyarticular joint disease 4- Basic immunology & immune diseases 56- Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus erythematosus Clinical cases 7Total Internal medicine department Lectures 1 hour per week 2 2 Clinical 10 hours per week 2 2 6 2 4 8 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 4 1 3 4 1 3 3 - 4 4 13 2 4 4 8 30 129 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications 6th year teaching NO. Subject Internal medicine department 1- 1-Rheumatoid arthritis 2- Sero-negative spondyloarthropathies Ankylosing - reactive 3- Sero-negative spondyloarthropathies Psoriasis & inflammatory bowel disease Lectures 2 hours per week 2 2 2 - Clinical 10 hours per week 2 - 2 - Rheumatology and rehabilitation department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per week per week 1 3 1 3 1 3 1 3 Total hours 8 6 8 8 4- Systemic lupus erythematosus 2 2 5- Scleroderma 2 2 1 3 8 6- Dermatomyositis and polymyositis 2 2 2 2 - 1 3 8 1 - 3 1 3 6 1 3 - 4 3 1 7- Vasculitis 8- Juvenile chronic arthritis 9- Degenerative joint diseases: -Osteoarthritis - Cervical and lumbar spondylosis 10- Crystal induced arthritis: 1 11- Metabolic bone disease (osteoporosis and others) 2 - - 12- Drugs in rheumatic diseases 2 - 1 13- Rehabilitation of rheumatic diseases: - - 1 - 14- Local examination of locomotor system Clinical cases: - 2 - 4 6 19 6 20 13 6 34 12 86 15Total 1 1 - 2 3 Total teaching hours: 126 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 130 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Hematology teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 12- Hematopoiesis Anemia: -Types -Investigations Lymphadenopathy 3Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 2 2 2 2 6 4 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per week per week -- Total hours Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per week per week -- Total hours 2 4 4 10 5th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Bleeding disorders: Purpura (types) Anticoagulants Blood transfusion Splenomegaly Lymphadenopathy 2345- Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 6 4 - - 2 4 4 10 6th year teaching NO. Subject 123456789101112Total Hematopoiesis Anemia Lymphadenopathy Acute leukemia Myeloproliferative disorders Chronic leukemias Aplastic anemia Bleeding disorders Anticoagulants Antiplatelets Blood transfusion Lymphomas Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 4 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2 4 4 2 2 1 2 4 27 16 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 2 hours per week per week -- Total hours 2 6 2 4 4 4 2 8 2 2 1 6 43 Total teaching hours: 63 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 131 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Endocrinology teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 123Total Vitamins and minerals Nutritional deficiency Obesity Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 4 2 8 - Special medicine department Lectures Clinical - -- Total hours 2 4 2 8 5th year teaching NO. Subject 12345- Thyroiditis Thyrotoxicosis Hypothyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Tetany and calcium homeostasis Metabolic bone diseases Goiter 67Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 16 6 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical -- -- Total hours 2 6 4 2 2 2 4 22 6th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Pituitary gland diseases: Acromegaly & gigantism Cushing disease Infantilism Sheehan's syndrome Hypo-pituitary disorders Diabetes insipidus & SIADH Stunted growth Thyroid disease: -Thyrotoxicosis -Hyperthyroidism -Hypothyroidism Cushing disease Addison's disease Pheochromocytoma Diabetes mellitus Dyslipidemia Gonadal disorders 23- 456789Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 2 hours 10 hours per week per week 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 1 2 32 14 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical --- -- Total hours 4 4 2 2 2 2 4 4 4 4 4 2 1 4 1 2 46 Total teaching hours: 76 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 132 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Neurology teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Neuro-anatomy & physiology Cranial nerve disorders Case taking: Neurological examination 234Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week - Neurology and psychiatry department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 2 2 4 4 4 8 Total hours 2 2 4 4 12 5th year teaching Subject Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week - NO. 1234- Brain tumors, headache and migraine Case taking: Neurological examination Case formulation and DD Total - Neurology and psychiatry department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 4 4 4 4 - 4 12 6 year teaching NO. 1234567891011121314151617181920- Total Case taking: Neurological examination Case formulation and DD Cerebro-vascular stroke Cranial nerves lesions Extra-pyramidal syndromes Involuntary movements Epilepsies Demyelinating disorders Intracranial infections Diseases of spinal cord Peripheral neuropathy and radiculopathies: Diseases of muscles Proximal limb weakness Distal limb weakness Degenerative and developmental disorders: Alzheimer disease Ataxia Metabolic encephalopathies Neuro-investigations: Adult EEG reading Brain CT reporting CSF report prime assessment Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week -2 2 - Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Neurology and psychiatry department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 4 4 4 3 8 4 2 4 2 2 1 2 2 2 8 2 2 4 4 4 4 16 th Subject Total hours Total hours 4 4 4 11 4 6 2 2 3 2 10 4 2 3 1 - 2 8 6 8 8 - 4 8 6 3 1 8 2 8 - 20 74 96 133 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Total teaching hours: 124 hours Psychiatry teaching 4th year teaching NO. Subject - - Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week - Total - - Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week - - Total hours - 5th year teaching NO. Subject - - Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week - Total - - Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week - - Total hours - 6th year teaching NO. Subject 12345- Theoretical part: General psychiatry Classification system Logarithm of diagnosis Intersections with organic medicine: Mood (affective) disorders: Somatoform, stress related and anxiety disorders: Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders: Child psychiatry: Geriatric psychiatry: Treatment modalities: Symptoms and signs: Case taking: Case analysis: Interview of patients with different diagnosis: 6789101112131415Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week -- - Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 32 26 38 Total hours 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 32 64 Total teaching hours: 64 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 134 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Nephrology lectures 4th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Symptoms and signs of renal disease Investigations of renal disease Urinary tract infection and reflux uropathy 23Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 1 2 2 2 5 2 4 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week -- Total hours 3 4 2 9 5th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Symptoms and signs of renal disease Investigations of renal disease Nephrotic syndrome 23Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 1 2 2 2 5 2 4 Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week -- Total hours Special medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week ---- Total hours 3 4 2 9 6th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Symptoms and signs of renal disease Investigations of renal disease Acute renal failure Chronic renal failure Urinary tract obstruction Urinary tract infection Nephrotic syndrome Acute nephritic syndrome Diabetic nephropathy Water, electrolytes and acid base balance Drugs and the kidney Renal replacement therapy Kidney in systemic diseases 2345678910111213Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 20 2 2 2 2 10 3 4 2 4 1 1 4 1 1 2 2 1 4 30 Total teaching hours: 48 hours Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 135 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Tropical medicine lectures 4th year teaching Subject NO. 1234Total General presentation of fevers Pyrexia of unknown etiology (PUO) Chemotherapy: Nutritional disorders: Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 2 2 4 - Tropical medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week 2 -2 2 2 8 - Total hours Tropical medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week -1 1 1 2 1 1 1 8 Total hours Tropical medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 2 hours per week per week -1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 - Total hours 2 4 2 4 12 5th year teaching Subject NO. 1- Bacterial infections: -Salmonelosis -Brucellosis -Cholera -Current epidemic bacterial infections Chemotherapy: -Antibacterial drugs -Antiviral drugs -Antifungal drugs 2- Total Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 1 1 1 1 -2 1 1 8 - 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 16 6th year teaching NO. Subject 1- Bacterial infections: Enteric fever Brucellosis Meningitis Cholera and tetanus Parasitic infections: Schistosomiasis Amoebiasis Malaria Leishmaniasis Fasciolasis Filariasis Viral infections: HIV infection Rabies Pyrexia of unknown etiology (PUO): Physical agents hazards: 2- 3- 45- Internal medicine department Lectures Clinical 1 hour 10 hours per week per week 1 1 1 1 -1 1 1 1 2 - Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 4 1 136 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University 6- Vaccines: Total Cours Specifications - - 1 10 - 16 - 1 26 Total teaching hours: 54 hours Clinical pathology teaching Academic year/ level 6th year medical students - One hour lecture/ week throughout the year (1 X 4 X 6 = 24 hours/ year). Lectures topics: NO. 1- 2- 3- 4- Subject Hematology: -Anemias -Leukemias -Hemostasis -Blood banking Biochemistry: -Carbohydrate metabolism -Protein metabolism -Lipid metabolism -Liver function tests -Kidney function tests -Hormones -Acid-base balance & Blood gases -Minerals and trace elements -CSF examination Immunology: -Basic immunology -Immuno-globulins & B& T lymphocytes - Serology - Autoimmunity -Hypersensitivity reactions -Anaphylaxis Microbiology: - Collection of samples - Bacteria identification & Cultures - Virology - Mycology - Molecular biology Total Sessions Hours 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 24 1 1 1 1 1 24 Total teaching hours: 24 hours Weighing of assessment: - Final-term written exam. -Final- term oral exam. 60% 40% Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 137 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Cours Specifications Dermatology and venereal diseases teaching Academic year/ level 6th year medical students A)Teaching and learning methods: 1- One hour lecture per week throughout the year (1 X 4 X 6 = 24 hours per year). 2- Two hours daily clinical round for 2 continuous weeks for clinical case demonstration and practical training (2 X 6 X 2=24 hours for two groups sections X 2 for whole group of student = 48 hours totally per year). Topics Dermatology A) Introduction to dermatological disease B) Parasitic diseases: Scabies Pediculosis C) Bacterial infections: -Impetigo -Erysipelas -Cellulitis -Intertrigo -Pycosis vulgaris -Furunculosis -Carbuncle -Erythema D) Leprosy: E) Tuberculosis of the skin: F) Fungus diseases of the skin: -Tinea capitis -Tinea barbae - Tinea cruris - Tinea corporis - Tinea pedis - Tinea versicolor - Candidiasis - Onychomycosis G) Viral diseases: -Herpes simplex -Chicken pox -Herpes zoster -Warts -Molluscum contagiosum H) Allergic diseases of the skin: - Eczema -Urticaria - Papular urticaria -Prurigo of hebra -Erythema multiforme -Erythema nodosum - Drug eruption I) Erythemato-squamous eruptions: - Pityriasis rosea - Psoriasis - Pityriasis rubra pilaris - Lichen plannus NO. of hours 32 Lectures 12 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System Practical hours for each section group of students 20 138 Faculty of Medicine, Minia University J) Sebaceous glands diseases: - Seborrheic dermatitis - Acne vulgaris K) Sweat glands disorders: - Miliaria L) Diseases of the hair: - Cicatricial alopecia - Non- cicatricial alopecia - Alopecia areata M) Collagen diseases: - Discoid lupus erythemat. N) Disturbances of melanin pigmentation: - Vitelligo Venereology: Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) -Anatomy of male sex organs -Diseases of male sex organs -Prostatitis -Seminal vesicles -Cowperitis -Gonorrhea -Urethral stricture -Syphilis -Chancroid -AIDS (HIV infection) Andrology: -Physiology of spermatogenesis - Semen analysis (normal semen parameters) Total Cours Specifications 9 7 2 7 5 2 48 24 24 Total teaching hours: 48 hours B) Assessment Schedule of dermatology and venereal diseases: Assessment 1:mid-term exam. in 20th Week Assessment 2:final-term exam. in 40th Week C) Weighing of assessment: - Mid-term clinical exam. - Mid-term oral exam. - Final-term clinical exam. -Final- term oral exam. 5% 15% 20% 60% Course Co-ordinator Head of the internal medicine department Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Motawea Date: 2010 Implementation of Internal Quality Assurance System 139