Online Karyotyping Activity - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

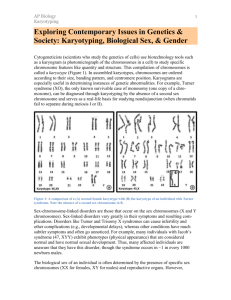
Online Karyotyping Activity Name_____________________________________________ Per____ Site 1: Online Karyotyping Activity Go to www.biology.arizona.edu - Click on the blue word “Karyotyping” found in the far left menu under the green “Activities” section. You can select English or Spanish for this activity. In this activity, you will use a computer model to look at chromosomes and prepare a karyotype, which is a map of all the chromosomes. You will diagnose patients for abnormalities and learn the correct notation for characterizing karyotypes. Introduction: Read the paragraphs and answer these questions. 1. What causes a dark band on the chromosome? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is a centromere? _________________________________________________________________ 3. Why are karyotypes useful? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Patient Histories: Click on the “Patient Histories” button. You’ll complete a karyotype for Patients A & B Patient A – 4. What is patient A's history? Patient A is the nearly-full-term _________________ of a forty-year-old female. Now, click “Complete Patient A’s Karyotype.” 5. Match the chromosome to its homologous pair (its matching partner). After all the matches are complete, you'll analyze your patient. (Scroll down to view your completed karyotype). When you are finished placing the chromosomes on the karyotype, answer this: How many total chromosomes are in Patient A’s karyotype? Count them: _________ 6. The last set of chromosomes that do not have any number is the sex chromosomes. If you see two large chromosomes, your patient is XX (female), one large and one small indicates an XY (male). What sex chromosomes does Patient A have? _____________ 7. Which chromosome number has an extra chromosome (instead of two chromosomes, you see three)? _______ 8. What diagnosis would you give this patient (what chromosomal abnormality do they have)? __________________________________ Patient B – Click on the link to go to Patient B and repeat the above process to create Patient B’s karyotype. 9. What is patient B's history? Patient B is a 28 year old male who is trying to find a cause for his _________________________. Now, click “Complete Patient B’s Karyotype.” 10. Match the chromosome to its homologous pair (its matching partner). After all the matches are complete, you'll analyze your patient. (Scroll down to view your completed karyotype). When you are finished placing the chromosomes on the karyotype, answer this: How many total chromosomes are in Patient B’s karyotype? Count them: _________ 11. The last set of chromosomes that do not have any number is the sex chromosomes. If you see two large chromosomes, your patient is XX (female), one large and one small indicates an XY (male). What sex chromosomes does Patient B have? _____________ 12. Which chromosome number has an extra chromosome – the small Y chromosome or the large X chromosome? _______ 13. What diagnosis would you give this patient (what chromosomal abnormality do they have)? __________________________________.