DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD'S ATTACHMENT
advertisement

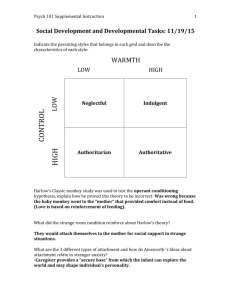
Running head: DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 1 Do parenting styles affect the child’s attachment style? Marcellus Colton University of Kentucky DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 2 Abstract Do parenting styles moderate children’s ability to communicate? Does the type of parenting style dictate the type of child they will become: a popular kid, adventurous kid/trouble maker, or a student who excels academically? This paper discovers the answers associated with these questions. It examines the attachment styles of 200 undergraduate students and 213 young adults using a series of questionnaires. It analyses these types of parenting styles and determines which style is better and which style has a better outcome on the child. It first looks at the three types of parenting styles: authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive. It analyses these types of parenting styles associated with the style and determines which is better and which style has a better outcome on the child. DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 3 Does parenting styles affect the children’s attachment style? No one actually knows how to teach and guide his or her children to success. Parenting is an on job training job; Everyday parents learn how to communicate and teach. With every child, the parent uses a different technique to mold its child to success. What is the best parent style to communicate with future offspring? Which parenting style is effective and ineffective? Do parenting styles affect the child’s attachment styles? There are two dimensions of parenting, parental acceptance and parental control. Parental acceptance is accepting the child’s feelings and opinion. Parental control is the chastisement of the child if the child expresses transgression through the rules the parents implied. The variations in the parent dimensions are defined as parenting styles Akhtar (2012). The parenting style of the interaction of parental acceptance and parental control are broken down in three parts: authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive. Authoritative Parenting Style is distinguished by placing strong ambitions and goals for their offspring. These parents are involved in children’s lives and they encourage their child with warmth and comfort. They want their child to reveal all parts of their life and interaction; they are willing to negotiate standards and provide less restriction on the before offspring. Authoritarian Parenting Style, the parent has low acceptance and high control over their offspring. They place rules for the children to follow and when offspring expresses transgression, they are punished. They believe that children should follow the rules emplaced in the household. They do not believe in comforting the child, but setting rules so they can protect their child and teach them the ways of life. Permissive Parenting Style is distinguished by providing few demands and exhibiting non-controlling behavior. They provide minimum punishment to their offspring. They want their children to learn from their mistakes but when they have to take charge, they will accept their position. If the actions of the DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 4 child do not bring harm, they will not step up and exhibit that parent role. They will give their offspring much freedom, hoping they can learn from their mistakes Akhtar (2012). There are various types of parenting styles that affect children’s attachment patterns, they are known as attachment styles. Attachment styles dictate how people interact in close relationships. There are three different types of attachment styles: secure, anxious, and avoidant. Secure attachment style is receiving a series of words that express the warmth feeling by making the person feel comfort and support. To compare this attachment style with parent and child relationship, the parent will exemplify an Authoritative Parenting Style Akhtar (2012). Anxious attachment style is an inconsistent response reflected. The parenting style is closely related to this attachment style is Authoritarian. People are fearful for their actions because they do not understand the outcome. They learn life through mistakes. They are not afraid to make friends but people are scared away by pursued idea of intimacy Akhtar (2012). Avoidant attachment style is the rejection of intimate relationships. They are fearful of getting hurt. They did not experience the comfort from their parents and can show resentment. It is understood that the child can become inconsistent after leaving the parents’ training. They feel the closer the person is to them, the more acceptable they are of getting their feelings hurt. They rather avoid the intimacy level to prevent rejection Akhtar (2012). Does the three parenting styles serve as moderators of the association between family conformity orientations, young adults’ self esteem, and depression? Conformity orientation is the degree to which family communicates and stresses a climate of homogeneity of attitudes, values, and beliefs. These relational schemata have influences on relationships and communication outside of the family interactions; it also has important implications on their psychological wellbeing (Hamon and Schroft, 2012). A conversation orientation refers to the degree to which DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 5 families create a climate in which all family members are encouraged to participate in unrestrained interactions about a wide array of topics. When families create an environment whereas, it is comfortable to disclose information; it will establish a high family conversation orientation. Families hold or share the same conceptions of life. They generally share the same norms and belief systems, which guided by the family members’ interactions. When families create a hostile environment whereas, it is uncomfortable to disclose information; it will establish a low conversation orientation. Families create individual beliefs systems and norms. They will emphasize equality among the family members (Hamon and Schroft, 2012). Different research studies were conducted to investigate the impact of parenting on child’s personality. In the research, it uses a series of questionnaires to discover the affects of the parenting style and family conformity on children’s behavior (Hamon and Schroft, 2012). In one research, two hundred students age ranging from fifteen to eighteen were selected as a cluster sampling technique. The hypothesis of the study is that authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting style of the father and mother has significant relationship with secure, anxious, and avoidant attachment style Akhtar (2012). The results stated that Authoritative Parenting style has no relationship with secure, anxious, and avoidant attachment style. Karavasilis, Doyle, and Markiewicz (2003) stated that positive association between authoritative parenting style and secure attachment style. The result of this experiment contradicts the findings of Rohner (1975). He said warm and accepting behavior of parents does not elevate aggression in children and adults. Authoritarian parents’ children developed anxious attachment styles. The children are reluctant to make intimate relationship with their parents. They feel their parents should be treated as parents. The parent’s tolerance for low acceptance is reflected in the fear of rejection through the DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 6 child. The children that expressed anxious attachment styles have listed their parents as unhappy. Coh, Cowan, and Pearson (2008) said insecure parents provide less structure in instruction with children as compared to secure parents Akhtar (2012). Permissive parents’ children develop avoidant attachment styles. The reason children development this attachment is because most participants stated that their father was not around. They experience a feeling of emptiness because they did not receive the support from their father. They are content with everyone entering and leaving their life. They do not feel stability in their relationships. Therefore, children believe that is better to avoid intimate relationship avoid the feeling of rejection and acceptance Akhtar (2012). In the second study, participants included two hundred thirteen young adult children. The hypothesis of this study tested the degree to which adults’ perceptions of parenting styles moderate the associations between family conformity orientation and their mental well-being: self-esteem and depression. It uses two separate sets of hierarchical regression analysis and they used the two variables: self-esteem and depression (Hamon and Schroft, 2012). The results of the conducted experiment did not provide any conclusive evidence to the hypothesis. However, the parents’ authoritativeness and permissiveness styles revealed small amounts of an effect of the child. When the parent provided warmth and comfort, the child expresses the comfort for affection from their mother and father Akhtar (2012). Overall, both of the experiments have concluded an overall assumption. When parents choose authoritarian and permissive parenting style, it does have an effect on the offspring. Authoritarian parents’ children developed anxious attachment styles and Permissive parents’ children develop avoidant attachment styles. However, the results do not determine which parent style is better. The results do not provide a clear answer on which parenting style is effective or DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 7 ineffective. The way parent’s raise their kids does determine the person they will become or somewhat influence their attachment. Based on the level of positive or negative reinforcement the parent provides, one can perceive it provides smalls amounts of influence. Overall, the parenting styles do not have an effect on the attachment styles of children. DO PARENTING STYLES AFFECT THE CHILD’S ATTACHMENT STYLE? 8 References Akhtar, Z. (2012). The effect of parenting style of parents on the attachment styles of undergraduate students. Language in India, 12(1), 555-566. Coh, D. A., Cowan, P. A., Cowan, C. P. and Pearson, J. (2008). Mother's and father's working models of childhood attachment relationships parenting style and child behavior. Development and psychology, 4, 417-431. Hamon, J. D., & Schrodt, P. (2012). Do parenting styles moderate the association between family conformity orientation and young adults mental well-being?. Journal of family communication, 12(2), 555-566, 151-166. Doi:10.1080/15267431.2011.561149 Karavasilis, L., Doyle, A. B., and Markiewicz. (2003). Associations between parenting style and attachment to mother in middle childhood and adolescence. International journal of behavioral development, 27: 153-164. Rohner, R. P. (1975). They love me, they love me not: A worldwide study of the effects of parental acceptance and rejection. New Haven, CT: Human relations area files.