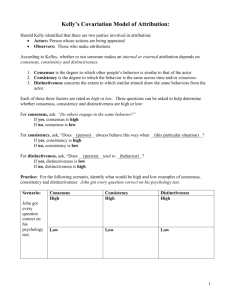
Kelley's covariation model states that perceivers use information
advertisement

Questions 1 and 2 below were developed by the TA from the text. Questions 3 and 4 were developed by Dr. Madon based on material covered in lecture. 1. Kelley’s covariation model states that perceivers use information form three dimensions when making attributions for another’s behavior. These three dimensions are: a. b. c. d. e. f. instinctiveness, consensus, consistency stability, distinctiveness, consensus inconsistency, consensus, distinctiveness uniqueness, inconsistency, consensus consensus, distinctiveness, consistency none of the above 2. According to Jones & Davis’ correspondence inference theory, in order to understand and predict the behavior of another, it is useful to know his/her ______. a. b. c. d. e. f. mood disposition locus of control inconsistencies occupation none of the above 3. Lepper, Greene & Nisbett (1975) observed that children get intrinsic rewards for playing with magic markers, and wondered whether the kind of attributions that children make might influence their tendency to engage in this behavior. They assigned children to an expected reward group, an unexpected reward group and a control group, and then assessed how much the children played with the magic markers in subsequent days. The findings of their research suggest which of the following implications? a) paying students for good grades will improve their school performance b) paying students for good grades will undermine their school performance c) positive reinforcement for good grades enhances children's self-esteem d) external attributions increases how intrinsically rewarding an enjoyable activity is e) rewards influence intrinsically enjoyable activities more than extrinsically enjoyable activities f) children self-verify their attitude toward playing with magic markers regardless of reward contingencies 4. Which of the following statements explains why the probabilistic view of schemas allows for the possibility that schema members may vary in typicality. a) it proposes that there are necessary, but not sufficient features needed for an instance to be categorized as a schema member b) it proposes that schema members share a family resemblance c) it proposes that an instance must have a minimum number of features in common with schema members to be categorized as a schema member d) it proposes that there are necessary and sufficient features needed for an instance to be categorized as a schema member e) a and c f) none of the above