Taxonomy Lab ()
advertisement

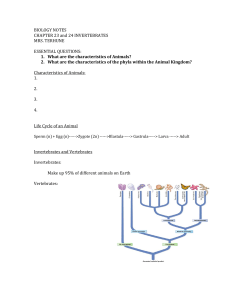
Date: ____________________ Biology Name: __________________________ Taxonomy and Phylogeny Lab Introduction: Taxonomy is used by biologists to name and classify all the various different species on the planet. The process of identifying organisms is difficult because there are so many of them. One of the tools used in biological identification is called a KEY. There are a number of different kinds of keys. The one we will use here is called a Dichotomous Key. The word dichotomous means “separating into two pairs,” and it describes the kind of choices you must make in using such a key. Objectives: Identify characteristics of organisms that are helpful in classification Introduction to the use of a Dichotomous Key Domain → Eukarya Kingdom → Animalia Figure 1: Human Taxonomic Classification Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Genus → Homo Species sapiens Vocabulary for Taxonomy Lab Radial symmetry Invertebrate vs. vertebrate Exoskeleton Cartilaginous vs. bony skeleton Segmented Antennae Tentacles Jointed legs Procedure: 1. You will find several numbered stations arranged around the room with labeled common names of various species. Listen to your teacher about how to switch stations. MAKE SURE that you write the correct labeled common names in Chart 1. 2. Place the common name in the space next to its number in Chart 1. 3. Use your Dichotomous Keys 1, 2 or 3 to go through the characteristics of your specimen. 4. Record in Chart 1 under “Dichotomous key steps” the steps you took to find the Phylum and/or Class of your specimen (e.g. 1a., 2b.) 5. Record in Chart 1 correct Phylum for your specimen. If your specimen falls under either Phylum Chordata or Arthropoda also record its Class in Chart 1. 1 Key 1: Dichotomous Key to selected Invertebrate Phyla – For Organisms 1-10 1a. Body Symmetry radial………………………………… go to 2 1b. Body Symmetry not radial…………………………….. go to 3 2a. Tentacles present, soft body…………………… Phylum Coelenterata 2b. Tentacles absent……………………………….. Phylum Echinodermata 3a. Exoskeleton present…………………………………… go to 4 3b. Exoskeleton absent……………………………………. go to 5 4a. Jointed legs present……………………………. Phylum Arthropoda (go to Key 3) 4b. Jointed legs absent……………………………... Phylum Mollusca 5a. Body segmented……………………………………….. Phylum Annelida 5b. Body not segmented…………………………………… Phylum Platyhelminthes Key 2: Dichotomous Key to the Classes of the Phylum Chordata – For Organisms 11-16 1a. Hairs present…………………………………………… Class Mammalia 1b. Hairs absent……………………………………………. go to 2 2a. Feathers present………………………………... Class Aves 2b. Feathers absent………………………………… go to 3 3a. Jaws present……………………………………………. go to 4 3b. Jaws absent…………………………………………….. Class Agnatha 4a. Paired fins present……………………………… go to 5 4b. Paired fins absent………………………………. go to 6 5a. Skeleton bony…………………………………………... Class Osteichthyes 5b. Skeleton cartilaginous………………………………….. Class Chondrichthyes 6a. scales present…………………………………… Class Reptilia 6b. scales absent……………………………………. Class Amphibia Key 3: Dichotomous Key to the Classes of the Phylum Arthropoda 1a. Walking legs, more than 5 pairs……………………….. go to 2 1b. Walking legs, 5 or fewer pairs…………………………. go to 3 2a. Legs, 1 pair per body segment…………………. Class Chilopoda 2b. Legs, 2 pairs per body segment…………………Class Diplopoda 3a. Antennae present……………………………………….. go to 4 3b. Antennae absent………………………………………... Class Arachnida 4a. Antennae, 1 pair………………………………... Class Insecta 4b. Antennae, more than 1 pair…………………….. Class Crustacea 2 Taxonomy Chart 1 # Organism common name Dichotomous key steps Phylum Class 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 3 Analysis Questions: 1. Use Keys 2 and 3 to figure out which Class the following organism description would be classified under. a. A hairless organism that has no feathers. A jaw is present and paired fins. After dissection the scientist notices a bony skeleton. ___________________________ b. This organism has many legs but not more than 3 pairs. Only one pair of antennae is present. ___________________________ c. This organism has a backbone and is hairy. It has two pair of limbs and through dissection the scientist observes a bony skeleton. __________________________ d. This organism is warm blooded but not hairy. The outer coat of the organism is covered in feathers. ___________________________ 2. Compare Figure 1 showing human classification from the first page of this lab to Figure 2 below. Explain TWO inferences you can make about the three different organisms listed in Figure 2 based on Figure 1. Figure 2: Taxonomic Classification of Three organisms Domain → 1. Eukarya 2. Eukarya 3. Eukarya Kingdom → Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum → Chordata Chordata Chordata Class → Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order → Primates Primates Primates Family → Hominidae Hominidae Hominidae Genus → Pan Pongo Gorilla Species troglodytes borneo gorilla Inference #1: ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Inference #2: ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 3. Pick one characteristic from all of the different species you observed in the lab (Chart 1). Explain how this characteristic is an adaptation that helps the organism survive. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Choose two organisms from the different species you observed in the lab (Chart 1) that you feel might interact in an environment. Describe what you might observe in this interaction. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4 5. Based upon the basic anatomical differences of the following phyla complete the phylogenic tree below: coelenterata, annelida, chordata, platyhelminthes & arthropoda. Remember the further back (to the left) means older and less related. Phylogenic Tree of Five Animal Phyla 6. Using a specific anatomical feature (e.g. exoskeleton, jointed legs) from the lab, explain why you chose the phyla for A and B. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. Using a specific anatomical feature (e.g. exoskeleton, jointed legs) from the lab, explain why you chose the phyla for D and E. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. Explain what “x” represents on the tree? __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5