Traditional Neurological Examination
advertisement

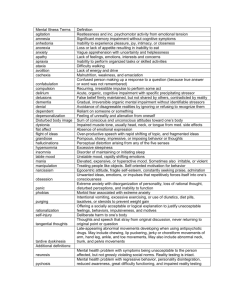
Albuquerque Public Schools Modality Mental Status Cranial Nerves Table 1 Traditional Neurological Examination Examiner Items Possible Pathological Signs Alertness/responsiveness Speed and overall appropriateness of responses to examiners questions Listlessness, lethargy, confusion, agitation combativeness General Knowledge Familiarity with issues of common knowledge Confusion, incorrect or absent answers Mood/Affect Orientation General physical appearance; apparent emotional state Correct knowledge of date, location and name Poor hygiene, disheveled, sadness, depression, euphoria, hostility Incorrect or absent responses to questions Motor Resting muscle tone, strength and mobility Weakness, paralysis, asymmetrical, facial musculature, drooping of eyelids, mouth Extra-occular movements Strabismus (fixed or intermittent deviation of one or both eyes), nystagmus (fine darting movements of eyes during visual pursuit) Pain (pin prick) Decreased or absent sensation Simple touch Decreased sensation, poor discrimination Visual and Auditory acuity Decreased hearing or vision Pupillary responses Unequal papillary size; absent, decreased or unequal papillary constriction to light stimulus Decreased or absent sensation Sensory Smell and taste Cranial Nerves Gross and Fine Motor Sensation Stance & Gait Reflexes Fundoscopic . Inspection of optic disc (head of optic nerve) Inspection of Retinal and retinal blood vessels Pallor, edema (swelling) Resting muscle tone Palpation of muscles and resistance to passive movement Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone) Hypertonia (increased muscle tone) Muscle Strength Ability to flex and extend against resistance Weakness or paralysis Pain Pin prick Decreased or absent response Temperature Hot/cold application Poor discrimination Touch Touch with Q-tip Poor localization Proprioception Position/movement in space Inability to determine direction of movement Stereognosis Discrimination of size/shape Inability to recognize common objects by size/shape Two point discrimination Simultaneous touch in 1 or 2 place Poor discrimination/localization 'Cerebellar" functions Normal gait, heel, tip-toe and tandem (includes assessment of gait cerebellum, vestibular system and basal ganglia) Coordination/smoothness of movements Hemorrhage, narrowed blood vessels Ataxia (broad based "drunken" gait) Tremors, irregularity, inconsistent rhythms Rhomberg sign Inability to maintain stance with arms extended, feet together and eyes open Deep Tendon Reflexes Tapping on tendons at knee, heel and elbow with percussion hammer Increased, decreased or asymmetrical reflexes Babinski Reflex Light scratching on lateral surface of sole with sharp object Upper movement of great toe and fanning of other toes * Not comprehensive but examples of possible questionable/abnormal findings 232 * JOSH 0 August 1984, Vol. 54, No. 7 6-95/neuroexm Section IV: Screening and Assessment APS Nursing Manual Page 1 of 3 Albuquerque Public Schools Table 2 Neurological Soft Signs* Gross Motor Fine Motor Sensory Test Items 1. Normal walking/running gait Abnormal Result Stiff legged; foot slapping quality. Unusual posturing of arms. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Difficulty in remaining on heels (10 ft.) Difficulty remaining remaining on toes (10 ft.) Difficulty walking heel to toe. Unusual posturing of arms (10 ft.). Inability to remain standing on one foot for more than 5 -10 seconds. Inability to rhythmicalIy hop on ea.ch foot alternatively. Difficulty in maintaining stance with arms extended in front, feet together and eyes closed: drifting of arms: mild writhing movements of hands/fingers. Heel walking Tip-toe walking Tandem gait One foot standing Hopping in place Motor-stance persistence 1. Visual tracking Difficulty in visually following with eyes from side to side without moving head; nystagmus (fine darting movement of eyes) 2. Rapid opposition of fingers Difficulty in rapidly opposing thumb to fingers in sequence; overflow to other hand 3. Rapid alternating movements of Irregular speed and rhythm hands 4. Finger-nose test Inability to consecutively touch examiner's finger and own nose 1. Right-left discrimination Inability to identify right and left sides of self or examiner 2. Two point discrimination 3. Graphesthesia Reflexes 1. Deep tendon reflexes 2. Plantar reflex Difficulty in localizing/discriminating when touched in one or two places Inability to identify geometric shapes drawn with examiner's finger on child's open palm. Asymmetric reflex responses Upward movement of great toe and fanning of other toes on stimulation of sole (Babinski reflex) Table 3 Developmental and Neurological Soft Signs Developmental 1. Synkinesia-inability to suppress mirror movements of hand not being tested on rapid thumb to finger opposition 2. Diadochomkinesia - uneven irregular movements in rapid movements in hands 3. Difficulty in hopping, heel-toe walking, poor rhythm foot dropping 4. Uneven irregular visual tracking 5. Poor right-left discrimination Neurological 1. Subtle abnormalities of muscle tone (mild flaccidity or rigidity) 2. Asymmetrical deep tendon reflexes 3. Mild choreoathetosis writhing movements of hands/fingers on testing of motor stance persistence Table 4 Neurodevelopmental Evaluation* Behavioral: 1. Selective attention 2. Distractibility Affective: 1. Anxiety 2. Spontaneity Fine Motor: 1. Imitative finger movements 2. Motor speed 3. Impulsivity 4. Motor activity 3. Self stability 4. Rapport 3. Finger opposition Section IV: Screening and Assessment APS Nursing Manual Page 2 of 3 Albuquerque Public Schools Orientation: 1. Identification of body parts Gross Motor: 1. Motor stance Fine Visual-Motor: 1. Visual matching 2. Discrimination of shapes (stereognosis) 2. Rapid alternating movements 2. Sentence copying 3. Visual tracking 3. Heel/toe walking 3. Visual tracking Visual Processing: 1. Visual matching 4 Tandem gait 5. Catching ball Sequential: 1. Object span 4. Figure copying 5. Block construction Linguistic: 1. Oral directions 2. Visual recognition 2. Word span. 2 3. Left-right discrimination 4. Visual retrieval 3. Digit span 1 4. Counting aloud 5. Telling time 3. Serial commands 4. Naming pictures 5. Naming symbols Complex sentences Levine MD: "The Pediatric Examination of Educational Readiness" Educators Publishing Services, Inc., Cambridge, MA. 1982, and Levine MID: "The Pediatric Early Elementary Examination" Educators Publishing Services, Inc., Cambridge, MA. 1982. 233 0 JOSH 0 August 1984, Vol. 54, No. 7 6-95/neursign Section IV: Screening and Assessment APS Nursing Manual Page 3 of 3