Cytoskeleton Question Bank: Biol 309 Practice Questions
advertisement

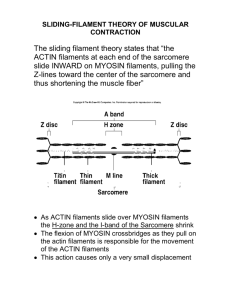
Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Multiple Choice 1. All of the following statements are true of microtubules and actin filaments, EXCEPT: A. Both are necessary for cell division. B. Both are composed of globular subunits. C. ‘Motor’ proteins participate in movements associated with both filaments. D. Both types of filaments display dynamic instability. E. Both filaments originate from a centrosome. 2. Which of the following statements correctly describes intermediate filaments? A. They are the only cytoskeletal filaments that are not composed of protein. B. Intermediate filaments are the principal component of the cell cortex. C. These filaments are always found outside of the cell. D. These filaments help the cell to withstand mechanical stress. E. None of the above answers are correct. 3. Cytoskeletal filaments that display "dynamic instability:” A. constantly slide past each other. B. move around in the cytoplasm with a whip-like motion. C. change in length due to polymerization or depolymerization. D. tend to make the cytoplasm dynamically unstable. 4. Dynein and kinesin: A. are the two subunits of microtubules. B. are motor proteins that generate movements associated with microtubules. C. are motor proteins that generate sliding of the sarcomere. D. create the crawling motion typical of amoeba. 5. Lamellipodia and filopodia frequently occur near the edges of cells. These membrane features: A. are supported by intermediate filaments, such as keratin. B. probably do not serve any useful purpose to the cell. C. result from the polymerization of actin filaments. D. are directly linked to the microtubule organizing center. 6. Which of the following statements best describes the movement of microtubules in an axoneme? A. The inner pair of microtubules slide up and down relative to the outer microtubule pairs. B. Outer pairs of microtubules slide slightly relative to each other. C. The two microtubules within each outer pair slide relative to each other. D. The outer-ring of microtubules rotates around the inner pair like a wheel. Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 1 7. Which one of the following statements correctly describes immotile cilia syndrome? A. It affects females but not males. B. It is caused by a mutation to the structure of microtubules themselves. C. It only affects epithelial cilia but not flagellum of sperm cells. D. It results from mutations that affect different parts of axoneme structure. 8. During contraction of a sarcomere: A. actin filaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere. B. myosin head groups bind together. C. Ca++ is released from the cell through exocytosis. D. microtubules slide relative to each other. E. None of the above answers are correct. 9. Which type(s) of cytoskeleton filament(s) display “dynamic instability?” (Circle all correct answers) A. actin C. microtubules B. myosin D. intermediate 10. Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP on microtubules: A. provides the energy for movement of the axoneme. B. drives the movement of motor proteins. C. leads to depolymerization of the microtubule. D. is necessary for polymerization of the tubulin subunits. 11. Which one of these figures shows the distribution of actin filaments within a typical cell? 12. Microtubules serve all of the following functions in cells, EXCEPT: A. They help to control movements of subcellular particles. B. They are the primary structural component of flagella. C. Microtubules mediate the movements of chromosomes during mitosis. D. Microtubules are the "thick filaments" of sarcomeres. E. Microtubules are components of centrioles and basal bodies. 13. In the figure to the right, which arrow points to a protein that generates the force (by hydrolyzing ATP) that causes movement of the axoneme? Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 2 14. In muscle cells, T-tubules function to: A. serve as storage compartment for Ca2+ within the cell. B. absorb Na+ ions moving into the cell from voltage-gated Na channels. C. transmit an action potential from the cell surface to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. D. trigger an action potential in the muscle cell when acetylcholine is released. 15. In the process called actin treadmilling: A. myosin proteins cause movement of actin filaments. B. actin filaments of muscle cells contract. C. subunits are added to the + end with the – end anchored to the membrane. D. subunits are simultaneously added and removed from a filament. 16. During the contraction of a sarcomere, binding of ATP to myosin causes: A. the myosin head group to bind to the actin filament. B. release of the head group from the actin filament. C. a change in the shape of myosin head group. D. sliding of the actin and myosin filaments relative to each other. True or False 1. All cytoskeletal filaments display dynamic instability. 2. Intermediate filaments contain globular proteins arrange in a helical arrangement. 3. The mitotic spindle is composed of actin filaments. 4. The nuclear lamina is composed of intermediate filaments. 5. Desmosomes are proteins on the cell membrane to which intermediate filaments bind. 6. Cellular particles can move in either direction along a single microtubule. 7. Eukaryotic flagella move with a rotary action (i.e., they spin). 8. The ‘cell cortex’ (the dense network of protein filaments just inside of the cell membrane) is composed of microtubules. 9. Each type of microtubule motor protein moves in either the ‘+ to –’ or the ‘– to +’ direction, but not both. 10. The cortex of the cell is composed principally of intermediate filaments. 11. Each muscle cell contains a single myofibril filament. 12. Tight junctions and desmosomes are terms that refer to the same structure. Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 3 13. Within an axoneme, motor proteins are attached to every microtubule filament. Matching Structure 1. centriole 2. basal body 3. tubulin 4. centrosome 5. -tubulin Structure or Function A. consist of two centrioles arranged at right angles B. protein subunit of microtubules C. located below cilia and flagella D. consists of microtubules arranged as a short cylinder E. protein that helps to initiate new cytoplasmic microtubules List all the letters of the functions associated with each type of cytoskeletal filament (some letters may be used more than once) 1. Microtubules 2. Actin 3. Intermediate filaments A. movements, e.g., ruffling, of membrane surfaces B. increasing cell and tissue strength and resilience C. the 9+2 structure of flagella D. mitotic movements of chromosomes E. binding to desmosomes F. contraction of muscle G. structure of a centriole H. movement of particles in the cytosol I. cytokinesis J. the nuclear lamina K. the cell cortex Fill in, etc 1. Each of these diagrams shows the cell membrane of a cell. For each type of cytosketal filament draw the general distribution and arrangement of these filaments within a typical cell. Actin Intermediate Microtubules 2. Complete the following sentence: Binding of _____________ to ________________________, a long filamentous protein bound to the surface of actin, causes it to expose sites to which _______________ can then bind. Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 4 3. These diagrams show growing and shrinking microtubules. A. Label the + and – ends of the MTs. B. What happens to the end of a MTs causing it to change from a state of polymerization to depolymerization? C. What happens that may stabilize (at least for a while) a MT? Label the diagrams to supplement your answer 4. Identify the structures labeled in this diagram of an axoneme: Explain the role of each cytoplasmic component in the generation of axoneme movement. 5. Label the diagrams below of a muscle cell and a sarcomere Diagrams are from Alberts et al, Essential Cell Biology, 2nd Ed, Garland Press, 2004 Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 5 6. A. Complete the following table. Type of cytoskeletal filament Are subunits Do subunits possess globular or enzymatic activity? filamentous If so, what type? Does filament possess polarity? Does filament display dynamic instability? Intermediate Microtubule Actin Myosin-II B. Considering the properties you have listed above, explain why the properties of each type of cytoskeletal filament are appropriate for its particular function. 7. Assuming that muscle contraction begins with myosin head-groups bound to actin, place the subsequent steps of the sliding filament model in their correct order. ___ A. Pi is released and the myosin head group binds to actin ___ B. ADP is released and the myosin ‘powerstroke’ occurs ___ C. ATP binds to myosin and the myosin head group is released ___ D. ATP is hydrolyzed and the myosin head group ‘cocks’ Biol 309 Question Bank Cytoskeleton Page 6