ASIA PACIFIC INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL KOLAR ROAD, BHOPAL
advertisement

ASIA PACIFIC INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL KOLAR ROAD, BHOPAL
SYLLABUS SPLIT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I - CLASS IX
SESSION 2015 - 2016
S.N. MONTH DAYS
UNIT
PROSE
1
APRIL
19
POETRY
LESSON
Fiction 1 - How I
taught my
Grandmother to read
Poem 1 - The Brook
WRITING
Letter Writing
SKILL
PROSE
Fiction 2 – A Dog
Named Duke
POETRY
Poem 2 - The Road
not taken
Notice Writing
2
JUNE
14
WRITING
SKILL
Grammar
PROSE
3
JULY
26
Drama 1 – Villa for
Sale
3) The Solitary
Reaper
POETRY
4) Lord Ullin’s
Daughter
1. Expansion of
ideas.
4
AUGUST
24
WRITING
SKILL
Grammar
5
SEPT
23
SUBJECT: - ENGLISH
CONTENT
FA ACTIVITY
FA I - ACTIVITY: Importance of
a) Name of the Activity – Inter
Adult Literacy
Disciplinary Project
Methodology – Individual
The different
Skill Enhanced – Reading, Thinking,
Moods of Life
and Writing
a) Letter to the
Number of sessions - One
Editor
Score –2 5 * 1
b) Letter to the
Public Authorities b) Name of the Activity – Bi Monthly
News letter
Love has no
Methodology – Group
bounds
Skill Enhanced –Thinking, Speaking,
Writing and Presentation
The Secret of
Number of sessions - Five
being Successful
Score –25 *1
a) For an Event.
c) Name of the Activity – Debate
b)For Inter Class Methodology – Pair
Competitions.
Skill Enhanced – Thinking and
Speaking.
Number of sessions - Two
Score – 25 * 1
d) Name of the Activity – Paper Pen
Test
Error corrections
Methodology – Individual
Skill Enhanced –Thinking and
Writing.
Number of sessions - One
Score – 25 * 1
People take
FA II - ACTIVITY: undue advantage a) Name of the Activity – Role Play
of the
Methodology – Group
opportunities.
Skill Enhanced – Reading, Thinking,
Writing and Speaking.
Music needs no
Number of sessions - One
language to
Score – 25 * 1
convey the
b) Name of the Activity – Story Writing
feelings
Methodology – Pair
Value of Sacrifice
Skill Enhanced –Thinking, Writing
cannot be
and Speaking.
measured in
Number of sessions - One
terms of money.
Score – 25*1
How to interpret,
c) Name of the Activity – Crossword
analyze events
Methodology – Individual
and programmes
Skill Enhanced – Vocabulary.
and draft the
Number of sessions - One
notes as per the
Score – 25 * 1
need.
d) Name of the Activity – Paper Pen
Test
Methodology – Individual
Jumbled words.
Skill Enhanced –Thinking, and
Headline writing
Writing
Number of sessions - One
Score – 25 * 1
Revision and conduct of Summative Assessment I
SYLLABUS SPLIT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II - CLASS IX
SESSION 2015 - 2016
S.N.
MONTH
DAYS
UNIT
PROSE
1
OCTOBER
24
LESSON
CONTENT
Fiction 3 – The Man
Who Knew Too Much
Boasting of one’s
knowledge leads
to grudges in the
heart of others
WRITING
Email Writing
SKILL
Fiction 4: - Keeping it
from Harold.
PROSE
Fiction 5: - Best Seller
2
NOVEMBER
23
POETRY
Poem 4 - The Seven
Ages
Message writing.
Formal and
informal
We should never
hide facts from
our family
members
Realities of life are
the motivating
factor for writers
The different
phases in a
Man’s life
To pass any kind
of information to
a third person
WRITING
SKILL
PROSE
3
DECEMBER
4
JANUARY
24
23
Grammar
Error corrections
Drama 2 – Bishop’s
Candlestick
Love and trust
can bring about
positive changes
in anybody’s life.
Poem 5 - Oh I wish I’d
Importance of
Looked After My
Dental Hygiene.
Teeth
POETRY
Nature’s
Poem 6 - Song of the
response to
Rain
man’s need
How to interpret,
analyze events
1. Expansion of
and programmes
ideas.
and draft the
notes as per the
WRITING
need.
SKILL
Grammar
5
FEBRUARY
\
SUBJECT: - ENGLISH
FA ACTIVITY
FA III - ACTIVITY: a) Name of the Activity – OTBA
Methodology – Individual
Skill Enhanced – Reading, Thinking
and Writing
Number of sessions -One
Score – 5 * 5
b) Name of the Activity – School
Magazine
Methodology – Group
Skill Enhanced –Thinking, Writing
and Presentation.
Number of sessions - One
Score – 5 * 5
c) Name of the Activity – Talk Show
Methodology – Show
Skill Enhanced – Speaking.
Number of sessions - One
Score – 25 * 1
d) Name of the Activity – Paper Pen
Test
Methodology – Individual
Skill Enhanced –Thinking and writing.
Number of sessions - One
Score – 25 * 1
FA IV- ACTIVITY: 1. PROBLEM SOLVING
ASSESSMENT TEST 2015
2. ASL Examination
Completion of
sentence using
correct tense.
22
Revision and Conduct of Pre - Board
23
Revision and Conduct of Summative Assessment II
ASIA PACIFIC INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
SYLLABUS SPLIT UP (2015-16)
CLASS-IX
SUBJECT: (MATHS)
TERM=1
MONTH
APRIL
(22)
UNIT/CHAPTER
1. REAL NUMBERS
2. POLYNOMIALS
JULY
LINES AND ANGLES
(CONTINUED)
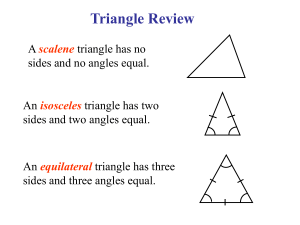
5. TRIANGLES
AUGUST
6. INTRODUCTION TO
EUCLID’S GEOMETRY
CONTENT/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Review of representation of natural numbers, integers,
rational numbers on the number line. Representation
of terminating / non-terminating recurring decimals, on
the number line through successive magnification.
Rational numbers as recurring/terminating decimals.
Examples of nonrecurring / non terminating decimals
such as v2, v3, v5 etc. Existence of non-rational
numbers (irrational numbers) such as v2, v3 and their
representation on the number line.
.Definition of a polynomial in one variable, its
coefficients, with examples and counter examples, its
terms, zero polynomial. Degree of a polynomial.
Constant, linear, quadratic, cubic polynomials;
monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and
multiples. Zeros/roots of a polynomial / equation.
State and the Remainder Theorem with examples
and analogy to integers. Statement and proof of the
Factor Theorem. Factorization
of ax2 + bx + c, a1 0 where a, b, c are real numbers,
and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem.
5. (Prove) The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 o.
6. If a side of a triangle is produced, the exterior angle
so formed is equal to the sum of the two interiors
opposite angles.
1. Two triangles are congruent if any two sides and
the included angle of one triangle is equal to any two
sides and the included angle of the other triangle
(SAS Congruence).
2. (Prove) Two triangles are congruent if any two
angles and the included side of one triangle is equal
to any two angles and the included side of the other
triangle (ASA Congruence).
3. Two triangles are congruent if the three sides of
one triangle are equal to three sides of the other
triangle (SSS Congruence).
4. Two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse
and a side of one triangle are equal (respectively) to
the hypotenuse and a side of the other triangle.
5. (Prove) The angles opposite to equal sides of a
triangle are equal.
6. The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are
equal.
7. Triangle inequalities and relation between 'angle
and facing side' inequalities in triangles.
History - Euclid and geometry in India. Euclid's
method of formalizing observed phenomenon into
rigorous mathematics with definitions,
common/obvious notions, axioms/postulates
MODE OF
ASSESSMENT
Note book
assessment
Worksheet,
quiz
Worksheet,
quiz
Oral test
7. HERON’S FORMULA
and theorems. The five postulates of Euclid.
Equivalent versions of the fifth
postulate. Showing the relationship between axiom
and theorem.
1. Given two distinct points, there exists one and only
one line through them.
2. (Prove) two distinct lines cannot have more than
one point in common.
Review concept of area, recall area of a rectangle.
1. (Prove) Parallelograms on the same base and
between the same parallels have the same area.
2. (Motivate) Triangles on the same base and
between the same parallels are equal in area and its
converse.
Worksheet,
CW/HW
assessment
SEPTEMBER REVISION FOR SA-1
TERM-2
CLASS-IX
OCTOBER
1. LINEAR EQUATIONS
IN
TWO VARIABLES
Recall of linear equations in one variable.
Introduction to the equation in two variables. Prove
that a linear equation in two variables has infinitely
many solutions and justify their being written as
ordered pairs of real numbers, plotting them and
showing that they seem to lie on a line. Examples,
problems from real life, including problems on Ratio
and Proportion and with algebraic and graphical
solutions being done simultaneously.
Bar graph
practice
Quiz
2. QUADRILATERALS
NOVEMBER 3. STATISTICS
SURFACE AREAS AND
VOLUMES
1. (Prove) The diagonal divides a parallelogram into
two congruent triangles.
2. In a parallelogram opposite sides are equal, and
conversely.
3. In a parallelogram opposite angles are equal, and
conversely.
4. A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of its
opposite sides is parallel and equal.
5. In a parallelogram, the diagonals bisect each other
and conversely.
6. In a triangle, the line segment joining the mid
points of any two sides is parallel to the third side
and its converse.
Introduction to statistics: Collection of data,
Presentation of data- tabular form, ungrouped /
grouped, bar graphs, histograms(with varying base
lengths), frequency polygons,
qualitative analysis of data to choose the correct form
of presentation for the
collected data. Mean, median, mode of ungrouped
data.
Worksheet
Quiz
Surface areas and volumes of cubes, cuboids,
spheres) including hemispheres) and right circular
and right circular cylinders/cones.
Review concept of area, recall area of a rectangle.
DECEMBER
AREA
CONSTRUCTIONS
JANUARY
PROBABILITY
1. (Prove) Parallelograms on the same base
and between the same parallels have the
same area
2. 2. (Motivate) Triangles on the same base
and between the same parallels are equal in
area and its converse.
1. Construction of bisectors of line segments &
angles, 60o, 90o, 45o angles etc., equilateral triangles.
2. Construction of a triangle given its base,
sum/difference of the other two sides and one base
angle.
3. Construction of a triangle of given perimeter and
base angles.
History, Repeated experiments and observed
frequency approach to probability. Focus is on
empirical probability.(A large amount of time to be
developed to group and to individual activities to
motivate the concept; the experiment to be drawn
from real - life situations, and from example used in
the chapter on statistics).
FEBRUARY
Complete revision for SA-2
Revision for SA-2
Theorem
test
Paper test
CW/HW
assessment
ASIA PACIFIC INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
ANNUAL SYLLABUS SPLIT-UP (2015-16)
CLASS 9 SOCIAL SCIENCES
S.NO.
MONTH/
WORKING
DAYS
NAME OF THE
CHAPTER
SUB TOPIC
CH-1 STORY OF
PALAMPUR,(E)
1
APRIL
(20)
CH-1 INDIA – SIZE
AND LOCATION(G)
No. Of Activities
Basic economic concepts
through an imaginary
story of a village
Factors of Production
Non- Farming activities in
Palampur
Eco-Group ACT.1.
Conduct a survey and
analyze the data in
groups
Location & size,
India and the world
India’s neighbour
Geo- 1Ind. Act.
Map Activity
worksheet
worksheet
JUNE
(12)
Worksheets
CH-1 The French
Revolution (H)
2.
Democracy in the
Contemporary
World (P)
i.
French Society During the Late
Eighteenth Century
The Struggle to Survive
A Growing Middle Class
Envisages an End to Privileges
The Outbreak of the Revolution
France Becomes a Constitutional
Monarchy
Abolition of Monarchy and
becomes Republic
The Reign of Terror
Women & Revolution
Abolition of Slavery
The Revolution and Everyday life
Democracy in Poland
Two feature of Democracy
The changing map of Democracy
Phases in the Expansion of
Democracy
His-Ch-1 Ind Act
Cross word Puzzle
Worksheet
Group Act.
Debate: “Democracy is
the best form of Govt”.
3.
Worksheets
JULY
(24)
MAJOR PHYSIOGRAPHIC DIVISIONS
(i) The Himalayan Mountains
(ii) The Northern Plains
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau
(iv) The Indian Desert
(v) The Coastal Plains
(vi) The Islands Definition
CH-2 PHYSICA L
FEATURES OF
INDIA(G)
CH-2 What is
Democracy? Why
Democracy?(P)
of Democracy
Features of democracy
Free and fair electoral
competition
One person, one vote,
one value
Rule of law and respect
for rights
Debating merits of
democracy
Arguments against & for
democracy
Broader meanings of
democracy
Group Act-Description
of sand
Model&Description
followed by MCQ test
Ind. Act-Educational
Excursion & Report
writing
Worksheets
Worksheets
Ch-2 PEOPLE AS
RESOURCE (E)
4.
Familiarization of a few population
related concepts and sensitization of
child that people as asset can
participate and contribute in nation
building
Ind.Act-Story Telling:
Factors affecting
Human Resource
AUGUST
(22)
CH-3
CONSTITUTIONAL
DESIGN(P)
Introduction to the process
of constitution making
Develop respect for the
constitution and
appreciation for
constitutional Values
Recognize that constitution
is a living document that
undergoes changes.
Drainage systems in India
The Himalayan rivers
The peninsular rivers
Lakes
Role of rivers in the
economy
Group Act. –Skit/Role
Play.
Topic : Racial
Discrimination in South
Africa
Worksheets
Model Making
River pollution
CH-3 DRAINAGE(G)
worksheet
Screening of the
Movie: Life is beautiful
Ch-II RISE OF
NAZISM(H)
5.
SEPTEMBER
(22)
SA1
The growth of social
democracy.
The crisis in Germany.
The basis of Hitler's rise to
power. The ideology of
Nazism.
The impact of Nazism
History-1&3, Politics1,23,Geography-1,2&3&
Economics 1&2
Understanding of poverty as a
challenge and sensitization of the
learner .Appreciation of the
government initiative to alleviate
poverty
6.
OCTOBER
(14)
Ch-3 Poverty as a
challenge facing
India
CLIMATE(G)
Climatic controls
Factors affecting India’s climate
The Indian monsoon
The onset of the monsoon and
withdrawal
The cold weather season (winter)
The hot weather season (summer)
Advancing monsoon (the rainy
season)
Retreating monsoon (the transition
season)
Distribution of rainfall
Monsoon as a unifying bond
Eco-Group Act- Quiz
Worksheets
Geo- Ind. Act
Picture analysis
Understand how agricultural
systems in India are different from
that in other countries
Ch-6 Peasants and
Farmers
7.
NOVEMBER
NATURAL
VEGETATION AND
Emergence of different forms of
Farming,constructing forms of
changes within rural economies in
Modern world in USA AND
ENGLAND
MCQ Worksheet
Relief
Climate
Ecosystem
Types of vegetation
Geo-Worksheets
Group activityA poster on the
(21)
WILD LIFE (G)
Electoral Politics(P)
History and Sport:
The story of cricket
(i) tropical rain forests
(ii) tropical deciduous forests
(iii) tropical thorn forests and scrubs
(iv) montane forests
(v) mangrove forests wild life
regional study of
forest, wildlife and
climate relationship.
Why elections?
What makes an election
democratic?
What is our system of elections?
Polling and counting of votes
What makes elections in India
democratic? Challenges to free and
fair elections
Election of class
Monitor
Historical development of cricket as
a game in England: Cricket and
Victorian England
Spread of Cricket: Cricket, Race and
Religion
Modern transformation of the
game: Decolonization and Sport
Commerce media and cricket today
DEBATE: Should the
government interfere
with sports
8.
DECEMBER
(19)
POPULATION(G)
Working of
Institutions(P)
Population size and distribution
Population growth and processes of
population change
National population policy
How is a major policy decision
taken?
The decision makers
Need for political institutions
Parliament - its need
Two houses of parliament
Political executive
Political and permanent executive
Prime minister and council of
ministers
Powers of the prime minister
The president
The judiciary
Group Discussion: Girl
child needs to be
protected
Worksheets
Class test
assignment
9.
JANUARY
(20)
Democratic
Rights(P)
Life without rights
Citizens’’ rights in Saudi Arabia
Rights in a democracy
What are rights?
Why do we need rights in a
democracy?
Rights in the Indian constitution
Right to equality
Right to freedom
Right against exploitation
Right to freedom of religion
Expanding scope of rights
Worksheets
Bulletin Board Display
10.
FEBRUARY
(20)
S A 1 Revision
SYLLABUS BREAKUP
SESSION 2015-16
CLASS - IX (TERM I & II)
SUBJECT-BIOLOGY
S.
NO.
MONTH
APRIL
1
NO. OF
WORKING DAYS
CHAPTER
CONTENT
CH-5 The
Fundamental Unit
of Life
What are living things made up of?contribution of
scientists, structural organisation of cell, plasma
membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm
practical: slide preparation of plant cell
JUNE
CH-5 The
Fundamental Unit
of Life
Cell organeles: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi
Apparatus, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Plastids,
Vacuoles
practical: slide
preparation of animal cell
JULY
CH-6 Tissues
Are plants and animals are made up of same types
of tissues? Plant Tissues: meristematic tissue,
permannt tissue, simple permanent tissue,
complex permanent tissue, Animal tissues,
epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular
tissue, nervous tissue
practical:
slide preparation of animal cell
CH- 15
Improvement in
food resources
Improvement in crop yields, crop variety
improvement, crop production management,
Nutrient managememt, manure, fertilizers,
irrigation, cropping pattern, crop protection
management, storage of grains, animal
husbandry: cattle farming, poultry farming,
egg and broiler productin, fish production:
marine fisheries, inland fisheries, bee keeping
Practical:(i) plant tissues and animal
tissues(ii) To test the presence of starch
2
3
AUGUST
4
OCTOBER
5
6
NOVEMBER
Biological
Diversity
Diversity of plants and animals, scintific naming,
bsis of classification, hierarchy of groups,
Practicals: To study the characteristics of
Spirogyra, Agaricus, Moss
Biological
Diversity
Major groups of plants and animals
Practicals: Fern, Pinus and Angiospermic plant
DECEMBER
Health and
Diseases:
JANUARY
Our Environment
7
8
Health and its failure, infectious and non
infectious diseases, Disease caused by
microbes,principles of treatment, pulse polio
programme
Practicals:To study
the external features of root, stem, leaf and
flower of monocot and dicot plants
Air, for respiration, combustion, movement of air,
air, water and soil pollution, ozone depletion, bogeo-chemical cycle in nature
MONTH(WD*)
Unit
Apr(19)
Unit: Matter - Nature
and Behaviour
June(14)
July(26)
Syllabus Split-Up (2015-16)
Chemistry Class-IX
Contents
Activities
TERM-I
Definition of matter;
To prepare:
solid, liquid and gas;
a) a true solution of common salt, sugar and alum
characteristics - shape,
b) a suspension of soil, chalk powder and fine sand in
volume, density;
water
change of state-melting c) a colloidal solution of starch in water and egg
(absorption of heat),
albumin/milk in water and distinguish between these
freezing, evaporation
on the basis of
(cooling by
transparency
evaporation),
filtration criterion
condensation,
stability
sublimation.
To prepare a) a mixture b) a compound
Nature of matter:
using iron filings and sulphur powder and distinguish
Elements, compounds
between these on the basis of:
and mixtures.
i. appearance, i.e., homogeneity and heterogeneity
Heterogenous and
ii. behaviour towards a magnet
homogenous mixtures,
iii. behaviour towards carbon disulphide as a solvent
colloids
iv. effect of heat
and suspensions
To carry out the following reactions and classify
them as physical or chemical changes:
a. Iron with copper sulphate solution in water
b. Burning of magnesium in air
c. Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid
d. Heating of copper sulphate
e. Sodium sulphate with barium chloride in the form
of their solutions in water
Aug(24)
Sep(23)
To separate the components of a mixture of sand,
common salt and ammonium chloride (or camphor)
by sublimation.
To determine the melting point of ice and the boiling
point of water.
Unit: Matter - Nature
and Behaviour
Oct(24)
Month(WD*)
Unit
TERM-II
Particle nature, basic
units: atoms and
molecules. Law of
constant proportions.
Atomic and molecular
masses.
Mole Concept:
Relationship of mole to
mass of the particles
and numbers. Valency.
Chemical formula of
common compounds.
Structure of atom:
Electrons, protons and
neutrons; Isotopes and
isobars.
To verify the law of conservation of mass in a
chemical reaction.
Syllabus Split-Up (2015-16)
Chemistry Class-X
Contents
Activities
TERM-I
Apr(19)
Chemical reactions
June(14)
Chemical equation, Balanced
chemical equation,
implications of a balanced
chemical equation, types of
chemical reactions:
combination, decomposition,
displacement, double
displacement,
precipitation, neutralization,
oxidation and reduction.
July(26)
Acids, bases and
salts
Their definitions in terms of
furnishing of H+ and OHions, General properties,
examples and uses, concept
ofpHscale(Definition
relating to logarithm not
required), importance of pH
o
ineveryday life; preparation
o
and
uses
of
sodium
hydroxide,Bleaching
o
powder,Bakingsoda,Washing
soda and Plaster of Paris. o
Aug(24)
Sep(23)
Metals and non
metals
Oct(24)
Carbon compounds
Nov(23)
Properties of metals and nonmetals, reactivity series,
formation and properties of
ionic compounds, basic
metallurgical processes,
corrosion and its prevention.
TERM-II
Covalent bonding in carbon
compounds. Versatile nature
of carbon. Homologous
series Nomenclature of
carbon compounds
containing functional groups
(halogens, alcohol, ketones,
aldehydes, alkanes and
alkynes), difference between
saturated hydrocarbons and
unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Chemical properties
of carbon compounds
(combustion, oxidation,
addition and substitution
reaction). Ethanol and
Ethanoic acid.
1. To find the pH of the following samples by
using pH paper/universal indicator:
a. Dilute Hydrochloric Acid
b. Dilute NaOH solution
c. Dilute Ethanoic Acid solution
d. Lemon juice
e. Water
f. Dilute Sodium Bicarbonate solution
2. To study the properties of acids and bases (HCl
& NaOH) by their reaction with:
a. Litmus solution (Blue/Red)
b. Zinc metal
c. Solid sodium carbonate
d. Al2(SO4)3 (aq)
3. To perform and observe the following reactions
and classify them into:
i. Combination reaction
ii. Decomposition reaction
iii. Displacement reaction
iv. Double displacement reaction
1) Action of water on quick lime
2) Action of heat on ferrous
sulphate crystals
3) Iron nails kept in copper
sulphate solution
4) Reaction between sodium
sulphate and barium chloride solutions
4. i) To observe the action of Zn, Fe, Cu and Al
metals on the following salt solutions:
a. ZnSO4 (aq)
b. FeSO4 (aq)
c. CuSO4 (aq)
d. Al2(SO4)3 (aq)
ii) Arrange Zn, Fe, Cu and Al (metals) in the
decreasing order of reactivity based on the above
result.
1. To study the following properties of acetic acid
(ethanoic acid):i) odour ii) solubility in water
iii) effect on litmus iv)reaction with sodium
bicarbonate
Dec(24)
Periodic
classification of
elements
Need for classification,
Modern
periodic
table,
gradation
in
properties, valency, atomic
number, metallic and nonmetallic properties.
2. To study saponification reaction for preparation
of soap.
3. To study the comparative cleaning capacity of a
sample of soap in soft and hard water.
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2015-16
SCIENCE CLASS IX
S.
No
Month
Expected
No.of
working
Days
Chapter No
& Chapter
Detailed
Split-up
First Term
1
April
24
8. Motion
2
june
10
8. Motion (contd.)
3
July
25
9. Force and laws
of motion
4
August
22
9. Force and laws of
motion (contd.)
10. Gravitation
5
September
15
10. Gravitation (contd.)
Motion : Distance and displacement, velocity;
uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight
line; acceleration, distancetimeand velocity-time
graphs for uniform motion and uniformly
accelerated motion
equations of motion by graphical
method;elementary idea of uniform circular
motion.
Force and Newton's laws: Force and motion,
Newton's laws of motion, inertia of a body, inertia
and mass, momentum, force and acceleration.
Elementary idea of conservation of momentum,
action and reaction forces.
Gravitation : Gravitation; universal law of
gravitation, force of gravitation of the earth
(gravity),
acceleration due to gravity;mass and weight; free
fall
Second Term
6
October
16
10. Gravitation
7
November
22
11. Work & Energy
8
December
17
12. Sound
9
January
25
12. Sound (contd.)
10
Febraury
22
12. Sound (contd.)
Revision
Floatation : Thrust and pressure. Archimedes'
principle, buoyancy, elementary idea of relative
density
Work, energy and power : Work done by a force,
energy, power; kinetic and potential energy; law
of conservation of energy
Sound : Nature of sound and its propagation in
various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in
humans; ultrasound
reflection of sound; echo and SONAR.
Structure of the human ear (auditory aspect only)
Revison for SA-II
,f”k;k isflfQd baVjus”kuy fo|ky;
okf"kZd ikB~;Øe& 2015&2016
d{kk& uoeha
fo"k;& fgUnh
dz
a
ekg
ikB dk uke
1
vizSy
(22)
ikB 1 &/kwy
ikB 2 & nq[k dk vf/kdkj
fxYyw
O;kdj.k & o.kZ & foPNsn]
2 ds fofHkUu ] #i ] uqDr
2
twu
ikB 9 & jSnkl
(14)
ikB 10 & jghe ds nksgs
Le`fr
O;kdj.k & vuqLokj rFkk
vuqukfld ] eqgkojs ,oa
okD; iz;ksx
FA - 1 iqujko`fRr
3
Tqkykb
Z
(26)
jpukRed xfrfof/k;kWa
,oa ifj;kstuk dk;Z
ns’k dh ekVh ls
tqM+us dk lans’k
fo"kSys lkWaiksa ds fp=
ifj;kstuk dkWih esa yxkukA
dgkuh dk uohu var &
lekt esa QSys
nq[k dk vf/kdkjA
HksnHkko ij dVk{k
dgkuh ys[ku ,oa izLrfr
i'kq & if{k;ksa ij vk/kkfjr A
ysf[kdk esa fxYyw
ifj;kstuk dk;Z & fdlh ,d
ds vkReh; laca/k dk o.kZu
i{kh ds fo"k; esa tkudkjh A
odZ’khV
jSnkl dh
xq#ukud ] dchj ]
ukenso vkSj ehjk ckbZ dh
izHkqHkfDr dk o.kZu
jpukvksa dk ladyu A
nksgksa ds ek/;e ls
izHkqHkfDr djrs gq, ljy
nksgksa dk lLi"V xk;u
thou fcrkus dk lans’k
djuk A
ckY;koLFkk dh
jksekapd ?kVuk dk ltho
o.kZu
fopkj ys[ku bZ’oj dh
loZO;kidrk A
ikB 3 & ,ojsLV esjh f’k[kj
;k=k
cNsUnzhiky dh
,ojsLV ;k=k dk o.kZu
ifjppZk eu ds gkjs gkj
gS] eu ds thrs thr A
ikB 4 & rqe dc tkvksxs
vfrfFk
yacs le; rd fVdus
okys esgekuksa ij O;aX;
vuqPNsn ys[ku o
izLrqrhdj.kA
ikB 11 & vkneh ukek
vPNkbZ;ksa]
lhekvksa o laHkoukvksa
ls euq"; dk ifjp;
O;kdj.k & i= ys[ku
4
fo"k; foLrkj
vxLr
FA – 2 iqujko`fRr
(24)
ikB 5 & oSKkfud psruk ds
okgd panz’ks[kj osadV
jeu
ikB 12 & ,d Qwy dh pkg
ikB 13 & xhr & vxhr
dYyw dqEgkj dh
odZ’khV
NqvkNwr dh leL;k ij
dsfUnzr Hkkouk A
,d Qwy dh pkg dfork dks
dgkuh ds #i esa fy[kuk A
MkW] jeu dh
vfHkyk"kk dk o.kZu A
odZ’khV
Qwy dh vfHkyk"kk
dk o.kZu A
f=iqjk dh
HkkSxksfyd fLFkfr dk
mukdksVh
laiw.kZ o.kZu A
O;kdj.k & vuqPNsn ] okD;
ds vax & ljy okD;] fojke
fpg~uksa dk iz;ksx
SA – 1 iqujko`fRr
flrEcj
5
(23)
esjk NksVk ;k futh
iqLrdky;
SA – 1 ijh{kk
vDVwcj
6
(24)
ikB 6 & dhpM+ dk dkO;
ikB 14 & vfXuiFk
gkfen [kkWa
O;kdj.k & vifBr x|ka’k
,oa i|ka’k dk vH;kl ] i= o
vuqPNsn ys[ku dk vH;kl
uoEcj
7
(23)
FA – 3 iqujko`fRr
FA – 3 ijh{kk
ikB 7 & /keZ dh vkM+
ykbczsjh cukus dh
izjs.kk rFkk iqLrdksa ds
j[k j[kko dh lqfuf’pr
O;oLFkk djuk A
dhpM+ esa lqanjrk dk
o.kZu A
lqanjrk dh mRifRr
dhpM+ A
fcuk vkxs cM+s dk
lans’k A
la?k"kZe; thou dk
o.kZu A
fgUnw vkSj eqfLyeksa
dh lg`n;rk ,oa ,drk dh
Hkkouk dk o.kZu A
/keZ dh vkM+ esa
LokFkZ flf) dk o.kZu A
xkWa/khth ds lfpo dh
izfrHkk rFkk O;Lrrk dk
o.kZu A
ikB 8 & 'kqdz rkjs ds leku
oxZ igsyh iqLrdksa ds
ukeksa ij vk/kkfjr A
odZ’khV
fp= o 'kCnksa ds vk/kkj ij
dfork ys[ku A
dfo o ys[kd ifjp;
izLrqrhdj.k A
odZ’kh
V
Lyksxu ys[k A
lkSj eaMy ds ukS
xzgksa ds uke o fp= lfgr
dk;Z dk o.kZu A
odZ’khV
O;kdj.k & fefJr vH;kl ]
'kCn laink ij vk/kkfjr oxZ
igsyh
fnlEcj
8
(24)
ikB & 15 u, bykds esa
[kq’kcw jprs gSa gkFk
fn, ty mBs
O;kdj.k & eqgkojs ]
fefJr vH;kl
Tkuojh
9
(23)
10
Qjojh
(22)
iqujko`fRr
SA – 2 ijh{kk
,d ,slh nqfu;k esa izos’k
dk vkea=.k tks ,d gh fnu
esa iqjkuh iM+ tkrh gS A
Lkekftd fo"kerkvksa dh
csudkc djrh dfork A
nkaMh ;k=k lacaf/k
o.kZuA
ca/kqvk etnwjh ij
vfHkO;fDr A
eqgkojksa ij vark{kjh
odZ’khV