CCND02 – Chapter 1: The Internet and Its Uses
advertisement
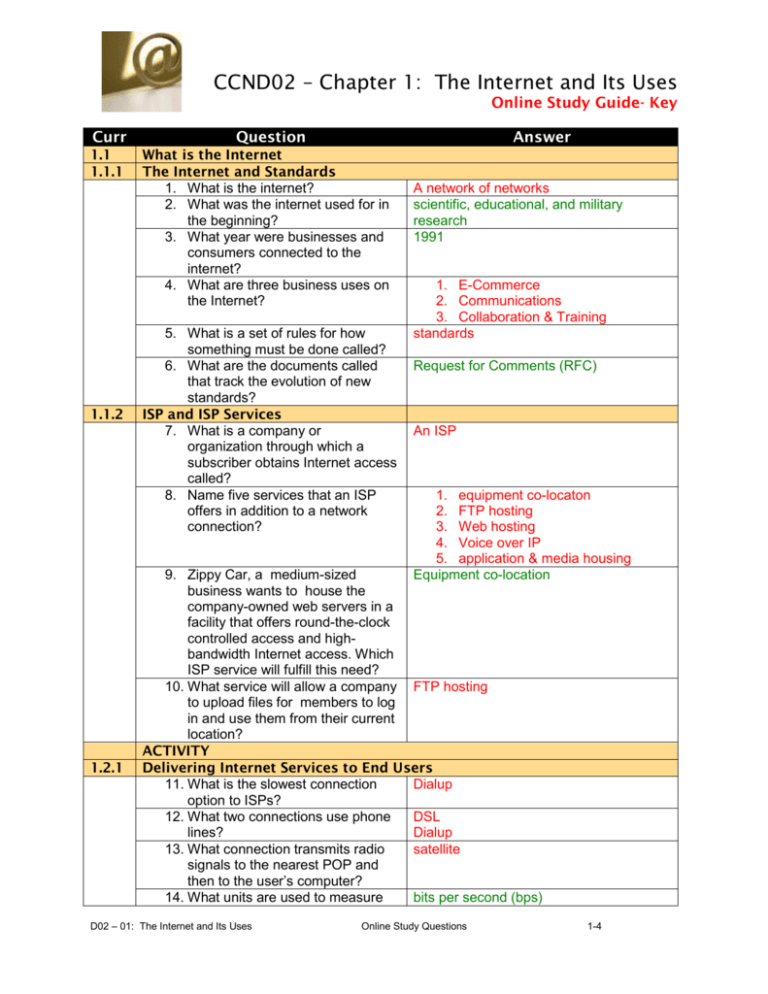
CCND02 – Chapter 1: The Internet and Its Uses Online Study Guide- Key Curr 1.1 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.2.1 Question Answer What is the Internet The Internet and Standards 1. What is the internet? 2. What was the internet used for in the beginning? 3. What year were businesses and consumers connected to the internet? 4. What are three business uses on the Internet? 5. What is a set of rules for how something must be done called? 6. What are the documents called that track the evolution of new standards? ISP and ISP Services 7. What is a company or organization through which a subscriber obtains Internet access called? 8. Name five services that an ISP offers in addition to a network connection? A network of networks scientific, educational, and military research 1991 1. E-Commerce 2. Communications 3. Collaboration & Training standards Request for Comments (RFC) An ISP 1. equipment co-locaton 2. FTP hosting 3. Web hosting 4. Voice over IP 5. application & media housing Equipment co-location 9. Zippy Car, a medium-sized business wants to house the company-owned web servers in a facility that offers round-the-clock controlled access and highbandwidth Internet access. Which ISP service will fulfill this need? 10. What service will allow a company FTP hosting to upload files for members to log in and use them from their current location? ACTIVITY Delivering Internet Services to End Users 11. What is the slowest connection Dialup option to ISPs? 12. What two connections use phone DSL lines? Dialup 13. What connection transmits radio satellite signals to the nearest POP and then to the user’s computer? 14. What units are used to measure bits per second (bps) D02 – 01: The Internet and Its Uses Online Study Questions 1-4 1.2.2 Internet bandwidth? 15. How are higher bandwidth speeds measured? 16. What are three main types of high bandwidth connection options used by medium-to-large-sized businesses? 17. What is the maximum T1 transmission speed? 18. T1 connections are symmetrical. What does this mean? 19. What type of business would use Metro Ethernet? 20. When using Metro Ethernet, what type of technology is used to connect the main office location and all the branches 21. Where do individual computers and business networks connect to the ISP? 22. What moves data between the various POPs? Internet Heirarchy 23. What is at the top of the Internet structure? 24. What do ISP POPs connect to? 25. What interconnects the internet backbone? 26. How many exchange points are there worldwide? 27. What is the primary medium that connects the Internet? 28. Where is most of the Internet cable installed? 29. How are the cables installed that connect continents? 30. How are ISPs classified into different tiers? 31. How do Tier 1 ISPs connect? 32. What do Tier 1 ISPs that join their individual network backbones together create? 33. Who owns , the Tier 1 ISPs routers, high-speed data links, and other pieces of equipment that join them to other Tier 1 ISP networks? 34. How do some Tier 2 ISPs carry data to other parts of the world? 35. What Tier of ISPs provide customers local access to the D02 – 01: The Internet and Its Uses kilobits per second (kbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). T1 T3 Metro Ethernet 1.544 the upload bandwidth is the same as the download bandwidth banks switched technology at a POP high-speed routers and switches ISP organizations Internet Exchange Point (IXP) IXPs Over 100 fiber-optic cable underground Fiber-optic cables also run under the sea according to how they access the Internet backbone Tier 1 ISPs are huge organizations that connect directly with each other through private peering the global Internet backbone the Tier 1 ISPs own their own equipment Pay Tier 1 ISPs to carry their traffic Tier 3 Online Study Questions 2-4 1.2.3 1.2.3 1.3.1 1.3.1 1.3.2 Internet? Identifying the Structure of the Internet 36. What command tests the average ping time it takes a packet to reach the destination and for the response to return to the source 37. What command tests whether or ping not the destination device is reachable through the network? 38. When you issue the ping an echo request packet to the destination command, what is sent to the address and then waits for an echo reply destination address? packet to return from that host 39. What utility displays the path that traceroute a packet takes from the source to the destination host? 40. What is each router that the Hop packet passes through called? 41. What command would show the Traceroute nslookup ping following: 1 15.0.0.6 4 msec Hands on Lab – Traceroute ISP Requirements 42. What devices enable the ISP to Border gateway routers connect and transfer data to other ISPs, IXPs, or large business enterprise customers? 43. What would cause ISP an overloaded network subscribers to wait for minutes for a web page to load, or may even lose their network connection? 44. What is the ability to allow for Scalability future change and growth of a network called? 45. What are the most scalable those that are modular and provide devices? expansion slots for adding modules Packet Tracer Activity Roles & Responsibilities within an ISP 46. What type of services are involved Network support services in all aspects of network management, including, adding new subscribers and, network repair? 47. What are five support service Help desk teams that are found within an Network Operations Center (NOC) ISP? On-site Installation Planning and Provisioning Customer Service 48. What will determine whether the Planning and Provisioning new customer has existing network hardware and circuits? 49. What monitors and tests the new The Network Operations Center (NOC) connection and ensures that it is performing properly? D02 – 01: The Internet and Its Uses Online Study Questions 3-4 1.4.1 50. What team will help the customer setup passwords? Activity Summary D02 – 01: The Internet and Its Uses Help Desk Online Study Questions 4-4











