U6E1 Paquete
advertisement

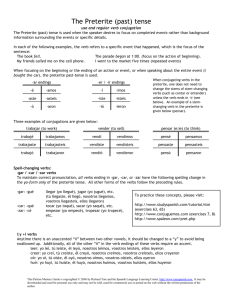
Nombre:_______________________________ Per: ________ Unidad 6 Etapa 1 pp. 396-417 LEARNING TARGETS: “By the end of this chapter I will be able to…” Tell what happened Make suggestions to a group Describe city buildings Talk about professions GRAMMAR: “I will use the grammar below to meet the learning targets.” Use preterite of regular –er and –ir verbs pp. 404-405 Use preterite of verbs with a y spelling change pp. 406-407 Use preterite of hacer, ir, ser pp. 407-411 CULTURE: “I will learn about culture to meet the learning targets.” History and culture of Quito, Ecuador pp.392-393, 407, 412-413 The dollar p. 409 Regional vocabulary p. 410 Colonial Ecuador p. 412 TRACKING MY PROGRESS La fecha Assessment (Vocabulary & Grammar Quizzes & Project) Nota (Points, Percent, Grade) 1 I. THE PRETERITE OF –er AND –ir VERBS p. 404 LEARNING TARGET: Learn about the preterite forms of –er and –ir verbs. Then practice using these verbs to say what you and others did. ENGLISH GRAMMAR CONNECTION: Remember that the preterite is a tense used to express an action completed at a definite time in the past. In English, regular verbs in the past tense end in –ed. APPLICATION: Regular –er and –ir verbs follow a pattern similar to regular –ar verbs in the preterite. Here’s how: In the preterite, -er and –ir verb endings are identical. preterite –er endings preterite –ir endings vender – to sell escribir – to write The yo forms and the él, ella, usted forms have accents. Vendí la computadora. I sold the computer. Tomás escribió una carta. Tomás wrote a card. 2 The nosotros(as) form of regular –ir verbs is the same in both the present and the preterite. Use context clues to determine the tense of the verb. Salimos a las ocho anoche. We left at eight o’clock last night. The word anoche tells you that salimos is in the preterite tense. ¡PARA y PIENSA! Did you get it? Conjugate the following verbs in the preterite form for the subjects given. 1. tú / comer 4. Uds. / asistir 2. él / beber 5. yo / correr 3. vosotros / recibir 3 II. TALKING ABOUT THE PAST: VERBS WITH A y SPELLING CHANGE p. 406 LEARNING TARGET: Learn about the verbs in the preterite form that have a y spelling change. Then practice using these verbs to say what you and others did. ENGLISH GRAMMAR CONNECTION: The spelling of some verbs in English changes in the past tense when –ed is added: for example: admit admitted, stop stopped, picnic picnicked. Spanish also has verbs that change their spelling in the preterite. APPLICATION: To write the third person preterite forms of –er and –ir verbs with stems that end in a vowel, change the í to y. oír – to hear leer – to read creer – to believe NOTICE that all of these preterite forms require an ______________, except the ______________________ forms. ¡PARA y PIENSA! Did you get it? Conjugate the following verbs in the preterite form for the subjects given. 1. tú / oír 4. Uds. / oír 2. él / leer 5. yo / leer 3. vosotros / creer 4 III. USING IRREGULAR VERBS IN THE PRETERITE: hacer, ir, ser p. 407 LEARNING TARGET: Learn about the irregular preterite forms of ir, ser, and hacer. Then practice these forms to say where you went and what you did. ENGLISH GRAMMAR CONNECTION: Irregular verbs do not follow the pattern of regular verbs. In English, irregular verbs in this tense do not end in –ed. She went to the aquarium. Ella fue al acuario. Irregular verb Irregular verb APPLICATION: Ir, ser and hacer are irregular in the preterite tense. The verb ir is irregular in the preterite. Its preterite forms are exactly the same as the preterite forms of ser. Hacer also has irregular preterite forms. These verbs don’t have any accents in the preterite. Here’s how: ir – to go ser –to be hacer – to do, to make The preterite forms of ir and ser are exactly the same. Use context clues to determine which verb is being used. Which sentence below used the verb ir and which sentence used the verb ser? How do you know? Fuimos a la escuela. ¡Fue un día fenomenal! Like ir and ser, the preterite forms of hacer have no accents. ¿Qué hiciste ayer? What did you do yesterday? Yo hice la tarea. I did homework. 5 ¡PARA y PIENSA! Did you get it? Complete the following sentences with the correct preterite forms of hacer and ir or ser. Then tell whether you used ir or ser. 1. Nosotros ________________ la tarea; ________________ muy fácil. 2. Yo _________________ a la playa. ________________ esquí acuático (water skiing). 3. ¿________________ ellos al parque. ¿Y qué _______________ allí? PRÁCTICA: Preterite Verbs – Conjugate the following verbs for the subject given. 1. yo / almorzar 16. nosotros / devolver 2. tú / ir 17. vosotros / lavar 3. vosotros / trabajar 18. Uds. / asistir 4. él / leer 19. vosotros / cenar 5. Ud. / estudiar 20. yo / ir 6. vosotros / ser 21. tú / bailar 7. nosotros / tomar 22. Ud. / creer 8. tú / escribir 23. ellas / trabajar 9. ellas / bailar 24. yo / ser 10. ella / aprender 25. nosotros / estudiar 11. yo / jugar 26. vosotros / lavar 12. ellos / oír 27. tú / mover 13. nosotros / preparar 28. nosotros / escribir 14. Uds. / hacer 29. él / hacer 15. tú / cenar 30. yo / sacar 6