6.5 Nervous System Cartoon Assignment
advertisement

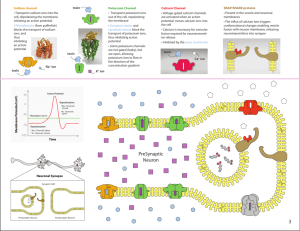
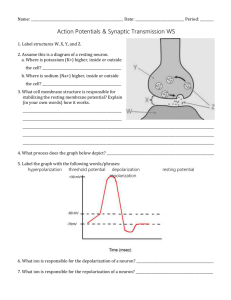
Transmission of a Nerve Impulse Cartoon 2014 Instructions: Make an annotated cartoon of Resting Potential, Action Potential, and Synaptic Transmission. Resource to help you include the following: IB Textbook Page 176 -178 6.5 Nervous System PowerPoint on Moodle. • ANIMATION: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter14/animation__the_nerve_impulse.html • Animation: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter14/animation__transmission_across_a_synapse.html Your cartoon should include all of the following Slide one: Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron. Be sure to label the following structures: o Dendrites, nodes of Ranvier, Myelin Sheaths, axons/ nerve fibre, motor end plates, nucleus, Slide two: Show how the resting potential inside your motor neuron is generated. Be sure to show the following features: o Sodium/Potassium protein pump in the cell membrane of the neuron. o Show how sodium is pumped out of the cell and potassium is pumped in using active transport and so ATP o Show that the charge how there is more sodium outside the cell & more potassium outside the cell o Show that because of a large quantity of negative ions inside the neuron cell, the inside has a NEGATVE charge and the outside has a positive charge. (This electrochemical gradient is a form of stored potential energy that will be used during the action potential) Slide three: Show the first step of an action potential occurs (self-propagating wave of ion movement and depolarization). o Show sodium ion protein channels in the neuron cell membrane open up and allow for sodium to diffuse from high concentration to low concentration. o Show how the flow of positively charge sodium ions inside the neuron cell, depolarizes the cell, that is, decreases the electrochemical gradient between the inside and the outside of the cell, and making the inside of the cell slightly more positive than the outside. o Show how this depolarization/ action potential propagates/ travels down the neuron’s axon. Slide four: Show how repolarization of the neuron occurs. Be sure to show the following o First, Potassium channel proteins in the cell membrane of the neuron open allowing for the facilitated diffusion of potassium from inside the cell/ high concentration to outside the cell/ low concentration. Re-establishing the electrochemical gradient o Second, Sodium/ Potassium pumps do exactly what they did in SLIDE two, that is, they pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. Until the electrochemical gradient is re-established to resting potential. Slide five: Synaptic transmission of an action potential Show the first step on how an action potential is pass from the motor end plates/ of one neuron/ presynaptic neuron to through the synapse to the dendrites of another neuron/ post-synaptic neuron. Be sure to include: o Action potential reaching the motor ends of the presynaptic neuron, and causing the opening of calcium ion protein channels. And calcium ions moving inside the presynaptic neuron from the synapse. Slide six Synaptic transmission of an action potential o Calcium Ions cause the vesicles of the neurotransmitters to exit presynaptic into the synapse and diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors of the membrane of the post-synaptic neuron. Slide seven: Synaptic transmission of an action potential o Show how the neurotransmitter binding to receptors on postsynaptic membrane causes the sodium protein channels imbedded on the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron open up and allow sodium ions to diffuse into the postsynaptic membrane causing a depolarization and an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron Slide eight: Breakdown of Neurotransmitter in the postsynaptic cell o Show how neurotransmitters are broken down. To prevent continuous synaptic transmission the neurotransmitter is quickly broken down by enzymes released from the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. o Fragments of the neurotransmitters diffuse back across the synaptic gap and be reabsorb by the presynaptic neuron by endocytosis. o These fragments inside the cells vesicles will be to the Golgi apparatus in the presynaptic neuron for reprocessing