Mitosis Worksheet Questions
advertisement

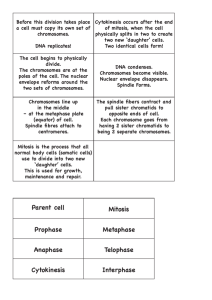
Directions: Use your book and notes to answer these questions! Cell Growth 1. Larger cells will divide because they have trouble doing what? ________________________________________________________________ 2. Where is DNA found (eukaryotes)? __________________________________________________ 3. As a cell gets larger, what kind of crisis might occur (related to DNA)? _______________________ 4. How does food, water and oxygen enter the cell? _______________________________________ 5. Understanding the relationship between a cell's volume and _______________________________ is the key to understanding why cells divide as they grow. 6. As a cell grows, the volume increases [ more / less ] rapidly than the surface area. 7. Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two _________________________________. 8. What must happen before cell division can occur? ________________________________________ Cell Division 9. What are the two phases of cell division? _______________________________________________ 10. The cells produced by mitosis are [ identical to / different from ] the parent cell. 11. How many chromosomes does a human cell have? _________ What about a fruit fly? _________ 12. Each chromosome consists of two identical parts called __________________________________ 13. Each pair of chromosomes is attached at the ___________________________________ 14. The "in-between" period of cell growth is called _________________________________ 15. The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide is called the _________________ 16. Interphase is divided into what three smaller phases? ____________________ (abbreviate) 17. During which phase is DNA replicated? _____________ MITOSIS 18. What are the four phases of mitosis? __________________________________________________ 19. What is the longest phase of mitosis? __________________________ 20. Tiny structures located in the nucleus that separate and go to opposite sides are called __________ 21. What structure helps to separate chromosomes during mitosis? _________________________ 22. What happens during metaphase? ___________________________________________________ 23. During what phase do the sister chromatids separate? ____________________________________ 24. In telophase, the chromosomes begin to disperse into a tangle of ___________________________ and the _________________________________ reforms. CYTOKINESIS 25. Cytokinesis usually occurs at the same time as ______________________________ 26. In order for cytokinesis to occur in plants, a cell ____________________________ forms between the two new cells. INTERPRETING GRAPHICS (see Mitosis figure in your book) 27. In which phase do you first see the spindle? _________________________________ 28. What phase occurs directly after metaphase? ________________________________ 29. In which phase do the chromosomes move apart? ________________________________ 30. In which phases are the chromosomes NOT visible (two phases) _________________________ TESTING YOURSELF – Do this without looking in your book! 1. The rate at which materials enter and leave through the cell membrane depends on the cell's? a. volume b. mass c. weight d. surface area 2. Sister chromatids are attached to each other at an area called the: a. centromere b. centriole c. spindle d. chromosome 3. The process of cell division results in: a. sister chromatids b. two daughter cells c. mitosis d. cell growth 4. If a cell has 12 chromsomes, how many chromosomes will be in each of its daughter cells after mitosis? a. 4 b. 6 c. 12 d. 24 5. DNA copies itself during which phase? a. prophase b. metaphase c. cytokinesis d. interphase Regulating the Cell Cycle 1. Not all cells move through the ________ ________ at the same rate. 2. Experiments show that the controls on cell ______________ and cell __________ can be turned on and off. 3. Tim Hunt and Mark Kirschner discovered that cells in mitosis contained a protein that when injected into a nondividing cell, would cause a ____________ spindle to form. 4. ____________ regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. 5. There are ___________ types of regulatory proteins. 6. ____________ ____________ allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain process have happened inside the cell. 7. External regulators direct cells to ____________ up or ____________ down the cell cycle. 8. Growth ____________ are among the most important external regulators. 9. Molecules found on the surfaces of _______________ cells often have an opposite effect, causing cells to slow down or stop their cell cycles. 10. ____________ is a disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth. 11. Cancer cells do not ____________ to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells. 12. Masses of cancer cells form ____________ that can damage normal tissues. nnn 13. The Various forms of cancer have many causes, including ____________________, ___________________, and even ____________________ 14. An astonishing number of cancer cells have a ____________ in a gene called p53. 15. Cancer is a disease of the _________ __________. 16. Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the potential to _______________. 17. Researchers have found that _______________ of stem cells can reverse the effects of brain injuries in mice. 18. Embryonic stem cell research is highly _______________.