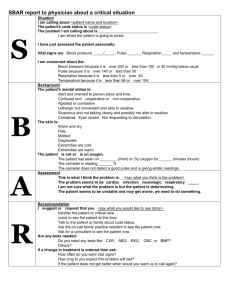
NURS 1100 LAB Unit 6 Work Sheet
advertisement

Unit 6 Worksheet Vocabulary Atelectasis – abnormal condition characterized by the collapse of alveoli, preventing CO2 and O2 exchange in part of the lungs Afebrile – without fever Apnea – the absence of spontaneous respiration Basal metabolic rate – lowest metabolic rate required for basic functioning of body Bronchi – prefix with relationship to a bronchus Bronchial breath sounds – sound of air passing in and out of the bronchial heard Bradypnea – abnormally low rate of breathing (lower than 12 breaths a minute) Cardiac output – the amount of blood pumped out by the heart (measured in L/min) Core temperature – temperature of structures deep within the body Crackles – popping sounds produced by air entering lungs that contain serous secretions Crepitus – crackling, popping and grating sounds heard from under the skin and joints Diaphoresis – secretion of sweat Cyanosis – bluish color of skin and mucous membrane due to the lack of O2 in blood Dyspnea – difficult or labored breathing; shortness of breath Eupnea – normal, relaxed breathing Expiration – to breathe out Fremitus – tremulous vibration of the chest wall caused by the vocalization that is palpated during a physical exam Fever – elevation of the body’s temperature above the normal circadian range resulting in increased core temperature Hyperventilation –pulmonary respiration rate greater than what is metabolically required Hypoventilation – decreased pulmonary respiration where gas exchange carries insufficient O2 for the body’s metabolic needs; usually leads to cyanosis Hypoxemia – abnormal concentration of O2 in arterial blood Hyperpyrexia – extremely elevated temperature that sometimes occurs in acute infectious diseases Hyperthermia – much higher than normal body temperature Hypothermia – much lower than normal body temperature usually induced by prolonged exposure to the cold Inspiration – the breathe in Pulse pressure – difference between systolic and diastolic pressures usually between 30-50 mm Hg Pyrexia – rise in the temperature of the body, usually associated with infection Orthopnea – the inability to breathe unless standing straight or sitting erect Stroke volume – amount of blood pumped out by the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction Ventilation – process of moving air into and out of the lungs Wheeze – associated with asthma and chronic bronchitis Questions 1. In order to properly interpret your client’s vital signs, you must compare the current reading to Acceptable ranges for adults o Temperature range: 36oC – 38oC o Pulse range: 60-100 BPM o Respiratory range: 12-20 breaths per minute o Blood pressure: 120/80 mmHg Pulse pressure: 30-50 mm Hg 2. You have just received a new stethoscope, and you are ready for lab! Identify the components of a stethoscope: to ensure the best reception of sound you will need to: 5 major components of a stethoscope: o Earpieces o Binaurals o Tubing o Bell chest piece o Diaphragm chest piece To ensure the best reception, the ear pieces follow the contour of the ear, pointing towards the face 3. Define inspection auscultation, percussion and palpation Inspection: physical examination technique using your visual, auditory and olfactory senses Ausculation: physical examination technique using your stethoscope to ausculate sounds created by vibration of movement of underlying tissues. Percussion: a technique in physical examination of tapping the body with the fingertips or fist to evaluate the size, borders, and consistency of some of the internal organs and to discover the presence of and evaluate the amount of fluid in a body cavity. 4. Explain the physiology of normal regulation of pulse, oxygen saturation and respirations Pulse: electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node travel thought the heart muscle to stimulate cardiac contraction o 60-70 mL blood enters aorta with each ventricular contraction (stroke volume) o with every stroke volume, the walls of the aorta distend, creating a pulse wave that travels toward the distal ends of the arteries o mechanical, neural, and chemical factors regulate the strength of the heart contractions and its stroke volume o as heart rate increases, the heart has less time to fill, without a change in stroke volume, blood pressure decreases o abnormally slow, rapid, or irregular pulse alters cardiac output Oxygen Saturation: to evaluate the respiratory processes of diffusion and perfusion measure the oxygen saturation o blood flow through the pulmonary capillaries contains red blood cells for oxygen attachment o after oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the pulmonary blood most attaches to hemoglobin molecules. o the percentage of hemoglobin that is bound with oxygen in the arteries is the percentage of saturation of hemoglobin Respirations: regulated by levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen and hydrogen ion concentration. C02 levels go up causes breathing rate and depth to increase. o if arterial 02 levels fall, receptors in the brain increase the rate and depth of respiration 5. Describe factors that cause variations in pulse, oxygen saturation and respirations Factors that cause variations in pulse could be: exercise, temperature (fever and heat), emotions (eg, anxiety), pain, drugs, hemorrhage, postural shiftage, and pulmonary conditions factors that cause variations in oxygen saturation could be oxygen therapy, hemoglobin level, temperature, and medications (eg, bronchodilators) factors causing variation in respiration are, exercise, acute pain, anxiety, smoking, body position, medications, neurological injury and hemoglobin function 6. Where are the following sounds located? How would you describe the sounds? Sound Location Description Bronchial Best heard over trachea High pitched and hollow Bronchovesicular Best heard posteriorly between scapula and anteriorly over the bronchioles lateral to the sternum at the first and second intercostal Medium pitched with medium intensity Vesicular Best heard over the peripheral lung fields (except over the scapula) Soft, breezy and low pitched 7. Normal breathing is referred to as: a) Apnea b) Tachypnea c) Bradynea d) Eupnea 8. The term that refers to reduced oxygen in blood is: a) Eupnea b) Cyanosis c) Hypoxia d) Hypoxemia 9. Discuss factors that affect boy temperature: age, exercise, stress, hormone levels, circadium rhythm and environment. Identify how each factor may increase and decrease body temperature. Age – children and infants have bad temperature regulation so they have a wider temp range. Older adults have colder temps due to reduced body systems (metabolism, sweat glands etc.) Exercise – increases body temp because of increase in muscle activity. Stress – physical and emotion increase brain activity because of hormonal and neural stimulation = increase in metabolism= increase in temp. Hormone level – Women experience more then men. Progesterone fluctuation in menstrual cycle cause change in temp. Low progesterone= lower body temp. Circadian rhythm – changes up to 1°C in the course of a day, coldest at night. Environment – hot environment could cause increase in temp and cold environment a decrease in body temp. Infants and older adults more at risk. 10. You client is an elderly confused man with a diagnosis of dementia. You need to take a temperature. What considerations would you need to make? Explain the procedure and use a tympanic thermometer because they’re quick efficient, noninvasive and safe 11. Your client’s oral temperature is 37.6oc at 0800 hrs. what are you next actions? 12. Fever increase the tissues’ need for more oxygen and as a result: a. Carbon dioxide decrease b. Cyanosis occurs c. Carbon dioxide increases d. Muscle mass increases 13. You are caring for patient whom requires pulse oximetry every 4 hours, explain to the patient ,using language the patient can understand, what you are “assessing” when you perform this skill By doing this test, we are able to measure how much oxygen your blood can carry 14. The most effective position for clients with cardiopulmonary diseases is the: a. Supine position **allows for enhanced circulation** b. Prone position c. High fowler’s d. 45o – semi-Fowler’s