BIO 306
advertisement

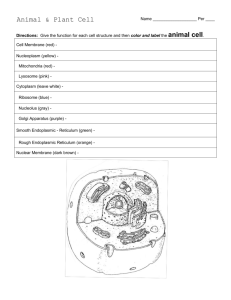
BIO 306 REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 3 1. What is the cell theory and what are the 5 components that comprise it? 2. What are the 2 categories of cell? Describe and contrast each. 3. What is meant by a “typical” cell? 4. What are the function(s) of the cell membrane? 5. Describe the structure of the cell membrane? 6. Describe the structure and characteristics of a phospholipid and the role they play in the cell membrane. 7. Differentiate between integral membrane proteins and peripheral membrane proteins. 8. Describe the 6 major functions of membrane proteins. 9. What is the cytoplasm, where is it located and what does it contain? 10. List the 13 cellular organelles. 11. What are the 2 forms of Endoplasmic Reticulum found in the cell, and structurally, how are they different? 12. What is the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER), and how is its structure suited for its function? 13. What are the function(s) of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)? 14. What are the function(s) of Ribosomes and give 2 places in the cell where they can be found. 15. Describe the structure of the Golgi Apparatus. 16. What are the function(s) of the Golgi Apparatus? 17. Where does much of the membrane of the Golgi apparatus originate? 18. Describe the structure of the mitochondria. 19. What are the function(s) of the mitochondria? 20. Name 3 metabolic pathways located in the mitochondria. 21. How do mitochondria adapt to the energy needs of a cell? 22. What is unique about the DNA located in the mitochondria? 1 23. What are the function(s) of the lysosomes? 24. How is the structure of a lysosome suited for its function? 25. Why are lysosomes necessary? 26. Briefly describe the condition known as “Tay-Sachs Disease”. 27. What are some of the function(s) of peroxisomes? 28. What is a centrosome, where are they located, and what do they contain? 29. What are centrioles, and what are their functions? 30. Differentiate between cilia and flagella, in terms of size, number and function. 31. What are vesicles, how are they formed and what is their function? 32. What are some of the functions of microtubules and microfilaments? 33. What are “inclusions”, and what are some of the substances found in the cell as “inclusions”? 34. What is the nucleus? 35. Describe the structure of the nuclear membrane. Why is it important that it has this structure? 36. What is the function of the nucleolus, and where is it found? 37. Differentiate between “chromatin” and “chromosome”. Where are each found? 38. List 3 types of passive forms of transport. Do these require energy? What must be present for them to occur? 39. Describe the process of diffusion. How long will the process of diffusion continue? 40. What is meant by the term “equilibrium”? 41. Describe the process of facilitated diffusion? How does it differ from simple diffusion? 42. The rate of facilitated diffusion is dependent on what 3 factors? 43. Define osmosis. 44. The rate of osmosis is dependent on what? 45. What is meant by the term “osmotic pressure” and how is it different from osmosis? 2 46. Define the following: a. Isotonic b. Hypertonic c. Hypotonic d. Hemolysis e. Crenation 47. Be able to predict which way water will move if a cell is placed in an isotonic, hypertonic or a hypotonic solution. 48. Describe the process of filtration. How is it different from osmosis? 49. What is an active transport system? 50. What is an active transport system able to accomplish that passive forms of transport cannot? Why? 51. Approximately how much of the cells energy is used by active transport pumps? 52. Give 2 examples of active transport pumps in the cell. 53. Give 3 forms of endocytosis. 54. Define and differentiate between pinocytosis and phagocytosis. 55. How is receptor-mediated endocytosis different from pinocytosis or phagocytosis? 56. What is exocytosis, and what is it used for? 3