Chapter 1
advertisement

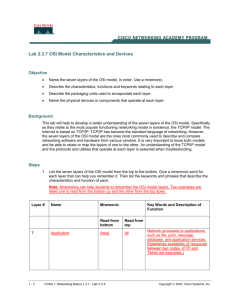
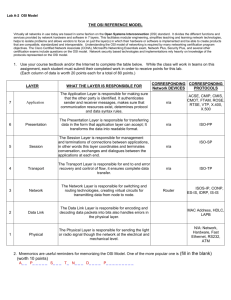
Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Chapter 2 Networking Standards and the OSI Model At a Glance Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional Resources 2-1 Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Lecture Notes Chapter Objectives Identify organizations that set standards for networking Describe the purpose of the OSI Model and each of its layers Explain specific functions belonging to each OSI Model layer Understand how two network nodes communicate through the OSI Model Discuss the structure and purpose of data packets and frames Describe the two types of addressing covered by the OSI Model Networking Standards Organizations Discuss the concept of standards. Explain that standards are vital for ensuring that products, processes, and services developed by different parties are able to work together. Mention that standards define a minimum set of specifications for acceptable performance. ANSI Explain that the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is composed of many industry and governmental representatives and develops standards for a wide range of technical fields, including computers and networking. If the classroom is equipped to do so, show the students ANSI’s Web site to illustrate that standards documents can be obtained online. EIA and TIA Present a brief overview of the missions of the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industries Alliance (TIA). Mention the TIA/EIA 568-B Series of network cabling installation guidelines. IEEE Describe the overall goals and mission of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Mention that IEEE technical publications are highly regarded and are used in the networking field. If the classroom is equipped to do so, show the students the IEEE Web site. ISO Discuss the mission of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Mention that this organization represents 146 countries and that the scope of its standards covers a wide range of industries and disciplines. 2-2 Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition 2-3 ITU Discuss the mission and power of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Stress that the ITU addresses global telecommunications issues more than industry technical specifications. ISOC Describe the overall goal of the Internet Society (ISOC). Mention that the ISOC oversees a number of groups with specific missions. Discuss the Internet Architecture Board (IAB) and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), including their respective missions, their relationship with ISOC, and their relationship with other standards organizations (such as ITU). IANA and ICANN Give a brief overview of Internet protocol (IP) addresses. Stress that these addresses are used to ensure that each computer on a network has a unique address. Describe the original purpose and responsibilities of the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). Describe the purpose of Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) and their relationship to IANA. Discuss the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) and the U.S. Department of Commerce’s (DOC’s) role in IP addressing standards. Mention that the DOC was ultimately responsible for the creation of ICANN. Also mention IANA’s continued role in IP address administration after ICANN was created. Present a brief overview of Internet service providers (ISPs) and their position between individuals and the organizations presented above. The OSI Model Present a brief overview of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Name the seven model layers and describe the general purpose of a layer in the model. Be sure to stress the intimate relationship between a protocol and a layer of the model. Mention that the OSI Model is a theoretical representation of network communication. Point out that the OSI Model is imperfect and that real-world network implementations often do not strictly adhere to the OSI specifications. Using Figure 2-1 as an example, illustrate the path that data takes between two computers under the OSI Model. Stress the fact that a given layer on one computer communicates with the corresponding layer on another computer. Teaching Tip Networking professionals often devise a mnemonic way of remembering the seven layers of the OSI Model. For instance, Programmers Dare Not Throw Salty Pretzels Away. Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Application Layer Present a brief overview of the Application layer. Mention that is it the top layer in the OSI Model. Stress that this layer’s services facilitate communication between software applications and lower-level layers of the OSI Model. Describe the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Give an overview of its function as an application layer protocol. Describe how this protocol is used in network communication using the example presented on page 46 of the text as a guide. Presentation Layer Present a brief overview of the Presentation layer. Stress the fact that this layer often serves as a translator between data formats, such as various graphics file formats. Mention that the Presentation layer is responsible for encryption and decryption in network communications. Session Layer Briefly describe the purpose of Session layer protocols. Mention that session refers to connection for ongoing data exchange between two parties. List some of the Session layer’s functions: Establishing and maintaining the communications link for the duration of the session; keeping the communication secure; synchronizing the dialogue between the two nodes; determining whether communications have been cut off; terminating communications; setting s of communication by deciding which node will communicate first and how long a node can communicate; and monitoring the identification of session participants. Transport Layer Give an overview of the functionality provided by the Transport layer protocols. Mention that Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a Transport layer protocol. Describe the difference between connection-oriented and connectionless protocols. Review the steps involved in a client requesting a Web page from a server via TCP. These steps are described on page 48 of the text. Describe the concept of a checksum and discuss how it is employed to ensure data integrity during network communication. Discuss the processes of segmentation, reassembly, and sequencing. Use Figure 2-2 to illustrate segmentation and reassembly. Mention the importance of the maximum transmission unit (MTU) and synchronization in these respective processes. Network Layer Present a brief overview of the Network layer protocols. Discuss the purpose of addressing. Discuss network addresses. Explain the example presented on page 51 of the text. Briefly touch on the concept of packets and explain that data units become packets as they pass through the Network layer. Present the concept of routing and discuss how the Network layer fits in with this concept. 2-4 Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition 2-5 Briefly introduce the IP protocol. Use Figure 2-4 in the text to illustrate an IP packet. Briefly introduce the concept of fragmentation. Mention that fragmentation at the Network layer is very similar to segmentation at the Transport layer. Data Link Layer Present a brief overview of the Data Link layer. Discuss the function of frames in network communication. Explain the purpose of the Frame Check Sequence (FCS). Mention that the FCS is calculated via a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). Mention that the Data Link layer is divided into two sub-layers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) and the Media Access Control (MAC) sub-layers. Use Figure 2-5 to illustrate. Explain the function of the LLC and MAC sub-layers. Mention that the LLC sub-layer communicates with the Network layer, while the MAC sub-layer communicates with the Physical layer. Discuss the two pieces of a MAC (MAC) address: the Block ID and Device ID. Illustrate how a MAC address for a Network Interface Card (NIC) can be identified, using Figure 2-6. Mention that a NIC’s MAC address can also be identified through your computer’s protocol configuration utility. Physical Layer Give a brief overview of the Physical layer. Explain that the protocols at this layer are responsible for physically sending and receiving signals. Discuss some of the hardware that operates at the Physical layer. Mention that a NIC operates at both the Physical and Data Link layers. Teaching Tip Explain to the students that network administrators are generally concerned with the bottom four layers of the OSI Model, while programmers would be more concerned with the top three layers. For this reason, this text and the Network+ exam concentrate on the bottom four layers of the OSI Model. Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition 2-6 Quick Quiz 1 1. Standards define the _____ acceptable performance of a product or service. Answer: minimum 2. Addresses used to identify computers on the Internet and other TCP/IP-based networks are known as _____ addresses. Answer: Internet Protocol (IP) 3. Which OSI Model layer is HTTP a protocol for? a. Network b. Presentation c. Application d. Data Link Answer: c 4. Transport layer protocols that do not establish a connection before transmitting and make no effort to ensure that data is delivered error-free are called _____ protocols. Answer: connectionless Applying the OSI Model Review the seven OSI Model layers and their functions, using Table 2-1 as a guide. Communication Between Two Systems Review the method by which data is passed from one network node to another in a typical client/server exchange. To illustrate, use Figure 2-7 and the detailed example presented on pages 56 through 58 of the text. Briefly describe the concept of encapsulation and discuss how it is used in network communication. Review s frame, packet, datagram, and PDU. Mention that, although these terms are often used interchangeably, there are differences among some of these terms. Frame Specifications Describe the two major categories of frame types: Ethernet and Token Ring. Stress the fact that these two categories of frame type will not interact on a network, and that most LANs only support one of these two frame types. Teaching Tip Make sure that students understand the importance of realizing the frame type(s) that a given network requires. This information is important when installing NOSs, configuring servers and client workstations, installing NICs, troubleshooting network problems, and purchasing network equipment. IEEE Networking Specifications Discuss IEEE’s 802 family of specifications. Using Table 2-2 as a guide, review some of the more important IEEE 802 standards. Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Teaching Tip 2-7 Remind students that the Network+ certification exam includes questions about IEEE 802 specifications, so they should begin to become familiar with a number of the standards listed in Table 2-2. Quick Quiz 2 1. Which OSI layer establishes, maintains, and terminates user connections? a. Application b. Session c. Data Link d. Physical Answer: b 2. Which OSI layer packages data in frames appropriate to network transmission method? a. Session b. Physical c. Data Link d. Network Answer: c 3. _____ is a networking technology that relies upon direct links between nodes and a ring topology. Answer: Token Ring 4. Which of the following IEEE 802 standards addresses standards for wireless networking for many different broadcast frequencies and usage techniques? a. 802.2 b. 802.8 c. 802.11 d. 802.12 Answer: c Class Discussion Topics 1. There are a number of standards organizations that specify standards relating to networking. Ask the students whether they feel that it is more efficient to have multiple standardization organizations, or if it would be more efficient to have a unified standards organization for the networking field. Do the students feel that it would be feasible to create such an organization? 2. Ask students what benefits they see in the OSI Model’s division of network communication into seven distinct layers. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this approach? Additional Projects 1. Have students use the Internet to research one or two organizations not mentioned in this chapter that are involved in creating standards for the computer industry (preferably standards that relate to the networking field). Compile the students’ results into a list, which can be distributed to the class. 2. Have students research some common protocols used at the Application layer of the OSI Model. Compile a list of the students’ results. Ask the students to identify any protocols on this list with which they are familiar. Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Additional Resources OSI Model Practice Quiz: http://gocertify.com/quizzes/osi/ OSI Protocols: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/osi_prot.htm TCP/IP Tutorial: http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~jain/cis677-00/e_8ip.htm Network Protocols Tutorial (two parts): o http://www.networkmagazine.com/article/NMG20000720S0002 o http://www.networkmagazine.com/article/NMG20000726S0007 2-8


![Network Technologies [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008490270_1-05a3da0fef2a198f06a57f4aa6e2cfe7-300x300.png)