Document
advertisement

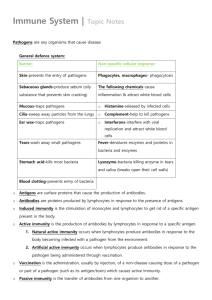
Student self-test Chapter 9 Medical Science: How will science keep me healthy? This paper is both question and answer sheet. There are 25 multiple-choice questions in this test. For each question there are four possible answers. Circle the letter of the answer of your choice. There is only one correct answer for each of the following questions. 1 2 3 4 A virus is: a a lifestyle choice that causes a disease such as a heart attack b a substance or organism that is capable of causing disease c a unicellular organism with a cell wall but no nucleus d something that contains genetic material surrounded by a protein coat, but not considered living. Antibiotics are a common method of killing: a viruses b helminths c bacteria d fungi. The skin is a good first line of defence against infection due to: a the fact that it forms a physical barrier and has oils and sweat b its acid c its enzymes d its mucous membranes and cilia. A cell called a phagocyte works in the body by: a surrounding a pathogen, engulfing it and destroying it b causing the blood to clot and bleeding to stop c producing antibodies that bind with antigens on the surface of a pathogen d providing immunity against catching the same pathogen ever again. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 5 6 7 8 In the diagram below, the pink shapes represent ____________ and the white shapes represent _______________. a pathogens; antibodies b antibodies; pathogens c pathogens; antibiotics d pathogens; phagocytes. Vaccination is an example of: a acquired passive immunity b natural active immunity c natural passive immunity d acquired active immunity. When a person develops antibodies in response to a pathogen and those antibodies lie dormant in their body in case they ever catch the same pathogen again, this type of immunity is called: a acquired passive immunity b natural active immunity c natural passive immunity d acquired active immunity. Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the: a circulatory system b neuromuscular system c urinary system d skeletal system. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 9 The entrances to the coronary arteries are located in the: a right ventricle b left ventricle c aorta d vena cava. 10 Atherosclerosis is the: a quivering of the heart instead of beating correctly b death of the heart muscle cells due to a lack of oxygen c build up of fatty plaques in the coronary arteries d same as a heart attack or acute myocardial infarction. 11 The treatment for ventricular fibrillation is: a bypass surgery b defibrillation c balloon angioplasty d CPR. 12 A narrowed segment of coronary artery may be opened up again using a procedure called: a a skin graft b defibrillation c balloon angioplasty d IVF. 13 Sunburn is an example of a: a full thickness burn b partial thickness burn c superficial burn d risk factor 14 Bowel cancer screening is done with a(n): a blood test b colonoscope c injection d operation Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 15 A major burn in an adult would cover at least: a 5% of the body b 20% of the body c 40% of the body d 60% of the body. 16 A stroke is caused when there is an interruption to the blood supply to the: a heart b lungs c skin d brain. 17 When the nucleus of an atom is unstable and it decays or changes into another isotope it is said to be: a radiation b radioactive c radioactivity d radioisotope. 18 Radionuclides can be: a naturally occurring b manufactured in a cyclotron c manufactured in a nuclear reactor d all of the above. 19 The type of radiation that is electromagnetic in nature, similar to X-rays is: a alpha b beta c gamma d all of the above. 20 Iodine is commonly used as a contrast agent for taking X-ray images of the: a brain b digestive system c bones d urinary system. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 21 To make a radiopharmaceutical: a a radionuclide is attached to a convenient chemical compound b a radionuclide is attached to a gamma camera c a gamma ray is attached to a convenient chemical compound d an X-ray is attached to a convenient chemical compound. 22 Radiography and radiotherapy are: a the same thing b similar in that they both treat illnesses with radiation c different because one deals with diagnosis and the other with treatment d similar in that they both diagnose illnesses with radiation. 23 Radiotherapy involves the use of: a X-rays b gamma rays c beta particles d all of the above. 24 80–90% of radionuclide diagnostic procedures use the radionuclide: a iodine-131 b technetium-99m c bismuth-213 d strontium-89. 25 The clarity of an X-ray image can be improved by: a using a contrast agent b using higher strength X-rays c exposing the patient for longer to the same strength X-rays d making the examination room as dark as possible. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia