State Morphology Worksheet
advertisement
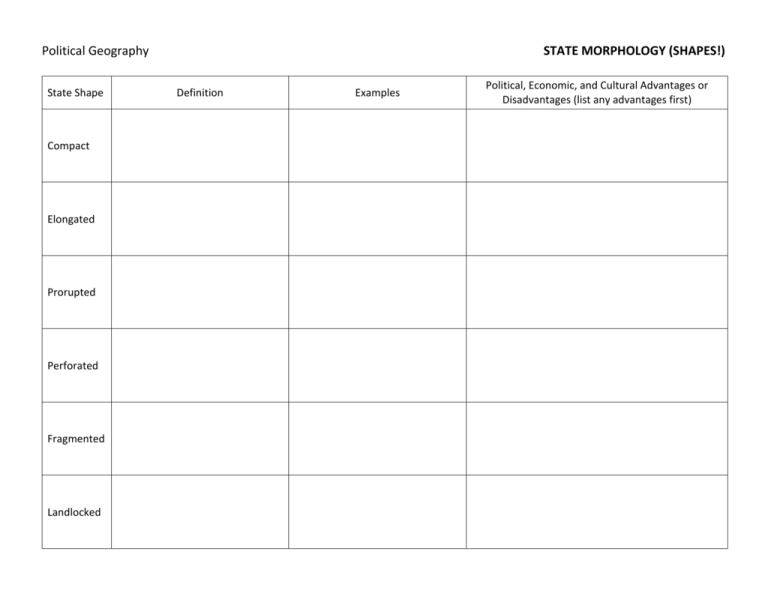
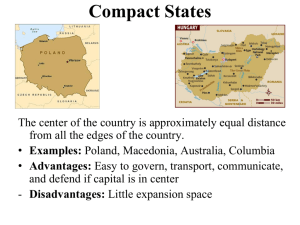
Political Geography State Shape Compact Elongated Prorupted Perforated Fragmented Landlocked STATE MORPHOLOGY (SHAPES!) Definition Examples Political, Economic, and Cultural Advantages or Disadvantages (list any advantages first) Define AND give examples of these terms related to state morphology: exclave: enclave (different from ethnic enclave): forward-thrust capital: devolution: Takeaway: Why is state morphology (state shapes) important? Political Geography state: a politically organized territory administered by a sovereign government, having a permanent population, and recognized by the international community STATE MORPHOLOGY (SHAPES!) morphology: the study of the form or structure of something A. On the map on the reverse side, shade in the ten largest states (countries) by area. Then circle and the approximate locations of and label the ten smallest states (so called "microstates"). (Data on reverse side.) B. Mark the location of two examples of each of the following types of states: compact (mark with "COM"), Elongated (mark with "ELO"), prorupted (mark with "PRO"), perforated (mark with "PER"), fragmented (mark with "FRA") and landlocked (mark with "LL"). World's Ten Largest States # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 State Russia China United States Canada Brazil Australia India Argentina Kazakhstan Algeria Area 16,995,800 sq km 9,326,410 sq km 9,161,923 sq km 9,093,507 sq km 8,456,510 sq km 7,617,930 sq km 2,973,190 sq km 2,736,690 sq km 2,669,800 sq km 2,381,740 sq km World's Ten Smallest States (Microstates) # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 State Vatican City Monaco Nauru Tuvalu San Marino Liechtenstein Saint Kitts and Nevis Maldives Malta Grenada What characteristics are common among the world's largest states? What characteristics are common among the world's smallest states (microstates)? Area 0.44 sq km 1.95 sq km 21 sq km 26 sq km 61 sq km 160 sq km 261 sq km 300 sq km 316 sq km 344 sq km